Deck 10: Externalities and Property Rights
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/196
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Externalities and Property Rights
1
The existence of externalities results in
A) harm to those directly involved.
B) a misallocation of resources.
C) a greater than optimal level of production.
D) a less than optimal level of production.
E) harm to those indirectly involved.
A) harm to those directly involved.
B) a misallocation of resources.
C) a greater than optimal level of production.
D) a less than optimal level of production.
E) harm to those indirectly involved.
a misallocation of resources.
2
If an unregulated activity produces a negative externality,one can infer that the
A) equilibrium price is greater than the socially optimal price.
B) demand for the activity is greater than the socially optimal demand.
C) equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
D) equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
E) supply of the activity is less than the socially optimal supply.
A) equilibrium price is greater than the socially optimal price.
B) demand for the activity is greater than the socially optimal demand.
C) equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
D) equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
E) supply of the activity is less than the socially optimal supply.
equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
3
Parties affected by externalities have an incentive to negotiate as long as
A) the cost of the negotiation is less than the surplus that could be gained.
B) the cost of the negotiation is greater than the surplus that could be gained.
C) the cost of the negotiation is equal to the surplus that could be gained.
D) there is no surplus.
E) the surplus is positive regardless of the cost.
A) the cost of the negotiation is less than the surplus that could be gained.
B) the cost of the negotiation is greater than the surplus that could be gained.
C) the cost of the negotiation is equal to the surplus that could be gained.
D) there is no surplus.
E) the surplus is positive regardless of the cost.
the cost of the negotiation is less than the surplus that could be gained.
4
When collective action is taken,e.g. ,the passing of a new law,it is frequently an attempt to
A) eliminate a negative externality.
B) encourage a positive externality.
C) increase the income of lawyers.
D) correct a resource misallocation due to an externality.
E) further burden the operation of the economy.
A) eliminate a negative externality.
B) encourage a positive externality.
C) increase the income of lawyers.
D) correct a resource misallocation due to an externality.
E) further burden the operation of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One of the reasons why private markets produce less than the socially optimal level of goods that yield positive externalities is that
A) producers do not know that their goods yield positive externalities.
B) the market does not benefit from goods that yield positive externalities.
C) positive externalities are often unpriced.
D) those goods are usually taxed heavily.
E) prices are already too high and consumers refuse to pay more.
A) producers do not know that their goods yield positive externalities.
B) the market does not benefit from goods that yield positive externalities.
C) positive externalities are often unpriced.
D) those goods are usually taxed heavily.
E) prices are already too high and consumers refuse to pay more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that coal mining produces a negative externality in the form of polluted streams.One can deduce that the unregulated
A) price of coal is too high.
B) quantity is too small.
C) quantity is too large.
D) supply is too low.
E) demand is too great.
A) price of coal is too high.
B) quantity is too small.
C) quantity is too large.
D) supply is too low.
E) demand is too great.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When some fraction of the benefit of an activity is received by people not participating in the activity,it is called a(n)
A) winner's curse.
B) positive externality.
C) external cost.
D) negative externality.
E) efficient allocation.
A) winner's curse.
B) positive externality.
C) external cost.
D) negative externality.
E) efficient allocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which one of the following factors would NOT lessen the ability of the Coase theorem to solve an externality?
A) Negotiating requires lawyers and legal documents.
B) Many individuals bear the external cost.
C) The externality is an external benefit.
D) Many individuals generate the external cost.
E) The parties involved distrust and dislike each other.
A) Negotiating requires lawyers and legal documents.
B) Many individuals bear the external cost.
C) The externality is an external benefit.
D) Many individuals generate the external cost.
E) The parties involved distrust and dislike each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT an example of an activity with an external benefit?
A) Eating a sandwich.
B) Planting flowers in the front yard.
C) Getting a haircut.
D) Washing and waxing the car.
E) Practicing safe sex.
A) Eating a sandwich.
B) Planting flowers in the front yard.
C) Getting a haircut.
D) Washing and waxing the car.
E) Practicing safe sex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Assume that reading produces a positive externality.It will be the case that the __________ than that which is socially optimal.
A) supply of reading will be greater
B) price of reading will be greater
C) supply of reading will be less
D) demand for reading will be greater
E) demand for reading will be less
A) supply of reading will be greater
B) price of reading will be greater
C) supply of reading will be less
D) demand for reading will be greater
E) demand for reading will be less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A motorist with a noisy muffler will continue to drive around town,creating noise pollution wherever he goes,as long as
A) the cost to him is less than the benefit he derives from it.
B) there is no cost to the other people in the town.
C) there is an economic benefit to the society.
D) there are by-laws against noise pollution.
E) he considers the noise a positive externality.
A) the cost to him is less than the benefit he derives from it.
B) there is no cost to the other people in the town.
C) there is an economic benefit to the society.
D) there are by-laws against noise pollution.
E) he considers the noise a positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The major implication of the Coase theorem is that
A) government regulation is necessary to solve externalities.
B) competitive pressures will eliminate externalities.
C) resolving externalities is more costly than allowing them.
D) individuals can solve many externalities if they can buy and sell the right to commit the externality.
