Deck 3: Cellular Structure, Proteins, and Metabolic Pathways
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Cellular Structure, Proteins, and Metabolic Pathways
1
The organelles that digest engulfed bacteria and cell debris are the:
A) peroxisomes.
B) endosomes.
C) lysosomes.
D) ribosomes.
E) mitochondria.
A) peroxisomes.
B) endosomes.
C) lysosomes.
D) ribosomes.
E) mitochondria.
C
2
The cell membrane is composed mainly of:
A) cytosol.
B) phospholipids and proteins.
C) phospholipids and nucleic acids.
D) water.
E) proteins and glycocalyx.
A) cytosol.
B) phospholipids and proteins.
C) phospholipids and nucleic acids.
D) water.
E) proteins and glycocalyx.
B
3
In which organelle are carbohydrate chains added to glycoproteins?
A) Golgi apparatus
B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C) nucleus
D) lysosome
E) mitochondrion
A) Golgi apparatus
B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C) nucleus
D) lysosome
E) mitochondrion
A
4
What are desmosomes?
A) low-resistance channel-like passages that let ions travel between the interiors of adjacent cells
B) cell organelles that contain enzymes for digesting cellular debris and foreign microbes
C) cellular organelles that transcribe RNA into DNA
D) membrane-bound vesicles that pinch off from the plasma membrane and enter the cell
E) dense plaques of proteins that maintain firm attachments between adjacent cells
A) low-resistance channel-like passages that let ions travel between the interiors of adjacent cells
B) cell organelles that contain enzymes for digesting cellular debris and foreign microbes
C) cellular organelles that transcribe RNA into DNA
D) membrane-bound vesicles that pinch off from the plasma membrane and enter the cell
E) dense plaques of proteins that maintain firm attachments between adjacent cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which is NOT a feature of the fluid-mosaic model of plasma membranes.
A) Integral membrane proteins are embedded in the membrane.
B) Phospholipids form a bilayer.
C) Cholesterol associates with phospholipid molecules.
D) Carbohydrates are linked to lipids and proteins on the interior surface, forming a glycocalyx layer.
E) Peripheral membrane proteins associate with polar regions of integral membrane proteins.
A) Integral membrane proteins are embedded in the membrane.
B) Phospholipids form a bilayer.
C) Cholesterol associates with phospholipid molecules.
D) Carbohydrates are linked to lipids and proteins on the interior surface, forming a glycocalyx layer.
E) Peripheral membrane proteins associate with polar regions of integral membrane proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which is a major function of the plasma membrane?
A) storing calcium ions
B) storing organic chemicals for metabolism
C) providing genetic information
D) generating ATP
E) regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the cell
A) storing calcium ions
B) storing organic chemicals for metabolism
C) providing genetic information
D) generating ATP
E) regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which best describes functions of the agranular (smooth) endoplasmic reticulum?
A) transcription of DNA into RNA
B) generation of ATP
C) digestion of engulfed bacteria and cellular debris
D) synthesis and packaging of proteins for secretion from the cell or export to other organelles
E) synthesis of lipids and intracellular storage of calcium ions
A) transcription of DNA into RNA
B) generation of ATP
C) digestion of engulfed bacteria and cellular debris
D) synthesis and packaging of proteins for secretion from the cell or export to other organelles
E) synthesis of lipids and intracellular storage of calcium ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is a codon?
A) a triplet of deoxyribonucleotides
B) a triplet of ribonucleotides
C) a sequence of ribonucleotides on tRNA
D) a very small gene
E) a very small genome
A) a triplet of deoxyribonucleotides
B) a triplet of ribonucleotides
C) a sequence of ribonucleotides on tRNA
D) a very small gene
E) a very small genome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Neurons have a very prominent nucleolus, which indicates that they are actively performing what function?
A) making ATP
B) synthesizing lipids
C) manufacturing ribosomes
D) breaking down carbohydrates
E) dividing by mitosis
A) making ATP
B) synthesizing lipids
C) manufacturing ribosomes
D) breaking down carbohydrates
E) dividing by mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which is true about the structure and function of a gene?
A) It is an uncoiled protein that contains information necessary for the synthesis of other proteins.
B) It is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that acts as an enzyme to digest proteins.
