Deck 4: Interpretation and Management of Basic Dysrhythmias
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Interpretation and Management of Basic Dysrhythmias
1
A patient is demonstrating second-degree heart block (Wenckebach [type I]). What characteristic of this rhythm should the nurse recognize?
1) Progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a QRS is dropped
2) Prolonged PR interval greater than 0.22
3) Complete disassociation of the atria and ventricles
4) Consistent PR interval with occasional dropped QRS complexes
1) Progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a QRS is dropped
2) Prolonged PR interval greater than 0.22
3) Complete disassociation of the atria and ventricles
4) Consistent PR interval with occasional dropped QRS complexes
1
Explanation: 1. Second-degree AV block type I, or Wenckebach, is characterized by an inconsistent PR interval that progresses in length until a QRS is dropped. The SA node "resets" to the previous shortest PR interval and repeats progressive lengthening.
2. The presence of a prolonged PR interval without dropped QRS is present with first-degree AV block.
3. Complete disassociation is third-degree heart block.
4. A consistent PR interval with occasional dropped QRS complexes is consistent with second-degree AV block type II.
Explanation: 1. Second-degree AV block type I, or Wenckebach, is characterized by an inconsistent PR interval that progresses in length until a QRS is dropped. The SA node "resets" to the previous shortest PR interval and repeats progressive lengthening.
2. The presence of a prolonged PR interval without dropped QRS is present with first-degree AV block.
3. Complete disassociation is third-degree heart block.
4. A consistent PR interval with occasional dropped QRS complexes is consistent with second-degree AV block type II.
2
A patient experiencing pulseless ventricular tachycardia is defibrillated twice and has received medications according to ACLS protocol. The following rhythm is now present. What should the nurse do next? 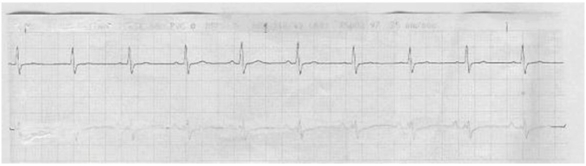
1) Continue monitoring and observing the patient for PVCs.
2) Place the patient on a maintenance lidocaine infusion.
3) Realize that the patient has been successfully converted to NSR.
4) Check the patient for a pulse and continue CPR if one is not present.

1) Continue monitoring and observing the patient for PVCs.
2) Place the patient on a maintenance lidocaine infusion.
3) Realize that the patient has been successfully converted to NSR.
4) Check the patient for a pulse and continue CPR if one is not present.
4
Explanation: 1. Further assessment is needed to determine if the treatment was successful.
2. Lidocaine is not indicated at this time and is used for ventricular dysrhythmias not responsive to other medications.
3. Without further assessment, this cannot be determined.
4. The return of a pulse should be assessed after defibrillating the patient to determine that the patient is not in pulseless electrical activity (PEA). Without verifying pulses, NSR cannot be determined.
Explanation: 1. Further assessment is needed to determine if the treatment was successful.
2. Lidocaine is not indicated at this time and is used for ventricular dysrhythmias not responsive to other medications.
3. Without further assessment, this cannot be determined.
4. The return of a pulse should be assessed after defibrillating the patient to determine that the patient is not in pulseless electrical activity (PEA). Without verifying pulses, NSR cannot be determined.
3
A patient's cardiac monitor shows a rate of 89 with a PR interval of 0.2 second and a QRS of 0.10 second. What is the most important nursing action?
1) Start the patient on O2 at 4 L/min via nasal cannula.
2) Obtain a 12-lead ECG immediately.
3) Report these abnormal findings to the health care provider.
4) Continue to monitor the patient's cardiac status.
1) Start the patient on O2 at 4 L/min via nasal cannula.
2) Obtain a 12-lead ECG immediately.
3) Report these abnormal findings to the health care provider.
4) Continue to monitor the patient's cardiac status.
4
Explanation: 1. Supplemental oxygen is not necessary at this time.
2. With the information provided, an ECG is not necessary.
3. Because these parameters are within normal limits, this response would not be appropriate.
4. The parameters given are within normal limits; continuing to monitor the patient is the most appropriate action.
Explanation: 1. Supplemental oxygen is not necessary at this time.
