
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 9780071283700
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 9780071283700 تمرين 8
The Easton plant produces sheet metal chassis for television sets. Its customer is General Electric Appliances. The chassis are manufactured on a computerized, numerically controlled (NC) machine that cuts, drills, and bends the metal to form the chassis for the television set. Two different chassis are produced: HX-3 and DX-55.
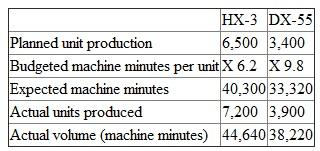
Easton has a single plantwide overhead account. Actual machine minutes on the NC machine are used to distribute overhead to the two products. There were no beginning inventories of work in process or finished goods. The following table summarizes the planned and actual production data for the year:
 The following data summarize the flexible overhead budget:
The following data summarize the flexible overhead budget:
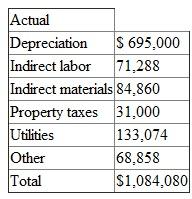
 At the end of the year, the following overhead amounts had been incurred:
At the end of the year, the following overhead amounts had been incurred:
 Any over- or underabsorbed overhead is written off to cost of goods sold. The ending finished goods inventory consists of 2,000 units of HX-3 and 1,000 units of DX-55, representing 13,400 minutes and 10,300 minutes of actual machine time, respectively.
Any over- or underabsorbed overhead is written off to cost of goods sold. The ending finished goods inventory consists of 2,000 units of HX-3 and 1,000 units of DX-55, representing 13,400 minutes and 10,300 minutes of actual machine time, respectively.
Required: (Round all dollars, including overhead rates, to two decimal places.)
a. Calculate the overhead absorption rate set at the start of the year.
b. Calculate the over- or underabsorbed overhead for the year.
c. The firm is considering switching to variable costing. What effect would this decision have on Easton's reported profit for this year To implement variable costing at the end of the year, variable overhead is calculated as $3.00 per machine minute times the actual number of machine minutes. Fixed overhead is the difference between total actual overhead and variable overhead.
d. Instead of defining fixed overhead as all overhead in excess of variable overhead as in part (c), assume the following: Fixed overhead is budgeted fixed overhead ($820,000), and variable overhead is the difference between total actual overhead and budgeted fixed overhead. What is the difference between absorption net income and variable costing income given these new assumptions
Easton has a single plantwide overhead account. Actual machine minutes on the NC machine are used to distribute overhead to the two products. There were no beginning inventories of work in process or finished goods. The following table summarizes the planned and actual production data for the year:
 The following data summarize the flexible overhead budget:
The following data summarize the flexible overhead budget: At the end of the year, the following overhead amounts had been incurred:
At the end of the year, the following overhead amounts had been incurred: Any over- or underabsorbed overhead is written off to cost of goods sold. The ending finished goods inventory consists of 2,000 units of HX-3 and 1,000 units of DX-55, representing 13,400 minutes and 10,300 minutes of actual machine time, respectively.
Any over- or underabsorbed overhead is written off to cost of goods sold. The ending finished goods inventory consists of 2,000 units of HX-3 and 1,000 units of DX-55, representing 13,400 minutes and 10,300 minutes of actual machine time, respectively.Required: (Round all dollars, including overhead rates, to two decimal places.)
a. Calculate the overhead absorption rate set at the start of the year.
b. Calculate the over- or underabsorbed overhead for the year.
c. The firm is considering switching to variable costing. What effect would this decision have on Easton's reported profit for this year To implement variable costing at the end of the year, variable overhead is calculated as $3.00 per machine minute times the actual number of machine minutes. Fixed overhead is the difference between total actual overhead and variable overhead.
d. Instead of defining fixed overhead as all overhead in excess of variable overhead as in part (c), assume the following: Fixed overhead is budgeted fixed overhead ($820,000), and variable overhead is the difference between total actual overhead and budgeted fixed overhead. What is the difference between absorption net income and variable costing income given these new assumptions
التوضيح
Absorption Costing
Sound accounting sta...
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








