Deck 8: Monopoly and Other Forms of Imperfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/236
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Monopoly and Other Forms of Imperfect Competition
1
The correct sequence of market structures from most to least competitive is
A) pure monopoly,oligopoly,perfect competition,monopolistic competition.
B) oligopoly,pure monopoly,perfect competition,imperfect competition.
C) perfect competition,monopolistic competition,oligopoly,pure monopoly.
D) perfect competition,imperfect competition,pure monopoly.
E) perfect competition,monopolistic competition,pure monopoly,oligopoly.
A) pure monopoly,oligopoly,perfect competition,monopolistic competition.
B) oligopoly,pure monopoly,perfect competition,imperfect competition.
C) perfect competition,monopolistic competition,oligopoly,pure monopoly.
D) perfect competition,imperfect competition,pure monopoly.
E) perfect competition,monopolistic competition,pure monopoly,oligopoly.
perfect competition,monopolistic competition,oligopoly,pure monopoly.
2
The most enduring source of market power is
A) economies of scale.
B) patents.
C) inelastic demand.
D) brand loyalty.
E) the existence of only a few firms in the market.
A) economies of scale.
B) patents.
C) inelastic demand.
D) brand loyalty.
E) the existence of only a few firms in the market.
economies of scale.
3
Patents and copyrights provide some degree of market power to holders because
A) patent holders often share their knowledge with others.
B) firms can often evade patents and copyrights by making slight changes in design.
C) patent holders are protected from direct competition in the short run.
D) very few patents are granted each year.
E) there is no penalty in duplicating the patented products at low cost.
A) patent holders often share their knowledge with others.
B) firms can often evade patents and copyrights by making slight changes in design.
C) patent holders are protected from direct competition in the short run.
D) very few patents are granted each year.
E) there is no penalty in duplicating the patented products at low cost.
patent holders are protected from direct competition in the short run.
4
Price setters face
A) perfectly elastic demand.
B) a market determined price.
C) perfectly inelastic demand.
D) less than perfectly elastic demand.
E) more than perfectly elastic demand.
A) perfectly elastic demand.
B) a market determined price.
C) perfectly inelastic demand.
D) less than perfectly elastic demand.
E) more than perfectly elastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Market power is enjoyed by
A) only large firms like General Motors.
B) all firms.
C) medium to large firms.
D) pure monopolists exclusively.
E) any firm that can raise its price without losing all of its sales.
A) only large firms like General Motors.
B) all firms.
C) medium to large firms.
D) pure monopolists exclusively.
E) any firm that can raise its price without losing all of its sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is NOT considered a source of market power?
A) Inelastic demand.
B) Economies of scale.
C) Patents.
D) Exclusive licences.
E) Control of important inputs.
A) Inelastic demand.
B) Economies of scale.
C) Patents.
D) Exclusive licences.
E) Control of important inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Pure monopoly exists when
A) many firms produce a good with no close substitutes.
B) a single firm produces a good with no close substitutes.
C) a single firm is present in the market.
D) a single firm produces a good with many close substitutes.
E) a few firms dominate an industry.
A) many firms produce a good with no close substitutes.
B) a single firm produces a good with no close substitutes.
C) a single firm is present in the market.
D) a single firm produces a good with many close substitutes.
E) a few firms dominate an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Patents and copyrights,which confer market power,exist to
A) protect the consumer from imitations.
B) ensure excessive profits to the holders.
C) protect research and development,and creative expression.
D) reduce competition in all sectors of the economy.
E) magnify the dominance of large firms.
A) protect the consumer from imitations.
B) ensure excessive profits to the holders.
C) protect research and development,and creative expression.
D) reduce competition in all sectors of the economy.
E) magnify the dominance of large firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A price taker __________ and a price setter __________.
A) equates price to marginal revenue;equates price to marginal cost
B) seeks to maximize revenue;seeks to maximize profit
C) never earns a profit;always earns a profit
D) must accept the market price;may charge any price he wants
E) equates price to marginal revenue;finds that price is greater than marginal revenue
A) equates price to marginal revenue;equates price to marginal cost
B) seeks to maximize revenue;seeks to maximize profit
C) never earns a profit;always earns a profit
D) must accept the market price;may charge any price he wants
E) equates price to marginal revenue;finds that price is greater than marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A monopolistically competitive firm is one
A) that behaves like a monopolist.
B) of many firms that produce slightly different but very similar goods.
