Deck 12: General Equilibrium and the Efficiency of Perfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/202
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: General Equilibrium and the Efficiency of Perfect Competition
1
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 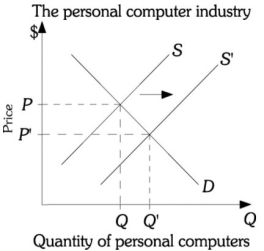 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2
Refer to Figure 12.2. The graph of this situation represents a partial equilibrium analysis because it
A) only shows a change in supply.
B) considers only the personal computer industry.
C) shows changes to both price and quantity.
D) only shows two possible equilibrium points.
 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2Refer to Figure 12.2. The graph of this situation represents a partial equilibrium analysis because it
A) only shows a change in supply.
B) considers only the personal computer industry.
C) shows changes to both price and quantity.
D) only shows two possible equilibrium points.
considers only the personal computer industry.
2
A new technology is developed for producing microwave ovens that reduces production costs by 10%. Which of the following is the most likely consequence of this technological change?
A) Firms will continue to operate efficiently as long as no firm adopts this new technology.
B) Firms must adopt this new technology to remain efficient.
C) This new technology will not affect efficiency, but it will change the equilibrium price and quantity for this industry.
D) If firms do not adopt this new technology, then the economy will remain in general equilibrium, because firms will not change their price and output decisions.
A) Firms will continue to operate efficiently as long as no firm adopts this new technology.
B) Firms must adopt this new technology to remain efficient.
C) This new technology will not affect efficiency, but it will change the equilibrium price and quantity for this industry.
D) If firms do not adopt this new technology, then the economy will remain in general equilibrium, because firms will not change their price and output decisions.
Firms must adopt this new technology to remain efficient.
3
Resources are allocated efficiently when
A) the market produces what people want.
B) economic profits are zero.
C) output is distributed in an equitable fashion.
D) output is produced in a sustainable fashion.
A) the market produces what people want.
B) economic profits are zero.
C) output is distributed in an equitable fashion.
D) output is produced in a sustainable fashion.
the market produces what people want.
4
Examining the equilibrium conditions of individual markets and for households and firms separately is referred to as
A) partial equilibrium analysis.
B) general equilibrium analysis.
C) comparative statics.
D) efficiency analysis.
A) partial equilibrium analysis.
B) general equilibrium analysis.
C) comparative statics.
D) efficiency analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 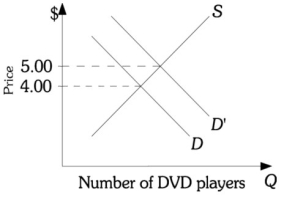 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1
Refer to Figure 12.1. The firm is
A) equally efficient when it produces at points A and B.
B) more efficient when it produces at point A than at point B.
C) more efficient when it produces at point B than at point A.
D) producing at least possible cost anywhere along the given ATC curve.
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Refer to Figure 12.1. The firm is
A) equally efficient when it produces at points A and B.
B) more efficient when it produces at point A than at point B.
C) more efficient when it produces at point B than at point A.
D) producing at least possible cost anywhere along the given ATC curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following questions is not answered by general equilibrium analysis?
A) Are equilibria in different markets compatible with one another?
B) Can all markets simultaneously be in equilibrium?
C) How will a change in one market affect another market?
D) What outcome is most desirable for the whole society?
A) Are equilibria in different markets compatible with one another?
B) Can all markets simultaneously be in equilibrium?
C) How will a change in one market affect another market?
D) What outcome is most desirable for the whole society?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Assume that an economy producing two products, skateboards and in‐line skates, is initially in equilibrium, and that skateboards and in‐line skates are substitutes. If consumer preferences shift away from skateboards and toward in‐line skates, which of the following will not occur?
A) In the short run, firms producing skateboards will incur losses.
B) In the short run, firms producing in‐line skates will earn a profit.
C) Additional capital will begin to flow into in‐line skates production in the long run.
D) Additional capital will begin to flow into skateboard production in the long run.
A) In the short run, firms producing skateboards will incur losses.
B) In the short run, firms producing in‐line skates will earn a profit.
C) Additional capital will begin to flow into in‐line skates production in the long run.