E) governmental solutions to externalities can only fail.
A) government regulation is necessary to solve externalities.
B) competitive pressures will eliminate externalities.
C) resolving externalities is more costly than allowing them.
D) individuals can solve many externalities if they can buy and sell the right to commit the externality.
E) governmental solutions to externalities can only fail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT an example of an activity with an external cost?
A) Noise pollution from a steel mill.
B) Keeping junk in the front yard.
C) A car burning oil.
D) Having to buy batteries for the remote that came with the new TV.
E) Speeding on the Trans-Canada Highway.
A) Noise pollution from a steel mill.
B) Keeping junk in the front yard.
C) A car burning oil.
D) Having to buy batteries for the remote that came with the new TV.
E) Speeding on the Trans-Canada Highway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An external benefit of an activity is one that is
A) not included in the social marginal cost.
B) received by those directly involved in the activity.
C) included in the private marginal benefit.
D) never present in the real world.
E) received by those not directly involved.
A) not included in the social marginal cost.
B) received by those directly involved in the activity.
C) included in the private marginal benefit.
D) never present in the real world.
E) received by those not directly involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Cigarettes are known to cause negative externalities.Which one of the following will help to reduce the consumption of cigarettes?
A) A subsidy paid to cigarette producers.
B) Compensation paid to the smokers who end up with lung cancer.
C) A special tax allowance for cigarette consumers.
D) A special tax imposed on the production of cigarettes.
E) Compensation paid to cigarette producers for the articles written about their product.
A) A subsidy paid to cigarette producers.
B) Compensation paid to the smokers who end up with lung cancer.
C) A special tax allowance for cigarette consumers.
D) A special tax imposed on the production of cigarettes.
E) Compensation paid to cigarette producers for the articles written about their product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An example of the way that externalities distort the allocation of resources is
A) positive economic surplus.
B) positive externalities only.
C) negative externalities only.
D) negative economic surplus.
E) both positive externalities and negative externalities.
A) positive economic surplus.
B) positive externalities only.
C) negative externalities only.
D) negative economic surplus.
E) both positive externalities and negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The motivation for private solutions to externalities is that
A) resources are misallocated and thus economic surplus can be increased.
B) individuals are more concerned about pollution now.
C) of profit maximization.
D) of utility maximization.
E) individuals mistrust governmental solutions.
A) resources are misallocated and thus economic surplus can be increased.
B) individuals are more concerned about pollution now.
C) of profit maximization.
D) of utility maximization.
E) individuals mistrust governmental solutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An external cost of an activity is one that is
A) borne by those not directly involved in the activity.
B) borne only by those directly involved in the activity.
C) included in the private marginal cost curve.
D) present only if the activity yields pollution.
E) transferred from consumers to producers.
A) borne by those not directly involved in the activity.
B) borne only by those directly involved in the activity.
C) included in the private marginal cost curve.
D) present only if the activity yields pollution.
E) transferred from consumers to producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If public school education was not free in Canada,we would expect
A) more consumption of education.
B) less consumption of education.
C) education to start yielding positive externalities.
D) education to start yielding negative externalities.
E) what economists refer to as the tragedy of the commons.
A) more consumption of education.
B) less consumption of education.
C) education to start yielding positive externalities.
D) education to start yielding negative externalities.
E) what economists refer to as the tragedy of the commons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the case of either a positive or a negative externality,it will always be true that,relative to the social optimum,the
A) price will be too low.
B) price will be too high.
C) quantity will be too large.
D) demand will be too small.
E) supply will be too great.
A) price will be too low.
B) price will be too high.
C) quantity will be too large.
D) demand will be too small.
E) supply will be too great.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Bob lives in a residential neighbourhood that takes pride on well-groomed lawns.Bob's neighbours find that the marginal benefit of someone else's well-groomed lawn is $10.Bob,however,receives the same net benefit from an unkempt lawn as a well-groomed lawn: zero (an unkempt lawn looks bad but costs nothing;a well groomed lawn looks nice but is costly). 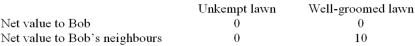
Refer to the information above.Suppose that Bob knows that his neighbours value his lawn being well groomed more than he does and demands $15 from them.The neighbours will
A) choose to pay him $15.
B) stop the negotiations.
C) choose to pay him the $15: $10 now and $5 later.
D) offer $9 as a final offer.
E) hope that he moves.
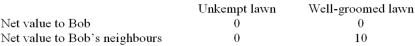
Refer to the information above.Suppose that Bob knows that his neighbours value his lawn being well groomed more than he does and demands $15 from them.The neighbours will
A) choose to pay him $15.
B) stop the negotiations.
C) choose to pay him the $15: $10 now and $5 later.
D) offer $9 as a final offer.
E) hope that he moves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
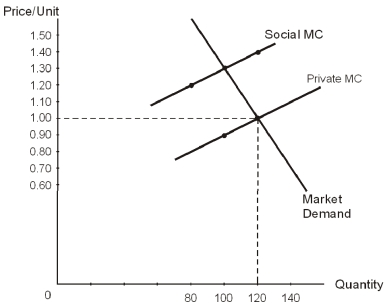
Refer to the diagram above.With the appropriate tax rate imposed on producers,the socially optimal level of output would be _____ units at the socially optimal price of _____ per unit.
A) 100;$1.30
B) 100;$0.90
C) 100;$1.50
D) 120;$1.00
E) 120;$1.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
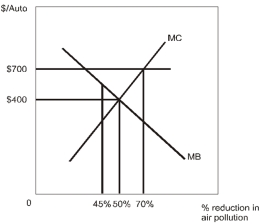
From the diagram above,one can infer that
A) the benefit of a 45% reduction in air pollution exceeds the cost.
B) the cost of a 50% reduction in air pollution exceeds the benefit.
C) the benefit of a 70% reduction in air pollution exceeds the cost.
D) the value of a 100% reduction in air pollution is large.
E) the cost of a 100% reduction in air pollution is small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

