Deck 3: Decision Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Decision Analysis
1
The decision theory processes of maximizing expected monetary value (EMV) and minimizing expected opportunity loss (EOL) should lead us to choose the same alternatives.
True
2
The nodes on decision trees represent either decisions or states of nature.
True
3
To determine the effect of input changes on decision results, we should perform a sensitivity analysis.
True
4
The maximin decision criterion is used by pessimistic decision makers and minimizes the maximum outcome for every alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The EMV approach and Utility theory always result in the same choice of alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Any problem that can be represented in a decision tree can be easily portrayed in a decision table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A decision table is sometimes called a payout table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Any problem that can be presented in a decision table can also be graphically portrayed in a decision tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The decision maker can control states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The several criteria (maximax, maximin, equally likely, criterion of realism, minimax regret) used for decision making under uncertainty may lead to the choice of different alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
EVPI (expected value of perfect information) is a measure of the maximum EMV as a result of additional information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All decisions that result in a favorable outcome are considered to be good decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Expected monetary value (EMV) is the payoff you should expect to occur when you choose a particular alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Utility theory may help the decision maker include the impact of qualitative factors that are difficult to include in the EMV model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a decision table, all of the alternatives are listed down the left side of the table, while all of the possible outcomes or states of nature are listed across the top.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Expected monetary value (EMV) is the average or expected monetary outcome of a decision if it can be repeated a large number of times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Optimistic decision makers tend to discount favorable outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When using the EOL as a decision criterion, the best decision is the alternative with the largest EOL value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The maximax decision criterion is used by pessimistic decision makers and maximizes the maximum outcome for every alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The difference in decision making under risk and decision making under uncertainty is that under risk, we think we know the probabilities of the states of nature, while under uncertainty we do not know the probabilities of the states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The following figure illustrates a utility curve for someone who is a risk seeker. 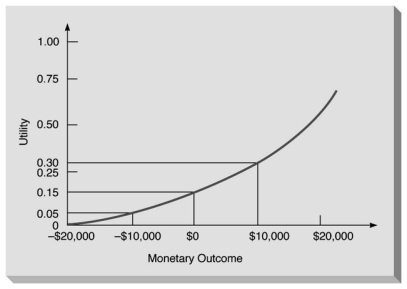


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The criterion of realism is also called the Laplace criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A utility curve that shows utility increasing at an increasing rate as the monetary value increases represents the utility curve of a risk seeker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following is a payoff table giving profits for various situations.  What decision would an optimist make?
What decision would an optimist make?
A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) Do Nothing
E) State of Nature A
 What decision would an optimist make?
What decision would an optimist make?A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) Do Nothing
E) State of Nature A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a decision problem where we wish to use Bayes' theorem to calculate posterior probabilities, we should always begin our analysis with the assumption that all states of nature are equally likely, and use the sample information to revise these probabilities to more realistic values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following is a payoff table giving profits for various situations. 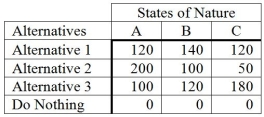 What decision would a pessimist make?
What decision would a pessimist make?
A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) Do Nothing
E) State of Nature A
 What decision would a pessimist make?
What decision would a pessimist make?A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) Do Nothing
E) State of Nature A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Expected monetary value (EMV) is
A) the average or expected monetary outcome of a decision if it can be repeated a large number of times.
B) the average or expected value of the decision, if you know what would happen ahead of time.
C) the average or expected value of information if it were completely accurate.
D) the amount you would lose by not picking the best alternative.
E) a decision criterion that places an equal weight on all states of nature.
A) the average or expected monetary outcome of a decision if it can be repeated a large number of times.
B) the average or expected value of the decision, if you know what would happen ahead of time.
C) the average or expected value of information if it were completely accurate.
D) the amount you would lose by not picking the best alternative.
