Deck 10: Understanding Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/175
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Understanding Monopoly
1
Which of the following is NOT a necessary characteristic of monopolies?
A) Prices are set by the seller,not the consumer.
B) There is just one firm in the role of seller.
C) The market is for a unique product without close substitutes.
D) Government plays a role in maintaining barriers to entry.
E) The seller has a high level of market power.
A) Prices are set by the seller,not the consumer.
B) There is just one firm in the role of seller.
C) The market is for a unique product without close substitutes.
D) Government plays a role in maintaining barriers to entry.
E) The seller has a high level of market power.
Government plays a role in maintaining barriers to entry.
2
Control of resources is an example of
A) an externality.
B) consumer surplus.
C) a government-created barrier.
D) a natural barrier.
E) rent seeking.
A) an externality.
B) consumer surplus.
C) a government-created barrier.
D) a natural barrier.
E) rent seeking.
a natural barrier.
3
Problems raising capital is an example of
A) a natural barrier.
B) consumer surplus.
C) a government-created barrier.
D) an externality.
E) inefficient output and price.
A) a natural barrier.
B) consumer surplus.
C) a government-created barrier.
D) an externality.
E) inefficient output and price.
a natural barrier.
4
Monopoly power is a measure of
A) a firm's ability to set prices.
B) the uniqueness of a firm's product.
C) the existence of close substitutes for a firm's product.
D) a firm's ability to overcome barriers to entry in its market.
E) a firm's profitability.
A) a firm's ability to set prices.
B) the uniqueness of a firm's product.
C) the existence of close substitutes for a firm's product.
D) a firm's ability to overcome barriers to entry in its market.
E) a firm's profitability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Monopolists
A) enjoy market power for their specific product.
B) have no market power for their specific product.
C) will never experience a loss.
D) always experience economies of scale.
E) exist in all markets.
A) enjoy market power for their specific product.
B) have no market power for their specific product.
C) will never experience a loss.
D) always experience economies of scale.
E) exist in all markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Barriers to entry
A) measure the ability of firms to set the price for a good.
B) do not exist for monopolies.
C) always lead to profits.
D) restrict the entry of new firms into the market.
E) exist for perfectly competitive firms.
A) measure the ability of firms to set the price for a good.
B) do not exist for monopolies.
C) always lead to profits.
D) restrict the entry of new firms into the market.
E) exist for perfectly competitive firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The best way to limit competition is to
A) lobby for a government-created barrier.
B) charge a low price.
C) produce a high quantity.
D) control a resource that is essential in the production process.
E) minimize costs.
A) lobby for a government-created barrier.
B) charge a low price.
C) produce a high quantity.
D) control a resource that is essential in the production process.
E) minimize costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A monopoly
A) always makes a profit.
B) can force consumers to purchase what it is selling.
C) is characterized by a single seller who produces a well-defined product for which there are no good substitutes.
D) always has naturally created barriers.
E) always has government-created barriers.
A) always makes a profit.
B) can force consumers to purchase what it is selling.
C) is characterized by a single seller who produces a well-defined product for which there are no good substitutes.
D) always has naturally created barriers.
E) always has government-created barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Economies of scale exist
A) only for monopolists.
B) when long-run average total costs increase.
C) when long-run average total costs decrease.
D) when long-run average total costs are constant.
E) when governments create barriers to entry.
A) only for monopolists.
B) when long-run average total costs increase.
C) when long-run average total costs decrease.
D) when long-run average total costs are constant.
E) when governments create barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Two conditions allow a single seller to become a monopolist.Those two conditions are that the firm must
A) have something unique to sell and it must be able to estimate its demand curve.
B) have something unique to sell and it must have a way to prevent potential competitors from entering the market.
C) be able to estimate its demand curve and it must have a way to prevent potential competitors from entering the market.
D) be able to segregate its consumers and it must have a way to prevent potential competitors from entering the market.
E) have something unique to sell and it must be able to segregate its consumers.
A) have something unique to sell and it must be able to estimate its demand curve.
B) have something unique to sell and it must have a way to prevent potential competitors from entering the market.
C) be able to estimate its demand curve and it must have a way to prevent potential competitors from entering the market.
D) be able to segregate its consumers and it must have a way to prevent potential competitors from entering the market.
E) have something unique to sell and it must be able to segregate its consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Control of resources,problems raising capital,and economies of scale are all examples of
A) government-created barriers.
B) market structures.
C) patents and copyright laws.
D) price makers.
E) natural barriers.
A) government-created barriers.
B) market structures.
C) patents and copyright laws.
D) price makers.