Refer to the diagram above.One of the reasons that a per-unit tax will result in the socially efficient level of production is that
A) producers are forced to include all costs of production,including social cost,in their supply curve.
B) producers are given a chance to make extra profit after the tax is imposed.
C) producers are given a chance to make extra profit since consumers are willing to pay more.
D) the government is collecting extra tax revenue.
E) consumers no longer consume the harmful product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

Refer to the diagram above.Private MC represents the
A) meaningful cost of private production.
B) supply curve of a product without taking into consideration the external cost to society.
C) marginal revenue of private production without taking external cost into consideration.
D) marginal cost including the per-unit external cost to society.
E) marginal equilibrium price of the product with external costs included.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Bob lives in a residential neighbourhood that takes pride on well-groomed lawns.Bob's neighbours find that the marginal benefit of someone else's well-groomed lawn is $10.Bob,however,receives the same net benefit from an unkempt lawn as a well-groomed lawn: zero (an unkempt lawn looks bad but costs nothing;a well groomed lawn looks nice but is costly). 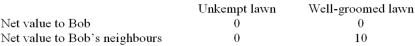
Refer to the information above.The largest whole number of dollars Bob's neighbours would pay him to keep a well groomed lawn is
A) $1.
B) $2.
C) $5.
D) $9.
E) $20.
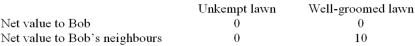
Refer to the information above.The largest whole number of dollars Bob's neighbours would pay him to keep a well groomed lawn is
A) $1.
B) $2.
C) $5.
D) $9.
E) $20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

Refer to the diagram above.Suppose that Environment Canada requires that all automobiles have a certain air pollution technology that costs $700 per automobile.The reduction in air pollution will be
A) 0%.
B) 45%.
C) 50%.
D) 70%.
E) 100%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

Which of the following situations is best illustrated by the diagram above?
A) A smoker whose lungs are being destroyed by smoking.
B) A biker whose motorbike creates noise pollution.
C) Leisure driving that adds to congestion during the rush hour.
D) A manufacturer who secretly dumps toxic waste in the nearby river.
E) A bee keeper whose bees enhance apple production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

