Deck 45: The Global Ecosystem
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/127
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 45: The Global Ecosystem
1
Based on our knowledge of the factors influencing primary productivity,the lowest level of net primary production would most likely be found in forests located in
A) Vietnam.
B) the Amazon.
C) northern Canada.
D) the United States.
E) the African Congo.
A) Vietnam.
B) the Amazon.
C) northern Canada.
D) the United States.
E) the African Congo.
C
2
Earth acts as a(n)_______ system in terms of materials and a(n)_______ system in terms of energy.
A) open;open
B) open;closed
C) open;recycling
D) closed;open
E) closed;recycling
A) open;open
B) open;closed
C) open;recycling
D) closed;open
E) closed;recycling
D
3
Which series represents the correct ranking of average NPP,from greatest to smallest?
A) Marsh river estuary
B) Marsh estuary river
C) Estuary marsh river
D) Estuary river marsh
E) River estuary marsh
A) Marsh river estuary
B) Marsh estuary river
C) Estuary marsh river
D) Estuary river marsh
E) River estuary marsh
Marsh estuary river
4
In ocean environments,the highest net primary productivity tends to be in coastal zones and upwelling zones,because they
A) receive the most rainfall.
B) receive constant inputs of nutrients.
C) are all in temperate or tropical zones.
D) are shallow and therefore receive the most sunlight.
E) are close to hydrothermal vents,which provide nutrients.
A) receive the most rainfall.
B) receive constant inputs of nutrients.
C) are all in temperate or tropical zones.
D) are shallow and therefore receive the most sunlight.
E) are close to hydrothermal vents,which provide nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Large-scale interconnections among ecosystems occur by all of the following processes except
A) geological processes within Earth.
B) transport of materials by wind currents.
C) transport of materials by water currents.
D) trophic interactions within an ecosystem.
E) movement of organisms between ecosystems.
A) geological processes within Earth.
B) transport of materials by wind currents.
C) transport of materials by water currents.
D) trophic interactions within an ecosystem.
E) movement of organisms between ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Primary productivity is likely to decrease in very wet environments,where soils are water-saturated,because plants receive
A) too much heat.
B) too much light.
C) too little water.
D) too few nutrients.
E) too little dissolved oxygen.
A) too much heat.
B) too much light.
C) too little water.
D) too few nutrients.
E) too little dissolved oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
NPP in aquatic ecosystems is most often limited by
A) light only.
B) light and nutrient availability.
C) temperature and latitude.
D) light and temperature.
E) latitude only.
A) light only.
B) light and nutrient availability.
C) temperature and latitude.
D) light and temperature.
E) latitude only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
To maximize net primary productivity,the best combination of climatic conditions is
A) high temperature and high precipitation.
B) high temperature and medium precipitation.
C) high temperature and low precipitation.
D) medium temperature and high precipitation.
E) medium temperature and medium precipitation.
A) high temperature and high precipitation.
B) high temperature and medium precipitation.
C) high temperature and low precipitation.
D) medium temperature and high precipitation.
E) medium temperature and medium precipitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Scientists currently estimate NPP using which type of measurement?
A) Wavelengths of light reflected from Earth's surface
B) Amount of nitrogen fixation
C) Atmospheric O2 concentrations
D) Atmospheric CO2 concentrations
E) Total yearly plant biomass
A) Wavelengths of light reflected from Earth's surface
B) Amount of nitrogen fixation
C) Atmospheric O2 concentrations
D) Atmospheric CO2 concentrations
E) Total yearly plant biomass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Organic materials are converted from a form that is accessible to life to a form that is inaccessible to life by the process of
A) uptake.
B) erosion.
C) weathering.
D) compaction.
E) decomposition.
A) uptake.
B) erosion.
C) weathering.
D) compaction.
E) decomposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In 1957,Dave Keeling used new sensitive instruments to begin to
A) measure aspects of the global nitrogen cycle.
B) obtain accurate measurements of atmospheric CO2.
C) estimate the extent of nitrogen fixation by microbes.
D) determine the effects of greenhouse warming on Hadley cells.
E) establish the connection between CO2 and the greenhouse effect.
A) measure aspects of the global nitrogen cycle.
B) obtain accurate measurements of atmospheric CO2.
C) estimate the extent of nitrogen fixation by microbes.
D) determine the effects of greenhouse warming on Hadley cells.
E) establish the connection between CO2 and the greenhouse effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Refer to the diagram below.Materials undergoing the processes of uplift or erosion would be leaving a(n)_______ form and most likely be entering the _______ compartment. 
A) accessible;decomposers
B) accessible;soil,sediments
C) inaccessible;decomposers
D) inaccessible;atmosphere
E) inaccessible;soil,sediments

A) accessible;decomposers
B) accessible;soil,sediments
C) inaccessible;decomposers
D) inaccessible;atmosphere
E) inaccessible;soil,sediments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which statement best describes the interaction of energy and materials,or process of ecosystem function,within an ecosystem?
A) Both energy and materials cycle through biotic,but not abiotic,components.
B) Energy cycles through biotic components;materials cycle through abiotic components.
C) Energy and materials both travel throughout ecosystems,but they follow separate,disconnected routes.
D) Energy and materials enter biotic components through primary producers;energy flows one way and materials cycle.
E) Materials travel through ecosystems in one direction and are constantly replenished;energy cycles and is used over and over.
A) Both energy and materials cycle through biotic,but not abiotic,components.
B) Energy cycles through biotic components;materials cycle through abiotic components.