E) a decision criterion that places an equal weight on all states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The assignment of a utility value of 1 to an alternative implies that alternative is preferred to all others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A second table (an opportunity loss table) must be computed when applying the maximin decision criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What makes the difference between good decisions and bad decisions?
A) A good decision is based on logic.
B) A good decision considers all available data.
C) A good decision considers all alternatives.
D) A good decision applies quantitative approaches.
E) All the above
A) A good decision is based on logic.
B) A good decision considers all available data.
C) A good decision considers all alternatives.
D) A good decision applies quantitative approaches.
E) All the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A utility curve that shows utility increasing at a decreasing rate as the monetary value increases represents the utility curve of a risk seeker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a good decision?
A) based on logic
B) considers all available data
C) considers all possible alternatives
D) employs appropriate quantitative techniques
E) always results in a favorable outcome
A) based on logic
B) considers all available data
C) considers all possible alternatives
D) employs appropriate quantitative techniques
E) always results in a favorable outcome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The equally likely decision criterion is also called the Laplace criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
By studying a person's Utility Curve, one can determine whether the individual is a risk seeker, risk avoider, or is indifferent to risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Utility theory provides a decision criterion that is superior to the EMV or EOL in that it may allow the decision maker to incorporate her own attitudes toward risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Utility values typically range from -1 to +1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is not considered a criteria for decision making under uncertainty?
A) optimistic
B) pessimistic
C) equally likely
D) random selection
E) minimax regret
A) optimistic
B) pessimistic
C) equally likely
D) random selection
E) minimax regret

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A pessimistic decision making criterion is
A) maximax.
B) equally likely.
C) maximin.
D) decision making under certainty.
E) minimax regret.
A) maximax.
B) equally likely.
C) maximin.
D) decision making under certainty.
E) minimax regret.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An analytic and systematic approach to the study of decision making is referred to as
A) decision making under risk.
B) decision making under uncertainty.
C) decision theory.
D) decision analysis.
E) decision making under certainty.
A) decision making under risk.
B) decision making under uncertainty.
C) decision theory.
D) decision analysis.
E) decision making under certainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is true about the expected value of perfect information?
A) It is the amount you would pay for any sample study.
B) It is calculated as EMV minus EOL.
C) It is calculated as expected value with perfect information minus maximum EMV.
D) It is the amount charged for marketing research.
E) None of the above
A) It is the amount you would pay for any sample study.
B) It is calculated as EMV minus EOL.
C) It is calculated as expected value with perfect information minus maximum EMV.
D) It is the amount charged for marketing research.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the following payoff table. 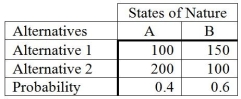 Based upon these probabilities, a person would select Alternative 2. Suppose there is concern about the accuracy of these probabilities. It can be stated that Alternative 2 will remain the best alternative as long as the probability of A is at least
Based upon these probabilities, a person would select Alternative 2. Suppose there is concern about the accuracy of these probabilities. It can be stated that Alternative 2 will remain the best alternative as long as the probability of A is at least
A) 0.33.
B) 0.50.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.60.
E) None of the above
 Based upon these probabilities, a person would select Alternative 2. Suppose there is concern about the accuracy of these probabilities. It can be stated that Alternative 2 will remain the best alternative as long as the probability of A is at least
Based upon these probabilities, a person would select Alternative 2. Suppose there is concern about the accuracy of these probabilities. It can be stated that Alternative 2 will remain the best alternative as long as the probability of A is at leastA) 0.33.
B) 0.50.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.60.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Nick has plans to open some pizza restaurants, but he is not sure how many to open. He has prepared a payoff table to help analyze the situation. 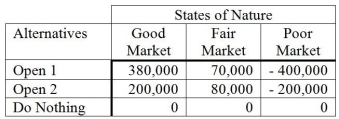 Nick believes there is a 40 percent chance that the market will be good, a 30 percent chance that it will be fair, and a 30 percent chance that it will be poor. A market research firm will analyze market conditions and will provide a perfect forecast (they provide a money back guarantee). What is the most that should be paid for this forecast?