Refer to the diagram above.Leaving the free market to decide on production,output would be _____ units and price would be ____ per unit.
A) 120;$1.00
B) 120;$0.90
C) 100;$0.90
D) 100;$1.00
E) 100;$1.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Bob lives in a residential neighbourhood that takes pride on well-groomed lawns.Bob's neighbours find that the marginal benefit of someone else's well-groomed lawn is $10.Bob,however,receives the same net benefit from an unkempt lawn as a well-groomed lawn: zero (an unkempt lawn looks bad but costs nothing;a well groomed lawn looks nice but is costly). 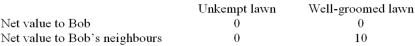
Refer to the information above.If Bob acts independently,he will have a(n)__________ and total economic surplus to the neighbourhood will be __________.
A) well groomed lawn;$0
B) well groomed lawn;$5
C) unkempt lawn;$0
D) unkempt lawn;$5
E) unkempt lawn;$10
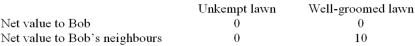
Refer to the information above.If Bob acts independently,he will have a(n)__________ and total economic surplus to the neighbourhood will be __________.
A) well groomed lawn;$0
B) well groomed lawn;$5
C) unkempt lawn;$0
D) unkempt lawn;$5
E) unkempt lawn;$10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to Coase,when thinking about solutions to externalities,it is important to remember that
A) only those indirectly involved need by considered.
B) government regulation in nearly always necessary.
C) only those directly involved need be considered.
D) externalities are reciprocal in nature.
E) those who generate external costs must be forced to stop.
A) only those indirectly involved need by considered.
B) government regulation in nearly always necessary.
C) only those directly involved need be considered.
D) externalities are reciprocal in nature.
E) those who generate external costs must be forced to stop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Private incentives in markets with external benefits lead to _____;private incentives in markets with external costs lead to _____.
A) maximum total economic surplus;deadweight loss
B) deadweight loss;deadweight loss
C) excess total economic surplus;efficiency
D) excess total economic surplus;deadweight loss
E) minimum total economic surplus;efficiency
A) maximum total economic surplus;deadweight loss
B) deadweight loss;deadweight loss
C) excess total economic surplus;efficiency
D) excess total economic surplus;deadweight loss
E) minimum total economic surplus;efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
From the perspective of an externality,speed limits on highways exist
A) to raise revenue for provincial governments.
B) to increase the smooth flow of traffic.
C) because negotiating compensation with each speeding driver is impractical.
D) because insurance companies demand them.
E) to conserve gasoline consumption.
A) to raise revenue for provincial governments.
B) to increase the smooth flow of traffic.
C) because negotiating compensation with each speeding driver is impractical.
D) because insurance companies demand them.
E) to conserve gasoline consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Bob lives in a residential neighbourhood that takes pride on well-groomed lawns.Bob's neighbours find that the marginal benefit of someone else's well-groomed lawn is $10.Bob,however,receives the same net benefit from an unkempt lawn as a well-groomed lawn: zero (an unkempt lawn looks bad but costs nothing;a well groomed lawn looks nice but is costly). 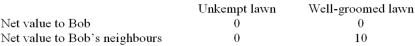
Refer to the information above.The issue of Bob,his neighbours,and the state of his lawn is an example of a(n)
A) positive externality.
B) external cost.
C) negative externality.
D) positional externality.
E) prisoner's dilemma.
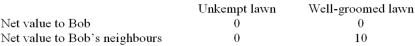
Refer to the information above.The issue of Bob,his neighbours,and the state of his lawn is an example of a(n)
A) positive externality.
B) external cost.
C) negative externality.
D) positional externality.
E) prisoner's dilemma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Bob lives in a residential neighbourhood that takes pride on well-groomed lawns.Bob's neighbours find that the marginal benefit of someone else's well-groomed lawn is $10.Bob,however,receives the same net benefit from an unkempt lawn as a well-groomed lawn: zero (an unkempt lawn looks bad but costs nothing;a well groomed lawn looks nice but is costly). 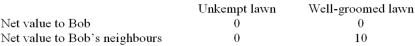
Refer to the information above.The Coase theorem suggests that
A) the rest of the neighbourhood will have to live with Bob.
B) Bob's neighbours should pass a law requiring well groomed lawns.
C) Bob's neighbours could pay Bob to have a well groomed lawn and be better off.
D) Bob's neighbours could pay Bob to have a well groomed lawn and be no better off.
E) Bob has undervalued a well groomed lawn.
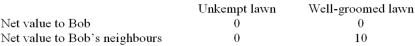
Refer to the information above.The Coase theorem suggests that
A) the rest of the neighbourhood will have to live with Bob.
B) Bob's neighbours should pass a law requiring well groomed lawns.
C) Bob's neighbours could pay Bob to have a well groomed lawn and be better off.
D) Bob's neighbours could pay Bob to have a well groomed lawn and be no better off.
E) Bob has undervalued a well groomed lawn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Bob lives in a residential neighbourhood that takes pride on well-groomed lawns.Bob's neighbours find that the marginal benefit of someone else's well-groomed lawn is $10.Bob,however,receives the same net benefit from an unkempt lawn as a well-groomed lawn: zero (an unkempt lawn looks bad but costs nothing;a well groomed lawn looks nice but is costly). 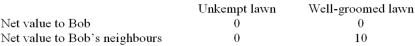
Refer to the information above.For Bob to have an unkempt lawn results in __________ because the total economic surplus is __________.
A) efficiency;non-negative
B) inefficiency;larger than it could have been
C) efficiency;the same in either case
D) inefficiency;smaller than it could have been
E) inefficiency;negative
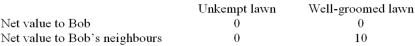
Refer to the information above.For Bob to have an unkempt lawn results in __________ because the total economic surplus is __________.
A) efficiency;non-negative
B) inefficiency;larger than it could have been
C) efficiency;the same in either case
D) inefficiency;smaller than it could have been
E) inefficiency;negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Refer to the diagram above.The socially optimal reduction in air pollution due to automobiles is
A) 0%.
B) 45%.
C) 50%.
D) 70%.
E) 100%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Bob lives in a residential neighbourhood that takes pride on well-groomed lawns.Bob's neighbours find that the marginal benefit of someone else's well-groomed lawn is $10.Bob,however,receives the same net benefit from an unkempt lawn as a well-groomed lawn: zero (an unkempt lawn looks bad but costs nothing;a well groomed lawn looks nice but is costly). 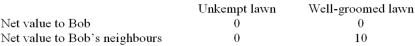
Refer to the information above.The smallest whole number of dollars Bob would accept from his neighbours to keep a well groomed lawn is
A) $1.
B) $2.
C) $5.
D) $9.
E) $10.
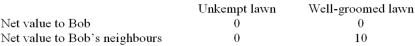
Refer to the information above.The smallest whole number of dollars Bob would accept from his neighbours to keep a well groomed lawn is
A) $1.
B) $2.
C) $5.
D) $9.
E) $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The major implication of the _______ is that individuals can solve many externalities if they can buy and sell the right to generate the externality.
A) positional arms race
B) Coase Theorem
C) tragedy of the commons
D) prisoner's dilemma
E) marginal abatement cost
A) positional arms race
B) Coase Theorem
C) tragedy of the commons
D) prisoner's dilemma
E) marginal abatement cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