C) Energy and materials both travel throughout ecosystems,but they follow separate,disconnected routes.
D) Energy and materials enter biotic components through primary producers;energy flows one way and materials cycle.
E) Materials travel through ecosystems in one direction and are constantly replenished;energy cycles and is used over and over.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The first time scientists hypothesized that changes in CO2 concentrations could cause climatic changes by trapping heat in the lower atmosphere was
A) before the U.S.Civil War.
B) around the time of World War I.
C) around the time of World War II.
D) during the 1950s.
E) during the 1970s.
A) before the U.S.Civil War.
B) around the time of World War I.
C) around the time of World War II.
D) during the 1950s.
E) during the 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Plants absorb most of the nutrients they need for growth and reproduction as ions dissolved in water.Which element do they obtain from air?
A) Carbon
B) Calcium
C) Nitrogen
D) Phosphorus
E) Potassium
A) Carbon
B) Calcium
C) Nitrogen
D) Phosphorus
E) Potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Agricultural soil in a relatively dry region of the United States has been tilled for many years and has undergone both erosion and irrigation.An inadequacy of which factor is most likely to limit plant productivity in this soil?
A) Nitrogen or phosphorus
B) Water
C) Oxygen
D) Temperature
E) Light
A) Nitrogen or phosphorus
B) Water
C) Oxygen
D) Temperature
E) Light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In general,given sufficient precipitation,what relationship does NPP show to latitude?
A) NPP is highest at low (equatorial)latitudes and decreases at high latitudes.
B) NPP is highest at high latitudes and decreases at low (equatorial)latitudes.
C) NPP is relatively equal at all latitudes;it varies with nutrients,not latitude.
D) NPP is relatively equal at all latitudes;it varies with temperature,not latitude.
E) NPP is variable with respect to latitude;high and low NPPs occur at all latitudes.
A) NPP is highest at low (equatorial)latitudes and decreases at high latitudes.
B) NPP is highest at high latitudes and decreases at low (equatorial)latitudes.
C) NPP is relatively equal at all latitudes;it varies with nutrients,not latitude.
D) NPP is relatively equal at all latitudes;it varies with temperature,not latitude.
E) NPP is variable with respect to latitude;high and low NPPs occur at all latitudes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
On average,NPP from cultivated land ecosystems is higher than NPP from _______ ecosystems.
A) swamp
B) estuary
C) boreal forest
D) temperate forest
E) temperate grassland
A) swamp
B) estuary
C) boreal forest
D) temperate forest
E) temperate grassland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which ocean environment is likely to have the lowest net primary productivity?
A) Estuary
B) Coral reef
C) Open ocean
D) Upwelling zone
E) Marine algal bed
A) Estuary
B) Coral reef
C) Open ocean
D) Upwelling zone
E) Marine algal bed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The second law of thermodynamics states that in every energy exchange,some energy is lost as heat;that is,it becomes unavailable for further use.Which of the following makes it possible for life to continue on Earth?
A) The greenhouse effect continually generates heat.
B) Earth is an open system and is continually receiving new matter.
C) Earth is an open system and is continually receiving new energy.
D) The slow mixing of water in the oceans allows usable energy to accumulate.
E) Earth's surface constantly receives inputs of energy from molten magma in its core.
A) The greenhouse effect continually generates heat.
B) Earth is an open system and is continually receiving new matter.
C) Earth is an open system and is continually receiving new energy.
D) The slow mixing of water in the oceans allows usable energy to accumulate.
E) Earth's surface constantly receives inputs of energy from molten magma in its core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
After microorganisms break down dead organic matter,the resulting materials are taken up in ionic form by plant roots.This represents biological uptake that converts materials from an _______ form to an _______ form.
A) accessible and inorganic;accessible and organic
B) accessible and organic;accessible and inorganic
C) inaccessible and inorganic;accessible and organic
D) inaccessible and inorganic;inaccessible and organic
E) inaccessible and organic;accessible and organic
A) accessible and inorganic;accessible and organic
B) accessible and organic;accessible and inorganic
C) inaccessible and inorganic;accessible and organic
D) inaccessible and inorganic;inaccessible and organic
E) inaccessible and organic;accessible and organic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The atmospheric pool of carbon will shrink as a result of which process?
A) Wildfires
B) Volcanic eruptions
C) Plant photosynthesis
D) Organism respiration
E) Fossil fuel combustion
A) Wildfires
B) Volcanic eruptions
C) Plant photosynthesis
D) Organism respiration
E) Fossil fuel combustion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How do human activities such as deforestation and cattle grazing affect Earth's water cycle?
A) They speed up the water cycle.
B) They slow down the water cycle.
C) They increase precipitation and decrease runoff.
D) They decrease precipitation and increase runoff.
E) They do not affect it.
A) They speed up the water cycle.
B) They slow down the water cycle.
C) They increase precipitation and decrease runoff.
D) They decrease precipitation and increase runoff.
E) They do not affect it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which example best describes both an elemental pool where an element accumulates and an elemental sink where it is removed from circulation and locked up for long periods?
A) Calcium in bones,which remains fairly stable throughout an animal's life
B) Nitrogen that is made available to plants from their bacterial endosymbionts
C) Fossil fuel deposits in which carbon is stored for hundreds of millions of years
D) Atmospheric oxygen levels,which are maintained stable by photosynthesis
E) Sulfur compounds,which react with water to produce acid precipitation
A) Calcium in bones,which remains fairly stable throughout an animal's life
B) Nitrogen that is made available to plants from their bacterial endosymbionts
C) Fossil fuel deposits in which carbon is stored for hundreds of millions of years
D) Atmospheric oxygen levels,which are maintained stable by photosynthesis
E) Sulfur compounds,which react with water to produce acid precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a biogeochemical cycle,a pool can remain balanced (that is,not increase or decrease in size)only if
A) rates of flux remain constant.