C) of many firms that produce goods with no close substitutes.
D) that behaves like a perfect competitor.
E) that is competitive but wants to be a monopolist.
A) that behaves like a monopolist.
B) of many firms that produce slightly different but very similar goods.
C) of many firms that produce goods with no close substitutes.
D) that behaves like a perfect competitor.
E) that is competitive but wants to be a monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A price setter finds that it has
A) to accept the price the market sets.
B) some control over the price it charges.
C) the ability to set the price at whatever value it wants.
D) the ability to always earn an economic profit.
E) few competitors.
A) to accept the price the market sets.
B) some control over the price it charges.
C) the ability to set the price at whatever value it wants.
D) the ability to always earn an economic profit.
E) few competitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Market power measures a firm's ability to
A) undercut its competitors.
B) resist union wage demands.
C) raise its price without losing all its sales.
D) influence the price its competitors charge.
E) force consumers to pay higher prices.
A) undercut its competitors.
B) resist union wage demands.
C) raise its price without losing all its sales.
D) influence the price its competitors charge.
E) force consumers to pay higher prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A single firm producing a good with no close substitutes is termed a(n)
A) pure monopolist.
B) oligopolist.
C) monopolistic competitor.
D) monopsonist.
E) dominant firm.
A) pure monopolist.
B) oligopolist.
C) monopolistic competitor.
D) monopsonist.
E) dominant firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A firm that exercises some control over the price it charges is termed a(n)
A) perfect competitor.
B) perfect non-competitor.
C) monopsonist.
D) polyopolist.
E) imperfect competitor.
A) perfect competitor.
B) perfect non-competitor.
C) monopsonist.
D) polyopolist.
E) imperfect competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The economic advantage of a large firm over its smaller competitors arises primarily from
A) its ability to prevent others from holding new patents.
B) economies of scale.
C) its ability to prevent others from buying key inputs.
D) its larger advertising budget.
E) its ability to get celebrities to help promote their products.
A) its ability to prevent others from holding new patents.
B) economies of scale.
C) its ability to prevent others from buying key inputs.
D) its larger advertising budget.
E) its ability to get celebrities to help promote their products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If anyone was free to copy a new product,or an exclusive work of art,there would be
A) a proliferation of innovations.
B) minimal developmental costs.
C) minimal fixed costs.
D) fewer innovations than otherwise.
E) more innovations than otherwise.
A) a proliferation of innovations.
B) minimal developmental costs.
C) minimal fixed costs.
D) fewer innovations than otherwise.
E) more innovations than otherwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An oligopolist is a firm that finds it is
A) the only supplier.
B) the only supplier of a good with no close substitutes.
C) one of many suppliers of a good with perfect substitutes.
D) one of a few firms.
E) one of a few firms that produce close substitutes.
A) the only supplier.
B) the only supplier of a good with no close substitutes.
C) one of many suppliers of a good with perfect substitutes.
D) one of a few firms.
E) one of a few firms that produce close substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Taxicab drivers who hold exclusive licences do not have market power because
A) they charge too much for their services.
B) they face competition from other modes of transportation.
C) some cab drivers lease their cabs to others during their off hours.
D) there are insufficient cabs in the city.
E) not enough licences are issued.
A) they charge too much for their services.
B) they face competition from other modes of transportation.
C) some cab drivers lease their cabs to others during their off hours.
D) there are insufficient cabs in the city.
E) not enough licences are issued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An industry that features a few firms that produce close substitutes is called
A) pure monopoly.
B) imperfect monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) competitive monopoly.
A) pure monopoly.
B) imperfect monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) competitive monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following provides market power to a natural monopolist?
A) Control of important inputs.
B) Patents.
C) Inelastic demand.
D) An exclusive licence.
E) Economies of scale.
A) Control of important inputs.
B) Patents.
C) Inelastic demand.
D) An exclusive licence.
E) Economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The condition where a single firm can supply an entire market at a lower unit cost than could a number of competing firms defines a
A) dominant firm oligopoly.
B) structured market.
C) natural monopoly.
D) trust.
E) duopoly.
A) dominant firm oligopoly.
B) structured market.
C) natural monopoly.
D) trust.
E) duopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is a major characteristic of a natural monopoly?
A) The firm is a single seller of a resource.
B) The firm sets price equal to marginal revenue.
C) There is extensive product advertising.
D) There is a large range of output to which economies of scale apply.
