
The Living World 6th Edition by George Johnson, Jonathan Losos,William Ober,Claire Garrison
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0077280086
The Living World 6th Edition by George Johnson, Jonathan Losos,William Ober,Claire Garrison
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0077280086 تمرين 1
Can Modified Genes Escape from GM Crops
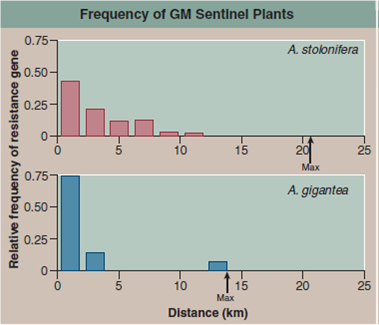
On the previous page of this chapter you read of a field experiment conducted in 2004 by the Environmental Protection Agency to assess the possibility that introduced genes could pass from genetically modified golf course grass to other plants. Investigators introduced a gene conferring herbicide resistance (the EPSP synthetase gene for resistance to glyphosate) into golf course bentgrass, A. stolonifera, and then looked to see if the gene passed from the GM grass to other plants of the same species, and also if it passed to other related species.
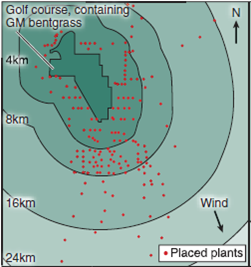
The map at the bottom displays the setup of this elaborate field study. A total of 178 A. stolonifera plants were placed outside the golf course, many of them downwind. An additional 69 bentgrass individuals were found to be already growing downwind, most of them the related species A. gigantea. Seeds were collected from each of these plants, and the DNA of resulting seedlings tested for the presence of the gene introduced into the GM golf course grass. In the graph, the upper red histogram (a histogram is a "bar graph" that sorts data into a series of discontinuous categories, the value of each bar representing the number of individuals in a category, or, as in this case, the average value of entries in that category) presents the relative frequency with which the gene was found in A. stolonifera plants located at various distances from the golf course. The lower blue histogram does the same for A. gigantea plants.

Applying Concepts
a. Variable. In the histogram, is there a dependent variable If so, what is it
b. Reading a Histogram. Does the gene conferring resistance to herbicide pass to other plants of this species, A. stolonifera to individuals of the related species A. gigantea
c. What is the maximal distance over which the herbicide resistance gene is transferred to other plants of this species of the related species what are these distances, expressed in miles
On the previous page of this chapter you read of a field experiment conducted in 2004 by the Environmental Protection Agency to assess the possibility that introduced genes could pass from genetically modified golf course grass to other plants. Investigators introduced a gene conferring herbicide resistance (the EPSP synthetase gene for resistance to glyphosate) into golf course bentgrass, A. stolonifera, and then looked to see if the gene passed from the GM grass to other plants of the same species, and also if it passed to other related species.
The map at the bottom displays the setup of this elaborate field study. A total of 178 A. stolonifera plants were placed outside the golf course, many of them downwind. An additional 69 bentgrass individuals were found to be already growing downwind, most of them the related species A. gigantea. Seeds were collected from each of these plants, and the DNA of resulting seedlings tested for the presence of the gene introduced into the GM golf course grass. In the graph, the upper red histogram (a histogram is a "bar graph" that sorts data into a series of discontinuous categories, the value of each bar representing the number of individuals in a category, or, as in this case, the average value of entries in that category) presents the relative frequency with which the gene was found in A. stolonifera plants located at various distances from the golf course. The lower blue histogram does the same for A. gigantea plants.



Applying Concepts
a. Variable. In the histogram, is there a dependent variable If so, what is it
b. Reading a Histogram. Does the gene conferring resistance to herbicide pass to other plants of this species, A. stolonifera to individuals of the related species A. gigantea
c. What is the maximal distance over which the herbicide resistance gene is transferred to other plants of this species of the related species what are these distances, expressed in miles
التوضيح
Genetically modified plants are those pl...
The Living World 6th Edition by George Johnson, Jonathan Losos,William Ober,Claire Garrison
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