2. With the information provided, an ECG is not necessary.
3. Because these parameters are within normal limits, this response would not be appropriate.
4. The parameters given are within normal limits; continuing to monitor the patient is the most appropriate action.
4
The nurse is analyzing a 6-second ECG rhythm strip with the following findings: P to QRS ratio is 1:1; four regular R waves were present; QRS width was 0.10 second; PR interval was 0.18 second. How should the nurse document this rhythm?
1) Atrioventricular (AV) block with 2:1 ratio
2) Sinus tachycardia noted with AV junctional rhythm
3) AV complete heart block noted
4) Sinus bradycardia
1) Atrioventricular (AV) block with 2:1 ratio
2) Sinus tachycardia noted with AV junctional rhythm
3) AV complete heart block noted
4) Sinus bradycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A patient is admitted to the telemetry unit with new onset of weakness and fatigue. The following rhythm is now seen on the monitor, and the patient is now complaining of shortness of breath and mild chest discomfort. Which medication would be appropriate for this patient? 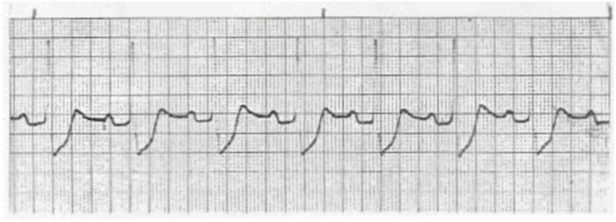
1) Epinephrine 1 mg IV
2) Atropine 0.5 mg IV
3) Adenosine 6 mg IV
4) Amiodarone 300 mg IV

1) Epinephrine 1 mg IV
2) Atropine 0.5 mg IV
3) Adenosine 6 mg IV
4) Amiodarone 300 mg IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The nurse receives the following ECG strip at shift report. Which action is most appropriate for this patient? 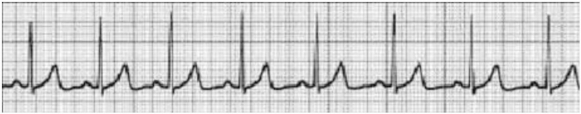
1) Place the patient on oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula.
2) Give atropine 1 mg IVP per protocol.
3) Start a second IV for normal saline bolus per protocol.
4) Assess the patient.

1) Place the patient on oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula.
2) Give atropine 1 mg IVP per protocol.
3) Start a second IV for normal saline bolus per protocol.
4) Assess the patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which assessment finding indicates that a patient has had a favorable response to adenosine (Adenocard)?
1) Complaints of a headache
2) Heart rate decreased to 80
3) Converts to sustained asystole
4) Heart rate increased to 64
1) Complaints of a headache
2) Heart rate decreased to 80
3) Converts to sustained asystole
4) Heart rate increased to 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which assessment finding indicates that a patient has had a favorable response to atropine?
1) An increase in heart rate to 80 bpm
2) Complaining of a headache
3) A decrease in heart rate to 40 bpm
4) Conversion to normal sinus rhythm from ventricular tachycardia
1) An increase in heart rate to 80 bpm
2) Complaining of a headache
3) A decrease in heart rate to 40 bpm
4) Conversion to normal sinus rhythm from ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The nurse is interpreting an ECG strip. What would describe paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) QRS width is 0.18 second.
2) Heart rate is between 150 and 250 beats per minute.
3) The P wave is hidden in the preceding T wave; therefore, the PR interval cannot be measured.
4) The increased rate can start abruptly and cease quickly when viewing a cardiac monitor to validate its presence.
5) It is treated with carotid massage.
1) QRS width is 0.18 second.
2) Heart rate is between 150 and 250 beats per minute.
3) The P wave is hidden in the preceding T wave; therefore, the PR interval cannot be measured.
4) The increased rate can start abruptly and cease quickly when viewing a cardiac monitor to validate its presence.
5) It is treated with carotid massage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A patient complaining of "feeling tired" has the following cardiac rhythm. The patient has a history of an irregular heartbeat and current vital signs are BP 134/78; RR 17; SaO2 97% on room air. What should be done first for this patient? 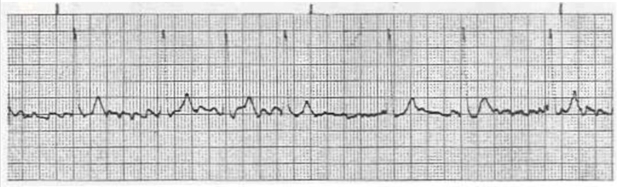
1) Perform a 12-lead ECG and compare it to previously recorded ECGs.