E) natural barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is NOT an example of a natural barrier to entry?
A) A software firm cannot get a loan to fund development of a new computer operating system.
B) A manufacturing firm has to buy a rare metal from the one company that controls most of the worldwide supply.
C) A small soft-drink company struggles to produce its product as cheaply as its much larger competitor can.
D) A single utility firm can deliver services to every home in an area more efficiently than a cluster of competing firms could.
E) A patent gives a pharmaceutical firm the exclusive right to manufacture and sell an anticancer drug.
A) A software firm cannot get a loan to fund development of a new computer operating system.
B) A manufacturing firm has to buy a rare metal from the one company that controls most of the worldwide supply.
C) A small soft-drink company struggles to produce its product as cheaply as its much larger competitor can.
D) A single utility firm can deliver services to every home in an area more efficiently than a cluster of competing firms could.
E) A patent gives a pharmaceutical firm the exclusive right to manufacture and sell an anticancer drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A natural monopoly
A) exists when many sellers experience lower average total costs than potential
Competitors do.
B) exists when a firm has sole ownership of a natural resource.
C) is an example of a government-created barrier.
D) is needed to make a profit in the long run.
E) exists when a single seller experiences lower average total costs than any potential competitor.
A) exists when many sellers experience lower average total costs than potential
Competitors do.
B) exists when a firm has sole ownership of a natural resource.
C) is an example of a government-created barrier.
D) is needed to make a profit in the long run.
E) exists when a single seller experiences lower average total costs than any potential competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Reginald has developed a new social media site that he feels can compete heavily with Facebook.Unfortunately,he cannot find someone to lend him enough money to market his product to consumers.Reginald is facing which kind of barrier to entry?
A) control of resources
B) problems raising capital
C) economies of scale
D) licensing
E) patents and copyright law
A) control of resources
B) problems raising capital
C) economies of scale
D) licensing
E) patents and copyright law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Raising capital to compete against an entrenched monopolist
A) is very easy.
B) is unnecessary.
C) can be done only through private investors.
D) is very difficult.
E) can be done only through banks.
A) is very easy.
B) is unnecessary.
C) can be done only through private investors.
D) is very difficult.
E) can be done only through banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the movie Forrest Gump,the title character's Bubba Gump Shrimp Company is able to gain monopoly power in its market because of
A) control of an essential resource.
B) high barriers to entry.
C) a unique product.
D) economies of scale.
E) Forrest's good luck.
A) control of an essential resource.
B) high barriers to entry.
C) a unique product.
D) economies of scale.
E) Forrest's good luck.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The typical result of monopoly is ________ prices and ________ output than we find in a competitive market.
A) lower; lower
B) higher; higher
C) higher; lower
D) lower; higher
E) higher; the same
A) lower; lower
B) higher; higher
C) higher; lower
D) lower; higher
E) higher; the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Economies of scale is an example of
A) rent seeking.
B) consumer surplus.
C) a government-created barrier.
D) an externality.
E) a natural barrier.
A) rent seeking.
B) consumer surplus.
C) a government-created barrier.
D) an externality.
E) a natural barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Three natural barriers to entry are
A) control of resources,patents and copyright law,and licensing.
B) economies of scale,problems raising capital,and control of resources.
C) problems raising capital,patents and copyright law,and licensing.
D) control of resources,patents and copyright law,and economies of scale.
E) control of resources,economies of scale,and licensing.
A) control of resources,patents and copyright law,and licensing.
B) economies of scale,problems raising capital,and control of resources.
C) problems raising capital,patents and copyright law,and licensing.
D) control of resources,patents and copyright law,and economies of scale.
E) control of resources,economies of scale,and licensing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Ash is the preferred wood to be used in the production of baseball bats.If a company was to buy the rights to harvesting the ash trees out of all the forests in North America,which of the following barriers of entry has this company created?
A) control of resources
B) problems raising capital
C) economies of scale
D) licensing
E) patents and copyright law
A) control of resources
B) problems raising capital
C) economies of scale
D) licensing
E) patents and copyright law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The output effect refers to how
A) lower prices affect the quantity sold.
B) firms can set their prices.
C) firms choose their quantities.
D) lower prices affect revenue.
E) lower output affects the price.
A) lower prices affect the quantity sold.
B) firms can set their prices.
C) firms choose their quantities.
D) lower prices affect revenue.
E) lower output affects the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The demand curve for the product of a firm in a competitive market is ________,and the demand curve for the product of a monopolist is ________.
A) horizontal; downward sloping
B) horizontal; horizontal
C) downward sloping; upward sloping
D) downward sloping; horizontal
E) upward sloping; downward sloping
A) horizontal; downward sloping