E) There are major legal restraints preventing other firms from entering the market.
A) The firm is a single seller of a resource.
B) The firm sets price equal to marginal revenue.
C) There is extensive product advertising.
D) There is a large range of output to which economies of scale apply.
E) There are major legal restraints preventing other firms from entering the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that a firm increases its inputs by 10% and observes a 13% increase in output.The firm is
A) experiencing increasing returns to scale.
B) experiencing constant returns to scale.
C) violating the law of diminishing marginal returns.
D) increasing its average cost.
E) reducing its total cost.
A) experiencing increasing returns to scale.
B) experiencing constant returns to scale.
C) violating the law of diminishing marginal returns.
D) increasing its average cost.
E) reducing its total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Of the sources of market power,the most common and enduring is
A) a patent.
B) a copyright.
C) exclusive ownership of an input.
D) a government franchise.
E) economies of scale.
A) a patent.
B) a copyright.
C) exclusive ownership of an input.
D) a government franchise.
E) economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Economies of scale exist when
A) constant returns to scale are present.
B) input prices are falling.
C) average cost falls as the scale of production grows.
D) a 10% increase in all inputs causes a 9% increase in output.
E) firms become extremely large.
A) constant returns to scale are present.
B) input prices are falling.
C) average cost falls as the scale of production grows.
D) a 10% increase in all inputs causes a 9% increase in output.
E) firms become extremely large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A firm has a production function Q = LK,where L is labour and K is capital.If L and K can take whole values ,then the firm has
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) constant returns to scale.
C) diseconomies of scale.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) rising average total costs.
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) constant returns to scale.
C) diseconomies of scale.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) rising average total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The defining characteristic of a natural monopoly is
A) positive economic profit.
B) that average cost always exceeds marginal cost.
C) that marginal cost always exceeds average cost.
D) diseconomies of scale.
E) that marginal revenue always equals price.
A) positive economic profit.
B) that average cost always exceeds marginal cost.
C) that marginal cost always exceeds average cost.
D) diseconomies of scale.
E) that marginal revenue always equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The most common source of market power is
A) a government franchise.
B) patents.
C) copyright.
D) economies of scale.
E) sole ownership of an important input.
A) a government franchise.
B) patents.
C) copyright.
D) economies of scale.
E) sole ownership of an important input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Industries where economies of scale exist will tend to be
A) dominated by either a single firm or a few firms.
B) resistant to cutting price.
C) comprised of many equal-sized firms.
D) less concerned with expanding output.
E) highly profitable.
A) dominated by either a single firm or a few firms.
B) resistant to cutting price.
C) comprised of many equal-sized firms.
D) less concerned with expanding output.
E) highly profitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following industries does not fit the natural monopoly model?
A) Electricity.
B) Cable TV.
C) Municipal water.
D) Natural gas.
E) Housing.
A) Electricity.
B) Cable TV.
C) Municipal water.
D) Natural gas.
E) Housing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a firm with constant returns to scale uses 30% more of all inputs and input prices remain unchanged,then
A) total cost rises by less than 30%.
B) average cost falls by 30%.
C) total cost rises by more than 30%.
D) average cost remains unchanged.
E) average cost rises by 30%.
A) total cost rises by less than 30%.
B) average cost falls by 30%.
C) total cost rises by more than 30%.
D) average cost remains unchanged.
E) average cost rises by 30%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose that a firm increases inputs by 10% and observes a 13% increase in output.If the prices of its inputs remain constant,then
A) constant returns to scale are present.
B) average cost decreases.
C) total cost decreases.
D) average cost is unchanged.
E) average cost could be higher or lower.
A) constant returns to scale are present.
B) average cost decreases.
C) total cost decreases.
D) average cost is unchanged.
E) average cost could be higher or lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a firm triples all its inputs and output triples as a result,then the firm
A) is experiencing increasing returns to scale.
B) is experiencing economies of scale.
C) is experiencing constant returns to scale.
D) will have lower total costs.
E) will have lower average total costs.
A) is experiencing increasing returns to scale.
B) is experiencing economies of scale.
C) is experiencing constant returns to scale.
D) will have lower total costs.
E) will have lower average total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The term natural monopoly refers to
A) government ownership of parks.
B) industries with constant returns to scale.
C) industries with small fixed costs.
D) industries with economies of scale.
E) the desire of all firms to be monopolists.
A) government ownership of parks.
B) industries with constant returns to scale.