B) fluxes into the pool equal fluxes out of the pool.
C) there are no fluxes into or out of the pool.
D) fluxes out of the pool remain the same size.
E) fluxes into the pool remain the same size.
A) rates of flux remain constant.
B) fluxes into the pool equal fluxes out of the pool.
C) there are no fluxes into or out of the pool.
D) fluxes out of the pool remain the same size.
E) fluxes into the pool remain the same size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Approximately what percentage of the total water on Earth is found in the oceans?
A) 70%
B) 80%
C) 90%
D) 97%
E) 99%
A) 70%
B) 80%
C) 90%
D) 97%
E) 99%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which sequence represents the correct size ranking of the compartments of global freshwater,from largest to smallest?
A) Living organisms surface freshwater ice/snow
B) Living organisms ice/snow surface freshwater
C) Ice/snow surface freshwater living organisms
D) Ice/snow living organisms surface freshwater
E) Surface freshwater ice/snow living organisms
A) Living organisms surface freshwater ice/snow
B) Living organisms ice/snow surface freshwater
C) Ice/snow surface freshwater living organisms
D) Ice/snow living organisms surface freshwater
E) Surface freshwater ice/snow living organisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A mountainous region undergoes a long period of windy,rainy weather,which increases the rate of weathering of the area's limestone rock.This releases calcium and carbonate ions,causing a flux of these ions from an _______ form to an _______ form.
A) accessible and organic;accessible and inorganic
B) accessible and inorganic;accessible and organic
C) accessible and inorganic;inaccessible and organic
D) inaccessible and inorganic;accessible and inorganic
E) inaccessible and inorganic;accessible and organic
A) accessible and organic;accessible and inorganic
B) accessible and inorganic;accessible and organic
C) accessible and inorganic;inaccessible and organic
D) inaccessible and inorganic;accessible and inorganic
E) inaccessible and inorganic;accessible and organic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of these possible changes in the global water cycle is least likely to occur as a direct result of global warming?
A) Higher evaporation rates
B) Greater percentage of rain compared to snow
C) More water stored in ice caps and glaciers
D) Earlier spring snowmelt and spring flooding
E) Changes in severity and patterns of precipitation
A) Higher evaporation rates
B) Greater percentage of rain compared to snow
C) More water stored in ice caps and glaciers
D) Earlier spring snowmelt and spring flooding
E) Changes in severity and patterns of precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Most plants lack symbiotic nitrogen-fixing microorganisms.An addition of nitrogen gas to these plants would
A) increase growth rate by providing additional nutrients.
B) decrease growth rate by interfering with photosynthesis.
C) accelerate metabolic rate by stimulating oxygen uptake.
D) have no effect,because plants cannot use nitrogen gas.
E) have no effect,because plants do not require nitrogen.
A) increase growth rate by providing additional nutrients.
B) decrease growth rate by interfering with photosynthesis.
C) accelerate metabolic rate by stimulating oxygen uptake.
D) have no effect,because plants cannot use nitrogen gas.
E) have no effect,because plants do not require nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Most organisms are unable to break down and use atmospheric nitrogen gas because the molecule's two nitrogen atoms are held together by a strong _______ bond.
A) ionic
B) double
C) triple
D) quadruple
E) hydrogen
A) ionic
B) double
C) triple
D) quadruple
E) hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of these regions of Earth is not part of the biosphere?
A) Mantle
B) Lower atmosphere
C) Soil and sediments
D) Photic zone of the ocean
E) Abyssal zone of the ocean
A) Mantle
B) Lower atmosphere
C) Soil and sediments
D) Photic zone of the ocean
E) Abyssal zone of the ocean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which process drives the cycling of water through the world system?
A) Melting
B) Evaporation
C) Precipitation
D) Transpiration
E) Condensation
A) Melting
B) Evaporation
C) Precipitation
D) Transpiration
E) Condensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the relationship between the processes of nitrogen fixation and denitrification?
A) Both processes move nitrogen from land to oceans.
B) Both processes release nitrogen into the atmosphere.
C) Both processes remove nitrogen from the atmosphere.
D) Denitrification takes nitrogen from the air and makes it usable by plants;nitrogen fixation reverses this process.
E) Nitrogen fixation takes nitrogen from the air and makes it usable by plants;denitrification reverses this process.
A) Both processes move nitrogen from land to oceans.
B) Both processes release nitrogen into the atmosphere.
C) Both processes remove nitrogen from the atmosphere.
D) Denitrification takes nitrogen from the air and makes it usable by plants;nitrogen fixation reverses this process.
E) Nitrogen fixation takes nitrogen from the air and makes it usable by plants;denitrification reverses this process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
About one-third of all the solar energy reaching Earth's surface is used in which process?
A) Evaporation
B) Precipitation
C) Photosynthesis
D) Human activities
E) Weathering and erosion
A) Evaporation
B) Precipitation
C) Photosynthesis
D) Human activities
E) Weathering and erosion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Nitrogen is often in short supply in terrestrial ecosystems because
A) there is very little free nitrogen in the air.
B) most organisms cannot use atmospheric nitrogen.
C) there are frequent local shortages of atmospheric nitrogen.