D) Additional capital will begin to flow into skateboard production in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
It is essential to establish specific criteria to judge the performance of any economic system. One such criterion is
A) efficiency.
B) profit opportunity.
C) technological progress.
D) achieving general equilibrium.
A) efficiency.
B) profit opportunity.
C) technological progress.
D) achieving general equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose there is a permanent shift of consumer preferences away from pretzels and toward potato chips. The most likely result would be
A) in the short run, economic losses in the potato chip market.
B) in the long run, a fall in the supply of potato chips.
C) in the short run, a rise in the price of pretzels.
D) short-run profits in the potato chip market increase.
A) in the short run, economic losses in the potato chip market.
B) in the long run, a fall in the supply of potato chips.
C) in the short run, a rise in the price of pretzels.
D) short-run profits in the potato chip market increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Efficiency occurs when
A) the economy is producing what people want at least possible cost.
B) the economy has a fair and just distribution of income.
C) all markets are in equilibrium.
D) unemployment is low and prices are stable.
A) the economy is producing what people want at least possible cost.
B) the economy has a fair and just distribution of income.
C) all markets are in equilibrium.
D) unemployment is low and prices are stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A technological change in the production of cars will
A) affect only the markets for inputs used to produce cars.
B) affect only the way cars are produced.
C) have no effect on consumers.
D) affect input and output markets in the automobile industry and other related industries.
A) affect only the markets for inputs used to produce cars.
B) affect only the way cars are produced.
C) have no effect on consumers.
D) affect input and output markets in the automobile industry and other related industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A gas tax holiday would
A) affect the market for gasoline.
B) affect the market for air travel.
C) affect the level of congestion on roads.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) affect the market for gasoline.
B) affect the market for air travel.
C) affect the level of congestion on roads.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To conduct a general equilibrium analysis of a change in consumer preferences away from beef and toward chicken, you must consider
A) changes in the equilibrium prices and quantities of beef and chicken.
B) changes in the amount of resources allocated to the production of beef and chicken.
C) changes in the price of resources allocated to the production of beef and chicken.
D) all of the above
A) changes in the equilibrium prices and quantities of beef and chicken.
B) changes in the amount of resources allocated to the production of beef and chicken.
C) changes in the price of resources allocated to the production of beef and chicken.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Because most people prefer smartphones to flip phones, firms can improve efficiency by
A) stopping production of flip phones and starting production of smartphones.
B) starting production of flip phones and stopping production of smartphones.
C) increasing production of both flip phones and smartphones.
D) stopping production of both flip phones and smartphones.
A) stopping production of flip phones and starting production of smartphones.
B) starting production of flip phones and stopping production of smartphones.
C) increasing production of both flip phones and smartphones.
D) stopping production of both flip phones and smartphones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Initially the beef and mutton markets are in equilibrium, then preferences shift away from beef and into mutton. If you are a cattle rancher, the best profit-maximizing strategy is to
A) shut down.
B) increase output so as to increase your market share.
C) shift some of your ranching capacity into cattle raising.
D) decrease output so as to minimize short run losses.
A) shut down.
B) increase output so as to increase your market share.
C) shift some of your ranching capacity into cattle raising.
D) decrease output so as to minimize short run losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Preferences have just shifted away from beef and into mutton. If you are a sheep rancher, the best profit-maximizing strategy is to
A) shut down.
B) produce as much as possible to earn profits in the short run.
C) shift some of your ranching capacity into cattle raising.
D) cut prices to increase market share.
A) shut down.
B) produce as much as possible to earn profits in the short run.
C) shift some of your ranching capacity into cattle raising.
D) cut prices to increase market share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2
Refer to Figure 12.2. A technological advance causes the supply of personal computers to increase. The graph of this situation represents a
A) general equilibrium analysis because it identifies what happens to both equilibrium price and quantity of personal computers.
B) partial equilibrium analysis because it considers only this one industry.
C) firm-specific analysis because only one firm would be affected by the technological advance.
D) technological analysis because the change resulted from a technological advance.
 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2Refer to Figure 12.2. A technological advance causes the supply of personal computers to increase. The graph of this situation represents a
A) general equilibrium analysis because it identifies what happens to both equilibrium price and quantity of personal computers.
