
Microeconomics 15th Edition by James Gwartney,Richard Stroup,Russell Sobel,David Macpherson
النسخة 15الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-1285453569
Microeconomics 15th Edition by James Gwartney,Richard Stroup,Russell Sobel,David Macpherson
النسخة 15الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-1285453569 تمرين 6
*Rod N. Reel owns a dealership that sells fishing boats in an open, price-searcher market. To develop his pricing strategy, Rod hired an economist to estimate his demand curve. Columns (1) and (2) of the chart on the next page provide the data for the expected weekly quantity demanded for Rod's fishing boats at alternative prices. Rod's marginal (and average) cost of supplying each boat is constant at $5,000 per boat no matter how many boats he sells per week in this range. This cost includes all opportunity costs and represents the economic cost per boat.
a. Find Rod's economic profits at each alternative price by calculating the difference between total revenue and total cost.
b. Find Rod's marginal revenue and marginal cost from the sale of each additional boat.
c. If Rod wants to maximize his profits, what price should he charge per boat
d. How many boats will Rod sell per week at the profit-maximizing price
e. What will Rod's profits be per week at this price and sales volume
f. At the price and sales level where profits are maximized, has Rod sold all boats that have higher marginal revenue than marginal cost
g. If Rod's profits are typical of all firms in the boat sales business, what might be expected to happen in the future Will more boat dealers open in the area, or will some of the existing ones go out of business What will happen to the profitability of the boat dealers in the future once the entry/exit has occurred
h. Challenge Question: Recall the relationship between elasticity of demand, price changes, and their impact on total revenues. As Rod lowers his price from $9,000 to $5,000, his total revenues keep increasing. Is demand in this price range elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic When Rod lowers his price from $5,000 to $4,000, his total revenues stay the same. Is demand in this price range elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic Can you guess what might happen at prices below $4,000 Explain.
*Asterisk denotes questions for which answers are given in Appendix B.
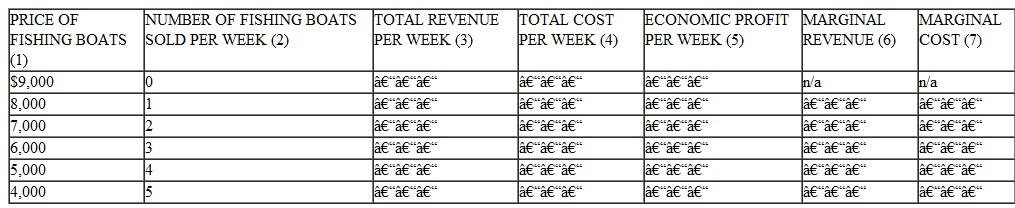
a. Find Rod's economic profits at each alternative price by calculating the difference between total revenue and total cost.
b. Find Rod's marginal revenue and marginal cost from the sale of each additional boat.
c. If Rod wants to maximize his profits, what price should he charge per boat
d. How many boats will Rod sell per week at the profit-maximizing price
e. What will Rod's profits be per week at this price and sales volume
f. At the price and sales level where profits are maximized, has Rod sold all boats that have higher marginal revenue than marginal cost
g. If Rod's profits are typical of all firms in the boat sales business, what might be expected to happen in the future Will more boat dealers open in the area, or will some of the existing ones go out of business What will happen to the profitability of the boat dealers in the future once the entry/exit has occurred
h. Challenge Question: Recall the relationship between elasticity of demand, price changes, and their impact on total revenues. As Rod lowers his price from $9,000 to $5,000, his total revenues keep increasing. Is demand in this price range elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic When Rod lowers his price from $5,000 to $4,000, his total revenues stay the same. Is demand in this price range elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic Can you guess what might happen at prices below $4,000 Explain.
*Asterisk denotes questions for which answers are given in Appendix B.

التوضيح
The solution of the table showing price ...
Microeconomics 15th Edition by James Gwartney,Richard Stroup,Russell Sobel,David Macpherson
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