B) horizontal; horizontal
C) downward sloping; upward sloping
D) downward sloping; horizontal
E) upward sloping; downward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following can fall below the x axis when graphing price and cost against quantity?
A) demand curve
B) marginal cost curve
C) total cost curve
D) fixed cost curve
E) marginal revenue curve
A) demand curve
B) marginal cost curve
C) total cost curve
D) fixed cost curve
E) marginal revenue curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The price effect refers to how
A) lower prices affect the quantity sold.
B) firms can set their prices.
C) firms choose their quantities.
D) lower prices affect revenue.
E) lower output affects the price.
A) lower prices affect the quantity sold.
B) firms can set their prices.
C) firms choose their quantities.
D) lower prices affect revenue.
E) lower output affects the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Patents and copyrights can
A) create strong incentives to develop new medicines.
B) provide heavy competition in markets.
C) never lead to deadweight loss.
D) assure firms that their products will make a profit.
E) be considered natural barriers.
A) create strong incentives to develop new medicines.
B) provide heavy competition in markets.
C) never lead to deadweight loss.
D) assure firms that their products will make a profit.
E) be considered natural barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Both monopolies and competitive firms
A) are price takers.
B) are price makers.
C) face barriers to entry.
D) make long-run economic profits.
E) try to maximize profits.
A) are price takers.
B) are price makers.
C) face barriers to entry.
D) make long-run economic profits.
E) try to maximize profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Licensing
A) is a natural barrier.
B) creates more competition.
C) causes more varieties of goods and services at different price levels.
D) creates an opportunity for corruption.
E) always results in zero economic profits.
A) is a natural barrier.
B) creates more competition.
C) causes more varieties of goods and services at different price levels.
D) creates an opportunity for corruption.
E) always results in zero economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Two government-created barriers to entry are
A) licensing and economies of scale.
B) economies of scale and patent system/copyright law.
C) licensing and patent system/copyright law.
D) economies of scale and control of resources.
E) licensing and control of resources.
A) licensing and economies of scale.
B) economies of scale and patent system/copyright law.
C) licensing and patent system/copyright law.
D) economies of scale and control of resources.
E) licensing and control of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A price maker
A) is a characteristic held by a perfectly competitive firm.
B) must set the price at the market price.
C) has some control over the price it charges.
D) can sell its product at any price.
E) will always make economic profits.
A) is a characteristic held by a perfectly competitive firm.
B) must set the price at the market price.
C) has some control over the price it charges.
D) can sell its product at any price.
E) will always make economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
After a patent on a product expires,
A) other firms must wait to mimic the product.
B) all negative and positive externalities are internalized.
C) rivals can start to mimic the product.
D) no other firms can mimic the product.
E) no further profits are able to be made by the original producer of the good.
A) other firms must wait to mimic the product.
B) all negative and positive externalities are internalized.
C) rivals can start to mimic the product.
D) no other firms can mimic the product.
E) no further profits are able to be made by the original producer of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Patents and copyright law
A) are natural barriers.
B) create more competition.
C) mean more varieties of goods and services at different price levels.
D) assure inventors that no one else will sell their ideas.
E) always result in zero economic profits.
A) are natural barriers.
B) create more competition.
C) mean more varieties of goods and services at different price levels.
D) assure inventors that no one else will sell their ideas.
E) always result in zero economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why do governments issue patents?
A) Patents foster economies of scale.
B) Inventors have a moral right to control their inventions.
C) Patents ensure that socially beneficial goods are affordable.
D) Firms benefit from the publicity associated with patents.
E) The prospect of large profits is an incentive to innovation.
A) Patents foster economies of scale.
B) Inventors have a moral right to control their inventions.
C) Patents ensure that socially beneficial goods are affordable.
D) Firms benefit from the publicity associated with patents.
E) The prospect of large profits is an incentive to innovation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
One argument against patent and copyright laws is that they
A) provide incentives to invest in research and development.
B) protect intellectual property.
C) hinder creativity.
D) increase competition.
E) limit exposure that can benefit companies and individuals.
A) provide incentives to invest in research and development.
B) protect intellectual property.
C) hinder creativity.
D) increase competition.
E) limit exposure that can benefit companies and individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the usual rationale for governments to issue monopoly-promoting licenses to firms providing services such as trash collection?
A) lower risk for investors in the firms
B) increased customer choice
C) better-quality services
D) economies of scale
E) public safety
A) lower risk for investors in the firms
B) increased customer choice
C) better-quality services
D) economies of scale
E) public safety