C) It is composed of many molecules of DNA and contains information needed to make RNA.
D) It is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that contains information necessary for the synthesis of proteins.
A) It is an uncoiled protein that contains information necessary for the synthesis of other proteins.
B) It is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that acts as an enzyme to digest proteins.
C) It is composed of many molecules of DNA and contains information needed to make RNA.
D) It is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that contains information necessary for the synthesis of proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What feature of phospholipids allows them to interact with aqueous cytosol and extracellular fluid, while still presenting a barrier to hydrophilic substances?
A) They are polar molecules.
B) They are nonpolar molecules.
C) They are lipids.
D) They are extremely rigid molecules.
E) They are amphipathic molecules.
A) They are polar molecules.
B) They are nonpolar molecules.
C) They are lipids.
D) They are extremely rigid molecules.
E) They are amphipathic molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not true of the cytoskeleton?
A) It refers to the cellular components of bone.
B) It refers to a network of cytoplasmic filaments.
C) It is important for cellular movement.
D) It helps to determine a cell's shape.
E) It includes actin filaments.
A) It refers to the cellular components of bone.
B) It refers to a network of cytoplasmic filaments.
C) It is important for cellular movement.
D) It helps to determine a cell's shape.
E) It includes actin filaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which organelles would you expect to be especially numerous in cells that utilize oxygen to generate a great deal of energy in the form of ATP?
A) peroxisomes
B) endosomes
C) lysosomes
D) ribosomes
E) mitochondria
A) peroxisomes
B) endosomes
C) lysosomes
D) ribosomes
E) mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the main function of cellular tight junctions?
A) They resist forces that tend to pull cells apart.
B) They form barriers that restrict the passage of materials through the extracellular space between cells.
C) They are protein channels that allow the movement of ions between the cytosol of adjacent cells.
D) They are spaces that allow movement of substances between the interior of the nucleus and the cytosol.
E) They hold the genetic material in a tightly coiled conformation.
A) They resist forces that tend to pull cells apart.
B) They form barriers that restrict the passage of materials through the extracellular space between cells.
C) They are protein channels that allow the movement of ions between the cytosol of adjacent cells.
D) They are spaces that allow movement of substances between the interior of the nucleus and the cytosol.
E) They hold the genetic material in a tightly coiled conformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What codon corresponds to the DNA sequence G-T-A?
A) G-T-A
B) A-T-G
C) C-A-T
D) C-A-U
E) T-A-C
A) G-T-A
B) A-T-G
C) C-A-T
D) C-A-U
E) T-A-C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What cellular structures are most closely associated with vaults?
A) nuclear pores
B) peroxisomes
C) lysosomes
D) mitochondria
E) gap junctions
A) nuclear pores
B) peroxisomes
C) lysosomes
D) mitochondria
E) gap junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Protein channels that link the cytosol of adjacent cells are called ___________ junctions.
A) cadherin
B) tight
C) gap
D) conjunction
E) nexus
A) cadherin
B) tight
C) gap
D) conjunction
E) nexus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these are functions of the Golgi apparatus?
A) modifying proteins synthesized on free ribosomes and storing calcium ions
B) digestion of engulfed bacteria and using oxygen to generate ATP
C) synthesizing lipids and intracellular storage of calcium ions
D) modifying proteins synthesized on free ribosomes and allowing the distribution of modified proteins throughout the cell in vesicles
E) modifying proteins synthesized on ribosomes associated with granular endoplasmic reticulum and allowing the distribution of modified proteins throughout the cell in vesicles
A) modifying proteins synthesized on free ribosomes and storing calcium ions
B) digestion of engulfed bacteria and using oxygen to generate ATP
C) synthesizing lipids and intracellular storage of calcium ions
D) modifying proteins synthesized on free ribosomes and allowing the distribution of modified proteins throughout the cell in vesicles
E) modifying proteins synthesized on ribosomes associated with granular endoplasmic reticulum and allowing the distribution of modified proteins throughout the cell in vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
RNA synthesis from a DNA template:
A) is called translation of the message.
B) requires DNA polymerase.
C) is called transcription.
D) occurs in the nucleolus.
E) occurs in the cytoplasm.