Nick believes there is a 40 percent chance that the market will be good, a 30 percent chance that it will be fair, and a 30 percent chance that it will be poor. A market research firm will analyze market conditions and will provide a perfect forecast (they provide a money back guarantee). What is the most that should be paid for this forecast?
A) $ 44,000
B) $ 53,000
C) $123,000
D) $176,000
E) $132,000
 Nick believes there is a 40 percent chance that the market will be good, a 30 percent chance that it will be fair, and a 30 percent chance that it will be poor. A market research firm will analyze market conditions and will provide a perfect forecast (they provide a money back guarantee). What is the most that should be paid for this forecast?
Nick believes there is a 40 percent chance that the market will be good, a 30 percent chance that it will be fair, and a 30 percent chance that it will be poor. A market research firm will analyze market conditions and will provide a perfect forecast (they provide a money back guarantee). What is the most that should be paid for this forecast?A) $ 44,000
B) $ 53,000
C) $123,000
D) $176,000
E) $132,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The following is a payoff table giving profits for various situations. 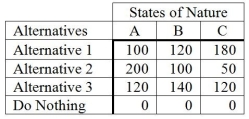 The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value with this perfect information?
The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value with this perfect information?
A) 130
B) 160
C) 166
D) 36
E) None of the above
 The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value with this perfect information?
The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value with this perfect information?A) 130
B) 160
C) 166
D) 36
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Optimistic decision makers tend to ________.
A) magnify favorable outcomes
B) ignore bad outcomes
C) discount favorable outcomes
D) A and B
E) B and C
A) magnify favorable outcomes
B) ignore bad outcomes
C) discount favorable outcomes
D) A and B
E) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In decision theory, we call the payoffs resulting from each possible combination of alternatives and outcomes ________.
A) marginal values
B) conditional values
C) conditional probabilities
D) Bayesian values
E) joint values
A) marginal values
B) conditional values
C) conditional probabilities
D) Bayesian values
E) joint values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How are decision tables organized?
A) alternatives down the left, states of nature on top, payoffs inside
B) states of nature down the left, alternatives on top, payoffs inside
C) alternatives down the left, payoffs on top, states of nature inside
D) payoffs down the left, alternatives on top, states of nature inside
E) states of nature down the left, payoffs on top, alternatives inside
A) alternatives down the left, states of nature on top, payoffs inside
B) states of nature down the left, alternatives on top, payoffs inside
C) alternatives down the left, payoffs on top, states of nature inside
D) payoffs down the left, alternatives on top, states of nature inside
E) states of nature down the left, payoffs on top, alternatives inside

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Dr. Mac, a surgeon, must decide what mode of treatment to use on Mr. Samuels. There are three modes of treatment: Mode A, B, and C; and three possible states of nature: 1.Treatment succeeds and patient leads a normal life, 2. Patient survives treatment but is permanently disabled, and 3. Patient fails to survive treatment. Dr. Mac has prepared the decision table below. What mode of treatment maximizes the expected value? 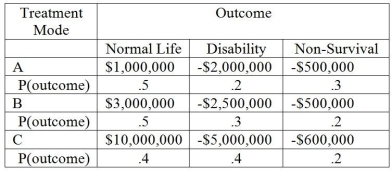
A) Mode A
B) Mode B
C) Mode C
D) All three treatments are equally desirable.
E) Normal Life

A) Mode A
B) Mode B
C) Mode C
D) All three treatments are equally desirable.
E) Normal Life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The following is a payoff table. 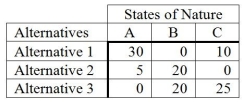 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) Does not matter
 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) Does not matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The following is a payoff table. 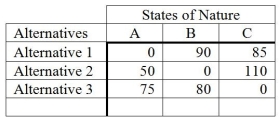 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) Does not matter
 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) Does not matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the following payoff table. 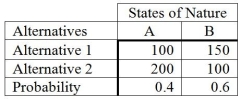 How much should be paid for a perfect forecast of the state of nature?