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The profit-maximizing rule for a monopolist is
A) marginal revenue = marginal cost.
B) price =marginal cost.
C) price = marginal revenue.
D) average total cost = marginal revenue.
E) average total cost = marginal cost.
A) marginal revenue = marginal cost.
B) price =marginal cost.
C) price = marginal revenue.
D) average total cost = marginal revenue.
E) average total cost = marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In instances when having a single firm in the market makes sense,governments ________ to minimize negative externalities.
A) will grant a patent or copyright
B) require licenses
C) deregulate industries
D) hand out subsidies
E) break down barriers to entry
A) will grant a patent or copyright
B) require licenses
C) deregulate industries
D) hand out subsidies
E) break down barriers to entry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Market-created and government-created barriers
A) are the same thing.
B) are regarded by all economists as bad.
C) increase competition in markets.
D) create monopolies.
E) are problems solved only by government intervention.
A) are the same thing.
B) are regarded by all economists as bad.
C) increase competition in markets.
D) create monopolies.
E) are problems solved only by government intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Apple and Google apply for hundreds of patents every year.These patents
A) allow Apple and Google to produce goods with no risk of monetary loss.
B) provide incentives for Apple and Google to spend large amounts of money up front on research and development of new products.
C) create more competition among Apple,Google,and other tech firms than would occur without government intervention.
D) make it easy for Apple and Google products to be similar.
E) make it easy for other firms to compete with Apple and Google.
A) allow Apple and Google to produce goods with no risk of monetary loss.
B) provide incentives for Apple and Google to spend large amounts of money up front on research and development of new products.
C) create more competition among Apple,Google,and other tech firms than would occur without government intervention.
D) make it easy for Apple and Google products to be similar.
E) make it easy for other firms to compete with Apple and Google.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why do copyrights expire after a set period of time?
A) so that creative industries will operate as efficiently as possible
B) to provide an incentive for artists and other creators of original work
C) to ensure that creative activity gets the publicity it deserves
D) so that in the long run,creative works are readily and cheaply available
E) to help writers and musicians become price makers
A) so that creative industries will operate as efficiently as possible
B) to provide an incentive for artists and other creators of original work
C) to ensure that creative activity gets the publicity it deserves
D) so that in the long run,creative works are readily and cheaply available
E) to help writers and musicians become price makers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the soda industry,production costs per unit continue to fall as the firm expands.In this type of industry,smaller rivals trying to enter the industry
A) will easily be able to gain market power.
B) have lower average costs.
C) do not have high fixed costs.
D) will have much higher average costs.
E) experience a government-created barrier.
A) will easily be able to gain market power.
B) have lower average costs.
C) do not have high fixed costs.
D) will have much higher average costs.
E) experience a government-created barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The demand curve for the product of a firm in a competitive market is ________,and the demand curve for the product of a monopolist is ________.
A) perfectly inelastic; downward sloping
B) horizontal; perfectly inelastic
C) downward sloping; perfectly elastic
D) downward sloping; horizontal
E) perfectly elastic; downward sloping
A) perfectly inelastic; downward sloping
B) horizontal; perfectly inelastic
C) downward sloping; perfectly elastic
D) downward sloping; horizontal
E) perfectly elastic; downward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 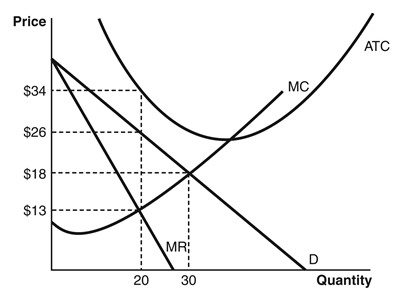
The profit-maximizing price and quantity are ________,respectively.
A) $34 and 20
B) $26 and 20
C) $18 and 20
D) $18 and 30
E) $13 and 20

