
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, James Stock
النسخة 3الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-9352863501
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, James Stock
النسخة 3الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-9352863501 تمرين 18
X and Z are two jointly distributed random variables. Suppose you know the value of Z , but not the value of X. Let 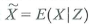 denote a guess of the value of X using the information on Z , and let
denote a guess of the value of X using the information on Z , and let 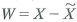 denote the error associated with this guess.
denote the error associated with this guess.
a. Show that E ( W ) = 0.
b. Show that E ( WZ ) = 0.
c. Let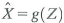 denote another guess of X using Z, and
denote another guess of X using Z, and 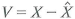 denote its error. Show that
denote its error. Show that 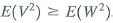 .
.
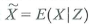 denote a guess of the value of X using the information on Z , and let
denote a guess of the value of X using the information on Z , and let 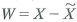 denote the error associated with this guess.
denote the error associated with this guess.a. Show that E ( W ) = 0.
b. Show that E ( WZ ) = 0.
c. Let
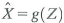 denote another guess of X using Z, and
denote another guess of X using Z, and 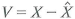 denote its error. Show that
denote its error. Show that 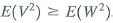 .
.التوضيح
It is told that:
• and
are two jointly...
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, James Stock
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