B) partial equilibrium analysis because it considers only this one industry.
C) firm-specific analysis because only one firm would be affected by the technological advance.
D) technological analysis because the change resulted from a technological advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1
Refer to Figure 12.1. This competitive firm is currently at Point B on the ATC curve. The firm's move toward an output where ATC will be at point A will make the economy
A) more fair and the distribution of outcome more equitable.
B) more stable.
C) less efficient.
D) less stable.
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Refer to Figure 12.1. This competitive firm is currently at Point B on the ATC curve. The firm's move toward an output where ATC will be at point A will make the economy
A) more fair and the distribution of outcome more equitable.
B) more stable.
C) less efficient.
D) less stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1
Refer to Figure 12.1. The firm is
A) equally efficient when it produces at points A and B.
B) less efficient when it produces at point A than at point B.
C) less efficient when it produces at point B than at point A.
D) producing at least possible cost anywhere along the given ATC curve.
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Refer to Figure 12.1. The firm is
A) equally efficient when it produces at points A and B.
B) less efficient when it produces at point A than at point B.
C) less efficient when it produces at point B than at point A.
D) producing at least possible cost anywhere along the given ATC curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1
Refer to Figure 12.1. This firm is currently at Point A on the ATC curve. If this firm moves toward Point B, this will make the
A) distribution of outcome more equitable.
B) economy more stable.
C) economy more efficient.
D) economy less stable.
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Refer to Figure 12.1. This firm is currently at Point A on the ATC curve. If this firm moves toward Point B, this will make the
A) distribution of outcome more equitable.
B) economy more stable.
C) economy more efficient.
D) economy less stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the equilibrium price of X will ________ and the equilibrium price of Y will ________.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the equilibrium price of X will ________ and the equilibrium price of Y will ________.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, sector X will likely see ________ and sector Y will likely see ________.
A) capital inflow; capital outflow
B) capital outflow; capital inflow
C) capital inflow; no change in capital flows
D) no change in capital flows; capital outflow
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, sector X will likely see ________ and sector Y will likely see ________.
A) capital inflow; capital outflow
B) capital outflow; capital inflow
C) capital inflow; no change in capital flows
D) no change in capital flows; capital outflow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Currently in sector X, price is
A) greater than average cost.
B) less than average cost.
C) equal to average cost.
D) More information is needed to answer the question.
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Currently in sector X, price is
A) greater than average cost.
B) less than average cost.
C) equal to average cost.
D) More information is needed to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The condition that exists when all markets in an economy are in simultaneous equilibrium is known as
A) market equity.
B) Pareto efficiency.
C) partial equilibrium.
D) general equilibrium.
A) market equity.
B) Pareto efficiency.
C) partial equilibrium.
D) general equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 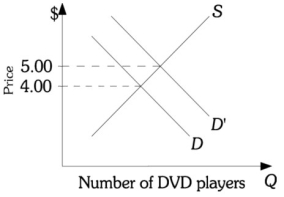 Figure 12.3
Figure 12.3
Refer to Figure 12.3. The DVD industry is a constant-cost industry. As the demand for DVD players shifts from D to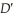 , which of the following is least likely to result?
, which of the following is least likely to result?
A) More resources will be allocated to produce DVD players.
B) The demand for DVDs will increase.
C) If the market for DVD players is competitive, the price will increase to $5.00 in the short and long run.
D) If the market for DVD players is perfectly competitive, economic profits in this industry will increase in the short run, but will fall back to zero in the long run.
 Figure 12.3
Figure 12.3Refer to Figure 12.3. The DVD industry is a constant-cost industry. As the demand for DVD players shifts from D to
 , which of the following is least likely to result?
, which of the following is least likely to result?A) More resources will be allocated to produce DVD players.
B) The demand for DVDs will increase.
C) If the market for DVD players is competitive, the price will increase to $5.00 in the short and long run.
D) If the market for DVD players is perfectly competitive, economic profits in this industry will increase in the short run, but will fall back to zero in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.3
Figure 12.3
Refer to Figure 12.3. The DVD industry is a constant-cost industry. As the demand for DVD players shifts from D' to D, which of the following will not occur?
A) Fewer resources will be allocated to produce DVD players.