Refer to the diagram above.The vertical distance between the private MC and the social MC represents
A) excess demand due to prices set too high.
B) excess demand due to prices set too low.
C) the per-unit external cost of production not picked up by the producing firm.
D) the per-unit external cost of production picked up by the consumers.
E) the per-unit external cost of production picked up by the government in the form of taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Paul owns a home on the top of a hill and enjoys an unobstructed view of a large wooded area.The view was a large factor in his decision to buy the house and Paul values his view at $5000 per month.Sid purchases the undeveloped wooded area with plans to build a retail shopping centre.Sid expects to earn $10,000 a month from the shopping centre,which is $3000 more than his next best alternative.
Refer to the information above.The reciprocal nature of externalities expressed by Coase is illustrated by noting that
A) Paul is the only one harmed.
B) Sid is the only one who benefits.
C) Sid does not have to build the shopping centre.
D) if Paul is successful in legally stopping construction of the shopping centre,Sid will be harmed.
E) Paul could move elsewhere.
Refer to the information above.The reciprocal nature of externalities expressed by Coase is illustrated by noting that
A) Paul is the only one harmed.
B) Sid is the only one who benefits.
C) Sid does not have to build the shopping centre.
D) if Paul is successful in legally stopping construction of the shopping centre,Sid will be harmed.
E) Paul could move elsewhere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When the market produces output where the marginal social cost of production exceeds the marginal private cost to the firm,it must be the case that the production of the good involves
A) negative production externalities.
B) negative consumption externalities.
C) positive production externalities.
D) positive consumption externalities.
E) both negative production and consumption externalities.
A) negative production externalities.
B) negative consumption externalities.
C) positive production externalities.
D) positive consumption externalities.
E) both negative production and consumption externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
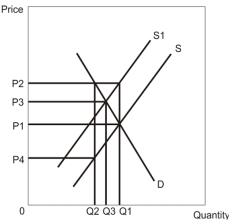
Refer to the diagram above.The distance __________ measures the extent of the __________.
A) 0Q1;underproduction
B) Q3Q1;overproduction
C) Q3Q1;underproduction
D) Q2Q1;overproduction
E) Q2Q3;underproduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Paul owns a home on the top of a hill and enjoys an unobstructed view of a large wooded area.The view was a large factor in his decision to buy the house and Paul values his view at $5000 per month.Sid purchases the undeveloped wooded area with plans to build a retail shopping centre.Sid expects to earn $10,000 a month from the shopping centre,which is $3000 more than his next best alternative.
Refer to the information above.Suppose that Paul rejects the idea of either buying the undeveloped land or paying Sid not to develop the land,and successfully blocks Sid from developing the land by getting the zoning law changed.As a result,
A) Paul's economic surplus will rise.
B) Sid's economic surplus will rise.
C) Paul's economic surplus is unchanged.
D) Sid is no worse off.
E) society is better off.
Refer to the information above.Suppose that Paul rejects the idea of either buying the undeveloped land or paying Sid not to develop the land,and successfully blocks Sid from developing the land by getting the zoning law changed.As a result,
A) Paul's economic surplus will rise.
B) Sid's economic surplus will rise.
C) Paul's economic surplus is unchanged.
D) Sid is no worse off.
E) society is better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Paul owns a home on the top of a hill and enjoys an unobstructed view of a large wooded area.The view was a large factor in his decision to buy the house and Paul values his view at $5000 per month.Sid purchases the undeveloped wooded area with plans to build a retail shopping centre.Sid expects to earn $10,000 a month from the shopping centre,which is $3000 more than his next best alternative.
Refer to the information above.Suppose that building the shopping centre and receiving $10,000 per month was $6000 more than Sid's next best alternative.As a result,
A) Sid and Paul can still reach a monetary arrangement.
B) Paul cannot pay Sid enough to stop construction.
C) Sid will be willing to pay Paul $1000 for his loss.
D) Paul has less incentive to seek a legal remedy.
E) Paul will re-evaluate his value of the view.
Refer to the information above.Suppose that building the shopping centre and receiving $10,000 per month was $6000 more than Sid's next best alternative.As a result,
A) Sid and Paul can still reach a monetary arrangement.
B) Paul cannot pay Sid enough to stop construction.
C) Sid will be willing to pay Paul $1000 for his loss.
D) Paul has less incentive to seek a legal remedy.
E) Paul will re-evaluate his value of the view.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Paul owns a home on the top of a hill and enjoys an unobstructed view of a large wooded area.The view was a large factor in his decision to buy the house and Paul values his view at $5000 per month.Sid purchases the undeveloped wooded area with plans to build a retail shopping centre.Sid expects to earn $10,000 a month from the shopping centre,which is $3000 more than his next best alternative.
Refer to the information above.The least Sid would accept to cease construction of the shopping centre is
A) $10,000.
B) $5000.
C) $3001.
D) $2000.
E) $0.
Refer to the information above.The least Sid would accept to cease construction of the shopping centre is
A) $10,000.
B) $5000.
C) $3001.
D) $2000.
E) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When negative externalities are present in a market,it implies that
A) the market price is too low to achieve optimum social surplus.
B) the market price is too high to achieve optimum social surplus.
C) the market price is just right to achieve optimum social surplus.
D) the market price should be lowered further to achieve optimum social surplus.
E) production should be increased to achieve optimum social surplus.
A) the market price is too low to achieve optimum social surplus.
B) the market price is too high to achieve optimum social surplus.
C) the market price is just right to achieve optimum social surplus.
D) the market price should be lowered further to achieve optimum social surplus.
E) production should be increased to achieve optimum social surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Environment Canada has proposed strict controls on the amount of sulphur contained in diesel fuel.The effect of the regulation is estimated to increase the equilibrium price of a litre of diesel fuel by 10 cents.Assuming the supply curve of diesel fuel has a positive slope and the demand curve has a negative slope,one can infer that
A) the external benefit of diesel fuel is less than 10 cents.
B) the external cost of diesel fuel is greater than 10 cents.
C) the external cost of diesel is less than 10 cents.
D) the external cost of diesel is equal to 10 cents.
E) the external benefit of diesel is equal to 10 cents.
A) the external benefit of diesel fuel is less than 10 cents.
B) the external cost of diesel fuel is greater than 10 cents.
C) the external cost of diesel is less than 10 cents.
D) the external cost of diesel is equal to 10 cents.
E) the external benefit of diesel is equal to 10 cents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