A) is called translation of the message.
B) requires DNA polymerase.
C) is called transcription.
D) occurs in the nucleolus.
E) occurs in the cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is a genome?
A) a cluster of genes that are all regulated in the same manner
B) a measure of the genetic variability in a population
C) a region of DNA that codes for a single protein
D) all of the protein in a cell at a given point in time
E) the total genetic information in a typical cell of an organism
A) a cluster of genes that are all regulated in the same manner
B) a measure of the genetic variability in a population
C) a region of DNA that codes for a single protein
D) all of the protein in a cell at a given point in time
E) the total genetic information in a typical cell of an organism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a reversible chemical reaction is at equilibrium,
A) the rate of the reaction in one direction is equal to the rate in the reverse direction.
B) the concentration of the reactants is equal to the concentration of the products.
C) both the forward and reverse reactions stop occurring.
D) the supply of reactants has become exhausted, so the forward reaction ceases and the rate of the reverse reaction increases.
E) catalysts no longer influence either the forward or reverse reaction rates.
A) the rate of the reaction in one direction is equal to the rate in the reverse direction.
B) the concentration of the reactants is equal to the concentration of the products.
C) both the forward and reverse reactions stop occurring.
D) the supply of reactants has become exhausted, so the forward reaction ceases and the rate of the reverse reaction increases.
E) catalysts no longer influence either the forward or reverse reaction rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which is the best definition of the term ligand?
A) a receptor composed of protein
B) a molecule or ion that binds to a protein
C) any molecule found in the intracellular fluid
D) any molecule found in the extracellular fluid
E) a carbohydrate molecule that binds weakly to membrane phospholipids
A) a receptor composed of protein
B) a molecule or ion that binds to a protein
C) any molecule found in the intracellular fluid
D) any molecule found in the extracellular fluid
E) a carbohydrate molecule that binds weakly to membrane phospholipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is "allosteric modulation"?
A) regulation of physiological functions by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
B) modification of the functional state of a protein by temperature or pH
C) the change in the shape and functional state of a protein that occurs when a ligand binds to a regulatory site
D) the fact that all binding sites on a protein must be occupied to have a biological effect
E) the ability of a single ligand-binding site to bind to molecularly similar ligands
A) regulation of physiological functions by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
B) modification of the functional state of a protein by temperature or pH
C) the change in the shape and functional state of a protein that occurs when a ligand binds to a regulatory site
D) the fact that all binding sites on a protein must be occupied to have a biological effect
E) the ability of a single ligand-binding site to bind to molecularly similar ligands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A certain protein receptor is capable of binding the neurotransmitter epinephrine but does not bind to the neurotransmitters dopamine, glutamate, or serotonin. This is because the receptor displays what characteristic?
A) saturation
B) inhibition
C) specificity
D) acclimatization
E) accommodation
A) saturation
B) inhibition
C) specificity
D) acclimatization
E) accommodation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the term for the segments of primary RNA that are cleaved and discarded by spliceosomes?
A) codons
B) introns
C) exons
D) anticodons
E) genes
A) codons
B) introns
C) exons
D) anticodons
E) genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How does the synthesis of proteins that are destined to be secreted differ from that of proteins with functions inside the cell?
A) Proteins destined to be secreted have a signal sequence.
B) Proteins destined to be secreted are synthesized on free ribosomes.
C) Proteins destined to be secreted are packaged into secretory vesicles in the granular endoplasmic reticulum.
D) Only proteins destined for secretion need transfer RNA to be synthesized.
E) Genes for proteins with functions inside the cell are located in the cytoplasm.
A) Proteins destined to be secreted have a signal sequence.
B) Proteins destined to be secreted are synthesized on free ribosomes.
C) Proteins destined to be secreted are packaged into secretory vesicles in the granular endoplasmic reticulum.
D) Only proteins destined for secretion need transfer RNA to be synthesized.
E) Genes for proteins with functions inside the cell are located in the cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which would be true about the following reaction? M + N 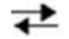 Y + Z
Y + Z
A) Adding a catalyst would alter the final concentrations of products and reactants at equilibrium.
B) Starting at chemical equilibrium, increasing the concentration of M will transiently increase the rate of formation of Y and Z.