B) The demand for DVDs will decrease.
C) If the market for DVD players is competitive the price will decrease to $4.00 in the short and long run.
D) If the market for DVD players is perfectly competitive, economic profits in this industry will decrease in the short run, but will fall back to zero in the long run.
 Figure 12.3
Figure 12.3Refer to Figure 12.3. The DVD industry is a constant-cost industry. As the demand for DVD players shifts from D' to D, which of the following will not occur?
A) Fewer resources will be allocated to produce DVD players.
B) The demand for DVDs will decrease.
C) If the market for DVD players is competitive the price will decrease to $4.00 in the short and long run.
D) If the market for DVD players is perfectly competitive, economic profits in this industry will decrease in the short run, but will fall back to zero in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0
-Refer to Figure 12.4. Currently in sector Y, price is
A) greater than average cost.
B) less than average cost.
C) equal to average cost.
D) More information is needed to answer the question.
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0
-Refer to Figure 12.4. Currently in sector Y, price is
A) greater than average cost.
B) less than average cost.
C) equal to average cost.
D) More information is needed to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
One criterion used to judge the performance of any economic system is
A) equity.
B) revenue generation.
C) nominal growth.
D) inflation.
A) equity.
B) revenue generation.
C) nominal growth.
D) inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
To conduct a partial equilibrium analysis of a change in consumer preferences toward coffee and away from tea, you must consider
A) changes in the equilibrium price and quantity of coffee.
B) changes in the amount of resources allocated to the production of coffee.
C) changes in the price of resources allocated to the production of coffee.
D) all of the above
A) changes in the equilibrium price and quantity of coffee.
B) changes in the amount of resources allocated to the production of coffee.
C) changes in the price of resources allocated to the production of coffee.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, firms in sector X are now ________ and firms in sector Y are now ________.
A) breaking even; suffering losses
B) earning profits; breaking even
C) earning profits; suffering losses
D) breaking even; breaking even
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, firms in sector X are now ________ and firms in sector Y are now ________.
A) breaking even; suffering losses
B) earning profits; breaking even
C) earning profits; suffering losses
D) breaking even; breaking even

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A new technology is developed for producing solar panels that reduces production costs by 40%. Which of the following is true?
A) Firms will continue to operate efficiently as long as no firm adopts this new technology.
B) For the economy to remain efficient, product produced with this new technology must be equitably distributed to all consumers.
C) This new technology will affect efficiency, and will change the equilibrium price and quantity for this industry.
D) If firms do not adopt this new technology, then the economy will remain in general equilibrium, because firms will not change their price and output decisions.
A) Firms will continue to operate efficiently as long as no firm adopts this new technology.
B) For the economy to remain efficient, product produced with this new technology must be equitably distributed to all consumers.
C) This new technology will affect efficiency, and will change the equilibrium price and quantity for this industry.
D) If firms do not adopt this new technology, then the economy will remain in general equilibrium, because firms will not change their price and output decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, sector X will likely see ________ and sector Y will likely see ________.
A) the entrance of new firms; the exit of existing firms
B) the exit of existing firms; the entrance of new firms
C) the entrance of new firms; no entry or exit of firms
D) no entry or exit of firms; the exit of existing firms
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, sector X will likely see ________ and sector Y will likely see ________.
A) the entrance of new firms; the exit of existing firms
B) the exit of existing firms; the entrance of new firms
C) the entrance of new firms; no entry or exit of firms
D) no entry or exit of firms; the exit of existing firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the equilibrium quantity of X will ________ and the equilibrium quantity of Y will ________.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the equilibrium quantity of X will ________ and the equilibrium quantity of Y will ________.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Partial equilibrium analysis refers to ________ examining the equilibrium conditions in individual markets and for households and firms.
A) separately
B) jointly
C) partially
D) simultaneously
A) separately
B) jointly
C) partially
D) simultaneously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose that a town has two major bottling plants. One of these bottling plants is unionized and the union has just negotiated a 7% wage increase each year for the next two years. Which of the following is most likely to occur?
A) The price of labor in the unionized bottling plant will increase, but there will be no changes in the price of labor in the nonunionized bottling plant.
B) The price of labor will change in both the unionized and nonunionized bottling plants, but no other input markets will be affected.