Refer to the diagram above.The distance __________ measures the __________.
A) 0P1;external cost
B) 0P2;external cost
C) P1P2;external cost
D) P1P3;external cost
E) P1P2;external benefit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

Refer to the diagram above.The reason the invisible hand does not allocate resources efficiently in the market is that
A) there is too much demand.
B) the private supply curve,S1,does not include the external cost of production.
C) the social supply curve,S,includes the external cost of production.
D) the private supply curve,S,does not include the external cost of production.
E) equilibrium cannot be achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51

Refer to the diagram above.Generally speaking,most remedies for external costs due to pollution in Canada have not been through taxation but regulations requiring firms to use a specific type of pollution-reduction technology.For the regulation to lead to the socially optimal level of output,one must assume that
A) firms will simply choose to go out of business and eliminate the externality.
B) requiring the technology will increase costs such that the private supply,S,shifts to S1.
C) it is easier to regulate than to tax.
D) requiring the technology will shift the social supply curve,S1,to S.
E) the best way to reduce pollution is to force firms to use a particular technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52

Refer to the diagram above.Assume that a Coase theorem solution (private negotiation)is impractical.The efficient equilibrium could be achieved by
A) banning production of the good.
B) compensating those injured by the externality.
C) taxing the good by an amount equal to the external cost.
D) subsidizing the good by an amount equal to the external benefit.
E) informing the public of the external cost produced by production of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Paul owns a home on the top of a hill and enjoys an unobstructed view of a large wooded area.The view was a large factor in his decision to buy the house and Paul values his view at $5000 per month.Sid purchases the undeveloped wooded area with plans to build a retail shopping centre.Sid expects to earn $10,000 a month from the shopping centre,which is $3000 more than his next best alternative.
Refer to the information above.The most Paul would offer Sid to prevent construction of the shopping centre is
A) $0.
B) $2000.
C) $3000.
D) $4999.
E) $10,000.
Refer to the information above.The most Paul would offer Sid to prevent construction of the shopping centre is
A) $0.
B) $2000.
C) $3000.
D) $4999.
E) $10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54

Refer to the diagram above.Taxing the production of this good by an amount equal to the external cost would
A) place the entire burden of the external cost on producers.
B) be ineffective because the external cost is not eliminated.
C) place the entire burden of the external cost on consumers.
D) not achieve an efficient solution.
E) divide the burden of the external cost between producers and consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

Refer to the diagram above.When the external cost is included,the efficient equilibrium is at price ____________ and quantity _________________.
A) P1;Q1
B) P2;Q3
C) P2;Q2
D) P4;Q2
E) P3;Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56

Refer to the diagram above.If S1 contains the entire amount of the external cost,then
A) too little was being produced.
B) demand was too large.
C) the socially optimal amount of production,and hence the socially optimal amount of the external cost,is not zero.
D) Q3 production is excessive.
E) the marginal benefit of Q3 is less than the marginal social cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When government officials have very little information about costs and benefits of the production of diesel fuel,a very high tax imposed on producers
A) will ensure optimal social efficiency.
B) will increase social efficiency but not necessarily be socially optimal.
C) will reduce social efficiency.
D) will leave social efficiency unchanged.
E) may or may not increase social efficiency.
A) will ensure optimal social efficiency.
B) will increase social efficiency but not necessarily be socially optimal.
C) will reduce social efficiency.
D) will leave social efficiency unchanged.
E) may or may not increase social efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An environmental activist describes an Environment Canada requirement for a $700 air pollution control device for all cars as a policy that leads to the socially optimal reduction in pollution.In terms of the diagram above,for this to be true,it must be the case that the
A) marginal cost is lower than MC.
B) marginal benefit is lower than MB.
C) true marginal cost is greater than MC.
D) true marginal benefit is greater than MB.
E) marginal benefit is the only issue to consider.
A) marginal cost is lower than MC.
B) marginal benefit is lower than MB.
C) true marginal cost is greater than MC.
D) true marginal benefit is greater than MB.
E) marginal benefit is the only issue to consider.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59

Refer to the diagram above.An Environment Canada requirement for a $700 air pollution control device for all cars would__________ the socially optimal reduction in pollution because __________.
A) be equal to;any and all reductions in pollution are warranted
B) not be equal to;the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit
C) not be equal to;the reduction is less than 100%
D) not be equal to;the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost
E) be equal to;there is no other way to force the auto industry to reduce emissions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

In the market,an externality exists.From the diagram above,one can deduce that it is a
A) negative externality.
B) positional externality.
C) positive externality.
D) positional arms race.
E) prisoner's dilemma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Glen is considering whether to paint his house and if so,what colour to choose.He settles on three options: leave it "as is",paint it brown,or paint it purple.Glen's neighbours are able to easily see his house.The following table shows the monetary values of utility for Glen and his neighbours under the three possibilities. 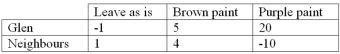
Refer to the information above.Suppose that an additional rule is adopted: maximize total economic surplus but no outcome with a negative value for either Glenn or his neighbours can be chosen.The outcome now is that Glen's house will
A) not be painted.
B) be painted purple.
C) be painted brown.
D) either remain as is or be painted brown.
E) be of an indeterminate colour.