C) Starting at chemical equilibrium, decreasing the concentration of M will increase the concentration of Y and Z.
D) Both the reaction is reversible and at chemical equilibrium and increasing the concentration of M will drive the reaction to the left are correct.
E) Because the reactants and products are different molecules, this is not a reversible reaction.
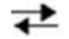 Y + Z
Y + ZA) Adding a catalyst would alter the final concentrations of products and reactants at equilibrium.
B) Starting at chemical equilibrium, increasing the concentration of M will transiently increase the rate of formation of Y and Z.
C) Starting at chemical equilibrium, decreasing the concentration of M will increase the concentration of Y and Z.
D) Both the reaction is reversible and at chemical equilibrium and increasing the concentration of M will drive the reaction to the left are correct.
E) Because the reactants and products are different molecules, this is not a reversible reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which is a function of transfer RNA (tRNA)?
A) transport mRNA out of the nucleus
B) binding specifically to mRNA and nonspecifically to amino acids
C) binding specifically to amino acids and nonspecifically to mRNA
D) binding specifically to both mRNA and to amino acids
A) transport mRNA out of the nucleus
B) binding specifically to mRNA and nonspecifically to amino acids
C) binding specifically to amino acids and nonspecifically to mRNA
D) binding specifically to both mRNA and to amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The term "metabolism":
A) is synonymous with the term "catabolism."
B) is synonymous with the term "anabolism."
C) refers to any chemical reaction that involves the production of energy.
D) is defined as the covalent modification and activation of a protein with binding sites for organic molecules.
E) refers to the synthesis and breakdown of organic molecules involved in cell structure and function.
A) is synonymous with the term "catabolism."
B) is synonymous with the term "anabolism."
C) refers to any chemical reaction that involves the production of energy.
D) is defined as the covalent modification and activation of a protein with binding sites for organic molecules.
E) refers to the synthesis and breakdown of organic molecules involved in cell structure and function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A solution containing proteins of a particular type is exposed to the same concentrations of ligands X and Y, but the percent saturation of molecule X is greater than the percent saturation of molecule Y. Which is most likely to be a true statement?
A) The binding sites for ligand X are 100% saturated.
B) The binding sites for ligand X have greater specificity than the binding site for ligand Y.
C) Ligand X must be a competitive inhibitor of ligand Y.
D) Both ligands must bind to the same binding site on the protein.
E) The protein has a higher affinity for ligand X than for ligand Y.
A) The binding sites for ligand X are 100% saturated.
B) The binding sites for ligand X have greater specificity than the binding site for ligand Y.
C) Ligand X must be a competitive inhibitor of ligand Y.
D) Both ligands must bind to the same binding site on the protein.
E) The protein has a higher affinity for ligand X than for ligand Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In skeletal muscle, when calcium binds to the regulatory protein troponin, it increases the affinity of neighboring troponin molecules for calcium. This is an example of
A) allosteric modulation.
B) cooperativity.
C) covalent modulation.
D) phosphorylation.
E) saturation.
A) allosteric modulation.
B) cooperativity.
C) covalent modulation.
D) phosphorylation.
E) saturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which is NOT a function of the Golgi apparatus?
A) sorting of proteins destined for various locations in the cell
B) modifying proteins destined for secretion
C) packaging enzymes destined for lysosomes
D) addition of carbohydrate groups to proteins
E) transcribing a signal sequence onto proteins destined for secretion
A) sorting of proteins destined for various locations in the cell
B) modifying proteins destined for secretion
C) packaging enzymes destined for lysosomes
D) addition of carbohydrate groups to proteins
E) transcribing a signal sequence onto proteins destined for secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The probability of a reaction occurring is increased
A) by decreasing reactant concentrations.
B) by increasing the activation energy.
C) by increasing the concentration of any of the products.
D) if the reaction uses a great deal of energy.
E) if the concentration of one of the reactants increases.
A) by decreasing reactant concentrations.
B) by increasing the activation energy.
C) by increasing the concentration of any of the products.
D) if the reaction uses a great deal of energy.
E) if the concentration of one of the reactants increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which is NOT true about a binding site on a protein?
A) It is an area of the protein with a shape complementary to that of a ligand.
