
The Living World 6th Edition by George Johnson, Jonathan Losos,William Ober,Claire Garrison
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0077280086
The Living World 6th Edition by George Johnson, Jonathan Losos,William Ober,Claire Garrison
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0077280086 تمرين 8
How Does Arrowgrass Tolerate Salt
Plants grow almost everywhere on earth, thriving in many places where exposure, drought, and other severe conditions challenge their survival. In deserts, a common stress is the presence of high levels of salt in the soils. Soil salinity is also a problem for millions of acres of abandoned farmland because of the accumulation of salt from irrigation water restricts growth. Why does excess salt in the soil present a problem for a plant For one thing, high levels of sodium ion that are taken up by the roots are toxic. For another, a plant's roots cannot obtain water when growing in salty soil. Osmosis (the movement of water molecules to areas of higher solute concentrations, see page 99) causes water to move in the opposite direction, drawn out of the roots by the soil's high levels of salt. And yet plants do grow in these soils. How do they manage
To investigate this, researchers have studied seaside arrowgrass ( Triglochin maritima ), the plant you see below. Arrowgrass plants are able to grow in very salty seashore soils, where few other plants survive. How are they able to survive Researchers found that their roots do not take up salt, and so do not accumulate toxic levels of salt.
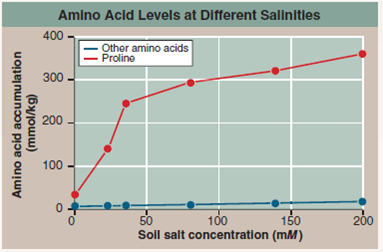
However, this still leaves the arrowgrass plant the challenge of preventing its root cells from losing water to the surrounding salty soil. How then do the roots achieve osmotic balance In an attempt to find out, researchers grew arrowgrass plants in nonsalty soil for two weeks, then transferred them to one of several soils which differed in salt level. After ten days, shoots were harvested and analyzed for amino acids, because accumulating amino acids could be one way that the cells maintain osmotic balance. Results are presented in the graph.

Making Inferences
a. In general, what is the effect of soil salt concentration on arrowgrass plant's accumulation of the amino acid proline of other amino acids
b. Is the effect of salt on proline accumulation the same at low salt (below 50 m M ) as at high salt (above 50 m M )
Plants grow almost everywhere on earth, thriving in many places where exposure, drought, and other severe conditions challenge their survival. In deserts, a common stress is the presence of high levels of salt in the soils. Soil salinity is also a problem for millions of acres of abandoned farmland because of the accumulation of salt from irrigation water restricts growth. Why does excess salt in the soil present a problem for a plant For one thing, high levels of sodium ion that are taken up by the roots are toxic. For another, a plant's roots cannot obtain water when growing in salty soil. Osmosis (the movement of water molecules to areas of higher solute concentrations, see page 99) causes water to move in the opposite direction, drawn out of the roots by the soil's high levels of salt. And yet plants do grow in these soils. How do they manage
To investigate this, researchers have studied seaside arrowgrass ( Triglochin maritima ), the plant you see below. Arrowgrass plants are able to grow in very salty seashore soils, where few other plants survive. How are they able to survive Researchers found that their roots do not take up salt, and so do not accumulate toxic levels of salt.
However, this still leaves the arrowgrass plant the challenge of preventing its root cells from losing water to the surrounding salty soil. How then do the roots achieve osmotic balance In an attempt to find out, researchers grew arrowgrass plants in nonsalty soil for two weeks, then transferred them to one of several soils which differed in salt level. After ten days, shoots were harvested and analyzed for amino acids, because accumulating amino acids could be one way that the cells maintain osmotic balance. Results are presented in the graph.


Making Inferences
a. In general, what is the effect of soil salt concentration on arrowgrass plant's accumulation of the amino acid proline of other amino acids
b. Is the effect of salt on proline accumulation the same at low salt (below 50 m M ) as at high salt (above 50 m M )
التوضيح
Plants are essential components of ecolo...
The Living World 6th Edition by George Johnson, Jonathan Losos,William Ober,Claire Garrison
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