Refer to the information above.Suppose that an additional rule is adopted: maximize total economic surplus but no outcome with a negative value for either Glenn or his neighbours can be chosen.The outcome now is that Glen's house will
A) not be painted.
B) be painted purple.
C) be painted brown.
D) either remain as is or be painted brown.
E) be of an indeterminate colour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When there are no externalities,
A) the market equilibrium occurs at the point where the marginal social benefit is equal to the marginal social cost.
B) society is not as well off as it could be.
C) the marginal social cost is different from the marginal private cost.
D) other people must bear part of the cost.
E) there is no market equilibrium.
A) the market equilibrium occurs at the point where the marginal social benefit is equal to the marginal social cost.
B) society is not as well off as it could be.
C) the marginal social cost is different from the marginal private cost.
D) other people must bear part of the cost.
E) there is no market equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose that a vaccine is developed for a highly contagious strain of flu.The likelihood that anyone will get this flu decreases as more people receive the vaccine. 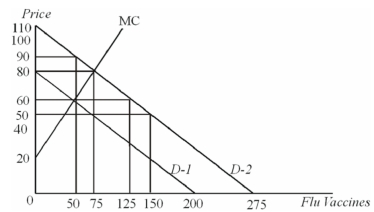
Private incentives will lead to _____ people receiving the vaccine at a cost of _____.
A) 75;$80
B) 75;$50
C) 50;$60
D) 50;$90
E) 125;$60

Private incentives will lead to _____ people receiving the vaccine at a cost of _____.
A) 75;$80
B) 75;$50
C) 50;$60
D) 50;$90
E) 125;$60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose that a vaccine is developed for a highly contagious strain of flu.The likelihood that anyone will get this flu decreases as more people receive the vaccine. 
Private benefits are measured by ______ and social benefits are measured by _____.
A) D-1;MC
B) D-2;MC
C) D-1;D-2
D) D-2;D-1
E) D-2 + D-1;MC

Private benefits are measured by ______ and social benefits are measured by _____.
A) D-1;MC
B) D-2;MC
C) D-1;D-2
D) D-2;D-1
E) D-2 + D-1;MC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Assume that the values in the table above are representative of most neighbourhoods,i.e. ,unique colours are an external cost while traditional colours are an external benefit.One could predict that
A) the distribution of unique and traditional colours will be 50-50.
B) if one house is uniquely coloured,all houses will be.
C) if one house is traditionally coloured,no unique coloured houses will be present.
D) colours of houses will be relatively homogeneous.
E) colours of houses will be relatively heterogeneous.
A) the distribution of unique and traditional colours will be 50-50.
B) if one house is uniquely coloured,all houses will be.
C) if one house is traditionally coloured,no unique coloured houses will be present.
D) colours of houses will be relatively homogeneous.
E) colours of houses will be relatively heterogeneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
After correcting an externality,the equilibrium price and quantity both rose.The externality must have been a(n)
A) negative externality.
B) positional externality.
C) prisoner's dilemma.
D) positive externality.
E) external cost.
A) negative externality.
B) positional externality.
C) prisoner's dilemma.
D) positive externality.
E) external cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Glen is considering whether to paint his house and if so,what colour to choose.He settles on three options: leave it "as is",paint it brown,or paint it purple.Glen's neighbours are able to easily see his house.The following table shows the monetary values of utility for Glen and his neighbours under the three possibilities. 
Refer to the information above.Given a goal of maximizing total economic surplus,a Coase theorem solution would result in
A) no change in the colour of Glen's house.
B) Glen painting his house purple and paying his neighbours $10.
C) Glen's neighbours paying him $20.
D) Glen painting his house brown.
E) Glen painting the front of his house brown and the back purple.

Refer to the information above.Given a goal of maximizing total economic surplus,a Coase theorem solution would result in
A) no change in the colour of Glen's house.
B) Glen painting his house purple and paying his neighbours $10.
C) Glen's neighbours paying him $20.
D) Glen painting his house brown.
E) Glen painting the front of his house brown and the back purple.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The socially optimal number of vaccines is _______.
A) 50
B) 75
C) 125
D) 150
E) 275
A) 50
B) 75
C) 125
D) 150
E) 275