B) It is determined by the amino acid sequence of the protein.
C) The binding of a ligand to a binding site typically changes the conformation of the protein.
D) There can only be one binding site on a given protein.
E) Binding of a ligand to the binding site typically activates or inactivates a protein's specific function.
A) It is an area of the protein with a shape complementary to that of a ligand.
B) It is determined by the amino acid sequence of the protein.
C) The binding of a ligand to a binding site typically changes the conformation of the protein.
D) There can only be one binding site on a given protein.
E) Binding of a ligand to the binding site typically activates or inactivates a protein's specific function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of these covalently modifies proteins by phosphorylation?
A) enzymes called protein phosphatases
B) other proteins called allosteric proteins
C) any ligand that can bind to specific binding sites
D) enzymes called protein kinases
E) metal ions, such as Fe2+
A) enzymes called protein phosphatases
B) other proteins called allosteric proteins
C) any ligand that can bind to specific binding sites
D) enzymes called protein kinases
E) metal ions, such as Fe2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which is NOT true about protein kinases?
A) They add phosphate groups to proteins.
B) They produce effects similar to allosteric modulation.
C) They perform the opposite function as phosphatases.
D) They use ATP to carry out their reactions.
E) They remove phosphate groups from proteins.
A) They add phosphate groups to proteins.
B) They produce effects similar to allosteric modulation.
C) They perform the opposite function as phosphatases.
D) They use ATP to carry out their reactions.
E) They remove phosphate groups from proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the defining characteristic of an allosteric protein?
A) They contain two polypeptide chains, with each being an exact mirror image of the other.
B) They contain only one ligand-binding site, but because the specificity is low, many different ligands can bind to it.
C) They contain two ligand-binding sites, one that activates the protein when a ligand binds, and the other that inactivates the protein when the same ligand binds.
D) They contain more than one ligand-binding site, and noncovalent binding of a ligand to one site alters the shape of other ligand-binding sites.
E) They contain no binding sites of their own, but act by modulating the activity of other proteins.
A) They contain two polypeptide chains, with each being an exact mirror image of the other.
B) They contain only one ligand-binding site, but because the specificity is low, many different ligands can bind to it.
C) They contain two ligand-binding sites, one that activates the protein when a ligand binds, and the other that inactivates the protein when the same ligand binds.
D) They contain more than one ligand-binding site, and noncovalent binding of a ligand to one site alters the shape of other ligand-binding sites.
E) They contain no binding sites of their own, but act by modulating the activity of other proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which describes the action of a ligand's competitive antagonist?
A) It decreases the amount of ligand required to activate the protein.
B) It blocks the binding of the ligand to its binding site and prevents activation of the protein.
C) It binds to a different binding site on the protein, altering the protein shape so that a ligand cannot bind.
D) When present, it increases the binding of a ligand to its receptor.
A) It decreases the amount of ligand required to activate the protein.
B) It blocks the binding of the ligand to its binding site and prevents activation of the protein.
C) It binds to a different binding site on the protein, altering the protein shape so that a ligand cannot bind.
D) When present, it increases the binding of a ligand to its receptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
With regard to reversible chemical reaction rates, which of the following statements is true?
A) Decreasing the concentration of the reactants will increase the forward reaction rate.
B) Increasing the temperature will increase the forward and reverse reaction rate.
C) Increasing the activation energy will increase the forward reaction rate.
D) Increasing the concentration of the products will increase the forward reaction rate.
E) As a reaction progresses, the rate of the forward reaction increases as the concentration of reactants decreases.
A) Decreasing the concentration of the reactants will increase the forward reaction rate.
B) Increasing the temperature will increase the forward and reverse reaction rate.
C) Increasing the activation energy will increase the forward reaction rate.
D) Increasing the concentration of the products will increase the forward reaction rate.
E) As a reaction progresses, the rate of the forward reaction increases as the concentration of reactants decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How does a chemical catalyst increase the rate of a reaction?
A) by acting as one of the reactant molecules
B) by decreasing the energy of activation
C) by increasing the energy content of the product molecules
D) by increasing the temperature of a solution
E) by phosphorylating a reactant
A) by acting as one of the reactant molecules
B) by decreasing the energy of activation
C) by increasing the energy content of the product molecules
D) by increasing the temperature of a solution
E) by phosphorylating a reactant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The site where most of the ATP is generated in a cell is the
A) nucleus.