2) Prepare the patient for transcutaneous pacing.
3) Place the patient on 100% via nonrebreather mask.
4) Give Versed 1 mg IVP.

1) Perform a 12-lead ECG and compare it to previously recorded ECGs.
2) Prepare the patient for transcutaneous pacing.
3) Place the patient on 100% via nonrebreather mask.
4) Give Versed 1 mg IVP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A patient arrives in the emergency department for chest pain, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath (SOB). The cardiac monitor shows sinus rhythm with the presence of multifocal PVCs. Which order should the nurse question?
1) Oxygen at 4 L/min via nasal cannula
2) Morphine sulfate 2 mg IV
3) Atropine 0.5 mg IV
4) Amiodarone 300 mg IV
1) Oxygen at 4 L/min via nasal cannula
2) Morphine sulfate 2 mg IV
3) Atropine 0.5 mg IV
4) Amiodarone 300 mg IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A patient has the following rhythm on the monitor. The patient is alert and oriented and denies any complaints at present. What should the nurse do first? 
1) Administer a precordial thump.
2) Check lead placement on the patient.
3) Begin CPR and call for a defibrillator.
4) Administer epinephrine 1 mg IV every 3 minutes.

1) Administer a precordial thump.
2) Check lead placement on the patient.
3) Begin CPR and call for a defibrillator.
4) Administer epinephrine 1 mg IV every 3 minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A patient has the following rhythm. Which assessment finding indicates a need for further treatment? 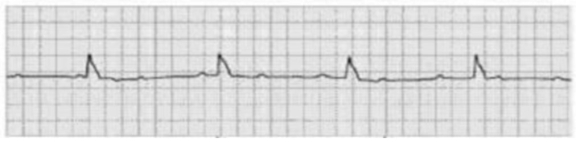
1) Short period of asystole followed by conversion to normal sinus rhythm
2) Warm, dry skin
3) Heart rate of 88 and BP 124/80
4) Heart rate of 42 and BP 78/60

1) Short period of asystole followed by conversion to normal sinus rhythm
2) Warm, dry skin
3) Heart rate of 88 and BP 124/80
4) Heart rate of 42 and BP 78/60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A patient is experiencing a new onset of the following rhythm. With complications related to this rhythm in mind, which intervention is a priority? 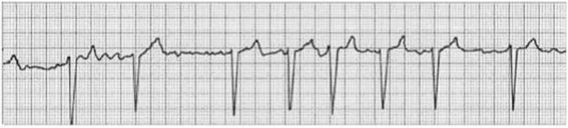
1) Monitor for sudden onset of ventricular tachycardia.
2) Perform neurologic checks every 4 hours.
3) Monitor for deterioration to third-degree block.
4) Assess skin turgor for dehydration.

1) Monitor for sudden onset of ventricular tachycardia.
2) Perform neurologic checks every 4 hours.
3) Monitor for deterioration to third-degree block.
4) Assess skin turgor for dehydration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A patient is experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, and lethargy. The patient's vital signs are BP 88/58, HR 40, RR 20. Which nursing action is a priority for this patient?
1) Nitroglycerin 1 tablet sublingual
2) Aspirin 325 mg PO
3) Morphine 2 mg IVP
4) Atropine 1 mg IVP
1) Nitroglycerin 1 tablet sublingual
2) Aspirin 325 mg PO
3) Morphine 2 mg IVP
4) Atropine 1 mg IVP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What best describes the ECG rhythm of atrial fibrillation?
1) No P wave but waves that can be described similar to a picket fence or sawtooth pattern that are regularly spaced between normal QRS waves
2) No consistent P waves, only an erratic and wavy baseline between normally configured QRS waves
3) A progressive deterioration of the wavy baseline with irregular R to R spacing that leads to ventricular tachycardia and a cardiac arrest situation
4) A QRS width greater than 0.12 second and lasting about 30 seconds before ventricular fibrillation occurs
1) No P wave but waves that can be described similar to a picket fence or sawtooth pattern that are regularly spaced between normal QRS waves
2) No consistent P waves, only an erratic and wavy baseline between normally configured QRS waves
3) A progressive deterioration of the wavy baseline with irregular R to R spacing that leads to ventricular tachycardia and a cardiac arrest situation
4) A QRS width greater than 0.12 second and lasting about 30 seconds before ventricular fibrillation occurs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A patient's monitor strip shows an irregular rhythm. Which count and approach should the nurse use to estimate this patient's heart rate?