The profit-maximizing price and quantity are ________,respectively.
A) $34 and 20
B) $26 and 20
C) $18 and 20
D) $18 and 30
E) $13 and 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The demand curve for Arnold's Airport Shuttle is downward sloping.With only this information,it can be concluded that Arnold's Airport Shuttle
A) is the only firm in the market for airport shuttles.
B) is currently maximizing profits.
C) is a price maker.
D) makes economic profits.
E) should produce where the demand curve crosses marginal cost.
A) is the only firm in the market for airport shuttles.
B) is currently maximizing profits.
C) is a price maker.
D) makes economic profits.
E) should produce where the demand curve crosses marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When marginal revenue is negative,the
A) lost revenues associated with the price effect outweigh the revenue gains created by the output effect.
B) lost revenues associated with the price effect are outweighed by the revenue gains created by the output effect.
C) output effect is negative.
D) firm is maximizing revenues.
E) firm cannot be maximizing profits.
A) lost revenues associated with the price effect outweigh the revenue gains created by the output effect.
B) lost revenues associated with the price effect are outweighed by the revenue gains created by the output effect.
C) output effect is negative.
D) firm is maximizing revenues.
E) firm cannot be maximizing profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Clarice's Campground is the only campground located in Abilene,Texas.Clarice's Campground's demand curve is
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) horizontal.
D) the market demand curve.
E) upward sloping.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) horizontal.
D) the market demand curve.
E) upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a monopolist is producing a quantity where marginal revenue is equal to $32 and the marginal cost is equal to $30,the monopolist should ________ to maximize profits.
A) increase production and lower the price
B) decrease production and increase the price
C) continue producing at the current price
D) increase production and increase the price
E) decrease production and decrease the price
A) increase production and lower the price
B) decrease production and increase the price
C) continue producing at the current price
D) increase production and increase the price
E) decrease production and decrease the price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Refer to the accompanying table, which represents the costs and production for a monopolist, to answer the following questions. 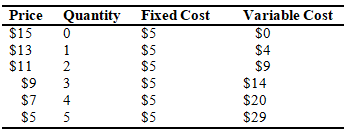
The profit-maximizing price for this firm is
A) $15.
B) $5.
C) $7.
D) $9.
E) $13.