C) The price of labor will change in both the unionized and nonunionized bottling plants. Employment of labor and other inputs is also likely to change in both bottling plants.
D) The only effect will be that the price charged by the unionized bottling plant will increase to cover the additional costs of labor.
A) The price of labor in the unionized bottling plant will increase, but there will be no changes in the price of labor in the nonunionized bottling plant.
B) The price of labor will change in both the unionized and nonunionized bottling plants, but no other input markets will be affected.
C) The price of labor will change in both the unionized and nonunionized bottling plants. Employment of labor and other inputs is also likely to change in both bottling plants.
D) The only effect will be that the price charged by the unionized bottling plant will increase to cover the additional costs of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Firms stop producing DVDs and start producing Blu-ray discs because people prefer Blu-ray discs discs to DVDs. This will
A) make the distribution of outcome more equitable.
B) make the economy more stable.
C) improve efficiency.
D) make the economy less stable.
A) make the distribution of outcome more equitable.
B) make the economy more stable.
C) improve efficiency.
D) make the economy less stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Scientists find that eating corn three times a day will prolong life. This leads to a shift in preferences away from wheat and toward corn. As we move from one equilibrium to another, we can predict that
A) all input markets are affected.
B) all input markets except land are affected because both products use land as an input.
C) labor markets are not affected because the wheat industry and the corn industry use laborers to drive tractors.
D) even if they use different technologies, no input markets are affected because they use the same inputs.
A) all input markets are affected.
B) all input markets except land are affected because both products use land as an input.
C) labor markets are not affected because the wheat industry and the corn industry use laborers to drive tractors.
D) even if they use different technologies, no input markets are affected because they use the same inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector X will cause the industry's short-run ________ curve to shift to the ________.
A) supply; left
B) supply; right
C) demand; left
D) demand; right
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector X will cause the industry's short-run ________ curve to shift to the ________.
A) supply; left
B) supply; right
C) demand; left
D) demand; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Resources are allocated efficiently when
A) everyone can afford what they want.
B) production occurs at least cost.
C) output is fairly distributed.
D) profits are maximized.
A) everyone can afford what they want.
B) production occurs at least cost.
C) output is fairly distributed.
D) profits are maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
________ occurs when the economy is producing what people want at least possible cost.
A) Efficiency
B) Equity
C) Stability
D) Maximum profit
A) Efficiency
B) Equity
C) Stability
D) Maximum profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Input and output markets operate independently and thus should be analyzed as separate entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
General equilibrium exists when all markets in an economy are simultaneously in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Efficiency is the condition in which the economy is producing what people want at the least possible cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Free markets, by definition, must always be efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Efficiency is another word for equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Partial equilibrium analysis is the process of examining the equilibrium conditions for households and firms combined for more than one but not all individual markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
General equilibrium exists when any one market in an economy is in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When all markets are in simultaneous equilibrium, the general equilibrium condition has been satisfied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flows in sectors X and Y will eventually________ in industry X and ________ in industry Y.
A) increase the price to P1; decrease the price to P1
B) decrease the price to P0; increase the price to P0
C) increase the price to P1; increase the price to P0
D) decrease the price to P0; decrease the price to P1
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flows in sectors X and Y will eventually________ in industry X and ________ in industry Y.
A) increase the price to P1; decrease the price to P1
B) decrease the price to P0; increase the price to P0
C) increase the price to P1; increase the price to P0
D) decrease the price to P0; decrease the price to P1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Pareto optimality is the condition in which
A) the distribution of income is equal.
B) no change is possible that will make some members of society better off without making at least one other member of society worse off.
C) firms are forced to internalize the effects of all externalities.
D) it is possible to make one person better off without making someone else worse off.
A) the distribution of income is equal.
B) no change is possible that will make some members of society better off without making at least one other member of society worse off.
C) firms are forced to internalize the effects of all externalities.
D) it is possible to make one person better off without making someone else worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, a new general equilibrium will eventually be reached in sector X with a price of ________ and a quantity of ________.
A) P1; Q1
B) P0; Q0
C) P1; Q0
D) P0; > Q1
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, a new general equilibrium will eventually be reached in sector X with a price of ________ and a quantity of ________.
