
Molecular Biology Of The Cell 6th Edition by Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0815345244
Molecular Biology Of The Cell 6th Edition by Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0815345244 تمرين 11
Look at the two yeast colonies in Figure Q4-3. Each of these colonies contains about 100,000 cells descended from a single yeast cell, originally somewhere in the mid- dle of the clump. A white colony arises when the 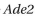 gene is expressed from its normal chromosomal location. When the
gene is expressed from its normal chromosomal location. When the 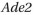 gene is moved to a location near a telomere, it is packed into heterochromatin and inactivated in most cells, giving rise to colonies that are mostly red. In these largely red colonies, white sectors fan out from the middle of the colony. In both the red and white sectors, the
gene is moved to a location near a telomere, it is packed into heterochromatin and inactivated in most cells, giving rise to colonies that are mostly red. In these largely red colonies, white sectors fan out from the middle of the colony. In both the red and white sectors, the 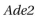
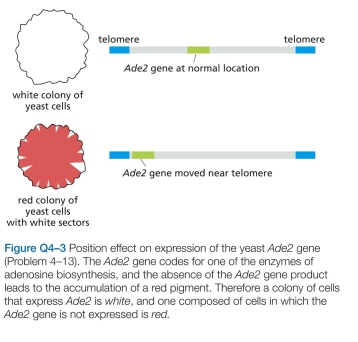 gene is still located near telomeres. Explain why white sec- tors have formed near the rim of the red colony. Based on the patterns observed, what can you conclude about the propagation of the transcriptional state of the
gene is still located near telomeres. Explain why white sec- tors have formed near the rim of the red colony. Based on the patterns observed, what can you conclude about the propagation of the transcriptional state of the 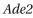 gene from mother to daughter cells in this experiment?
gene from mother to daughter cells in this experiment?
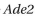 gene is expressed from its normal chromosomal location. When the
gene is expressed from its normal chromosomal location. When the 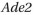 gene is moved to a location near a telomere, it is packed into heterochromatin and inactivated in most cells, giving rise to colonies that are mostly red. In these largely red colonies, white sectors fan out from the middle of the colony. In both the red and white sectors, the
gene is moved to a location near a telomere, it is packed into heterochromatin and inactivated in most cells, giving rise to colonies that are mostly red. In these largely red colonies, white sectors fan out from the middle of the colony. In both the red and white sectors, the 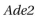
 gene is still located near telomeres. Explain why white sec- tors have formed near the rim of the red colony. Based on the patterns observed, what can you conclude about the propagation of the transcriptional state of the
gene is still located near telomeres. Explain why white sec- tors have formed near the rim of the red colony. Based on the patterns observed, what can you conclude about the propagation of the transcriptional state of the 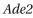 gene from mother to daughter cells in this experiment?
gene from mother to daughter cells in this experiment?التوضيح
Transposable elements are mobile pieces ...
Molecular Biology Of The Cell 6th Edition by Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