The profit-maximizing price for this firm is
A) $15.
B) $5.
C) $7.
D) $9.
E) $13.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At high price levels,demand tends to be ________ and the price effect is ________,relative to the output effect.
A) inelastic; small
B) inelastic; large
C) elastic; small
D) elastic; large
E) inelastic; insignificant
A) inelastic; small
B) inelastic; large
C) elastic; small
D) elastic; large
E) inelastic; insignificant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When a monopolist lowers a price from $80 to $70,the quantity that the firm is able to sell increases from 100 to 150.The change in revenue associated with the price effect is equal to
A) $3,500.
B) -$3,500.
C) $1,000.
D) -$1,000.
E) $4,000.
A) $3,500.
B) -$3,500.
C) $1,000.
D) -$1,000.
E) $4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
-This profit-maximizing firm's total profit is equal to
A) $160.
B) -$160.
C) $320.
D) -$320.
E) $100.

-This profit-maximizing firm's total profit is equal to
A) $160.
B) -$160.
C) $320.
D) -$320.
E) $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
This firm
A) is in a competitive market.
B) can make a profit.
C) does not want to maximize profit.
D) cannot make a profit.
E) is not a monopolist because it is incurring a loss.

This firm
A) is in a competitive market.
B) can make a profit.
C) does not want to maximize profit.
D) cannot make a profit.
E) is not a monopolist because it is incurring a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Because the demand curve for a monopolist is downward sloping,
A) there is no limit on the monopolist's ability to make a profit.
B) the monopolist can sell its product at any price it wants.
C) the monopolist can sell as many units of its product as it wants.
D) the monopolist is a price taker.
E) the monopolist is a price maker.
A) there is no limit on the monopolist's ability to make a profit.
B) the monopolist can sell its product at any price it wants.
C) the monopolist can sell as many units of its product as it wants.
D) the monopolist is a price taker.
E) the monopolist is a price maker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When marginal revenue is positive,the
A) lost revenues associated with the price effect outweigh the revenue gains created by the output effect.
B) lost revenues associated with the price effect are outweighed by the revenue gains created by the output effect.
C) output effect is relatively small compared to the price effect.
D) firm is maximizing revenues.
E) firm cannot be maximizing profits.
A) lost revenues associated with the price effect outweigh the revenue gains created by the output effect.
B) lost revenues associated with the price effect are outweighed by the revenue gains created by the output effect.
C) output effect is relatively small compared to the price effect.
D) firm is maximizing revenues.
E) firm cannot be maximizing profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The marginal revenue lies ________ the demand curve because there is a(n)________ effect whenever the price is lowered.
A) above; price
B) below; price
C) below; output
D) above; output
E) on; price
A) above; price
B) below; price
C) below; output
D) above; output
E) on; price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a monopolist is producing a quantity where marginal revenue is equal to $125 and the marginal cost is equal to $125,the monopolist should ________ to maximize profits.
A) increase production and lower the price
B) decrease production and increase the price
C) continue producing at the current price
D) increase production and increase the price
E) decrease production and decrease the price
A) increase production and lower the price
B) decrease production and increase the price
C) continue producing at the current price
D) increase production and increase the price
E) decrease production and decrease the price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Refer to the accompanying table, which represents the costs and production for a monopolist, to answer the following questions. 
The profit made by this profit-maximizing firm is
A) $8.
B) $4.
C) $3.
D) $7.
E) $9.

The profit made by this profit-maximizing firm is
A) $8.
B) $4.
C) $3.
D) $7.
E) $9.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a monopolist is producing a quantity where marginal revenue is equal to $16 and the marginal cost is equal to $17,the monopolist should ________ to maximize profits.
A) increase production and lower the price
B) decrease production and increase the price
C) continue producing at the current price
D) increase production and increase the price
E) decrease production and decrease the price
A) increase production and lower the price
B) decrease production and increase the price
C) continue producing at the current price
D) increase production and increase the price
E) decrease production and decrease the price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the accompanying table, which represents the costs and production for a monopolist, to answer the following questions. 
The profit-maximizing quantity for this firm is
A) zero.
B) one.
C) three.
D) four.
E) five.

The profit-maximizing quantity for this firm is
A) zero.
B) one.
C) three.
D) four.
E) five.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the accompanying table, which represents the costs and production for a monopolist, to answer the following questions. 
As production increases,the price consumers pay for the good
A) increases and then decreases.
B) decreases and then increases.
C) stays the same.
D) increases.
E) decreases.

As production increases,the price consumers pay for the good
A) increases and then decreases.
B) decreases and then increases.
C) stays the same.
D) increases.
E) decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
At low price levels,demand tends to be ________ and the price effect is ________,relative to the output effect.
A) inelastic; small
B) inelastic; large
C) elastic; small
D) elastic; large
E) elastic; insignificant
A) inelastic; small
B) inelastic; large
C) elastic; small
D) elastic; large
E) elastic; insignificant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions.
For a firm in a competitive market, the demand curve is horizontal, as shown.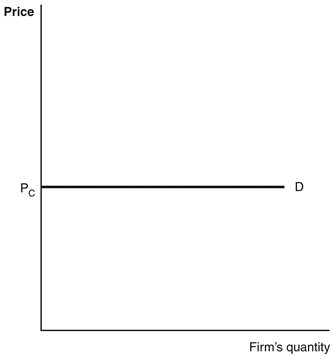
What will happen if the firm offers its product at a price slightly above price PC?
A) The marginal revenue will drop below zero.
B) The firm will slightly increase its profits.
C) The sales volume will plummet to essentially zero.
D) The firm will run into high barriers to exit from the market.
E) The number of units sold will slightly increase.
For a firm in a competitive market, the demand curve is horizontal, as shown.

What will happen if the firm offers its product at a price slightly above price PC?
A) The marginal revenue will drop below zero.
B) The firm will slightly increase its profits.
C) The sales volume will plummet to essentially zero.
D) The firm will run into high barriers to exit from the market.
E) The number of units sold will slightly increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 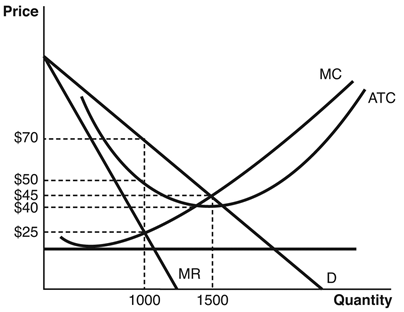
The total revenue when a firm is profit maximizing is
A) $70,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $67,500.
D) $60,000.
E) $25,000.