How much should be paid for a perfect forecast of the state of nature?
A) 170
B) 30
C) 10
D) 100
E) 40
 How much should be paid for a perfect forecast of the state of nature?
How much should be paid for a perfect forecast of the state of nature?A) 170
B) 30
C) 10
D) 100
E) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Pessimistic decision makers tend to ________.
A) magnify favorable outcomes
B) ignore bad outcomes
C) discount favorable outcomes
D) A and B
E) B and C
A) magnify favorable outcomes
B) ignore bad outcomes
C) discount favorable outcomes
D) A and B
E) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The following is an opportunity-loss table. 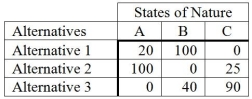 The probabilities for the states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person were to use the expected opportunity loss criterion, what decision would be made?
The probabilities for the states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person were to use the expected opportunity loss criterion, what decision would be made?
A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) State of Nature B
 The probabilities for the states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person were to use the expected opportunity loss criterion, what decision would be made?
The probabilities for the states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person were to use the expected opportunity loss criterion, what decision would be made?A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) State of Nature B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The following is an opportunity loss table. 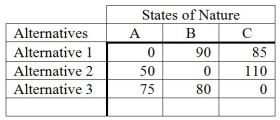 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature A
E) Does not matter
 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature A
E) Does not matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Another name for a decision table is a ________.
A) payment table
B) payout table
C) payoff table
D) pay-up table
E) decision tree
A) payment table
B) payout table
C) payoff table
D) pay-up table
E) decision tree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is the fourth step of the "Six Steps in Decision Making"?
A) Select one of the mathematical decision theory models.
B) List the possible alternatives.
C) Apply the model and make your decision.
D) List the payoff or profit of each combination of alternatives and outcomes.
E) Identify the possible outcomes or states of nature.
A) Select one of the mathematical decision theory models.
B) List the possible alternatives.
C) Apply the model and make your decision.
D) List the payoff or profit of each combination of alternatives and outcomes.
E) Identify the possible outcomes or states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The following is an opportunity loss table. 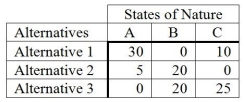 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) Does not matter
 What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?
What decision should be made based on the minimax regret criterion?A) Alternative 1
B) Alternative 2
C) Alternative 3
D) State of Nature C
E) Does not matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is not one of the steps considered in the "Six Steps in Decision Making"?
A) Clearly define the problem at hand
B) List the possible alternatives.
C) Apply the model and make your decision.
D) List the payoff or profit of each combination of alternatives and outcomes.
E) Evaluate the success of the decision.
A) Clearly define the problem at hand
B) List the possible alternatives.
C) Apply the model and make your decision.
D) List the payoff or profit of each combination of alternatives and outcomes.
E) Evaluate the success of the decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Nick has plans to open some pizza restaurants, but he is not sure how many to open. He has prepared a payoff table to help analyze the situation. 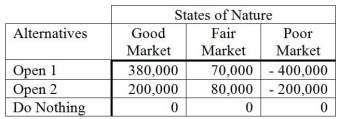 As Nick does not know how his product will be received, he assumes that all three states of nature are equally likely to occur. If he uses the equally likely criterion, what decision would he make?
As Nick does not know how his product will be received, he assumes that all three states of nature are equally likely to occur. If he uses the equally likely criterion, what decision would he make?
A) Open 1
B) Open 2
C) Good market
D) Fair market
E) Do nothing
 As Nick does not know how his product will be received, he assumes that all three states of nature are equally likely to occur. If he uses the equally likely criterion, what decision would he make?
