Deck 19: The Macroeconomic Perspective
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/137
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: The Macroeconomic Perspective
1
Between 1968 and 2010, income inequality in the United States:
A) became greater.
B) became less unequal.
C) remained unchanged.
D) showed a dramatic increase in equality.
A) became greater.
B) became less unequal.
C) remained unchanged.
D) showed a dramatic increase in equality.
became greater.
2
According to the text, it is generally agreed that in the United States in the first two decades following World War II:
A) income distribution in the United States became less equal.
B) income equality measures stayed the same.
C) income distribution became more equal.
D) there was no way to determine income distribution.
A) income distribution in the United States became less equal.
B) income equality measures stayed the same.
C) income distribution became more equal.
D) there was no way to determine income distribution.
income distribution became more equal.
3
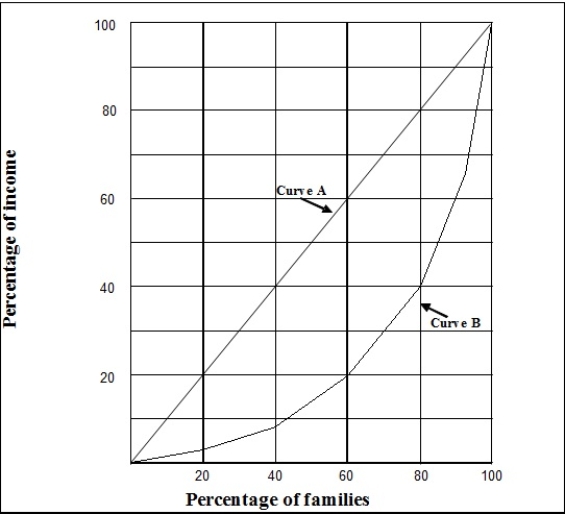
(Exhibit: Income Distribution) Curve _______ indicates that the lowest ________ percent of families would receive _______ of the income.
A) B; 40; 40
B) A; 60; 20
C) A; 40; 40
D) B; 80; 80
A; 40; 40
4
Studies of family income over time reveal that:
A) most people in the lowest quintile tend to stay there over their lifetimes.
B) income mobility is rare for all quintiles of the income distribution.
C) many people who move down the income ladder tend to be young.
D) many people who start out at the bottom of the income ladder when they are young move up the income ladder as they age.
A) most people in the lowest quintile tend to stay there over their lifetimes.
B) income mobility is rare for all quintiles of the income distribution.
C) many people who move down the income ladder tend to be young.
D) many people who start out at the bottom of the income ladder when they are young move up the income ladder as they age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Between 1968 and 2010, the income group in the United States showing the greatest income gains was the _______ 20 percent.
A) bottom
B) third
C) fourth
D) top
A) bottom
B) third
C) fourth
D) top

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

(Exhibit: Income Distribution) Curve B indicates that:
A) the lowest 60 percent of the families get 40 percent of the income.
B) the lowest 80 percent of the families get 40 percent of the income.
C) the lowest 80 percent of the families get 80 percent of the income.
D) income is quite equally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

(Exhibit: Income Distribution) Curve B shows that the fourth quintile of families gets approximately _______ percent of the income.
A) 20
B) 40
C) 60
D) 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The primary evidence of income inequality in the United States is provided by:
A) the IRS.
B) census data.
C) the Department of Agriculture.
D) research economists.
A) the IRS.
B) census data.
C) the Department of Agriculture.
D) research economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Since 1968, a factor that is associated with the _______ in income _______ in the United States has been the _______ in the percentage of families headed by _______ .
A) decrease; inequality; increase; women.
B) increase; equality; increase; married couples
C) increase; inequality; increase; women
D) decrease; equality; increase; married couples
A) decrease; inequality; increase; women.
B) increase; equality; increase; married couples
C) increase; inequality; increase; women
D) decrease; equality; increase; married couples