B) plasma membrane.
C) endoplasmic reticulum.
D) Golgi apparatus.
E) mitochondria.
A) nucleus.
B) plasma membrane.
C) endoplasmic reticulum.
D) Golgi apparatus.
E) mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
ATP is
A) a nucleotide.
B) a lipid.
C) an amino acid.
D) a carbohydrate.
E) a steroid.
A) a nucleotide.
B) a lipid.
C) an amino acid.
D) a carbohydrate.
E) a steroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is a coenzyme?
A) an organic cofactor that directly participates as one of the substrates in an enzymatic reaction
B) a metal, such as zinc, that participates in enzymatic reactions
C) a term regarding enzymatic reactions that is synonymous with "cofactor"
D) any ligand that binds to a specific site on a protein receptor
E) an inorganic molecule that catalyzes enzymatic reactions
A) an organic cofactor that directly participates as one of the substrates in an enzymatic reaction
B) a metal, such as zinc, that participates in enzymatic reactions
C) a term regarding enzymatic reactions that is synonymous with "cofactor"
D) any ligand that binds to a specific site on a protein receptor
E) an inorganic molecule that catalyzes enzymatic reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What are the products of glycolysis under anaerobic conditions?
A) 2 molecules of NADH and 2 molecules of water
B) 2 molecules of pyruvate, 2 molecules of lactate, and 2 ATP
C) 2 molecules of pyruvate and 36 molecules of ATP
D) 2 molecules of ATP, 2 molecules of water, and 2 molecules of lactate
E) 2 molecules of pyruvate, 2 molecules of water, and 2 NADH
A) 2 molecules of NADH and 2 molecules of water
B) 2 molecules of pyruvate, 2 molecules of lactate, and 2 ATP
C) 2 molecules of pyruvate and 36 molecules of ATP
D) 2 molecules of ATP, 2 molecules of water, and 2 molecules of lactate
E) 2 molecules of pyruvate, 2 molecules of water, and 2 NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which is NOT true about cofactors involved in enzymatic reactions?
A) They may alter the conformation of the enzyme.
B) They may be a metal such as iron.
C) They may be a substrate in a catalyzed reaction.
D) There must be equal quantities of enzyme and cofactor molecules for a reaction to proceed.
E) Only a small number of cofactor molecules may be needed to maintain enzyme activity.
A) They may alter the conformation of the enzyme.
B) They may be a metal such as iron.
C) They may be a substrate in a catalyzed reaction.
D) There must be equal quantities of enzyme and cofactor molecules for a reaction to proceed.
E) Only a small number of cofactor molecules may be needed to maintain enzyme activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the function of a catalyst in a chemical reaction?
A) It lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
B) It is split into individual molecules that are products of the reaction.
C) It changes the energy content of the reactants.
D) It generates heat that makes the reaction proceed.
E) It ensures that the reaction can proceed only in one direction, from reactants to products.
A) It lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
B) It is split into individual molecules that are products of the reaction.
C) It changes the energy content of the reactants.
D) It generates heat that makes the reaction proceed.
E) It ensures that the reaction can proceed only in one direction, from reactants to products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is NOT a product of glycolysis?
A) carbon dioxide
B) ATP
C) pyruvate
D) NADH
A) carbon dioxide
B) ATP
C) pyruvate
D) NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is true concerning the rate-limiting step in a metabolic pathway?
A) It is likely to be the slowest reaction in the pathway, and it is always the last step in a metabolic pathway.
B) It is likely to be the fastest reaction in the pathway, and it is always the last step in a metabolic pathway.
C) It is always the first step in the pathway, and may be subject to end-product inhibition.
D) It is likely to be the slowest reaction in the pathway and it may be subject to end-product inhibition.
E) It is likely to be the fastest reaction in the pathway and it may be subject to end-product inhibition.
A) It is likely to be the slowest reaction in the pathway, and it is always the last step in a metabolic pathway.
B) It is likely to be the fastest reaction in the pathway, and it is always the last step in a metabolic pathway.