As Nick does not know how his product will be received, he assumes that all three states of nature are equally likely to occur. If he uses the equally likely criterion, what decision would he make?A) Open 1
B) Open 2
C) Good market
D) Fair market
E) Do nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The following is a payoff table giving profits for various situations. 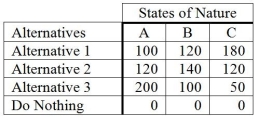 The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person selected Alternative 1, what would the expected profit be?
The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person selected Alternative 1, what would the expected profit be?
A) 120
B) 133.33
C) 126
D) 180
E) None of the above
 The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person selected Alternative 1, what would the expected profit be?
The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a person selected Alternative 1, what would the expected profit be?A) 120
B) 133.33
C) 126
D) 180
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The following is a payoff table giving profits for various situations. 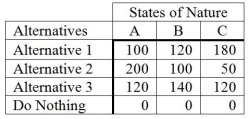 The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value of perfect information (EVPI)?
The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value of perfect information (EVPI)?
A) 166
B) 0
C) 36
D) 40
E) None of the above
 The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value of perfect information (EVPI)?
The probabilities for states of nature A, B, and C are 0.3, 0.5, and 0.2, respectively. If a perfect forecast of the future were available, what is the expected value of perfect information (EVPI)?A) 166
B) 0
C) 36
D) 40
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The equally likely criterion is also called the ________ criterion.
A) Hurwicz
B) uncertainty
C) Laplace
D) LaFlore
E) Huchenmeizer
A) Hurwicz
B) uncertainty
C) Laplace
D) LaFlore
E) Huchenmeizer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Hurwicz criterion is also called the criterion of ________.
A) regret
B) equality
C) optimism
D) realism
E) pessimism
A) regret
B) equality
C) optimism
D) realism
E) pessimism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The three decision-making environments are decision making under ________.
A) utility, risk, and certainty
B) utility, risk, and uncertainty
C) utility, certainty, and uncertainty
D) utility, equity, and certainty
E) risk, certainty, and uncertainty
A) utility, risk, and certainty
B) utility, risk, and uncertainty
C) utility, certainty, and uncertainty
D) utility, equity, and certainty
E) risk, certainty, and uncertainty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In decision making under ________, there are several possible outcomes for each alternative, and the decision maker does not know the probabilities of the various outcomes.
A) risk
B) utility
C) certainty
D) probability
E) uncertainty
A) risk
B) utility
C) certainty
D) probability
E) uncertainty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A utility curve showing utility increasing at an increasing rate as the monetary value increases represents
A) a risk avoider.
B) utility assessment.
C) a risk seeker.
D) conditional values.
E) expected utilities.
A) a risk avoider.
B) utility assessment.
C) a risk seeker.
D) conditional values.
E) expected utilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The Hurwicz criterion coefficient of realism measures the decision maker's degree of ________.
A) utility
B) pessimism
C) certainty
D) optimism
E) regret
A) utility
B) pessimism
C) certainty
D) optimism
E) regret

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A market research survey is available for $10,000. Using a decision tree analysis, it is found that the expected monetary value with no survey is $62,000. If the expected value of sample information is -$7,000, what is the expected monetary value with the survey?
A) $45,000
B) $62,000
C) -$17,000
D) $55,000
E) None of the above
A) $45,000
B) $62,000
C) -$17,000
D) $55,000
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A risk avoider is a person for whom the utility of an outcome
A) decreases as the monetary value increases.
B) stays the same as monetary value increases.
C) increases at an increasing rate as the monetary value increases.
D) increases at a decreasing rate as monetary value increases.
E) None of the above
A) decreases as the monetary value increases.
B) stays the same as monetary value increases.
C) increases at an increasing rate as the monetary value increases.
D) increases at a decreasing rate as monetary value increases.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the construction of decision trees, which of the following shapes represents a state of nature node?