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

(Exhibit: Income Distribution) Curve B:
A) is called a Lorenz curve.
B) shows that the lowest 20% of the families gets 60% of the income.
C) shows that 60 percent of the families get 40 percent of the income.
D) shows an equal distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When economists speak of the lowest 20 percent or the middle 20 percent of the families receiving a certain percentage of income, they are speaking of:
A) static groups.
B) families that move in and out of the various groups.
C) very immobile income classes.
D) a typical family of 4 with both parents present.
A) static groups.
B) families that move in and out of the various groups.
C) very immobile income classes.
D) a typical family of 4 with both parents present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Changes in the distribution of income in the United States over the past 40 years have brought to the forefront the issue of:
A) child labor.
B) early retirement income.
C) fairness.
D) credit card gouging.
A) child labor.
B) early retirement income.
C) fairness.
D) credit card gouging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The _______ a Lorenz curve lies to (from) the 45-degree line, the _______ the distribution of income.
A) further; more equal
B) closer; less equal
C) further; more unequal
D) closer; better as far as economists are concerned.
A) further; more equal
B) closer; less equal
C) further; more unequal
D) closer; better as far as economists are concerned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
From 1968 to 2010, the share of income going to the rich has _______ and the share going to the poor has _______ .
A) risen; fallen
B) fallen; risen
C) stayed about the same; risen
D) risen; risen
A) risen; fallen
B) fallen; risen
C) stayed about the same; risen
D) risen; risen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

(Exhibit: Income Distribution) Curve A represents:
A) a line of unequal income distribution.
B) a line of equal distribution of income.
C) a distribution of income where 20 percent of the families get 60 percent of the income, and 60 percent of the families get 20 percent of the income.
D) the ideal distribution of income, according to market economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
America's poverty rate is _______ than that of most _______ .
A) higher; developing nations
B) higher; other industrialized nations
C) just a little lower; other industrialized nations
D) no lower; developing
A) higher; developing nations
B) higher; other industrialized nations
C) just a little lower; other industrialized nations
D) no lower; developing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If there is considerable _______ among the quintiles of the distribution of income in a country, then there would be many families moving from _______ and others moving from _______ quintiles .
A) immobility; lower to higher; higher to lower
B) mobility; higher to lower; lower to higher
C) immobility; lower to lower; higher to higher
D) stability; lower to higher; higher to higher
A) immobility; lower to higher; higher to lower
B) mobility; higher to lower; lower to higher
C) immobility; lower to lower; higher to higher
D) stability; lower to higher; higher to higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Between 1968 and 2010, the Lorenz curve of the United States became:
A) a straight line.
B) closer to the 45-degree line.
C) more bowed out.
D) more bowed in.
A) a straight line.
B) closer to the 45-degree line.
C) more bowed out.
D) more bowed in.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

(Exhibit: Income Distribution) Curve B shows that the lowest quintile of families gets approximately _______ percent of the income.
A) 2-4
B) 7-10
C) 12-14
D) 17-19