The total revenue when a firm is profit maximizing is
A) $70,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $67,500.
D) $60,000.
E) $25,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A big difference between a competitive firm and a monopolist is that a monopolist
A) does not charge a price equal to marginal revenue.
B) does not set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost to maximize profits.
C) does not try to maximize profits.
D) can always make positive economic profits.
E) cannot set its price at the market price.
A) does not charge a price equal to marginal revenue.
B) does not set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost to maximize profits.
C) does not try to maximize profits.
D) can always make positive economic profits.
E) cannot set its price at the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When marginal revenue intersects marginal cost on a graph,
A) profits are maximized for a monopolist but not for a competitive firm.
B) profits are maximized for a competitive firm but not for a monopolist.
C) a monopolist prices the good at that point.
D) a monopolist always makes an economic profit.
E) a monopolist must go up to the demand curve to find the price.
A) profits are maximized for a monopolist but not for a competitive firm.
B) profits are maximized for a competitive firm but not for a monopolist.
C) a monopolist prices the good at that point.
D) a monopolist always makes an economic profit.
E) a monopolist must go up to the demand curve to find the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
At the profit-maximizing output in a monopoly controlled market,the price a monopolist charges is ________ cost.
A) below marginal
B) above marginal
C) above average total
D) below average total
E) equal to marginal
A) below marginal
B) above marginal
C) above average total
D) below average total
E) equal to marginal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 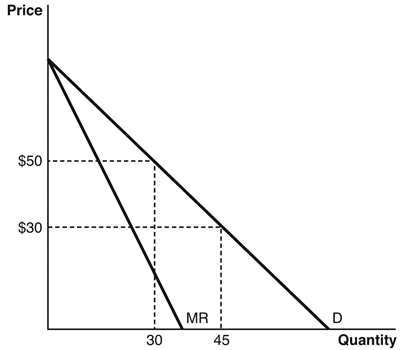
When the price changes from $50 to $30,the price effect leads to a loss of ________ in revenue.
A) $20
B) $15
C) $900
D) $600
E) $450

When the price changes from $50 to $30,the price effect leads to a loss of ________ in revenue.
A) $20
B) $15
C) $900
D) $600
E) $450

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is a characteristic of a monopoly but not a characteristic of a competitive market?
A) A monopoly contains many firms.
B) A monopoly produces an efficient level of output.
C) A producer in a monopoly may earn long-run economic profits.
D) A producer in a monopoly has no market power.
E) A producer in a monopoly is a price taker.
A) A monopoly contains many firms.
B) A monopoly produces an efficient level of output.
C) A producer in a monopoly may earn long-run economic profits.
D) A producer in a monopoly has no market power.
E) A producer in a monopoly is a price taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
The profit when a firm is profit maximizing is
A) $70,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $20,500.
D) $20,000.
E) $25,000.

The profit when a firm is profit maximizing is
A) $70,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $20,500.
D) $20,000.
E) $25,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions.
For a firm in a competitive market, the demand curve is horizontal, as shown.
What will happen if the firm offers its product at a price slightly below price PC?
A) The sales volume will plummet to essentially zero.
B) The number of units sold will slightly decrease.
C) The average total cost will slightly increase.
D) The firm will run into high barriers to exit from the market.
E) The firm will lose money on each unit sold.
For a firm in a competitive market, the demand curve is horizontal, as shown.

What will happen if the firm offers its product at a price slightly below price PC?
A) The sales volume will plummet to essentially zero.
B) The number of units sold will slightly decrease.
C) The average total cost will slightly increase.
D) The firm will run into high barriers to exit from the market.
E) The firm will lose money on each unit sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The equation of a firm's marginal revenue curve is estimated to be P = 50 - Q (quantity),and the equation of its marginal cost curve is estimated to be P = 10 + 3Q.The profit-maximizing price for this firm is
A) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) $50.
E) $40.
A) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) $50.
E) $40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 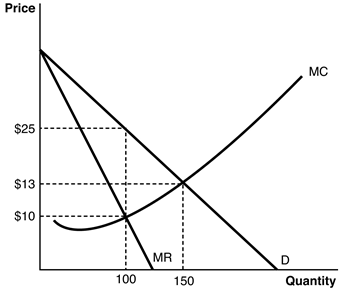
If a firm is producing a quantity of 100 and charging a price of $10,it
A) should continue to produce 100 units but raise the price to $13 to maximize profits.
B) should increase production to 150 units but raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
C) should continue to produce 100 units but raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
D) should increase production to 100 units and raise the price to $13 to maximize profits.
E) is already maximizing profits and should not change the price or quantity produced.