1) Small blocks between two consecutive R waves and divide by 1500
2) Large blocks between two consecutive R waves and divide by 300
3) QRS complexes in 6 seconds and multiply by 10
4) Large blocks in 3 seconds and multiply by 20
1) Small blocks between two consecutive R waves and divide by 1500
2) Large blocks between two consecutive R waves and divide by 300
3) QRS complexes in 6 seconds and multiply by 10
4) Large blocks in 3 seconds and multiply by 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A patient in the emergency department is in supraventricular tachycardia. Which actions should be taken for this patient? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Start CPR and defibrillate at 200 joules.
2) Start oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula.
3) Give atropine 1 mg IVP.
4) Give epinephrine 1 mg IVP.
5) Give adenosine 6 mg IVP.
1) Start CPR and defibrillate at 200 joules.
2) Start oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula.
3) Give atropine 1 mg IVP.
4) Give epinephrine 1 mg IVP.
5) Give adenosine 6 mg IVP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What should the nurse include in the plan of care for a patient with atrial fibrillation? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Monitor neurological status every 4 hours.
2) Administer anticoagulants as ordered to minimize risk for an embolic event.
3) Prepare the patient for defibrillation to assist in conversion to normal sinus rhythm.
4) Administer beta blockers (atenolol) and calcium channel blockers (diltiazem) to lower heart rate in order to maximize cardiac output.
5) Use vagal stimulation to control heart rate.
1) Monitor neurological status every 4 hours.
2) Administer anticoagulants as ordered to minimize risk for an embolic event.
3) Prepare the patient for defibrillation to assist in conversion to normal sinus rhythm.
4) Administer beta blockers (atenolol) and calcium channel blockers (diltiazem) to lower heart rate in order to maximize cardiac output.
5) Use vagal stimulation to control heart rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
CPR is started on a patient who has developed ventricular fibrillation. The patient is defibrillated once with the resulting rhythm. Which intervention should the nurse implement next? 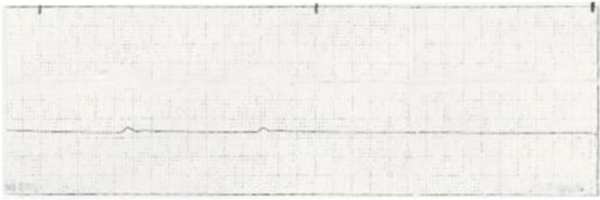
1) Defibrillate the patient with 360 joules.
2) Administer atropine 1 mg IV push and repeat every 3 minutes.
3) Infuse amiodarone 300 mg IV push slowly.
4) Administer epinephrine 1 mg IV push.

1) Defibrillate the patient with 360 joules.
2) Administer atropine 1 mg IV push and repeat every 3 minutes.
3) Infuse amiodarone 300 mg IV push slowly.
4) Administer epinephrine 1 mg IV push.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In order to correctly manage ventricular dysrhythmias, the nurse should expect to implement which treatment?
1) Magnesium to terminate ventricular tachycardia pattern called torsades de pointes that was noted on the ECG strip
2) Potassium chloride (KCl) replacement for a potassium level of 4 mEq/mL
3) Procainamide for developing coarse ventricular fibrillation
4) Synchronized cardioversion after atropine is given for ventricular tachycardia
1) Magnesium to terminate ventricular tachycardia pattern called torsades de pointes that was noted on the ECG strip
2) Potassium chloride (KCl) replacement for a potassium level of 4 mEq/mL
3) Procainamide for developing coarse ventricular fibrillation
4) Synchronized cardioversion after atropine is given for ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The ECG strip of a patient with a transvenous ventricular demand pacemaker shows QRS complexes without pacer spikes. What should the nurse do?
1) Plan for immediate removal of pacer lead wires.