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to the text, it is generally agreed that in the United States since World War II, the distribution of income has:
A) become more equal.
B) become less equal.
C) stayed about the same.
D) changed first toward greater equality and then, after 1968, toward greater inequality.
A) become more equal.
B) become less equal.
C) stayed about the same.
D) changed first toward greater equality and then, after 1968, toward greater inequality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If you establish the value of goods and services necessary to provide a minimum standard of living below which people are poor, you have come up with an income test that is called a(n):
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test.
C) absolute income test.
D) nominal income test.
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test.
C) absolute income test.
D) nominal income test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the United States in the 1990s and 2000s, the gap between the wages of college- and high-school-trained workers _______ and contributed to _______ .
A) narrowed; rising equality
B) widened; rising inequality
C) narrowed; decreasing inequality
D) widened; rising equality
A) narrowed; rising equality
B) widened; rising inequality
C) narrowed; decreasing inequality
D) widened; rising equality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The poverty line for a household with one person in 2010 was:
A) about $8,000.
B) between $11,000 and $12,000.
C) between $16,000 and $17,000.
D) between $22,000 and $23,000.
A) about $8,000.
B) between $11,000 and $12,000.
C) between $16,000 and $17,000.
D) between $22,000 and $23,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The percentage of families headed by women with no spouse present ________ since 1968 in the United States.
A) increased by about 20 percent
B) increased by about 30 percent
C) increased by 60 percent
D) nearly doubled
A) increased by about 20 percent
B) increased by about 30 percent
C) increased by 60 percent
D) nearly doubled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A factor that has been associated with the increase in income inequality in the United States is the:
A) increase in households headed by single women.
B) reduction in the percentage of the population over the age of 65.
C) smaller gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
D) slowdown in technological change.
A) increase in households headed by single women.
B) reduction in the percentage of the population over the age of 65.
C) smaller gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
D) slowdown in technological change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The annual income level that marks the dividing line between poor households and those that are not poor is the:
A) income line.
B) poverty line.
C) minimum-wage line.
D) relative income test.
A) income line.
B) poverty line.
C) minimum-wage line.
D) relative income test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Since the late 1970s in the United States, the demand for _______ labor _______ and the demand for _______ labor _______ .
A) skilled; decreased; unskilled; increased
B) skilled; increased; unskilled; decreased
C) unskilled; stayed the same; skilled; increased
D) unskilled; increased; skilled; stayed the same
A) skilled; decreased; unskilled; increased
B) skilled; increased; unskilled; decreased
C) unskilled; stayed the same; skilled; increased
D) unskilled; increased; skilled; stayed the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Relative poverty might be defined based on the:
A) ratio of food expenditures to housing expenditures.
B) ratio of housing expenditures to total expenditures.
C) relative proportion of income spent on food.
D) upper limit of income in the lowest one-fifth of the income distribution.
A) ratio of food expenditures to housing expenditures.
B) ratio of housing expenditures to total expenditures.
C) relative proportion of income spent on food.
D) upper limit of income in the lowest one-fifth of the income distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An income test devised to indicate poverty for those people whose incomes fall at the bottom of the income distribution is called a(n):
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test.
C) absolute income test.
D) nominal income test.
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test.
C) absolute income test.
D) nominal income test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If you establish that a family is on the low end of the income scale and is thus considered poor, you have come up with a (n):
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test
C) absolute income test
D) nominal income test.
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test
C) absolute income test
D) nominal income test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A factor that has been associated with the increase in income inequality in the United States is the:
A) decrease in households headed by single women.
B) reduction in the percentage of the population over the age of 65.
C) smaller gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
D) way that technological change has affected labor demand.
A) decrease in households headed by single women.
B) reduction in the percentage of the population over the age of 65.
C) smaller gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
D) way that technological change has affected labor demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements about the distribution of income in the United States is true?
A) Since 1968, the distribution of income has become more unequal.
B) Since 1968, the share of income going to the richest families has decreased.
C) Since 1968, the share of income going to the poorest families has risen.
D) The degree of inequality in the distribution of income remained stable between 1968 and 2010.
A) Since 1968, the distribution of income has become more unequal.
B) Since 1968, the share of income going to the richest families has decreased.
C) Since 1968, the share of income going to the poorest families has risen.
D) The degree of inequality in the distribution of income remained stable between 1968 and 2010.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Setting a specific income level and then defining a person (or household) as poor if his or her (or its) income falls below that income level is called a(n):
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test.
C) absolute income test.
D) nominal income test.
A) means-tested test.
B) relative income test.
C) absolute income test.
D) nominal income test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Case in Point titled "Attitudes and Inequality" suggested that:
A) more Americans than Europeans believe that the poor could become rich with enough hard work.
B) more Europeans than Americans believe that the poor could become rich with enough hard work.
C) the majority of both Americans and Europeans believe that the poor could become rich with enough hard work.
D) the majority of both Americans and Europeans believe that success is based on luck, connections, and corruption.
A) more Americans than Europeans believe that the poor could become rich with enough hard work.
B) more Europeans than Americans believe that the poor could become rich with enough hard work.
C) the majority of both Americans and Europeans believe that the poor could become rich with enough hard work.
D) the majority of both Americans and Europeans believe that success is based on luck, connections, and corruption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The poverty line for a household with nine people in 2010 was:
A) between $11,000 and $12,000.
B) between $16,000 and $17,000.
C) between $22,000 and $23,000.
D) over $45,000.
A) between $11,000 and $12,000.
B) between $16,000 and $17,000.
C) between $22,000 and $23,000.
D) over $45,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The percentage of the population that falls below the poverty line is called the:
A) poor rate.
B) poverty rate.
C) homeless rate.
D) absolute number of people in poverty.
A) poor rate.
B) poverty rate.
C) homeless rate.
D) absolute number of people in poverty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A factor that has been associated with the increase in income inequality in the United States is the:
A) decrease in households headed by single women.
B) reduction in the percentage of the population over the age of 65.
C) larger gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
D) slowdown in technological change.
A) decrease in households headed by single women.
B) reduction in the percentage of the population over the age of 65.
C) larger gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
D) slowdown in technological change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following has not been considered as a possible factor in increasing income inequality in the United States since 1968?
A) changes in family structure
B) changes in tax policy
C) technological change
D) a reduction in the number of people attending college
A) changes in family structure
B) changes in tax policy
C) technological change
D) a reduction in the number of people attending college