A) square
B) circle
C) diamond
D) triangle
E) None of the above
A) square
B) circle
C) diamond
D) triangle
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The optimistic decision criterion is the criterion of ________.
A) maximax
B) maximin
C) realism
D) equally likely
E) minimax regret
A) maximax
B) maximin
C) realism
D) equally likely
E) minimax regret

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In decision making under ________, there are several possible outcomes for each alternative, and the decision maker knows the probability of occurrence of each outcome.
A) risk
B) utility
C) certainty
D) probability
E) uncertainty
A) risk
B) utility
C) certainty
D) probability
E) uncertainty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Utilization of Bayes' theorem requires the use of all but
A) prior probabilities.
B) marginal probabilities.
C) conditional probabilities.
D) posterior probabilities.
E) expected monetary values (EMV).
A) prior probabilities.
B) marginal probabilities.
C) conditional probabilities.
D) posterior probabilities.
E) expected monetary values (EMV).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The expected value of sample information (EVSI) can be used to
A) establish a maximum amount to spend on additional information.
B) calculate conditional probabilities.
C) establish risk avoidance.
D) provide points on a utility curve.
E) None of the above
A) establish a maximum amount to spend on additional information.
B) calculate conditional probabilities.
C) establish risk avoidance.
D) provide points on a utility curve.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In Bayesian analysis, conditional probabilities are also known as which of the following?
A) anterior probabilities
B) posterior probabilities
C) prior probabilities
D) marginal probabilities
E) joint probabilities
A) anterior probabilities
B) posterior probabilities
C) prior probabilities
D) marginal probabilities
E) joint probabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Decision trees are particularly useful when
A) perfect information is available.
B) formulating a conditional values table.
C) the opportunity loss table is available.
D) a sequence of decisions must be made.
E) all possible outcomes and alternatives are not known.
A) perfect information is available.
B) formulating a conditional values table.
C) the opportunity loss table is available.
D) a sequence of decisions must be made.
E) all possible outcomes and alternatives are not known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A market research survey is available for $10,000. Using a decision tree analysis, it is found that the expected monetary value with the survey is $75,000. The expected monetary value with no survey is $62,000. What is the expected value of sample information?
A) -$7,000
B) $3,000
C) $7,000
D) $13,000
E) None of the above
A) -$7,000
B) $3,000
C) $7,000
D) $13,000
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A company is considering producing a new children's bar soap. A market research firm has told the company that if they perform a survey, a positive survey of a favorable market occurs 65 percent of the time. That is, P(positive survey ∣ favorable market) = 0.65. Similarly, 40 percent of the time the survey falsely predicts a favorable market; thus, P(positive survey ∣ unfavorable market) = 0.40. These statistics indicate the accuracy of the survey. Prior to contacting the market research firm, the company's best estimate of a favorable market was 50 percent. So, P(favorable market) = 0.50 and P(unfavorable market) = 0.50. Using Bayes' theorem, determine the probability of a favorable market given a favorable survey.
A) 0.62
B) 0.38
C) 0.53
D) 0.65
E) None of the above
A) 0.62
B) 0.38
C) 0.53
D) 0.65
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the construction of decision trees, which of the following shapes represents a decision node?
A) square
B) circle
C) diamond
D) triangle
E) None of the above
A) square
B) circle
C) diamond
D) triangle
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the range of the Hurwicz criterion coefficient of realism α?
A) 1 to 100
B) 1 to 10
C) 0 to 10
D) 0 to 1
E) −1 to 1
A) 1 to 100
B) 1 to 10
C) 0 to 10
D) 0 to 1
E) −1 to 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Bayes' theorem enables decision makers to revise probabilities based on
A) perfect information.
B) knowing, ahead of time, the actual outcome of the decision.
C) additional information.
D) measurements of utility.
E) None of the above
A) perfect information.
B) knowing, ahead of time, the actual outcome of the decision.
C) additional information.
D) measurements of utility.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