C) It is always the first step in the pathway, and may be subject to end-product inhibition.
D) It is likely to be the slowest reaction in the pathway and it may be subject to end-product inhibition.
E) It is likely to be the fastest reaction in the pathway and it may be subject to end-product inhibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the reaction: H2CO3 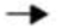 CO2 + H2O + 4 kcal/mol. Which of the following is TRUE?
CO2 + H2O + 4 kcal/mol. Which of the following is TRUE?
A) The reaction is anabolic and the energy content of the reactant is greater than that of the products.
B) The reaction is catabolic and the energy content of the reactant is greater than that of the products.
C) The reaction is anabolic and the energy content of the products is greater than that of the reactant.
D) The reaction is catabolic and the energy content of the products is greater than that of the reactant.
E) The reaction is catabolic and the energy content of the products are equal to that of the reactant.
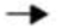 CO2 + H2O + 4 kcal/mol. Which of the following is TRUE?
CO2 + H2O + 4 kcal/mol. Which of the following is TRUE?A) The reaction is anabolic and the energy content of the reactant is greater than that of the products.
B) The reaction is catabolic and the energy content of the reactant is greater than that of the products.
C) The reaction is anabolic and the energy content of the products is greater than that of the reactant.
D) The reaction is catabolic and the energy content of the products is greater than that of the reactant.
E) The reaction is catabolic and the energy content of the products are equal to that of the reactant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which is NOT true about fatty acid synthesis?
A) takes place in the cytosol of cells
B) results in molecules with an even number of carbon atoms only
C) requires more energy than is produced by the catabolism of the same fatty acid
D) begins with a molecule of acetyl coenzyme A
E) The enzymes that catalyze it are in the same location as those that mediate fatty acid catabolism.
A) takes place in the cytosol of cells
B) results in molecules with an even number of carbon atoms only
C) requires more energy than is produced by the catabolism of the same fatty acid
D) begins with a molecule of acetyl coenzyme A
E) The enzymes that catalyze it are in the same location as those that mediate fatty acid catabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following metabolic pathways can proceed in the absence of oxygen?
A) glycolysis
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) Krebs cycle
D) the breakdown of fatty acids to CO2 and H2O
E) None of the choices are correct.
A) glycolysis
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) Krebs cycle
D) the breakdown of fatty acids to CO2 and H2O
E) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Most energy in the body is stored in what form?
A) ATP
B) glucose
C) fat
D) protein
E) DNA
A) ATP
B) glucose
C) fat
D) protein
E) DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which is a series of reactions by which fatty acid catabolism occurs?
A) glycolysis
B) lipogenesis
C) beta-oxidation
D) glycogenolysis
E) phosphorylation
A) glycolysis
B) lipogenesis
C) beta-oxidation
D) glycogenolysis
E) phosphorylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Enzymes
A) are catalysts in chemical reactions.
B) can be carbohydrate molecules.
C) are broken down during chemical reactions they catalyze.
D) have names generally ending in the suffix "-ose."
E) are polymers of ATP that store large amounts of energy.
A) are catalysts in chemical reactions.
B) can be carbohydrate molecules.
C) are broken down during chemical reactions they catalyze.
D) have names generally ending in the suffix "-ose."
E) are polymers of ATP that store large amounts of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The reactions of the Krebs cycle:
A) take place in the cytosol of human cells.
B) generate ATP directly by substrate-level phosphorylation.
C) are important for the metabolism of carbohydrates but not other molecules.
D) take place only when no oxygen is present.
E) produce pyruvate and lactate as end products.
A) take place in the cytosol of human cells.
B) generate ATP directly by substrate-level phosphorylation.
C) are important for the metabolism of carbohydrates but not other molecules.
D) take place only when no oxygen is present.
E) produce pyruvate and lactate as end products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
At equilibrium, in an irreversible reaction:
A) almost all of the reactants will have been converted to products.
B) there will be an equal number of products and reactants.
C) there will be very few molecules of product.
D) small amounts of energy will have been released.
E) large amounts of energy must have been input to reach that state.
A) almost all of the reactants will have been converted to products.
B) there will be an equal number of products and reactants.
C) there will be very few molecules of product.
D) small amounts of energy will have been released.
