Deck 11: Product Differentiation, Monopolistic Competition, and Oligopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/169
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Product Differentiation, Monopolistic Competition, and Oligopoly
1
A producer will want to differentiate his or her product somewhat from other producers' similar products because
A)no producer has production facilities exactly like those of other producers.
B)of government trademark protections.
C)different consumers have different wants and needs, and the producer may be able to fill a niche.
D)doing so guarantees that someone will buy it.
E)one must be careful not to flatter the competition by copying their product.
A)no producer has production facilities exactly like those of other producers.
B)of government trademark protections.
C)different consumers have different wants and needs, and the producer may be able to fill a niche.
D)doing so guarantees that someone will buy it.
E)one must be careful not to flatter the competition by copying their product.
C
2
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Economists do not know if optimal product differentiation is achieved.
B)According to the theory of monopolistic competition, the cost of product differentiation is that firms often suffer losses.
C)Methods to measure the benefits of product differentiation are well developed.
D)Product differentiation has its costs, but it does not result in any benefit.
E)Product differentiation is always desirable for consumers.
A)Economists do not know if optimal product differentiation is achieved.
B)According to the theory of monopolistic competition, the cost of product differentiation is that firms often suffer losses.
C)Methods to measure the benefits of product differentiation are well developed.
D)Product differentiation has its costs, but it does not result in any benefit.
E)Product differentiation is always desirable for consumers.
A
3
Product differentiation refers to
A)sellers' price differences for the same product.
B)at least slightly-different products offered by sellers.
C)quality differences in products under perfect competition.
D)unique products that have no close substitutes.
E)firms' unethical practice of deception.
A)sellers' price differences for the same product.
B)at least slightly-different products offered by sellers.
C)quality differences in products under perfect competition.
D)unique products that have no close substitutes.
E)firms' unethical practice of deception.
B
4
The term that best describes the behavior in which each firm needs to anticipate what other firms will do and develop a strategy to respond is called
A)extrapolating.
B)strategic behavior.
C)rationalizing.
D)monopolizing.
E)perfect competition.
A)extrapolating.
B)strategic behavior.
C)rationalizing.
D)monopolizing.
E)perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a monopolistically competitive market, firms produce
A)an identical product.
B)totally different products.
C)similar but not identical products.
D)products that other firms do not produce.
E)any kinds of products, but at the same price.
A)an identical product.
B)totally different products.
C)similar but not identical products.
D)products that other firms do not produce.
E)any kinds of products, but at the same price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Product differentiation is important only for final consumer goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Product differentiation is
A)the ability of consumers to determine differences in different units of the same product.
B)the existence of varying degrees of differences among similar items.
C)the spin-off of one product line from another.
D)an attempt by salespeople to make the products they sell appear different from products others sell.
E)the opposite of production.
A)the ability of consumers to determine differences in different units of the same product.
B)the existence of varying degrees of differences among similar items.
C)the spin-off of one product line from another.
D)an attempt by salespeople to make the products they sell appear different from products others sell.
E)the opposite of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In an oligopoly, there is limited entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Product differentiation is most important to
A)monopolistic competition.
B)perfect competition.
C)monopoly.
D)a regulated industry.
E)government enterprises.
A)monopolistic competition.
B)perfect competition.
C)monopoly.
D)a regulated industry.
E)government enterprises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
One way in which oligopoly differs from monopolistic competition is that an oligopoly operates in an industry that
A)makes no profits.
B)incurs losses.
C)has fewer sellers.
D)has more sellers.
E)incurs higher costs.
A)makes no profits.
B)incurs losses.
C)has fewer sellers.
D)has more sellers.
E)incurs higher costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The economically desirable thing about product variety is
A)that there is always free entry and exit.
B)that different individuals' diverse tastes are satisfied.
C)the increased economic activity that results from it.
D)that many firms participate in a market with product variety.
E)the freedom it gives firms to produce in slightly different ways.
A)that there is always free entry and exit.
B)that different individuals' diverse tastes are satisfied.
C)the increased economic activity that results from it.
D)that many firms participate in a market with product variety.