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is an example of a governmental solution to an external benefit?
A) Requiring autos to meet minimum emissions standards.
B) Building safety requirements for office buildings.
C) Regulations of food additives.
D) Public service ads encouraging exercise and good nutrition.
E) Public service ads discouraging smoking.
A) Requiring autos to meet minimum emissions standards.
B) Building safety requirements for office buildings.
C) Regulations of food additives.
D) Public service ads encouraging exercise and good nutrition.
E) Public service ads discouraging smoking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Brady owns a beachfront lot with a small house.During hurricanes,he refuses to leave and afterward he applies for government assistance to rebuild and files insurance claims for damages.By doing so,Brady is
A) increasing his economic surplus without harm to others.
B) imposing an external cost on himself.
C) imposing an external cost on rescue workers,taxpayers,and insurance policy holders.
D) treating his property as common property.
E) in a positional arms race.
A) increasing his economic surplus without harm to others.
B) imposing an external cost on himself.
C) imposing an external cost on rescue workers,taxpayers,and insurance policy holders.
D) treating his property as common property.
E) in a positional arms race.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the flu vaccine is provided by private markets,deadweight loss will be _______.
A) zero
B) $375
C) $500
D) $1,125
E) $2,250
A) zero
B) $375
C) $500
D) $1,125
E) $2,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that a vaccine is developed for a highly contagious strain of flu.The likelihood that anyone will get this flu decreases as more people receive the vaccine. 
The dollar value of the external ______ is _____.
A) benefit;$30
B) benefit;$20
C) benefit;$75
D) cost;$20
E) cost;$75

The dollar value of the external ______ is _____.
A) benefit;$30
B) benefit;$20
C) benefit;$75
D) cost;$20
E) cost;$75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the external cost of an activity is added to the private cost,then the
A) supply curve shifts right.
B) quantity supplied rises.
C) supply curve shifts left.
D) quantity supplied falls.
E) demand curve shifts left.
A) supply curve shifts right.
B) quantity supplied rises.
C) supply curve shifts left.
D) quantity supplied falls.
E) demand curve shifts left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Glen is considering whether to paint his house and if so,what colour to choose.He settles on three options: leave it "as is",paint it brown,or paint it purple.Glen's neighbours are able to easily see his house.The following table shows the monetary values of utility for Glen and his neighbours under the three possibilities. 
Refer to the information above.The ranking of choices from highest to lowest for Glen is
A) brown,no change,purple.
B) purple,no change,brown.
C) purple,brown,no change.
D) no change,brown,purple.
E) brown,purple,no change.

Refer to the information above.The ranking of choices from highest to lowest for Glen is
A) brown,no change,purple.
B) purple,no change,brown.
C) purple,brown,no change.
D) no change,brown,purple.
E) brown,purple,no change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If the external benefit of an activity is added to the private benefit,then the
A) demand curve shifts left.
B) quantity demanded rises.
C) supply curve shifts right.
D) demand curve shifts right.
E) quantity demanded falls.
A) demand curve shifts left.
B) quantity demanded rises.
C) supply curve shifts right.
D) demand curve shifts right.
E) quantity demanded falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
This externality could most effectively be corrected by
A) taxing vaccines.
B) encouraging people to negotiate private payments to those who receive the vaccine.
C) subsidizing vaccines.
D) free provision of 275 vaccines
E) relying strictly on market allocation of vaccines.
A) taxing vaccines.
B) encouraging people to negotiate private payments to those who receive the vaccine.
C) subsidizing vaccines.
D) free provision of 275 vaccines
E) relying strictly on market allocation of vaccines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Glen is considering whether to paint his house and if so,what colour to choose.He settles on three options: leave it "as is",paint it brown,or paint it purple.Glen's neighbours are able to easily see his house.The following table shows the monetary values of utility for Glen and his neighbours under the three possibilities. 
Refer to the information above.The ranking of total economic surplus for Glen and his neighbours from highest to lowest is
A) purple,brown,no change.
B) brown,no change,purple.
C) neon purple,no change,brown.
D) no change,brown,purple.
E) brown,purple,no change.

Refer to the information above.The ranking of total economic surplus for Glen and his neighbours from highest to lowest is
A) purple,brown,no change.
B) brown,no change,purple.
C) neon purple,no change,brown.
D) no change,brown,purple.
E) brown,purple,no change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If,after an externality is corrected,the equilibrium price rises and the equilibrium quantity falls,the externality must have been a(n)
A) external benefit.
B) internal cost.
C) external cost.
D) positive externality.
E) positional externality.
A) external benefit.
B) internal cost.
C) external cost.
D) positive externality.
E) positional externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In the case of either an external cost or an external benefit,the invisible hand fails to generate the efficient outcome because
A) the model is not capable of incorporating externalities.
B) buyers and sellers only take their self interest into account.
C) too much is produced.
D) too little is produced.
E) the environment is treated as a common property.
A) the model is not capable of incorporating externalities.
B) buyers and sellers only take their self interest into account.
C) too much is produced.
D) too little is produced.
E) the environment is treated as a common property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Glen is considering whether to paint his house and if so,what colour to choose.He settles on three options: leave it "as is",paint it brown,or paint it purple.Glen's neighbours are able to easily see his house.The following table shows the monetary values of utility for Glen and his neighbours under the three possibilities. 
Refer to the information above.Assume that Glen and his neighbours both know the payoffs to the three choices.If maintaining relations with his neighbours is valuable,Glen will likely choose
A) brown.
B) purple.
C) to not change the colour.
D) to consider different colours.
E) to move.

Refer to the information above.Assume that Glen and his neighbours both know the payoffs to the three choices.If maintaining relations with his neighbours is valuable,Glen will likely choose
A) brown.
B) purple.
C) to not change the colour.
D) to consider different colours.
E) to move.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 196 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