2) Continue to observe the patient and the ECG rhythm.
3) Call the health care provider and explain that capture has been lost.
4) Call a code for ventricular fibrillation.
1) Plan for immediate removal of pacer lead wires.
2) Continue to observe the patient and the ECG rhythm.
3) Call the health care provider and explain that capture has been lost.
4) Call a code for ventricular fibrillation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The nurse notes that a patient on continuous cardiac monitoring has PR intervals that last 0.08 seconds. What should the nurse suspect as the reason for this finding?
1) An ectopic pacemaker in the atria
2) An ectopic pacemaker in the ventricles
3) A delay in impulse conduction through the atria
4) Cardiac cell necrosis for a previous myocardial infarction
1) An ectopic pacemaker in the atria
2) An ectopic pacemaker in the ventricles
3) A delay in impulse conduction through the atria
4) Cardiac cell necrosis for a previous myocardial infarction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A patient with sick sinus syndrome loses consciousness for 15 seconds during periods of asystole. What should the nurse expect to be prescribed for this patient?
1) Atropine
2) Stress reduction
3) Carotid massage
4) Permanent pacemaker
1) Atropine
2) Stress reduction
3) Carotid massage
4) Permanent pacemaker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The nurse reviews synchronized cardioversion with a new graduate. What should the nurse include when reviewing this procedure? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) The shock is synchronized with the QRS complex.
2) The shock will occur on the R wave.
3) A sedative will be provided before the procedure.
4) Pain medication will be provided before the procedure.
5) The shock will occur on the T wave.
1) The shock is synchronized with the QRS complex.
2) The shock will occur on the R wave.
3) A sedative will be provided before the procedure.
4) Pain medication will be provided before the procedure.
5) The shock will occur on the T wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The nurse determines that a patient is experiencing sinus tachycardia. What did the nurse assess on the patient's ECG rhythm strip? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Regular heart rhythm
2) Heart rate 110 beats per minute
3) 1:1 P to QRS ratio
4) PR interval 0.16 second
5) Notched P waves
1) Regular heart rhythm
2) Heart rate 110 beats per minute
3) 1:1 P to QRS ratio
4) PR interval 0.16 second
5) Notched P waves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which criteria should the nurse use when assessing an ECG strip for atrial fibrillation?
1) Ventricular rate is usually regular in R to R distancing.
2) Atrial rate runs 350 to 600 with an unequal ratio of P to QRS.
3) P waves are regular and vary in ratio to QRS.
4) QRS width is wide due to a conductivity delay.
1) Ventricular rate is usually regular in R to R distancing.
2) Atrial rate runs 350 to 600 with an unequal ratio of P to QRS.
3) P waves are regular and vary in ratio to QRS.
4) QRS width is wide due to a conductivity delay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A patient receiving procainamide develops pulseless ventricular tachycardia. What should the nurse expect to be done for this patient?
1) Unsynchronized shock
2) Synchronized cardioversion
3) Temporary pacemaker insertion
4) Insertion of a permanent pacemaker
1) Unsynchronized shock
2) Synchronized cardioversion
3) Temporary pacemaker insertion
4) Insertion of a permanent pacemaker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The nurse reviews a patient's prescribed scheduled and PRN medications. Which medication affects cardiac contractility? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Digoxin
2) Dopamine
3) Epinephrine
4) Morphine
5) Atropine
1) Digoxin
2) Dopamine
3) Epinephrine
4) Morphine
5) Atropine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A patient with atrial fibrillation is scheduled for elective cardioversion. What teaching should the nurse prepare for this patient?