E) large amounts of energy must have been input to reach that state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In order to increase the overall rate of a metabolic pathway consisting of five reactions catalyzed by five different enzymes, which must occur?
A) increasing the reaction rate of all five enzymes
B) increasing the reaction rate of the fastest enzyme
C) increasing the reaction rate of the slowest enzyme
D) increasing the reaction rate of the first enzyme in the pathway
E) increasing the reaction rate of the last enzyme in the pathway
A) increasing the reaction rate of all five enzymes
B) increasing the reaction rate of the fastest enzyme
C) increasing the reaction rate of the slowest enzyme
D) increasing the reaction rate of the first enzyme in the pathway
E) increasing the reaction rate of the last enzyme in the pathway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Ammonia is
A) a waste product of fatty acid metabolism.
B) exhaled by the lungs into the air.
C) processed by the liver to form urea, a less toxic compound.
D) a waste product of fatty acid metabolism and is excreted by the kidneys into urine.
E) a polypeptide containing many amino acids.
A) a waste product of fatty acid metabolism.
B) exhaled by the lungs into the air.
C) processed by the liver to form urea, a less toxic compound.
D) a waste product of fatty acid metabolism and is excreted by the kidneys into urine.
E) a polypeptide containing many amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
ATP is
A) formed during the hydrolysis of ADP.
B) used by cells for the storage of energy.
C) used to transfer energy within a cell.
D) a protein.
E) a molecule with less total energy content than ADP.
A) formed during the hydrolysis of ADP.
B) used by cells for the storage of energy.
C) used to transfer energy within a cell.
D) a protein.
E) a molecule with less total energy content than ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which is TRUE about glycolysis?
A) It does not occur in the absence of O2.
B) It does not occur in the presence of O2.
C) It may result in the formation of two molecules of lactate for each molecule of glucose.
D) It is a series of metabolic reactions that occur mainly inside the inner membrane of a mitochondrion.
E) It is a metabolic reaction in which glucose is manufactured from large carbohydrates like glycogen.
A) It does not occur in the absence of O2.
B) It does not occur in the presence of O2.
C) It may result in the formation of two molecules of lactate for each molecule of glucose.
D) It is a series of metabolic reactions that occur mainly inside the inner membrane of a mitochondrion.
E) It is a metabolic reaction in which glucose is manufactured from large carbohydrates like glycogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
There are twenty different molecules of tRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Living cells cannot be viewed under an electron microscope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A light microscope can be used to view very large proteins in a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Lysosomes are organelles specialized for breaking down intracellular debris or malfunctioning parts of cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Desmosomes are structures that permit direct communication between cells by allowing the cells to exchange small molecules in their cytoplasms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Ribosomes transcribe DNA into RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A ribosome is composed of one molecule of RNA and several proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The major lipids in cellular membranes are phospholipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The promoter sequence of nucleotides in a gene is present on both strands of the DNA molecule, allowing transcription of both strands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The special functions of plasma and organelle membranes depend primarily on the specific composition of the phospholipids of those membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The nucleotide triplet in tRNA that base-pairs with a complementary triplet in mRNA is called the codon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Intracellular fluid is defined as the fluid in the cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
One function of integral membrane proteins in the plasma membrane of cells is to form channels to allow passage of nonpolar solutes into the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Before an amino acid can be broken down for energy:
A) the side chain must be removed.
B) the carboxyl group must be removed.
C) it must be converted to NAD+.
D) the amino group must be removed.
E) it must be phosphorylated.
A) the side chain must be removed.
B) the carboxyl group must be removed.
C) it must be converted to NAD+.
D) the amino group must be removed.
E) it must be phosphorylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Peripheral membrane proteins are involved in regulating cell shape and motility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Once protein synthesis is completed, the protein that was synthesized may undergo further changes prior to its secretion or use within the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Free ribosomes differ from membrane-bound ribosomes in that free ribosomes specialize in synthesizing proteins for export (secretion) from the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
One striking feature of plasma membrane structure is its symmetry, with the extracellular and cytoplasmic surfaces virtual mirror images of each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Transcription factors activate or repress the transcription of specific genes by binding to regions of DNA that interact with the promoter region of a gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Chromosomes are composed mainly of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