E)the freedom it gives firms to produce in slightly different ways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
There is limited entry in a monopolistically competitive industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Product differentiation is often the key to a successful business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Product differentiation occurs only among homogeneous products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Firms engage in product differentiation
A)to gain market power.
B)to gain entry into a market of pure competition.
C)to minimize average total cost.
D)to maximize total revenue.
E)to be classified as price-takers.
A)to gain market power.
B)to gain entry into a market of pure competition.
C)to minimize average total cost.
D)to maximize total revenue.
E)to be classified as price-takers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The type of industry that is characterized by many firms selling differentiated products is called
A)competition.
B)pure competition.
C)monopoly.
D)monopolistic competition.
E)oligopoly.
A)competition.
B)pure competition.
C)monopoly.
D)monopolistic competition.
E)oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Product differentiation is a common feature of monopolistic competition and oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The type of industry in which there are a few firms and each of these firms reacts to the other firms' moves is called
A)monopoly.
B)oligopoly.
C)monopolistic competition.
D)pure competition.
E)competition.
A)monopoly.
B)oligopoly.
C)monopolistic competition.
D)pure competition.
E)competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following phenomena is not explained by the existence of product differentiation?
A)The need for consumer information services
B)Intraindustry trade
C)Price discrimination
D)Advertising
E)Brand loyalty
A)The need for consumer information services
B)Intraindustry trade
C)Price discrimination
D)Advertising
E)Brand loyalty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Product differentiation occurs with ____ goods.
A)final
B)consumer
C)intermediate
D)capital
E)all types of
A)final
B)consumer
C)intermediate
D)capital
E)all types of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A firm will work to differentiate its product up to the point that
A)it develops a product unlike anything else in the market.
B)the increase in revenue equals the cost of development.
C)revenue is maximized.
D)all innovation is exhausted.
E)the increase in product price as a result of research equals the price of the competition.
A)it develops a product unlike anything else in the market.
B)the increase in revenue equals the cost of development.
C)revenue is maximized.
D)all innovation is exhausted.
E)the increase in product price as a result of research equals the price of the competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A firm seeks to differentiate its products from others so as to
A)motivate employees by producing a unique product.
B)maximize profits.
C)sell more than its competitors.
D)be proud of its product.
E)minimize production costs.
A)motivate employees by producing a unique product.
B)maximize profits.
C)sell more than its competitors.
D)be proud of its product.
E)minimize production costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Advertising may do any of the following except
A)mislead consumers into thinking one product is better than another.
B)inform consumers of how a product is different from others.
C)persuade individuals to continue buying a product even when they do not need it.
D)inform consumers of a product's existence.
E)persuade people to try a product.
A)mislead consumers into thinking one product is better than another.
B)inform consumers of how a product is different from others.
C)persuade individuals to continue buying a product even when they do not need it.
D)inform consumers of a product's existence.
E)persuade people to try a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Interindustry trade occurs mostly because of product differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The main objective of product differentiation is to increase market demand for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Advertising can help a monopolistically competitive firm differentiate its products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Intraindustry trade occurs among industries producing homogeneous products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Product differentiation can be of value to a firm because
A)no other firm will be able to meet the same consumer need.
B)the product will always be patented.
C)some consumers with certain tastes will likely buy the product.
D)money is often spent to develop a differentiated product.
E)product differentiation lowers product prices for consumers.
A)no other firm will be able to meet the same consumer need.
B)the product will always be patented.
C)some consumers with certain tastes will likely buy the product.
D)money is often spent to develop a differentiated product.
E)product differentiation lowers product prices for consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is true?
A)A cost of differentiating one's product from another is that some consumers will stop buying it.
B)Economists are very good at identifying the proper amount of differentiation to bring about maximum benefit to society.
C)There is no advantage to making one's product slightly different from another successful product.
D)Product differentiation will succeed only if an existing firm is driven from the market.
E)Most firms trying to establish themselves try to copy the competition.
A)A cost of differentiating one's product from another is that some consumers will stop buying it.
B)Economists are very good at identifying the proper amount of differentiation to bring about maximum benefit to society.
C)There is no advantage to making one's product slightly different from another successful product.
D)Product differentiation will succeed only if an existing firm is driven from the market.