A) P1; Q1
B) P0; Q0
C) P1; Q0
D) P0; > Q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When one market reaches a new equilibrium, the general equilibrium condition has been satisfied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Both economists and mathematicians have shown there exists at least one set of prices that will clear all markets in a system simultaneously, known as equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector Y will cause the industry's short-run ________ curve to shift to the ________.
A) supply; left
B) supply; right
C) demand; left
D) demand; right
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector Y will cause the industry's short-run ________ curve to shift to the ________.
A) supply; left
B) supply; right
C) demand; left
D) demand; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector X will eventually
A) eliminate all profits.
B) eliminate all losses.
C) generate excess profits.
D) result in excess losses.
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector X will eventually
A) eliminate all profits.
B) eliminate all losses.
C) generate excess profits.
D) result in excess losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A condition in which no change is possible that will make some members of society better off without making some other members of society worse off is called
A) Pareto optimality.
B) partial equilibrium.
C) general equilibrium.
D) market failure.
A) Pareto optimality.
B) partial equilibrium.
C) general equilibrium.
D) market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Equity is the condition in which the economy is producing what people want at the least possible cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, a new general equilibrium will eventually be reached in sector Y with a price of ________ and a quantity of ________.
A) P1; Q1
B) P0; Q0
C) P1; Q0
D) P0; < Q1
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, a new general equilibrium will eventually be reached in sector Y with a price of ________ and a quantity of ________.
A) P1; Q1
B) P0; Q0
C) P1; Q0
D) P0; < Q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Capital tends to flow into markets earning short-run profits and out of markets suffering short-term losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4
There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector Y will eventually
A) eliminate all profits.
B) eliminate all losses.
C) generate excess profits.
D) result in excess losses.
 Figure 12.4
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.
Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flow in sector Y will eventually
A) eliminate all profits.
B) eliminate all losses.
C) generate excess profits.
D) result in excess losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A voluntary exchange between Mike (the purchaser) and Wayne (the seller) occurs because
A) Mike stands to gain and Wayne to lose.
B) Mike stands to lose and Wayne to gain.
C) they both gain from the transaction.
D) they had no choice.
A) Mike stands to gain and Wayne to lose.
B) Mike stands to lose and Wayne to gain.
C) they both gain from the transaction.
D) they had no choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In making labor supply decisions, households weigh
A) the market wage against the value of market produced goods.
B) the market wage against the value of their marginal product of labor.
C) the market wage against the value of leisure and time spent in unpaid household production.
D) child care costs.
A) the market wage against the value of market produced goods.
B) the market wage against the value of their marginal product of labor.
C) the market wage against the value of leisure and time spent in unpaid household production.
D) child care costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An economist has estimated that the maintenance of a public park costs $25,000 a year and that the public park generates $30,000 a year in revenue for merchants near the park. From society's point of view, the maintenance of this park is
A) inefficient because everyone in the community pays taxes to support the park, but only the merchants near the park benefit.
B) inefficient because the additional revenues generated by the park are so low.
C) potentially efficient because the value of the gains exceed the value of the costs.
D) potentially efficient because no one would be made worse off as a result of maintaining the park.
A) inefficient because everyone in the community pays taxes to support the park, but only the merchants near the park benefit.
B) inefficient because the additional revenues generated by the park are so low.
C) potentially efficient because the value of the gains exceed the value of the costs.
D) potentially efficient because no one would be made worse off as a result of maintaining the park.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A ________ system is one in which all possible trades that make some societal members better off without making others worse off have been exhausted.
A) Pareto maximized
B) Pareto optimal
C) market
D) general equilibrium
A) Pareto maximized
B) Pareto optimal
C) market
D) general equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When all the conditions for perfect competition are met
A) resources are allocated among firms efficiently.
B) final products are distributed among households efficiently.
C) the system produces the goods and services consumers want.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) resources are allocated among firms efficiently.
B) final products are distributed among households efficiently.
C) the system produces the goods and services consumers want.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
You value your economics textbook at $10. Someone else values it at $25, and that person is willing to pay you $20 for your textbook. Would selling your textbook to this person for $20 be Pareto efficient?