D) nitrogen enters cells slowly because of its low solubility in water.
E) atmospheric nitrogen seldom comes into contact with terrestrial ecosystems.
A) there is very little free nitrogen in the air.
B) most organisms cannot use atmospheric nitrogen.
C) there are frequent local shortages of atmospheric nitrogen.
D) nitrogen enters cells slowly because of its low solubility in water.
E) atmospheric nitrogen seldom comes into contact with terrestrial ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A bacterium living in nodules on the roots of legumes is able to convert nitrogen gas from the atmosphere into a soluble form that can be taken up and used by the legume. This soluble form is most likely
A) urea.
B) nitrate.
C) nitrite.
D) nitric acid.
E) ammonium.
A) urea.
B) nitrate.
C) nitrite.
D) nitric acid.
E) ammonium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The pool of a phosphorus compartment is 645 units.Two fluxes enter the pool: one is 13 units per day;the other is 34 units per day.Two fluxes leave: one is 22 units per day;the other rate is unknown.If the pool of phosphorus is balanced,the size of the second outgoing flux is _______ units per day.
A) 12
B) 25
C) 47
D) 72
E) 645
A) 12
B) 25
C) 47
D) 72
E) 645

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Some fluxes of water through compartments of the water cycle are driven by the sun's energy,which causes water to change states,from solid to liquid to gas (vapor).Other fluxes are driven by which force?
A) Gravity
B) Electricity
C) Osmosis
D) Nuclear energy
E) Geological energy
A) Gravity
B) Electricity
C) Osmosis
D) Nuclear energy
E) Geological energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The process in the water cycle that moves the most water during a given time is
A) precipitation over land.
B) precipitation over oceans.
C) evaporation from oceans.
D) evaporation and transpiration from land.
E) movement through living biomass.
A) precipitation over land.
B) precipitation over oceans.
C) evaporation from oceans.
D) evaporation and transpiration from land.
E) movement through living biomass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a huge solar flare causes an increase in the sun's surface temperature,the sun will emit wavelengths that are
A) longer and less energetic.
B) longer and more energetic.
C) shorter and less energetic.
D) shorter and more energetic.
E) shorter,with the same energy.
A) longer and less energetic.
B) longer and more energetic.
C) shorter and less energetic.
D) shorter and more energetic.
E) shorter,with the same energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The rate of nitrogen recycling is slowest when the nitrogen is located in which global pool?
A) Terrestrial soils
B) Marine biomass
C) Terrestrial plant biomass
D) Benthic sediments and rocks
E) Nitrogen dissolved in ocean water
A) Terrestrial soils
B) Marine biomass
C) Terrestrial plant biomass
D) Benthic sediments and rocks
E) Nitrogen dissolved in ocean water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Based on studies of leaf-cutter ants,in which part of the ant colony would you expect to find the highest levels of the enzyme nitrogenase?
A) In leaf refuse
B) In fungal gardens
C) In leaf-cutter ant workers
D) In leaves collected by workers
E) In both leaves and leaf refuse
A) In leaf refuse
B) In fungal gardens
C) In leaf-cutter ant workers
D) In leaves collected by workers
E) In both leaves and leaf refuse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The two largest reservoirs of carbon on Earth are
A) rocks and fossil fuels.
B) rocks and ocean waters.
C) rocks and the atmosphere.
D) fossil fuels and ocean waters.
E) ocean waters and the atmosphere.
A) rocks and fossil fuels.
B) rocks and ocean waters.
C) rocks and the atmosphere.
D) fossil fuels and ocean waters.
E) ocean waters and the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the best and most complete description of the relationship between various biogeochemical cycles on Earth,as we currently understand these cycles?
A) The cycles are unrelated;each element cycles independently.
B) Only water-soluble elements are interrelated,because they are all transported in water.
C) All materials present in organisms are interrelated,because they combine to form biological molecules.
D) Material interactions are far too complex to follow,and scientists have little or no idea how they interact in nature.
E) Materials interact through both abiotic parts of the cycle (for example,water transport)and through biotic parts (formation and decomposition of organic matter).
A) The cycles are unrelated;each element cycles independently.
B) Only water-soluble elements are interrelated,because they are all transported in water.
C) All materials present in organisms are interrelated,because they combine to form biological molecules.
D) Material interactions are far too complex to follow,and scientists have little or no idea how they interact in nature.
E) Materials interact through both abiotic parts of the cycle (for example,water transport)and through biotic parts (formation and decomposition of organic matter).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If Earth lacked an atmosphere,its surface temperature would be approximately _______ it is now.
A) 18°C warmer than
B) 18°C colder than
C) 34°C warmer than
D) 34°C colder than
E) the same as
A) 18°C warmer than
B) 18°C colder than
C) 34°C warmer than
D) 34°C colder than
E) the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
According to the diagram below,humans are responsible for approximately _______ percent of the total amount of global nitrogen fixation on land. 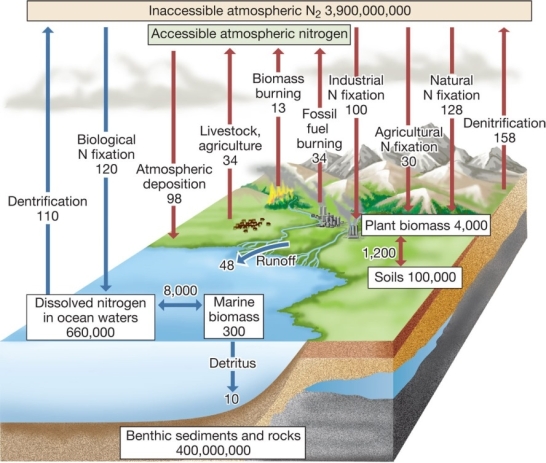
A) 1
B) 10
C) 25
D) 50
E) 80

A) 1
B) 10
C) 25
D) 50
E) 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the least likely fate of any given molecule of carbon dioxide dissolved in ocean water?