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the United States since 1999, the gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers:
A) increased.
B) decreased.
C) stayed the same.
D) increased and then decreased.
A) increased.
B) decreased.
C) stayed the same.
D) increased and then decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The poverty line is described by which of the following?
A) It is a dollar figure. When a household income is equal to or less than this figure, the household is not considered to be poor.
B) It is a dollar figure above which a household's income is considered to be in the poor category.
C) In 2010 in the United States, the poverty line for a family of four was an income of $22,314.
D) The poverty line is the same for all family sizes.
A) It is a dollar figure. When a household income is equal to or less than this figure, the household is not considered to be poor.
B) It is a dollar figure above which a household's income is considered to be in the poor category.
C) In 2010 in the United States, the poverty line for a family of four was an income of $22,314.
D) The poverty line is the same for all family sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The demographic group in the United States with the highest poverty rate is:
A) married couples between 25 and 44 years old.
B) college graduates.
C) whites between 45 and 64 years old.
D) households headed by females with no husband present.
A) married couples between 25 and 44 years old.
B) college graduates.
C) whites between 45 and 64 years old.
D) households headed by females with no husband present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In 2010, approximately ________ percent of the families in the United States headed by ________ fell below the poverty line.
A) 45; single men with no female present
B) 20; married couples with husband present
C) 15; unmarried women with no male present
D) 30; women with no husband present
A) 45; single men with no female present
B) 20; married couples with husband present
C) 15; unmarried women with no male present
D) 30; women with no husband present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The total number of poor people in the United States in 2010 was about ________ million.
A) 10
B) 25
C) 32
D) 46
A) 10
B) 25
C) 32
D) 46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In 2010, approximately _______ percent of people below the poverty line received some form of cash assistance.
A) 4
B) 14
C) 20
D) 54
A) 4
B) 14
C) 20
D) 54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The age group in the United States with the highest poverty rate is _______ years old.
A) under 18
B) 25-44
C) 35-44
D) 45-64
A) under 18
B) 25-44
C) 35-44
D) 45-64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In 2010, approximately _______ percent of those counted as poor received food stamps.
A) 33
B) 45
C) 73
D) 93
A) 33
B) 45
C) 73
D) 93