1) Short-term use of beta blockers
2) Short-term use of anticoagulant therapy
3) Long-term use of calcium channel blockers
4) Long-term use of antiarrhythmic medication
1) Short-term use of beta blockers
2) Short-term use of anticoagulant therapy
3) Long-term use of calcium channel blockers
4) Long-term use of antiarrhythmic medication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The nurse identifies that a patient is experiencing ventricular tachycardia. What did the nurse assess on the patient's ECG rhythm strip? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Three premature ventricular contractions in rapid succession
2) Heart rate 150 beats per minute
3) Absent P waves
4) Absent PR interval
5) Undetectable QRS complex
1) Three premature ventricular contractions in rapid succession
2) Heart rate 150 beats per minute
3) Absent P waves
4) Absent PR interval
5) Undetectable QRS complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A patient's heart rhythm shows a regular rate of 50 bpm. The P wave looks like an inverted notch and appears after the QRS complex. What should the nurse suspect as the reason for this patient's rhythm? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Takes digitalis
2) Consumes large amounts of caffeine
3) Being treated for aortic regurgitation
4) Recovering from cardiac bypass surgery
5) Diagnosed with acute myocardial infarction
1) Takes digitalis
2) Consumes large amounts of caffeine
3) Being treated for aortic regurgitation
4) Recovering from cardiac bypass surgery
5) Diagnosed with acute myocardial infarction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The nurse is reviewing normal cardiac conduction with a new graduate nurse. What should the nurse explain when the impulse reaches the bundle of His? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Conduction of the impulse penetrates the atrioventricular valves.
2) Conduction of the impulse bifurcates into the right and left bundle branches.
3) Conduction of the impulse continues to the Purkinje fibers.
4) Conduction of the impulse is slowed because of calcium ions.
5) Conduction creates a flat line after the P wave on the ECG rhythm.
1) Conduction of the impulse penetrates the atrioventricular valves.
2) Conduction of the impulse bifurcates into the right and left bundle branches.
3) Conduction of the impulse continues to the Purkinje fibers.
4) Conduction of the impulse is slowed because of calcium ions.
5) Conduction creates a flat line after the P wave on the ECG rhythm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The nurse reviews the characteristics of a normal QRS complex on a patient's cardiac rhythm strip. What should the nurse identify as characteristics of this complex? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) The first downward deflection after the P wave is the Q wave.
2) The first upward deflection after the P wave is the R wave.
3) The first downward deflection after the R wave is the S wave.
4) It usually measures less than 0.12 seconds or less than 3 small boxes.
5) It ends at the beginning of the T wave.
1) The first downward deflection after the P wave is the Q wave.
2) The first upward deflection after the P wave is the R wave.
3) The first downward deflection after the R wave is the S wave.
4) It usually measures less than 0.12 seconds or less than 3 small boxes.
5) It ends at the beginning of the T wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The nurse suspects that a patient's pacemaker is malfunctioning. What should the nurse assess when analyzing this patient's rhythm strip? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Failure to pace
2) Failure to capture
3) Failure to sense
4) Oversensing
5) Failure to discharge
1) Failure to pace
2) Failure to capture
3) Failure to sense
4) Oversensing
5) Failure to discharge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A patient is scheduled for surgery to implant a cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). What should the nurse expect to see documented in the patient's medical record?
1) Documented episodes of bigeminy
2) Permanent pacemaker failing to pace
3) History of episodes of ventricular fibrillation
4) Malfunctioning lead on an external temporary pacemaker
1) Documented episodes of bigeminy
2) Permanent pacemaker failing to pace
3) History of episodes of ventricular fibrillation
4) Malfunctioning lead on an external temporary pacemaker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When evaluating the health history of a patient with complete heart block, what should the nurse identify as potential causes for this health problem? Select all that apply. Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
1) Myocarditis
2) Degenerative heart disease
3) Severe aortic stenosis
4) Digitalis toxicity
5) Currently being treated for acute myocardial infarction
1) Myocarditis
2) Degenerative heart disease
3) Severe aortic stenosis
4) Digitalis toxicity
5) Currently being treated for acute myocardial infarction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A patient is placed on continuous cardiac monitoring. What should the nurse realize is occurring when the rhythm displays a flat, isoelectric line?
1) Polarization
2) Depolarization
3) Repolarization
4) Absolute refractory period
1) Polarization
2) Depolarization
3) Repolarization
4) Absolute refractory period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The nurse prepares to analyze a patient's ECG rhythm strip. Place in order the steps the nurse should use to interpret this strip.
A) Determine the heart rhythm.
B) Measure the heart rate.
C) Examine the P waves.
D) Examine the P to QRD ratio.
E) Measure the PR interval.
F) Examine the QRS complex.
G) Interpret the rhythm.
H) None of the above.
A) Determine the heart rhythm.
B) Measure the heart rate.
C) Examine the P waves.
D) Examine the P to QRD ratio.
E) Measure the PR interval.
F) Examine the QRS complex.
G) Interpret the rhythm.
H) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