C) industries with small fixed costs.
D) industries with economies of scale.
E) the desire of all firms to be monopolists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Constant returns to scale occur when a doubling of all inputs
A) doubles the price of outputs.
B) more than doubles output.
C) less than doubles the price of the inputs.
D) exactly doubles output.
E) less than doubles output.
A) doubles the price of outputs.
B) more than doubles output.
C) less than doubles the price of the inputs.
D) exactly doubles output.
E) less than doubles output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A firm that emerges as the only seller in an industry with economies of scale is called a(n)
A) monopoly.
B) oligopoly.
C) monopsony.
D) natural oligopoly.
E) natural monopoly.
A) monopoly.
B) oligopoly.
C) monopsony.
D) natural oligopoly.
E) natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Increasing returns to scale occur when a 50% increase in all inputs
A) increases output by 50%.
B) increases output by more than 50%.
C) increases input prices by more than 50%.
D) increases output by less than 50%.
E) decreases output by more than 50%.
A) increases output by 50%.
B) increases output by more than 50%.
C) increases input prices by more than 50%.
D) increases output by less than 50%.
E) decreases output by more than 50%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Market power refers to a firm's ability to
A) undercut the price of rivals in order to capture the entire market.
B) ignore environmental regulations.
C) resist unionization efforts by workers.
D) charge any price it wants.
E) raise price without losing 100% of its sales.
A) undercut the price of rivals in order to capture the entire market.
B) ignore environmental regulations.
C) resist unionization efforts by workers.
D) charge any price it wants.
E) raise price without losing 100% of its sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If economies of scale in an industry are so extensive that a single firm can supply the entire market at lower unit cost than could a number of competing firms,this industry is called a(n)
A) conglomerate.
B) natural monopoly.
C) oligopoly.
D) restraint of trade.
E) monopolistic competition.
A) conglomerate.
B) natural monopoly.
C) oligopoly.
D) restraint of trade.
E) monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose that a single firm supplying a particular good has a cost function of the form TC = a + bQ,where both a and b are positive constants,a is large and Q is output.This firm would be classified as
A) a regulated monopoly.
B) an oligopoly.
C) a monopoly.
D) a natural monopoly.
E) unknown since there is insufficient information available.
A) a regulated monopoly.
B) an oligopoly.
C) a monopoly.
D) a natural monopoly.
E) unknown since there is insufficient information available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In order to sell another unit,an imperfectly competitive firm must
A) raise its price.
B) increase the value of its product.
C) lower its price.
D) lower its quality.
E) increase its advertising.
A) raise its price.
B) increase the value of its product.
C) lower its price.
D) lower its quality.
E) increase its advertising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Monopolistic competition is a market in which there are __________ firms that sell ___________ products,and there are ______ barriers to entry.
A) many;differentiated;no
B) many;homogeneous;many
C) few;differentiated;no
D) few;homogeneous;many
E) many;differentiated;many
A) many;differentiated;no
B) many;homogeneous;many
C) few;differentiated;no
D) few;homogeneous;many
E) many;differentiated;many

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Given the total cost function,TC = 100 + 7Q,fixed cost is
A) $100.
B) $100/Q.
C) $7.
D) $7/Q.
E) $107.
A) $100.
B) $100/Q.
C) $7.
D) $7/Q.
E) $107.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Industries with large fixed cost and small,constant marginal cost will,over time,
A) have more and more small firms.
B) see one firm,or a few large firms,emerge.
C) see no change in the average size of firms.
D) see no change in the average number of firms.
E) see the size of their market decline.
A) have more and more small firms.
B) see one firm,or a few large firms,emerge.
C) see no change in the average size of firms.
D) see no change in the average number of firms.
E) see the size of their market decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) To sell more,a price setter must lower price.
B) A price taker must charge the market price.
C) If a price setter raises price,they will sell less.
D) A price taker's revenue will rise if they sell more.
E) Price setters can sell any quantity at any price.
A) To sell more,a price setter must lower price.
B) A price taker must charge the market price.
C) If a price setter raises price,they will sell less.
D) A price taker's revenue will rise if they sell more.
E) Price setters can sell any quantity at any price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following industries could be described as being monopolistically competitive?
A) Wheat.
B) Gas stations.
C) Electricity.
D) Diamonds.
E) Natural gas.
A) Wheat.
B) Gas stations.
C) Electricity.
D) Diamonds.