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The poverty rate for blacks in the United States in 2010 was about _______ percent.
A) 3
B) 7
C) 25
D) 40
A) 3
B) 7
C) 25
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A money payment that a recipient may spend as he or she wishes is:
A) the income effect.
B) the wealth effect.
C) noncash assistance.
D) cash assistance.
A) the income effect.
B) the wealth effect.
C) noncash assistance.
D) cash assistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The characteristic most associated with poverty is:
A) age.
B) female-headed households with no husband present.
C) education level.
D) geographic location.
A) age.
B) female-headed households with no husband present.
C) education level.
D) geographic location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The provision of specific goods and services to poor people is:
A) the income effect.
B) the wealth effect.
C) noncash assistance.
D) cash assistance.
A) the income effect.
B) the wealth effect.
C) noncash assistance.
D) cash assistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The benefits provided to the poor through Head Start are primarily in the form of:
A) education.
B) housing.
C) cash.
D) medical care.
A) education.
B) housing.
C) cash.
D) medical care.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The benefits provided to the poor through Temporary Assistance for Needy Families are primarily in the form of:
A) education.
B) housing.
C) cash.
D) medical care.
A) education.
B) housing.
C) cash.
D) medical care.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In general, cash assistance is _______ noncash assistance in the welfare and poverty alleviation programs in the United States.
A) significantly more than
B) slightly more than
C) slightly less than
D) significantly less than
A) significantly more than
B) slightly more than
C) slightly less than
D) significantly less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In 2010, approximately ________ percent of the families in the United States headed by ________ fell below the poverty line.
A) 2; women with no husband present
B) 5; married couples with husband present
C) 47; unmarried males
D) 14; married couples with husband present
A) 2; women with no husband present
B) 5; married couples with husband present
C) 47; unmarried males
D) 14; married couples with husband present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The percentage of the U.S. population living in poverty in 2010 was:
A) approximately 15 percent.
B) 20-24 percent.
C) 25-29 percent.
D) 30-35 percent.
E) greater than 35 percent.
A) approximately 15 percent.
B) 20-24 percent.
C) 25-29 percent.
D) 30-35 percent.
E) greater than 35 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The percentage of the population living in households whose income falls below the poverty line is the:
A) income distribution.
B) poverty rate.
C) wealth effect.
D) subsidy ratio.
A) income distribution.
B) poverty rate.
C) wealth effect.
D) subsidy ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The poverty rate for Hispanics of any race in the United States in 2010 was about _______ percent.
A) 3
B) 10
C) 25
D) 40
A) 3
B) 10
C) 25
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The poverty rate for whites (not Hispanic) in 2010 in the United States was approximately ________ percent.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 25
D) 45
A) 5
B) 10
C) 25
D) 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the United States today, poor people have much ________ incomes than _______ .
A) higher; poor people in poor countries
B) lower incomes; poor people in America five years ago
C) higher; most Americans had five years ago
D) lower; the average person in less developed countries.
A) higher; poor people in poor countries
B) lower incomes; poor people in America five years ago
C) higher; most Americans had five years ago
D) lower; the average person in less developed countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Poverty, in large measure (and according to the authors of the text), is a(n) ________ concept.
A) worthless
B) absolute
C) relative
D) irrelevant
A) worthless
B) absolute
C) relative
D) irrelevant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Economists define discrimination as occurring when:
A) one person receives a lower income for doing an apparently similar job as another.
B) people with similar characteristics experience different economic outcomes because of sex, race, or other noneconomic characteristics.
C) a male professor receives a higher salary than a female professor.
D) people don't like others because of their sex or race.
A) one person receives a lower income for doing an apparently similar job as another.
B) people with similar characteristics experience different economic outcomes because of sex, race, or other noneconomic characteristics.
C) a male professor receives a higher salary than a female professor.
D) people don't like others because of their sex or race.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The economist Gary Becker concluded that discrimination occurs because of people's:
A) preferences.
B) innate meanness.
C) lack of education.
D) greed.
A) preferences.
B) innate meanness.
C) lack of education.
D) greed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Reform to the welfare system in the United States in 1996:
A) defined a minimum period of eligibility.
B) gave states the power to design their own welfare programs.
C) increased noncash benefits after 2 years.
D) increased cash benefits after 2 years.
A) defined a minimum period of eligibility.
B) gave states the power to design their own welfare programs.
C) increased noncash benefits after 2 years.
D) increased cash benefits after 2 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
After adjusting for noncash aid, the poverty rate in the United States is:
A) unchanged.
B) higher.
C) lower.
D) in some regions lower, but in most regions higher.
A) unchanged.
B) higher.
C) lower.
D) in some regions lower, but in most regions higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When people with similar economic characteristics experience different economic outcomes because of their race, sex, or other noneconomic characteristics the result is:
A) uncertainty.
B) discrimination.
C) efficiency.
D) marginality.
A) uncertainty.
B) discrimination.
C) efficiency.
D) marginality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
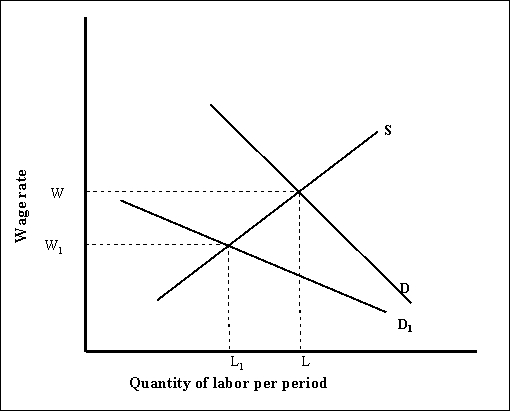
(Exhibit: Discrimination Model) If blacks and white have the same supply curve, but employers have discriminatory attitudes that cause them to assume a black worker is less productive, then the demand curve for blacks will be _______ and the wage for blacks will be _______ .
A) D; W1
B) D; W
C) D1; W1
D) D1; W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Noncash benefits provide more satisfaction to recipients than an equal level of cash benefits.
B) An equal level of cash benefits and noncash benefits provide recipients with the same level of satisfaction.
C) Cash benefits provide more satisfaction to recipients than an equal level of noncash benefits.
D) Most welfare aid in the United States is in the form of cash payments.
A) Noncash benefits provide more satisfaction to recipients than an equal level of cash benefits.
B) An equal level of cash benefits and noncash benefits provide recipients with the same level of satisfaction.
C) Cash benefits provide more satisfaction to recipients than an equal level of noncash benefits.
D) Most welfare aid in the United States is in the form of cash payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Reform to the welfare system in the United States in 1996 eliminated:
A) work requirements.
B) poverty.
C) noncash benefits.
D) the entitlement aspect of welfare.
A) work requirements.
B) poverty.
C) noncash benefits.
D) the entitlement aspect of welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69