A) Uptake by phytoplankton
B) Incorporation into fossil fuels
C) Diffusion back into the atmosphere
D) Remaining dissolved in ocean water
E) Incorporation into a calcium carbonate shell
A) Uptake by phytoplankton
B) Incorporation into fossil fuels
C) Diffusion back into the atmosphere
D) Remaining dissolved in ocean water
E) Incorporation into a calcium carbonate shell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Indian pipe plant,Monotropa uniflora,lacks chlorophyll and instead is a parasite of soil fungi.Indian pipes therefore differ from most plants in terms of how they obtain
A) water.
B) sulfur.
C) carbon.
D) nitrogen.
E) phosphorus.
A) water.
B) sulfur.
C) carbon.
D) nitrogen.
E) phosphorus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the relationship between the processes of photosynthesis and respiration in the global carbon cycle?
A) Both photosynthesis and respiration cycle carbon through organic pools.
B) Both photosynthesis and respiration cycle carbon through inorganic pools.
C) Photosynthesis moves carbon from organic to inorganic pools;respiration does the opposite.
D) Photosynthesis moves carbon from inorganic to organic pools;respiration does the opposite.
E) Photosynthesis occurs primarily over land;respiration occurs primarily over the oceans.
A) Both photosynthesis and respiration cycle carbon through organic pools.
B) Both photosynthesis and respiration cycle carbon through inorganic pools.
C) Photosynthesis moves carbon from organic to inorganic pools;respiration does the opposite.
D) Photosynthesis moves carbon from inorganic to organic pools;respiration does the opposite.
E) Photosynthesis occurs primarily over land;respiration occurs primarily over the oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If global respiration exceeded global photosynthesis,how would the global carbon cycle be affected?
A) Atmospheric CH4 would increase.
B) Atmospheric CH4 would decrease.
C) Atmospheric CO2 would increase.
D) Atmospheric CO2 would decrease.
E) Less CO2 would dissolve in the oceans.
A) Atmospheric CH4 would increase.
B) Atmospheric CH4 would decrease.
C) Atmospheric CO2 would increase.
D) Atmospheric CO2 would decrease.
E) Less CO2 would dissolve in the oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which processes occurring in the ocean cycling of carbon are both physical,rather than biotic,processes?
A) Dissolving and outgassing
B) Dissolving and respiration
C) Respiration and photosynthesis
D) Outgassing and trophic interactions
E) Outgassing and calcium carbonate formation
A) Dissolving and outgassing
B) Dissolving and respiration
C) Respiration and photosynthesis
D) Outgassing and trophic interactions
E) Outgassing and calcium carbonate formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Nitrogen enters a grassland ecosystem and cycles through the grassland food web.During this process,it undergoes several more transformations.Which transformation does not retain nitrogen within the grassland food web?
A) Denitrification
B) Nitrogen fixation
C) Dissolving of nitrates and nitrites
D) Formation and breakdown of proteins
E) Decomposition of dead organic matter
A) Denitrification
B) Nitrogen fixation
C) Dissolving of nitrates and nitrites
D) Formation and breakdown of proteins
E) Decomposition of dead organic matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the fate of the greatest percentage of photons of solar energy reaching Earth?
A) They are reflected back into space by clouds.
B) They are reflected back into space by atmospheric gases.
C) They are reflected back into space after hitting Earth's surface.
D) They are absorbed by Earth's surface and warm the Earth.
E) They are absorbed by Earth's surface and reflected back into space.
A) They are reflected back into space by clouds.
B) They are reflected back into space by atmospheric gases.
C) They are reflected back into space after hitting Earth's surface.
D) They are absorbed by Earth's surface and warm the Earth.
E) They are absorbed by Earth's surface and reflected back into space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The thin atmosphere on Mars warms the surface of that planet by about 3°C,while the thick atmosphere on Venus warms the surface of that planet by approximately 468°C.To make these two planets suitable for life,scientists would need to _______ the atmospheric density on Mars and _______ the density on Venus.
A) increase;increase
B) increase;decrease
C) decrease;increase
D) decrease;decrease
E) make no changes to;decrease
A) increase;increase
B) increase;decrease
C) decrease;increase
D) decrease;decrease
E) make no changes to;decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Eutrophication in water bodies can lead to the formation of dead zones due to a depletion of
A) carbon.
B) oxygen.
C) nitrogen.
D) all nutrients.
E) decomposers.
A) carbon.
B) oxygen.
C) nitrogen.
D) all nutrients.
E) decomposers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Greenhouse gases absorb photons from the _______ part of the spectrum,which are reradiated back from Earth and are _______ energetic than light received from the sun.
A) visible;less
B) infrared;more
C) infrared;less
D) ultraviolet;more
E) ultraviolet;less
A) visible;less
B) infrared;more
C) infrared;less
D) ultraviolet;more
E) ultraviolet;less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
All of the human activities listed below release nitrogen compounds into the atmosphere except
A) coal burning.
B) rice cultivation.
C) growing soybeans.
D) fertilizer manufacture.
E) explosives manufacture.
A) coal burning.
B) rice cultivation.
