
Molecular Biology Of The Cell 6th Edition by Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0815345244
Molecular Biology Of The Cell 6th Edition by Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0815345244 تمرين 12
0 The affinity of integrins for matrix components can be modulated by changes to their cytoplasmic domains: a process known as inside-out signaling. You have iden- tified a key region in the cytoplasmic domains of 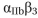 integrin that seems to be required for inside-out signaling (Figure Q19-3). Substitution of alanine for either D723 in the
integrin that seems to be required for inside-out signaling (Figure Q19-3). Substitution of alanine for either D723 in the 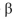 chain or R995 in the
chain or R995 in the 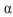 chain leads to a high level of spontaneous activation, under conditions where the wild-type chains are inactive. Your advisor suggests that you convert the aspartate in the
chain leads to a high level of spontaneous activation, under conditions where the wild-type chains are inactive. Your advisor suggests that you convert the aspartate in the 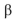 chain to an arginine (D723R) and the arginine in the
chain to an arginine (D723R) and the arginine in the 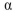 chain to an aspartate (R995D). You compare all three
chain to an aspartate (R995D). You compare all three 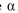 chains (R995, R995A, and R995D) against all three
chains (R995, R995A, and R995D) against all three 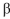 chains (D723, D723A, and D723R). You find that all pairs have a high level of sponta- neous activation, except D723 vs R995 (the wild type) and D723R vs R995D, which have low levels. Based on these results, how do you think the
chains (D723, D723A, and D723R). You find that all pairs have a high level of sponta- neous activation, except D723 vs R995 (the wild type) and D723R vs R995D, which have low levels. Based on these results, how do you think the 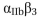 integrin is held in its inactive state?
integrin is held in its inactive state? 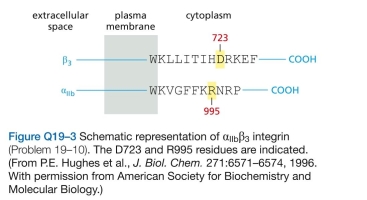
 integrin that seems to be required for inside-out signaling (Figure Q19-3). Substitution of alanine for either D723 in the
integrin that seems to be required for inside-out signaling (Figure Q19-3). Substitution of alanine for either D723 in the  chain or R995 in the
chain or R995 in the  chain leads to a high level of spontaneous activation, under conditions where the wild-type chains are inactive. Your advisor suggests that you convert the aspartate in the
chain leads to a high level of spontaneous activation, under conditions where the wild-type chains are inactive. Your advisor suggests that you convert the aspartate in the 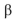 chain to an arginine (D723R) and the arginine in the
chain to an arginine (D723R) and the arginine in the 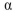 chain to an aspartate (R995D). You compare all three
chain to an aspartate (R995D). You compare all three 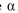 chains (R995, R995A, and R995D) against all three
chains (R995, R995A, and R995D) against all three 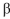 chains (D723, D723A, and D723R). You find that all pairs have a high level of sponta- neous activation, except D723 vs R995 (the wild type) and D723R vs R995D, which have low levels. Based on these results, how do you think the
chains (D723, D723A, and D723R). You find that all pairs have a high level of sponta- neous activation, except D723 vs R995 (the wild type) and D723R vs R995D, which have low levels. Based on these results, how do you think the 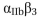 integrin is held in its inactive state?
integrin is held in its inactive state? 
التوضيح
The extracellular matrix is an important...
Molecular Biology Of The Cell 6th Edition by Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