(Exhibit: Discrimination Model) If blacks and whites have the same supply curve, but employers have discriminatory attitudes that cause them to assume a black worker is less productive, the wage of whites will be _______ , the quantity of whites hired will be ________ , the wage of blacks will be _______ , and the quantity of blacks hired will be ________ .
A) W; L; W1; L1
B) W; L1; W; L1
C) W1; L1; W; L
D) W1; L; W; L1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

(Exhibit: Discrimination Model) If there is no discrimination in the market and blacks have the same demand and supply curves as whites, then the wage will be _______ and the quantity of labor hired will be _______ .
A) W1; L1
B) W; L1
C) W; L
D) W1; L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
One explanation for why the poor tend to receive more noncash assistance than cash assistance is that:
A) the poor are better off with noncash assistance.
B) the poor prefer to receive noncash assistance.
C) taxpayers prefer to give noncash assistance.
D) those who supply noncash services have less political power than the poor.
A) the poor are better off with noncash assistance.
B) the poor prefer to receive noncash assistance.
C) taxpayers prefer to give noncash assistance.
D) those who supply noncash services have less political power than the poor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In determining the official poverty rate in the United States:
A) only cash income is counted.
B) cash and noncash income are counted.
C) cash, food stamps, and TANF payments are all that is counted.
D) food and medical care are counted.
A) only cash income is counted.
B) cash and noncash income are counted.
C) cash, food stamps, and TANF payments are all that is counted.
D) food and medical care are counted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
According to consumer choice theory, poor people, from their own perspective, are better off with:
A) cash assistance than with noncash assistance.
B) noncash assistance than with cash assistance.
C) either cash assistance or noncash assistance.
D) neither cash assistance nor noncash assistance.
A) cash assistance than with noncash assistance.
B) noncash assistance than with cash assistance.
C) either cash assistance or noncash assistance.
D) neither cash assistance nor noncash assistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The Case in Point titled "Welfare Reform in Britain and the United States indicated that the program in _____ did not require recipients to obtain jobs and that the reduction in case loads was smaller in _____.
A) Britain; Britain
B) Britain; the United States
C) the United States; Britain
D) Britain; the United States.
A) Britain; Britain
B) Britain; the United States
C) the United States; Britain
D) Britain; the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

(Exhibit: Discrimination Model) If blacks and whites have the same supply curve, but employers have discriminatory attitudes that cause them to assume a black worker is less productive, the wage of whites will be _______ , the wage of blacks will be _______ , and the quantity hired of whites will be _______ .
A) W1; W; L1
B) W; W1; L
C) W1; W; L
D) W; W1 ; L1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For the most part, poverty programs are funded by _______ government(s).
A) state
B) the federal
C) municipal
D) a combination of state and local
A) state
B) the federal
C) municipal
D) a combination of state and local

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
One explanation for why the poor tend to receive more noncash assistance than cash assistance is that:
A) the poor are better off with noncash assistance.
B) the poor prefer to receive noncash assistance.
C) taxpayers prefer to give cash assistance.
D) those who supply noncash services have more political power than the poor.
A) the poor are better off with noncash assistance.
B) the poor prefer to receive noncash assistance.
C) taxpayers prefer to give cash assistance.
D) those who supply noncash services have more political power than the poor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements is true regarding welfare reform in 1996?
A) It was designed to move people out of welfare and into work.
B) It extended the years individuals could receive welfare.
C) It changed the poverty rate determination to include the value of noncash benefits.
D) It changed the entire process for calculating the poverty rate.
A) It was designed to move people out of welfare and into work.
B) It extended the years individuals could receive welfare.
C) It changed the poverty rate determination to include the value of noncash benefits.
D) It changed the entire process for calculating the poverty rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The text concludes that poor people, from their own perspective, would be better off with _______ than with _______ .
A) noncash aid; cash grants
B) TANF; cash grants
C) cash grants; noncash aid
D) welfare payments; social security
A) noncash aid; cash grants
B) TANF; cash grants
C) cash grants; noncash aid
D) welfare payments; social security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Reform to the welfare system in the United States in 1996:
A) defined a maximum period of eligibility.
B) gave states less scope in designing their own welfare programs.
C) increased noncash benefits after 2 years.
D) increased cash benefits after 2 years.
A) defined a maximum period of eligibility.
B) gave states less scope in designing their own welfare programs.
C) increased noncash benefits after 2 years.
D) increased cash benefits after 2 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