E) Natural gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Given the total cost function,TC = 531 + 14Q,marginal cost is
A) $531/Q.
B) $14/Q.
C) $531.
D) $14.
E) impossible to calculate with the information provided.
A) $531/Q.
B) $14/Q.
C) $531.
D) $14.
E) impossible to calculate with the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Given the total cost function,TC = 120 + 12Q,the average cost function is
A) 12Q + (12/Q).
B) (120/Q)+ 12.
C) 120Q + 12Q2.
D) 120Q + 12.
E) 132.
A) 12Q + (12/Q).
B) (120/Q)+ 12.
C) 120Q + 12Q2.
D) 120Q + 12.
E) 132.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose that a firm is collecting $100 in total revenue when it sells 10 units and $99 in total revenue when it sells 11 units.The firm is a(n)
A) pure monopolist.
B) oligopolist.
C) perfect competitor.
D) imperfect competitor.
E) monopolistic competitor.
A) pure monopolist.
B) oligopolist.
C) perfect competitor.
D) imperfect competitor.
E) monopolistic competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Advertising is used by
A) both a monopolistically competitive firm and a perfectly competitive firm.
B) neither a monopolistically competitive firm nor a perfectly competitive firm.
C) a perfectly competitive firm but not by a monopolistically competitive firm.
D) a perfectly competitive firm occasionally,but never by a monopolistically competitive firm.
E) a monopolistically competitive firm but not by a perfectly competitive firm.
A) both a monopolistically competitive firm and a perfectly competitive firm.
B) neither a monopolistically competitive firm nor a perfectly competitive firm.
C) a perfectly competitive firm but not by a monopolistically competitive firm.
D) a perfectly competitive firm occasionally,but never by a monopolistically competitive firm.
E) a monopolistically competitive firm but not by a perfectly competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A monopolistic competitor faces ____________ demand curve.
A) an upward-sloping
B) a horizontal
C) a vertical
D) a downward-sloping
E) an unknown
A) an upward-sloping
B) a horizontal
C) a vertical
D) a downward-sloping
E) an unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The only difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition is that a firm in monopolistic competition _____________ and a firm in perfect competition ____________.
A) is in an industry with only a few other firms;is in an industry with many other firms
B) sells a differentiated product;sells a homogeneous product
C) sells a homogeneous product;sells a differentiated product
D) cannot easily leave the industry;can easily leave the industry
E) can easily leave the industry;cannot easily leave the industry
A) is in an industry with only a few other firms;is in an industry with many other firms
B) sells a differentiated product;sells a homogeneous product
C) sells a homogeneous product;sells a differentiated product
D) cannot easily leave the industry;can easily leave the industry
E) can easily leave the industry;cannot easily leave the industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The common feature of pure monopoly,oligopoly,and monopolistic competition is
A) the absence of close substitutes.
B) blocked entry.
C) interdependent decision making by firms.
D) price discrimination.
E) downward-sloping demand.
A) the absence of close substitutes.
B) blocked entry.
C) interdependent decision making by firms.
D) price discrimination.
E) downward-sloping demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose that a firm is collecting $100 in total revenue when it sells 10 units and $110 in total revenue when it sells 11 units.The firm is a(n)
A) pure monopolist.
B) oligopolist.
C) monopolistic competitor.
D) monopsonist.
E) perfect competitor.
A) pure monopolist.
B) oligopolist.
C) monopolistic competitor.
D) monopsonist.
E) perfect competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A total cost function of the form TC = a + bQ,with both a > 0 and b > 0,best describes a firm that has
A) small fixed cost and increasing marginal cost.
B) significant fixed cost and increasing marginal cost.
C) small fixed cost and decreasing marginal cost.
D) significant fixed cost and small,constant marginal cost.
E) significant fixed cost and decreasing marginal cost.
A) small fixed cost and increasing marginal cost.
B) significant fixed cost and increasing marginal cost.
C) small fixed cost and decreasing marginal cost.
D) significant fixed cost and small,constant marginal cost.
E) significant fixed cost and decreasing marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following monopolists would likely face zero marginal cost?
A) An airline monopoly.
B) A diamond monopoly.
C) A monopolist selling spring water.
D) A monopolist selling the daily newspaper in a small town.
E) A monopolist selling a video game.
A) An airline monopoly.
B) A diamond monopoly.
C) A monopolist selling spring water.
D) A monopolist selling the daily newspaper in a small town.