C) growing soybeans.
D) fertilizer manufacture.
E) explosives manufacture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which process contributes to global warming primarily by increasing the atmospheric pool of methane?
A) Deforestation
B) Biomass burning
C) Fossil fuel burning
D) Cement production
E) Livestock production
A) Deforestation
B) Biomass burning
C) Fossil fuel burning
D) Cement production
E) Livestock production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Studies show that,since 1979,dry seasons in the southern Amazon rainforest have lasted approximately one week longer each decade.Thus,current dry seasons are three to four weeks longer than they were in 1979,causing the rain forest to die back.The likely effect of this change on global carbon cycle and climate change will be a(n)_______ in atmospheric CO2,leading to _______ world temperatures.
A) increase;increased
B) increase;decreased
C) increase;no change in
D) decrease;increased
E) decrease;decreased
A) increase;increased
B) increase;decreased
C) increase;no change in
D) decrease;increased
E) decrease;decreased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Winter moths in the Netherlands are part of a food chain that includes oak trees (which provide food for moth caterpillars)and great tits (which feed nestlings on moth caterpillars).Climate change has caused a disruption in this food chain.What is the major reason for this disruption?
A) Winter moths are adapting to warming temperatures,but oak trees and great tits are not.
B) Oak trees are adapting to warming temperatures,but winter moths and great tits are not.
C) Oak trees and winter moths are adapting to warming temperatures,but great tits are not.
D) None of the species is adapting to warming temperatures,and all are decreasing in viability as a result.
E) The three species are adapting to warming temperatures in different ways,causing mismatches in timing of their emergence.
A) Winter moths are adapting to warming temperatures,but oak trees and great tits are not.
B) Oak trees are adapting to warming temperatures,but winter moths and great tits are not.
C) Oak trees and winter moths are adapting to warming temperatures,but great tits are not.
D) None of the species is adapting to warming temperatures,and all are decreasing in viability as a result.
E) The three species are adapting to warming temperatures in different ways,causing mismatches in timing of their emergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Studies done between 1960 and 1994 showed an increased oscillation in seasonal levels of atmospheric CO2.Which factor might be implicated in these increases?
A) Longer growing seasons,leading to greater total summer photosynthesis
B) Longer growing seasons,leading to greater photosynthesis in the tropics
C) Increased global use of nitrogen fertilizers,leading to more eutrophication
D) More global droughts,leading to worldwide decreases in photosynthesis
E) More severe storms,leading to greater variations in photosynthesis and respiration
A) Longer growing seasons,leading to greater total summer photosynthesis
B) Longer growing seasons,leading to greater photosynthesis in the tropics
C) Increased global use of nitrogen fertilizers,leading to more eutrophication
D) More global droughts,leading to worldwide decreases in photosynthesis
E) More severe storms,leading to greater variations in photosynthesis and respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the desert southwest of the United States,the rainy season now appears later in the year.This change in climate will most likely favor plants that use _______ as a cue to germinate.
A) cool-season moisture
B) shorter day length
C) the presence of sunlight
D) longer day length
E) warm-season moisture
A) cool-season moisture
B) shorter day length
C) the presence of sunlight
D) longer day length
E) warm-season moisture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which statement most accurately represents the effect of human activities on Earth's climate?
A) All human activities are leading to increased warming of Earth's climate.
B) Some human activities are actually reducing the temperature of Earth,but on balance,human activity is leading to a warmer Earth.
C) Some human activities are leading to warming,while others are leading to cooling;at this point,the net effect is unclear.
D) Some human activities are actually increasing the temperature of Earth,but on balance,human activity is leading to a cooler Earth.
E) Human activity has no effect on Earth's temperature.
A) All human activities are leading to increased warming of Earth's climate.
B) Some human activities are actually reducing the temperature of Earth,but on balance,human activity is leading to a warmer Earth.
C) Some human activities are leading to warming,while others are leading to cooling;at this point,the net effect is unclear.
D) Some human activities are actually increasing the temperature of Earth,but on balance,human activity is leading to a cooler Earth.
E) Human activity has no effect on Earth's temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How likely is it that organisms will respond to rapid climate change by undergoing short-term evolutionary adaptations?
A) It is very likely;all organisms respond to environmental change through evolution.
B) It is very likely;the rate of evolution will speed up to accommodate rapid climate change.
C) It is very likely;populations are much more likely to respond to short-term changes than to long-term ones.
D) It is not very likely;evolution will not begin to occur until it is clear that climate change is a long-term process.
E) It is not very likely;evolution occurs continually,but it may be too slow,or a population's genetic variation may be too small,to keep up with rapid climate change.
A) It is very likely;all organisms respond to environmental change through evolution.
B) It is very likely;the rate of evolution will speed up to accommodate rapid climate change.
C) It is very likely;populations are much more likely to respond to short-term changes than to long-term ones.
D) It is not very likely;evolution will not begin to occur until it is clear that climate change is a long-term process.
E) It is not very likely;evolution occurs continually,but it may be too slow,or a population's genetic variation may be too small,to keep up with rapid climate change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Of the following factors,which one leads to a decrease in heat absorption and therefore counteracts the effects of global warming?
A) Deforestation
B) Fossil fuel burning
C) Cement production
D) Increasing atmospheric aerosols
E) Black carbon particles on snow and ice
A) Deforestation
B) Fossil fuel burning
C) Cement production
D) Increasing atmospheric aerosols
E) Black carbon particles on snow and ice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A bird species responds to earlier spring weather in its wintering grounds by flying north several weeks earlier.It arrives at its summer location several weeks before the snow melts.How is this situation likely to affect bird populations?