E)Most firms trying to establish themselves try to copy the competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consumer information services are demanded only when product differentiation exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Products may be differentiated in all of the following ways except
A)physical characteristics.
B)method of production.
C)time.
D)convenience.
E)service after the sale.
A)physical characteristics.
B)method of production.
C)time.
D)convenience.
E)service after the sale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Some economists say that advertising is wasteful because they believe that
A)most advertising is deceiving and, therefore, the resources used to advertise are not used for productive purposes.
B)efforts to persuade use resources, but persuasion is not a useful product.
C)it takes advantage of gullible people.
D)people who make commercials are already rich and do not need the money.
E)it creates a perception of product differences when products are not really different at all.
A)most advertising is deceiving and, therefore, the resources used to advertise are not used for productive purposes.
B)efforts to persuade use resources, but persuasion is not a useful product.
C)it takes advantage of gullible people.
D)people who make commercials are already rich and do not need the money.
E)it creates a perception of product differences when products are not really different at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Product differentiation exists when producers perceive the products to be different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Product differentiation results in
A)interindustry trade.
B)intraindustry trade.
C)no trade.
D)trade zones.
E)trade tariffs.
A)interindustry trade.
B)intraindustry trade.
C)no trade.
D)trade zones.
E)trade tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Firms can differentiate a product by making it easier for consumers to find substitutable products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When Burger King says you can "Have it your way," it is differentiating itself from McDonald's by stressing
A)personal service.
B)time savings.
C)physical characteristics.
D)safety.
E)location.
A)personal service.
B)time savings.
C)physical characteristics.
D)safety.
E)location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Specialized magazines that give product reviews on such products as cameras, stereo equipment, cars, and computers exist because of
A)single-minded people.
B)poor-quality products.
C)product differentiation.
D)greed.
E)hobbyists.
A)single-minded people.
B)poor-quality products.
C)product differentiation.
D)greed.
E)hobbyists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is an example of intraindustry trade?
A)The United States imports some vehicle models from Canada, while exports other vehicle models to Canada.
B)Japan buys computers from both the United States and China.
C)Chinese residents buy computers made in different factories across China.
D)Mexico exports banana to the United States, while the United States exports corn to Mexico.
E)Canada and Mexico import wheat from the United States, but not from each other.
A)The United States imports some vehicle models from Canada, while exports other vehicle models to Canada.
B)Japan buys computers from both the United States and China.
C)Chinese residents buy computers made in different factories across China.
D)Mexico exports banana to the United States, while the United States exports corn to Mexico.
E)Canada and Mexico import wheat from the United States, but not from each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When one country trades goods from one industry for goods from a different industry in another country, it is called
A)NAFTA.
B)free trade.
C)laissez faire.
D)specialized trade.
E)interindustry trade.
A)NAFTA.
B)free trade.
C)laissez faire.
D)specialized trade.
E)interindustry trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When two nations trade goods produced by the same industry, they are engaging in
A)collusive behavior.
B)mercantilism.
C)the creation of deadweight loss.
D)intraindustry trade.
E)conspiracy.
A)collusive behavior.
B)mercantilism.
C)the creation of deadweight loss.
D)intraindustry trade.
E)conspiracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The entry of new firms into a monopolistically competitive industry
A)will cause existing firms' costs to decrease if existing firms experience economies of scale.
B)is likely to occur when firms are breaking even.
C)will cause existing firms' demand curves to change.
D)will cause existing firms to decrease advertising expenditures.
E)is limited by significant barriers to entry.
A)will cause existing firms' costs to decrease if existing firms experience economies of scale.
B)is likely to occur when firms are breaking even.
C)will cause existing firms' demand curves to change.
D)will cause existing firms to decrease advertising expenditures.
E)is limited by significant barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A profit-maximizing firm will differentiate its products only if doing so incurs no additional costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For a monopolistically competitive firm, in both the short run and the long run price is
A)below marginal cost.
B)equal to marginal cost.
C)greater than marginal cost.
D)below marginal revenue.
E)equal to marginal revenue.
A)below marginal cost.
B)equal to marginal cost.
C)greater than marginal cost.
D)below marginal revenue.
E)equal to marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The model of monopolistic competition was developed by
A)Milton Friedman.