E) A monopolist selling a video game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The demand curve of a perfectly competitive firm is __________,while the demand curve of a monopolist is __________.
A) perfectly elastic;downward-sloping
B) vertical;downward-sloping
C) perfectly elastic;perfectly inelastic
D) perfectly inelastic;perfectly elastic
E) perfectly elastic;elastic
A) perfectly elastic;downward-sloping
B) vertical;downward-sloping
C) perfectly elastic;perfectly inelastic
D) perfectly inelastic;perfectly elastic
E) perfectly elastic;elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The elasticity of demand for an imperfectly competitive firm is
A) infinity.
B) greater than zero and less than infinity.
C) zero.
D) greater than zero and less than one.
E) greater than one.
A) infinity.
B) greater than zero and less than infinity.
C) zero.
D) greater than zero and less than one.
E) greater than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An industry that features many,relatively small,firms that produce close substitutes is called
A) pure monopoly.
B) imperfect oligopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) competitive oligopoly.
A) pure monopoly.
B) imperfect oligopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) competitive oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Given the total cost function TC = a + bQ,with both a > 0 and b > 0,average cost will
A) be approximately constant over most of the output range.
B) fall at first and then rise as output rises.
C) fall over the entire range of output.
D) rise at first and then fall as output rises.
E) rise over the entire range of output.
A) be approximately constant over most of the output range.
B) fall at first and then rise as output rises.
C) fall over the entire range of output.
D) rise at first and then fall as output rises.
E) rise over the entire range of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Marginal revenue is
A) total revenue divided by output.
B) the extra revenue that results from selling one extra unit.
C) always equal to price.
D) never equal to price.
E) always positive.
A) total revenue divided by output.
B) the extra revenue that results from selling one extra unit.
C) always equal to price.
D) never equal to price.
E) always positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If a firm collects $100 in revenue when it sells five units and $114 when it sells six units,one can infer the firm is
A) a perfect competitor.
B) probably a perfect competitor.
C) either a perfect competitor or a monopolist.
D) a monopolist.
E) of an unknown structure;there is insufficient information available.
A) a perfect competitor.
B) probably a perfect competitor.
C) either a perfect competitor or a monopolist.
D) a monopolist.
E) of an unknown structure;there is insufficient information available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
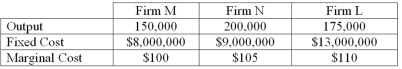
According to the data above,firm __________ has the lowest average total cost,while firm __________ has the highest.
A) M;L
B) M;N
C) N;M
D) N;L
E) L;N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64

Refer to the data above.Assume that firm L loses sales of 75,000 units,with 40,000 units going to firm N and 35,000 units going to firm M.Firm L now has average total cost of
A) $240.
B) $184.
C) $153.
D) $150.
E) $143.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In equilibrium,the perfectly competitive firm finds that price __________ marginal revenue,while a monopolist finds that price __________ marginal revenue.
A) is equal to;is equal to
B) is greater than;is equal to
C) is equal to;is greater than
D) is less than;is equal to
E) is equal to;is less than
A) is equal to;is equal to
B) is greater than;is equal to
C) is equal to;is greater than
D) is less than;is equal to
E) is equal to;is less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When a monopolist faces a U-shaped average cost curve in the short run as more and more output is produced,the upward-sloping portion of the curve is the result of
A) an upward-sloping demand curve.
B) the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) economies of scale.
D) an increase in taxes.
E) a vertical supply curve.
A) an upward-sloping demand curve.
B) the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) economies of scale.
D) an increase in taxes.
E) a vertical supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Both the perfectly competitive firm and the monopolist find that
A) price and marginal revenue are the same.
B) they can sell all they want to at the market price.
C) it is best to expand production until the benefit and the cost of the last unit produced are equal.
D) price is less than marginal revenue.
E) demand is not perfectly elastic.
A) price and marginal revenue are the same.
B) they can sell all they want to at the market price.
C) it is best to expand production until the benefit and the cost of the last unit produced are equal.
D) price is less than marginal revenue.
E) demand is not perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

Given the total cost function TC = 1,000 + 2Q,when output is 1,000 units,average total cost __________ and when output is 10,000 units,average total cost __________.
A) is $3;is $2.10
B) is $3,000;is $21,000
C) is $1.002;is 0.0102 cents
D) is $1,000;is $10,000
E) cannot be calculated;cannot be calculated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When a monopolist faces a U-shaped average cost curve in the short run,we know that as more and more output is produced,the
A) law of diminishing marginal returns eventually overrules the decrease in average fixed cost.