A) No, because you did not receive the maximum amount the other person would have been willing to pay for the textbook.
B) No, the person paid you $20 for the book so his net benefit was only $5, whereas your net benefit was $10. For this change to be Pareto efficient, each of you should have the same net benefit.
C) Yes, because both of you are better off as a result of the trade.
D) Yes, because even though you gain from the trade and he loses, there is the potential for you to compensate him for his loss.
A) No, because you did not receive the maximum amount the other person would have been willing to pay for the textbook.
B) No, the person paid you $20 for the book so his net benefit was only $5, whereas your net benefit was $10. For this change to be Pareto efficient, each of you should have the same net benefit.
C) Yes, because both of you are better off as a result of the trade.
D) Yes, because even though you gain from the trade and he loses, there is the potential for you to compensate him for his loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 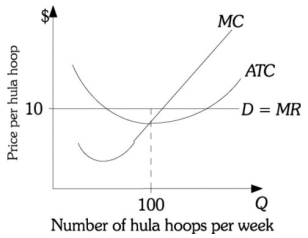 Figure 12.5
Figure 12.5
Refer to Figure 12.5. Hula hoops are produced in a perfectly competitive market. This hula hoop firm is currently producing and selling 100 hula hoops per week. Which of the following is true?
A) Society would be better off if more hula hoops were produced because at the current level of production price is greater than marginal cost.
B) Society would be better off if fewer hula hoops were produced because if this firm reduced its production, its profits would increase.
C) Hula hoop production is at the efficient level because ATC is minimized.
D) Fewer resources should be devoted to hula hoop production because ATC is less than price.
 Figure 12.5
Figure 12.5Refer to Figure 12.5. Hula hoops are produced in a perfectly competitive market. This hula hoop firm is currently producing and selling 100 hula hoops per week. Which of the following is true?
A) Society would be better off if more hula hoops were produced because at the current level of production price is greater than marginal cost.
B) Society would be better off if fewer hula hoops were produced because if this firm reduced its production, its profits would increase.
C) Hula hoop production is at the efficient level because ATC is minimized.
D) Fewer resources should be devoted to hula hoop production because ATC is less than price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A person who chooses not to be in the labor force reveals that
A) his potential product in the market is zero.
B) either leisure or the value of nonpaid labor is worth more to him than the value that society places on his potential product in the market.
C) either leisure or the value of nonpaid labor is worth less to him than the value that society places on his potential product in the market.
D) either leisure or the value of nonpaid labor is worth zero to him.
A) his potential product in the market is zero.
B) either leisure or the value of nonpaid labor is worth more to him than the value that society places on his potential product in the market.
C) either leisure or the value of nonpaid labor is worth less to him than the value that society places on his potential product in the market.
D) either leisure or the value of nonpaid labor is worth zero to him.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose a policy change will generate $100,000 of benefits for low-income families and $120,000 of costs for high-income families. This change can best be described as
A) Pareto efficient.
B) inefficient.
C) potentially efficient.
D) equitable.
A) Pareto efficient.
B) inefficient.
C) potentially efficient.
D) equitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a restaurant runs a special and sells a lobster dinner for $4.50, Amy buys one lobster dinner a week. If lobster dinners are not on special and the price is $16.00, Amy buys zero lobster dinners per week. Which of the following is true?
A) Amy's demand for lobster is inelastic.
B) Amy's marginal utility from a lobster dinner is less than $4.50.
C) The value of Amy's marginal utility from a lobster dinner is at least $4.50 and less than $16.00.
D) Amy's marginal utility from a lobster dinner is greater than $16.00.
A) Amy's demand for lobster is inelastic.
B) Amy's marginal utility from a lobster dinner is less than $4.50.
C) The value of Amy's marginal utility from a lobster dinner is at least $4.50 and less than $16.00.
D) Amy's marginal utility from a lobster dinner is greater than $16.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An activity that makes some people better off and nobody worse off is a
A) government transfer program such as Social Security.
B) reduction in interest rates.
C) price floor that increases income to suppliers.
D) voluntary exchange.
A) government transfer program such as Social Security.
B) reduction in interest rates.
C) price floor that increases income to suppliers.