B)Adam Smith.
C)Paul Samuelson.
D)Edward Chamberlin.
E)Alfred Marshall.
A)Milton Friedman.
B)Adam Smith.
C)Paul Samuelson.
D)Edward Chamberlin.
E)Alfred Marshall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following properly describes monopolistic competition?
A)All firms produce exactly the same product.
B)There are only a few firms.
C)The industry is highly regulated.
D)Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
E)The cost curves of the typical firm are horizontal.
A)All firms produce exactly the same product.
B)There are only a few firms.
C)The industry is highly regulated.
D)Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
E)The cost curves of the typical firm are horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is the least likely example of a monopolistically competitive firm?
A)A barbershop
B)A restaurant
C)An electric company
D)A brewer
E)A clothing store
A)A barbershop
B)A restaurant
C)An electric company
D)A brewer
E)A clothing store

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A monopolistically competitive firm can increase its price without losing all its market share because of product differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a monopolistic competitor lowers the price of its product,
A)it is a signal that the monopolistic competitor is trying to drive its competition out of the market.
B)it is a signal that quality has been reduced.
C)losses will result.
D)some customers will be drawn from its competitors, ceteris paribus.
E)it will not be able to advertise and will lose customers.
A)it is a signal that the monopolistic competitor is trying to drive its competition out of the market.
B)it is a signal that quality has been reduced.
C)losses will result.
D)some customers will be drawn from its competitors, ceteris paribus.
E)it will not be able to advertise and will lose customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain economists' view of how a firm determines how much product differentiation is best for the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Because of the large number of firms in a monopolistically competitive market, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The difference between short-run demand and long-run demand for a monopolistic competitor is
A)There is no difference between long-run and short-run demand for a monopolistic competitor.
B)long-run demand results in no economic profit, whereas short-run demand might result in profits or losses.
C)in the long run demand slopes downward, but in the short run it is horizontal.
D)the long-run demand is elastic, whereas the short-run demand is inelastic.
E)in the short run demand slopes downward, but in the long run it is horizontal.
A)There is no difference between long-run and short-run demand for a monopolistic competitor.
B)long-run demand results in no economic profit, whereas short-run demand might result in profits or losses.
C)in the long run demand slopes downward, but in the short run it is horizontal.
D)the long-run demand is elastic, whereas the short-run demand is inelastic.
E)in the short run demand slopes downward, but in the long run it is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which is more important, product differentiation as perceived by firms producing the product, or product differentiation as perceived by consumers of the product? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A monopolistically competitive firm has a downward-sloping demand curve because
A)market demand is downward-sloping.
B)it is a monopoly in a small segment of the market.
C)there are so few firms producing in the market.
D)competition is being eliminated in a monopolistic market.
E)its product is differentiated from others.
A)market demand is downward-sloping.
B)it is a monopoly in a small segment of the market.
C)there are so few firms producing in the market.
D)competition is being eliminated in a monopolistic market.
E)its product is differentiated from others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Explain why a firm will expend funds to differentiate its product from the products of other firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A monopolistically competitive firm can increase its price without losing all its market share because
A)of product differentiation.
B)of the small number of firms in the industry.
C)the demand curve is very inelastic.
D)of the unavailability of close substitutes.
E)the products are homogeneous.
A)of product differentiation.
B)of the small number of firms in the industry.
C)the demand curve is very inelastic.
D)of the unavailability of close substitutes.
E)the products are homogeneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the short run, a monopolistically competitive firm
A)will go out of business if it is incurring an economic loss.
B)always earns a positive economic profit.
C)may earn a positive, negative, or zero economic profit.
D)never incurs an economic loss.
E)will maximize profit by producing output such that price equals rising marginal cost.
A)will go out of business if it is incurring an economic loss.
B)always earns a positive economic profit.
C)may earn a positive, negative, or zero economic profit.
D)never incurs an economic loss.
E)will maximize profit by producing output such that price equals rising marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements about monopolistic competition in the short run is false?
A)The firm always earns an economic profit.
B)The firm maximizes profits.
C)Price is greater than marginal cost.
D)Demand is downward-sloping.
E)Price is greater than marginal revenue.
A)The firm always earns an economic profit.