A) It will have little effect;birds will simply wait for the snow to melt.
B) It will have little effect;birds will again fly south to warmer areas.
C) It will have a minor effect;it will delay but not inhibit breeding.
D) It will have a minor effect;birds will adapt and breed successfully.
E) It will have a major effect;many birds may die of starvation before breeding.
A) It will have little effect;birds will simply wait for the snow to melt.
B) It will have little effect;birds will again fly south to warmer areas.
C) It will have a minor effect;it will delay but not inhibit breeding.
D) It will have a minor effect;birds will adapt and breed successfully.
E) It will have a major effect;many birds may die of starvation before breeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Before the Industrial Revolution,the concentration of CO2 in Earth's atmosphere was 265 parts per million (ppm).At the end of 2012,the concentration was 393 parts per million.Given the correlation of atmospheric CO2 concentration with global temperature rise,what does this change suggest about the global carbon budget?
A) It is balanced;CO2 concentration is not related to the global carbon budget.
B) It is balanced;rises in CO2 concentrations measured in ppm will have no effect.
C) It is unbalanced;CO2 is entering the atmosphere much faster than it can be removed.
D) It is unbalanced;CO2 is being removed from the atmosphere much faster than it can enter.
E) It is unbalanced,but the imbalance is insignificant because the tiny CO2 concentrations will have no effect.
A) It is balanced;CO2 concentration is not related to the global carbon budget.
B) It is balanced;rises in CO2 concentrations measured in ppm will have no effect.
C) It is unbalanced;CO2 is entering the atmosphere much faster than it can be removed.
D) It is unbalanced;CO2 is being removed from the atmosphere much faster than it can enter.
E) It is unbalanced,but the imbalance is insignificant because the tiny CO2 concentrations will have no effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The mountains of western North America are warming rapidly,leading to more rapid death of whitebark pines in this alpine ecosystem.The mountain pine bark beetle,which once lived at lower elevations,has invaded the warming alpine ecosystem and now attacks and destroys whitebark pines.How are these responses to global warming likely to affect alpine ecosystems?
A) Both pines and beetles will likely adapt to climate change and reach an equilibrium.
B) Both pines and beetles will likely go extinct because they cannot exist in the changed climate.
C) Beetles will likely hasten the loss of pine populations,resulting in massive ecosystem disruption.
D) Pines will likely die out and beetles will move south again,returning to their original habitats.
E) Because the climate is continuing to change,there is no basis for predicting the likely changes in either tree or beetle populations.
A) Both pines and beetles will likely adapt to climate change and reach an equilibrium.
B) Both pines and beetles will likely go extinct because they cannot exist in the changed climate.
C) Beetles will likely hasten the loss of pine populations,resulting in massive ecosystem disruption.
D) Pines will likely die out and beetles will move south again,returning to their original habitats.
E) Because the climate is continuing to change,there is no basis for predicting the likely changes in either tree or beetle populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In general,how have patterns of precipitation around the globe changed in response to global warming?
A) Precipitation has increased uniformly around the globe.
B) Precipitation has decreased uniformly around the globe.
C) Precipitation has increased in all mid-latitude areas and decreased in all tropical and polar regions.
D) Precipitation has increased in all tropical and polar regions and decreased in all mid-latitude areas.
E) Precipitation has increased at high latitudes and some tropical regions,but it has decreased at dry mid-latitudes,with local variations.
A) Precipitation has increased uniformly around the globe.
B) Precipitation has decreased uniformly around the globe.
C) Precipitation has increased in all mid-latitude areas and decreased in all tropical and polar regions.
D) Precipitation has increased in all tropical and polar regions and decreased in all mid-latitude areas.
E) Precipitation has increased at high latitudes and some tropical regions,but it has decreased at dry mid-latitudes,with local variations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How are warming temperatures likely to affect species ranges?
A) Most species will be able to move into any habitat.
B) Most species will move to higher latitudes and elevations.
C) Most species will move to lower latitudes and elevations.
D) Most species will remain in the same habitats and adapt to changes.
E) Most species will be unable to change their ranges and will go extinct.
A) Most species will be able to move into any habitat.
B) Most species will move to higher latitudes and elevations.
C) Most species will move to lower latitudes and elevations.
D) Most species will remain in the same habitats and adapt to changes.
E) Most species will be unable to change their ranges and will go extinct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which development is not one of the consequences of increased concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere?
A) More intense hurricanes
B) More evaporation and precipitation
C) The poleward expansion of Hadley cells
D) Increased average global temperatures
E) Wet regions becoming drier and dry regions becoming wetter.
A) More intense hurricanes
B) More evaporation and precipitation
C) The poleward expansion of Hadley cells
D) Increased average global temperatures
E) Wet regions becoming drier and dry regions becoming wetter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Leaves of most deciduous trees in Mediterranean ecosystems open approximately 16 days earlier and fall approximately 13 days later than they did 50 years ago.This shift is most likely due to
A) longer day lengths.
B) shorter day lengths.
C) changed behaviors of leaf predators.
D) higher average temperatures.
E) lower average temperatures.
A) longer day lengths.
B) shorter day lengths.
C) changed behaviors of leaf predators.
D) higher average temperatures.
E) lower average temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which organism response most likely represents a change in timing based on environmental cues related to climate change?
A) A northern plant flowers several days earlier each year.
B) An alpine plant begins to grow as soon as the snow melts.