If a firm is producing a quantity of 100 and charging a price of $10,it
A) should continue to produce 100 units but raise the price to $13 to maximize profits.
B) should increase production to 150 units but raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
C) should continue to produce 100 units but raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
D) should increase production to 100 units and raise the price to $13 to maximize profits.
E) is already maximizing profits and should not change the price or quantity produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
When this firm is producing at the profit-maximizing price and quantity,its total revenue is
A) $1,000.
B) $1,950.
C) $2,500.
D) $3,750.
E) $5,000.

When this firm is producing at the profit-maximizing price and quantity,its total revenue is
A) $1,000.
B) $1,950.
C) $2,500.
D) $3,750.
E) $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
To maximize profits,a monopolist chooses the quantity where
A) revenues are maximized.
B) marginal revenue equals zero.
C) marginal cost equals zero.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E) costs are minimized.
A) revenues are maximized.
B) marginal revenue equals zero.
C) marginal cost equals zero.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E) costs are minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
If a firm is producing a quantity of 100 and charging a price of $25,it
A) should raise production to 150 units but lower the price to $10 to maximize profits.
B) should raise production to 150 units and continue to charge $25 to maximize profits.
C) should keep production at 100 units but lower the price to $13 to maximize profits.
D) should keep production at 100 units and lower the price to $10 to maximize profits.
E) is already maximizing profits and should not change the price or quantity produced.

If a firm is producing a quantity of 100 and charging a price of $25,it
A) should raise production to 150 units but lower the price to $10 to maximize profits.
B) should raise production to 150 units and continue to charge $25 to maximize profits.
C) should keep production at 100 units but lower the price to $13 to maximize profits.
D) should keep production at 100 units and lower the price to $10 to maximize profits.
E) is already maximizing profits and should not change the price or quantity produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
The total cost when a firm is profit maximizing is
A) $70,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $67,500.
D) $60,000.
E) $25,000.

The total cost when a firm is profit maximizing is
A) $70,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $67,500.
D) $60,000.
E) $25,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
The profit-maximizing price and quantity are ________,respectively.
A) $25 and 100
B) $25 and 150
C) $13 and 100
D) $10 and 100
E) $10 and 150

The profit-maximizing price and quantity are ________,respectively.
A) $25 and 100
B) $25 and 150
C) $13 and 100
D) $10 and 100
E) $10 and 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
If a firm is producing a quantity of 150 and charging a price of $13,it
A) should continue to produce 150 units but lower the price to $10 to maximize profits.
B) should continue to produce 150 units but raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
C) should lower production to 100 units but keep charging $13 to maximize profits.
D) should lower production to 100 units and raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
E) is already maximizing profits and should not change the price or quantity produced.

If a firm is producing a quantity of 150 and charging a price of $13,it
A) should continue to produce 150 units but lower the price to $10 to maximize profits.
B) should continue to produce 150 units but raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
C) should lower production to 100 units but keep charging $13 to maximize profits.
D) should lower production to 100 units and raise the price to $25 to maximize profits.
E) is already maximizing profits and should not change the price or quantity produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
When the price changes from $50 to $30,the output effect leads to an increase of ________ in revenue.
A) $20
B) $15
C) $900
D) $600
E) $450

When the price changes from $50 to $30,the output effect leads to an increase of ________ in revenue.
A) $20
B) $15
C) $900
D) $600
E) $450

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 
The profit-maximizing price and quantity are ________,respectively.
A) $25 and 1,000
B) $40 and 1,500
C) $45 and 1,500
D) $50 and 1,000
E) $70 and 1,000

The profit-maximizing price and quantity are ________,respectively.
A) $25 and 1,000
B) $40 and 1,500
C) $45 and 1,500
D) $50 and 1,000
E) $70 and 1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is a characteristic of a monopoly but not of a competitive market?
A) A monopoly contains many firms.
B) price marginal cost
C) price marginal cost
D) price = marginal cost
E) A firm in a monopoly is a price taker.
A) A monopoly contains many firms.
B) price marginal cost
C) price marginal cost
D) price = marginal cost
E) A firm in a monopoly is a price taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