B) decrease in average fixed cost eventually overrules the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) decrease in average fixed cost always overrules the law of diminishing marginal returns.
D) law of diminishing marginal returns always overrules the decrease in average fixed cost.
E) law of diminishing marginal returns coincides with the decrease in average fixed cost.
A) law of diminishing marginal returns eventually overrules the decrease in average fixed cost.
B) decrease in average fixed cost eventually overrules the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) decrease in average fixed cost always overrules the law of diminishing marginal returns.
D) law of diminishing marginal returns always overrules the decrease in average fixed cost.
E) law of diminishing marginal returns coincides with the decrease in average fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A firm is classified as a natural monopoly if
A) there are few substitutes.
B) it is the only supplier of all-natural products.
C) its marginal cost is always less than its average cost.
D) it is the only producer.
E) it is regulated by government.
A) there are few substitutes.
B) it is the only supplier of all-natural products.
C) its marginal cost is always less than its average cost.
D) it is the only producer.
E) it is regulated by government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For all firms,the extra revenue collected from the sale of one extra unit of output is
A) price.
B) average revenue.
C) marginal profit.
D) marginal revenue.
E) marginal price.
A) price.
B) average revenue.
C) marginal profit.
D) marginal revenue.
E) marginal price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
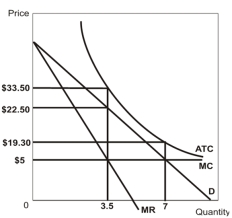
Refer to the graph above.The firm illustrated in the graph is a(n)
A) oligopolist.
B) monopolistic competitor.
C) perfect competitor.
D) natural monopolist.
E) structure that is impossible to classify.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When a monopolist sells additional units,
A) total revenue always increases.
B) marginal revenue is constant.
C) total revenue always decreases.
D) marginal revenue increases.
E) total revenue may increase,decrease,or remain unchanged.
A) total revenue always increases.
B) marginal revenue is constant.
C) total revenue always decreases.
D) marginal revenue increases.
E) total revenue may increase,decrease,or remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74

Refer to the data above.Assume that firm M acquires firm L.After the merger,firm M has an average total cost of __________,while firm N has an average total cost of __________.
A) $143;$150
B) $125;$150
C) $150;$125
D) $143;$143
E) $153;$150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a firm collects $100 in revenue when it sells five units and $120 when it sells six units,one can infer the firm is
A) a perfect competitor.
B) a monopolistic competitor.
C) either a perfect competitor or a monopolist.
D) a monopolist.
E) an oligopolist.
A) a perfect competitor.
B) a monopolistic competitor.
C) either a perfect competitor or a monopolist.
D) a monopolist.
E) an oligopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is TRUE if a monopolist faces a constant marginal cost? The monopolist faces a
A) constant total cost.
B) constant average variable cost.
C) perfectly elastic demand curve.
D) vertical demand curve.
E) vertical supply curve.
A) constant total cost.
B) constant average variable cost.
C) perfectly elastic demand curve.
D) vertical demand curve.
E) vertical supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If it is possible to spread total fixed cost efficiently over a larger and larger quantity of output,then a firm will not experience
A) an elastic demand curve.
B) economies of scale.
C) increasing returns to scale.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) the law of demand.
A) an elastic demand curve.
B) economies of scale.
C) increasing returns to scale.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

Refer to the data above.Assume that firm L loses sales of 75,000 units,with 40,000 units going to firm N and 35,000 units going to firm M.Firm N now has average total cost of
A) $240.
B) $184.50.
C) $153.
D) $150.
E) $142.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The primary objective of a monopolist is to
A) charge the highest possible price.
B) maximize total revenue.
C) minimize total cost.
D) maximize profit.
E) maximize the deadweight loss to society.
A) charge the highest possible price.
B) maximize total revenue.
C) minimize total cost.
D) maximize profit.
E) maximize the deadweight loss to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When a perfect competitor sells additional units,
A) total revenue always increases.
B) marginal revenue decreases.
C) total revenue always decreases.
D) total revenue remains unchanged.
E) total revenue may increase or decrease.
A) total revenue always increases.
B) marginal revenue decreases.
C) total revenue always decreases.
D) total revenue remains unchanged.
E) total revenue may increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 236 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