C) A desert plant undergoes a rapid bloom cycle after a rainstorm.
D) A night-blooming cereus always blooms once a year,for one night only.
E) A plant reaches peak flowering at the same time its major pollinator emerges.
A) A northern plant flowers several days earlier each year.
B) An alpine plant begins to grow as soon as the snow melts.
C) A desert plant undergoes a rapid bloom cycle after a rainstorm.
D) A night-blooming cereus always blooms once a year,for one night only.
E) A plant reaches peak flowering at the same time its major pollinator emerges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Refer to the graph below.The Keeling curve,shown here,provides us with more than a half-century of precise measurements of atmospheric CO2 concentrations over Mauna Loa,Hawaii.Do these data show a trend,and if so,what is the trend? 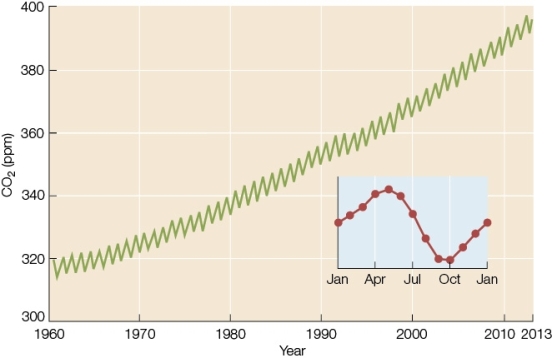
A) No;the data appear random.
B) No;the data show constant variability,not a definite trend.
C) Yes;the data show a slight,but insignificant,upward trend.
D) Yes;the data show an upward trend,but variability makes it invalid.
E) Yes;the data show a definite upward trend with predictable seasonal variations.

A) No;the data appear random.
B) No;the data show constant variability,not a definite trend.
C) Yes;the data show a slight,but insignificant,upward trend.
D) Yes;the data show an upward trend,but variability makes it invalid.
E) Yes;the data show a definite upward trend with predictable seasonal variations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the relationship between global warming and the greenhouse effect?
A) They are the same phenomenon;the two different terms mean the same thing.
B) Global warming occurs when the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere becomes unbalanced;more gases enter than leave the atmosphere.
C) They are different processes,both of which are keeping Earth's climate constant.
D) Global warming occurs when the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere becomes unbalanced;more gases leave than enter the atmosphere.
E) They are different processes,both of which are destabilizing Earth's climate.
A) They are the same phenomenon;the two different terms mean the same thing.
B) Global warming occurs when the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere becomes unbalanced;more gases enter than leave the atmosphere.
C) They are different processes,both of which are keeping Earth's climate constant.
D) Global warming occurs when the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere becomes unbalanced;more gases leave than enter the atmosphere.
E) They are different processes,both of which are destabilizing Earth's climate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If Hadley cells were to shrink rather than expand,rain near the equator would likely _______ and rain in the mid-latitudes would likely _______.
A) increase;increase
B) increase;decrease
C) not change;decrease
D) decrease;increase
E) decrease;decrease
A) increase;increase
B) increase;decrease
C) not change;decrease
D) decrease;increase
E) decrease;decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the major reason scientists think declines in lizard populations around the world will lead to losses in community diversity?
A) Loss of each lizard species will decrease community diversity by one species.
B) Lizards provide food for many species,which will go extinct as lizards disappear.
C) Lizards will move out of regions that are too cool,and no species will be able to replace them.
D) Loss of lizard species will cause a trophic cascade,affecting all species and leading to loss of community function.
E) Lizards interact with insects;their loss will affect only insect populations,but will have a great effect because there are so many insects.
A) Loss of each lizard species will decrease community diversity by one species.
B) Lizards provide food for many species,which will go extinct as lizards disappear.
C) Lizards will move out of regions that are too cool,and no species will be able to replace them.
D) Loss of lizard species will cause a trophic cascade,affecting all species and leading to loss of community function.
E) Lizards interact with insects;their loss will affect only insect populations,but will have a great effect because there are so many insects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How do scientists expect communities to change as global temperatures continue to increase?
A) Nearly all communities will fail to adapt and their species will go extinct.
B) Some species will move to higher latitudes and elevations and others will not,resulting in changed species compositions in many communities.
C) Some communities will adapt and remain in the same locations;others will go extinct.
D) All species in a community will move as a group to higher latitudes and elevations,resulting in the same communities in different locations.
E) Nearly all communities will adapt and their species will remain in the same locations.
A) Nearly all communities will fail to adapt and their species will go extinct.
B) Some species will move to higher latitudes and elevations and others will not,resulting in changed species compositions in many communities.
C) Some communities will adapt and remain in the same locations;others will go extinct.
D) All species in a community will move as a group to higher latitudes and elevations,resulting in the same communities in different locations.
E) Nearly all communities will adapt and their species will remain in the same locations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
CO2 concentrations in the Northern Hemisphere follow which pattern of seasonality?
A) They show no seasonality;they increase linearly.
B) They are highest in spring and fall,coinciding with upwellings.
C) They are highest in winter,coinciding with lowest photosynthetic rates.
D) They are highest in winter,coinciding with the highest atmospheric density.
E) They are highest in summer,correlating with the highest animal metabolism.
A) They show no seasonality;they increase linearly.
B) They are highest in spring and fall,coinciding with upwellings.
C) They are highest in winter,coinciding with lowest photosynthetic rates.
D) They are highest in winter,coinciding with the highest atmospheric density.
E) They are highest in summer,correlating with the highest animal metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