D) voluntary exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A household will buy a good as long as the
A) good's price is greater than the maximum a consumer would be willing to pay for it.
B) marginal utility from its consumption is greater than or equal to its market price.
C) good still provides the consumer with average utility.
D) good's use value is less than the price being charged for the good.
A) good's price is greater than the maximum a consumer would be willing to pay for it.
B) marginal utility from its consumption is greater than or equal to its market price.
C) good still provides the consumer with average utility.
D) good's use value is less than the price being charged for the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose a new government policy will generate $5,000 of benefits for local businesses and $3,000 of costs. This policy can best be described as
A) Pareto efficient.
B) inefficient.
C) potentially efficient.
D) equitable.
A) Pareto efficient.
B) inefficient.
C) potentially efficient.
D) equitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose a policy change will generate $180,000 of benefits for low-income families and $150,000 of costs for high-income and middle-class families. This change can best be described as
A) inefficient.
B) Pareto efficient.
C) potentially efficient.
D) equitable.
A) inefficient.
B) Pareto efficient.
C) potentially efficient.
D) equitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
You value your favorite shirt at $110. Someone else values it at $150, and that person is willing to pay you $120 for your shirt. Would selling your shirt to this person for $120 be Pareto efficient?
A) No, because you did not receive the maximum amount the other person would have been willing to pay for the shirt.
B) No, the person paid you $120 for the shirt so his net benefit was $30, while your net benefit was $10. For this change to be Pareto efficient, each of you should have the same net benefit.
C) Yes, because even though you gain from the trade and he loses, there is the potential for you to compensate him for his loss.
D) Yes, because both of you are better off as a result of the trade.
A) No, because you did not receive the maximum amount the other person would have been willing to pay for the shirt.
B) No, the person paid you $120 for the shirt so his net benefit was $30, while your net benefit was $10. For this change to be Pareto efficient, each of you should have the same net benefit.
C) Yes, because even though you gain from the trade and he loses, there is the potential for you to compensate him for his loss.
D) Yes, because both of you are better off as a result of the trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If some gain and some lose as the result of a change, and it can be demonstrated that the value of the gains exceeds the value of the losses, then the change is said to be
A) potentially efficient.
B) inefficient.
C) unequivocally Pareto optimal.
D) technically efficient.
A) potentially efficient.
B) inefficient.
C) unequivocally Pareto optimal.
D) technically efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Marginal cost is a good measure of
A) the social value of a marginal unit of a good.
B) the least costly way to produce all units of a good.
C) what society gives up by using resources to produce more of a good or service.
D) what society gains by using resources to produce more of a good or service.
A) the social value of a marginal unit of a good.
B) the least costly way to produce all units of a good.
C) what society gives up by using resources to produce more of a good or service.
D) what society gains by using resources to produce more of a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In perfect competition, when firms are maximizing profits and households are maximizing utility
A) Pareto optimality has been obtained.
B) voluntary exchange can be used to make both firms and households better off.
C) the outcome is inefficient.
D) individual welfare is maximized, but social welfare is not.
A) Pareto optimality has been obtained.
B) voluntary exchange can be used to make both firms and households better off.
C) the outcome is inefficient.
D) individual welfare is maximized, but social welfare is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The opportunity cost of using resources to produce more of one good instead of more of another good is its
A) marginal revenue.
B) marginal cost.
C) price.
D) total cost.
A) marginal revenue.
B) marginal cost.
C) price.
D) total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 12.5
Figure 12.5
Refer to Figure 12.5. A firm produces hula hoops in a perfectly competitive market and currently produces and sells 100 per week. At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best served
A) if the price was lower than $10 per hula hoop.
B) if the price was higher than $10 per hula hoop.
C) if the price remained at $10 per hula hoop.
D) Society cannot be best served at a production quantity of 100, regardless of the price per hula hoop.
 Figure 12.5
Figure 12.5Refer to Figure 12.5. A firm produces hula hoops in a perfectly competitive market and currently produces and sells 100 per week. At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best served
A) if the price was lower than $10 per hula hoop.
B) if the price was higher than $10 per hula hoop.
C) if the price remained at $10 per hula hoop.
D) Society cannot be best served at a production quantity of 100, regardless of the price per hula hoop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 202 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