B)The firm maximizes profits.
C)Price is greater than marginal cost.
D)Demand is downward-sloping.
E)Price is greater than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Profit maximization is not a useful concept for examining firms' decisions about how to configure and market their products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
With monopolistic competition, market demand is
A)constantly changing.
B)horizontal.
C)the same as firm demand.
D)nonexistent.
E)like any other market demand.
A)constantly changing.
B)horizontal.
C)the same as firm demand.
D)nonexistent.
E)like any other market demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is not a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A)Firms reacting to others' actions
B)Differentiated products
C)Many firms
D)Free entry and exit
E)Firms facing downward-sloping demand curves
A)Firms reacting to others' actions
B)Differentiated products
C)Many firms
D)Free entry and exit
E)Firms facing downward-sloping demand curves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is not true regarding a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run?
A)Advertising may enable the firm to charge a higher price than that charged by rival firms.
B)The firm may be able to earn a normal profit, earn an economic profit, or incur an economic loss.
C)Entry into the market is fairly easy.
D)Profits will be maximized at the point at which price equals marginal cost.
E)It faces a negatively-sloped demand curve.
A)Advertising may enable the firm to charge a higher price than that charged by rival firms.
B)The firm may be able to earn a normal profit, earn an economic profit, or incur an economic loss.
C)Entry into the market is fairly easy.
D)Profits will be maximized at the point at which price equals marginal cost.
E)It faces a negatively-sloped demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exhibit 11-1 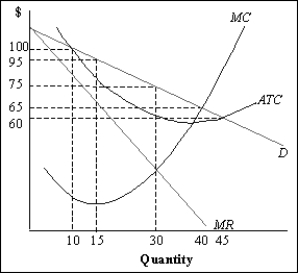
Refer to Exhibit 11-1. In the long run,
A)firms will enter the market.
B)the firm's demand curve will get steeper.
C)economic profits will increase.
D)firm output will increase.
E)nothing will change, given that the firm is in long-run equilibrium.

Refer to Exhibit 11-1. In the long run,
A)firms will enter the market.
B)the firm's demand curve will get steeper.
C)economic profits will increase.
D)firm output will increase.
E)nothing will change, given that the firm is in long-run equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Firms leave a monopolistically competitive industry when
A)other firms enter.
B)average total cost is greater than marginal revenue.
C)price is equal to marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
E)average total cost is greater than price.
A)other firms enter.
B)average total cost is greater than marginal revenue.
C)price is equal to marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
E)average total cost is greater than price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a monopolistically competitive firm is earning above-normal profits, then in the long run its demand will shift to the right and become more elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 11-1 
When firms leave a monopolistically competitive industry, remaining firms' demands increase because
A)consumers who were buying from the exiting firms add to the demand of those remaining.
B)those firms that are left become monopolies, and consumers have no choice but to buy from them.
C)the remaining firms improve their product in order to avoid the same fate as those that failed.
D)costs of production fall as there is not as much demand for inputs.
E)remaining firms increase production capacity and can serve wider markets.

When firms leave a monopolistically competitive industry, remaining firms' demands increase because
A)consumers who were buying from the exiting firms add to the demand of those remaining.
B)those firms that are left become monopolies, and consumers have no choice but to buy from them.
C)the remaining firms improve their product in order to avoid the same fate as those that failed.
D)costs of production fall as there is not as much demand for inputs.
E)remaining firms increase production capacity and can serve wider markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A monopolistically competitive firm is said to produce with excess costs in the long run because
A)the average fixed cost of production is greater than the minimum average fixed cost.
B)the firm will incur a loss and therefore needs to bring down costs.
C)the average total cost of production is greater than the minimum average total cost.
D)price is greater than marginal revenue.
E)there are too many firms in the market.
A)the average fixed cost of production is greater than the minimum average fixed cost.
B)the firm will incur a loss and therefore needs to bring down costs.
C)the average total cost of production is greater than the minimum average total cost.
D)price is greater than marginal revenue.
E)there are too many firms in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm sets output so that
A)P = MC.
B)MR = MC.
C)MR = P.
D)P = AVC.
E)MR = AVC.
A)P = MC.
B)MR = MC.
C)MR = P.
D)P = AVC.
E)MR = AVC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose that A-Mart sells fashion clothing in a shopping mall along with many other fashion retail stores. If A-Mart earns economic profits in the short run, then in the long run
A)no more fashion retail stores will open and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift left.
B)no more fashion retail stores will close and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift right.
C)some fashion retail stores will open and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift left.
D)some fashion retail stores will close and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift right.
E)the number of fashion retail stores will remain the same and the demand curve will stay constant.
A)no more fashion retail stores will open and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift left.
B)no more fashion retail stores will close and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift right.
C)some fashion retail stores will open and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift left.
D)some fashion retail stores will close and the demand curve for A-Mart will shift right.
E)the number of fashion retail stores will remain the same and the demand curve will stay constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, then
A)ATC = MR.
B)AFC = MR.
C)P = ATC and P > MC.
D)P = ATC and P = MC.
E)d = AR and AR = MR
A)ATC = MR.
B)AFC = MR.
C)P = ATC and P > MC.
D)P = ATC and P = MC.
E)d = AR and AR = MR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Monopolistic competitors can always prevent entry and exit of other firms over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm
A)makes an economic profit.
B)charges a price that is above average total cost.
C)has a horizontal demand curve.
D)becomes a monopoly.
E)makes a normal profit.
A)makes an economic profit.
B)charges a price that is above average total cost.
C)has a horizontal demand curve.
D)becomes a monopoly.
E)makes a normal profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 11-1 
Refer to Exhibit 11-1. The profit-maximizing output is ____ units.
A)15
B)10
C)40
D)45
E)30

Refer to Exhibit 11-1. The profit-maximizing output is ____ units.
A)15
B)10
C)40
D)45
E)30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If additional firms enter a monopolistically competitive industry, the demand facing a typical firm increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm charges a price that is
A)equal to marginal cost.
B)less than marginal cost.
C)greater than the minimum average total cost.
D)equal to the minimum average total cost.
E)equal to marginal revenue.
A)equal to marginal cost.
B)less than marginal cost.
C)greater than the minimum average total cost.
D)equal to the minimum average total cost.
E)equal to marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm produces with excess capacity because the
A)firm is producing too much output to maximize profit.
B)firm does not produce at the point at which marginal cost is minimized.
C)long-run output level occurs at the point at which average total cost is falling.
D)firm could produce more and reduce average fixed cost.
E)firm fails to minimize average fixed costs.
A)firm is producing too much output to maximize profit.
B)firm does not produce at the point at which marginal cost is minimized.
C)long-run output level occurs at the point at which average total cost is falling.
D)firm could produce more and reduce average fixed cost.
E)firm fails to minimize average fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
As new firms enter a monopolistically competitive industry, the demand curve facing a typical firm will most likely
A)become horizontal.
B)become vertical.
C)not change.
D)shift to the right.
E)shift to the left.
A)become horizontal.
B)become vertical.
C)not change.
D)shift to the right.
E)shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 11-1 
Refer to Exhibit 11-1. The profit-maximizing, monopolistically competitive firm as represented in the figure
A)is in long-run equilibrium.
B)is earning only a normal profit in the short run.
C)is making an economic profit in the short run.
D)will earn the same amount of profit in the short run as in the long run.
E)is incurring an economic loss in the short run.

Refer to Exhibit 11-1. The profit-maximizing, monopolistically competitive firm as represented in the figure
A)is in long-run equilibrium.
B)is earning only a normal profit in the short run.
C)is making an economic profit in the short run.
D)will earn the same amount of profit in the short run as in the long run.
E)is incurring an economic loss in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A monopolistic competitor behaves like a monopoly in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For a monopolistically competitive firm, the demand curve is more elastic in the long run than in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 11-1 
Refer to Exhibit 11-1. The firm will maximize profits at the price of
A)$60 per unit.
B)$65 per unit.
C)$100 per unit.
D)$75 per unit.
E)$95 per unit.

Refer to Exhibit 11-1. The firm will maximize profits at the price of
A)$60 per unit.
B)$65 per unit.
C)$100 per unit.
D)$75 per unit.
E)$95 per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



