Deck 18: Searching and Sorting Algorithms
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Searching and Sorting Algorithms
1
The selection sort algorithm finds the location of the smallest element in the unsorted portion of the list.
True
2
The sequential search algorithm uses a(n)____ variable to track whether the item is found.
A) int
B) bool
C) char
D) double
A) int
B) bool
C) char
D) double
B
3
Consider the following list: int list[] = {4,8,19,25,34,39,45,48,66,75,89,95}
When performing a binary search for 75,after the first comparison,the search is restricted to ____.
A) list[0]...list[6]
B) list[0]...list[7]
C) list[5]...list[11]
D) list[6]...list[11]
When performing a binary search for 75,after the first comparison,the search is restricted to ____.
A) list[0]...list[6]
B) list[0]...list[7]
C) list[5]...list[11]
D) list[6]...list[11]
D
4
A sequential search of an n-element list takes ____ key comparisons if the item is not in the list.
A) 0
B) n/2
C) n
D) n2
A) 0
B) n/2
C) n
D) n2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During the sorting phase of insertion sort,the array containing the list is divided into two sublists,sorted and unsorted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that L is a sorted list of size 1024,and we want to determine whether an item x is in L.From the binary search algorithm,it follows that every iteration of the while loop cuts the size of the search list by half.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
During the second iteration of a selection sort,the smallest item is moved to the top of the list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A sequential search of an n-element list takes ____ key comparisons on average to determine whether the search item is in the list.
A) 0
B) n/2
C) n
D) n2
A) 0
B) n/2
C) n
D) n2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The swap function of quick sort is written differently from the swap function for selection sort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
With the binary search algorithm,____ key comparison(s)is/are made in the successful case-the last time through the loop.
A) one
B) two
C) n-2
D) n
A) one
B) two
C) n-2
D) n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The sequential search algorithm does not require that the list be sorted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The binary search algorithm can be written iteratively or recursively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the average case,sequential search typically searches ____.
A) one quarter of the list
B) one third of the list
C) one half of the list
D) the entire list
A) one quarter of the list
B) one third of the list
C) one half of the list
D) the entire list

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a binary search,first,the search item is compared with the last element of the list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the following list: int list[] = {4,8,19,25,34,39,45,48,66,75,89,95}
When performing a binary search,the target is first compared with ____.
A) 4
B) 25
C) 39
D) 95
When performing a binary search,the target is first compared with ____.
A) 4
B) 25
C) 39
D) 95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a bubble sort,the smaller elements move toward the bottom,and the larger elements move toward the top of the list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
After the second iteration of bubble sort for a list of length n,the last ____ elements are sorted.
A) two
B) three
C) n-2
D) n
A) two
B) three
C) n-2
D) n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If n = 1000,then to sort the list,selection sort makes about 50,000 key comparisons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In a bubble sort for list of length n,the first step is to compare elements ____.
A) list[0] and list[n]
B) list[0] and list[n-1]
C) list[0] and list[1]
D) list[n-1] and list[n+1]
A) list[0] and list[n]
B) list[0] and list[n-1]
C) list[0] and list[1]
D) list[n-1] and list[n+1]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The formula to find the index of the middle element of a list is ____.
A) (mid + last)/2
B) (first + last) - 2
C) (first + last) / 2
D) (first + mid ) * 2
A) (mid + last)/2
B) (first + last) - 2
C) (first + last) / 2
D) (first + mid ) * 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Assume that list consists of the following elements.What is the result after bubble sort completes? int list[] = {2,56,34,25,73,46,89,10,5,16};
A) 89 73 56 46 34 25 16 10 5 2
B) 2 56 34 25 5 16 89 46 73
C) 2 5 10 16 25 34 46 56 73 89
D) 2 10 16 25 34 46 56 73 89
A) 89 73 56 46 34 25 16 10 5 2
B) 2 56 34 25 5 16 89 46 73
C) 2 5 10 16 25 34 46 56 73 89
D) 2 10 16 25 34 46 56 73 89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following correctly states the quick sort algorithm?
A) if (the list size is greater than 1) {
A) Partition the list into four sublists.
B) Quick sort sublist1.
C) Quick sort sublist2.
D) Quick sort sublist3.
E) Quick sort sublist4.
D) Combine the sorted lists.
}
B) a. Find the location of the smallest element. b. Move the smallest element to the beginning of the
Unsorted list.
C) if (the list size is greater than 1) {
A) Partition the list into two sublists, say lowerSublist and
UpperSublist.
B) Quick sort lowerSublist.
C) Quick sort upperSublist.
D) Combine the sorted lowerSublist and sorted upperSublist.
}
D) if the list is of a size greater than 1 {
A) Divide the list into two sublists.
B) Merge sort the first sublist.
C) Merge sort the second sublist.
D) Merge the first sublist and the second sublist.
}
A) if (the list size is greater than 1) {
A) Partition the list into four sublists.
B) Quick sort sublist1.
C) Quick sort sublist2.
D) Quick sort sublist3.
E) Quick sort sublist4.
D) Combine the sorted lists.
}
B) a. Find the location of the smallest element. b. Move the smallest element to the beginning of the
Unsorted list.
C) if (the list size is greater than 1) {
A) Partition the list into two sublists, say lowerSublist and
UpperSublist.
B) Quick sort lowerSublist.
C) Quick sort upperSublist.
D) Combine the sorted lowerSublist and sorted upperSublist.
}
D) if the list is of a size greater than 1 {
A) Divide the list into two sublists.
B) Merge sort the first sublist.
C) Merge sort the second sublist.
D) Merge the first sublist and the second sublist.
}

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
With insertion sort,the variable firstOutOfOrder is initialized to ____,assuming n is the length of the list.
A) 0
B) 1
C) n - 1
D) n
A) 0
B) 1
C) n - 1
D) n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Let f and g be real-valued functions. Assume that f and g are nonnegative, that is, for all real numbers
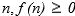 and
and 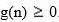 We say that
We say that 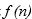 is of g(n). written
is of g(n). written 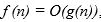
if there exist positive constants c and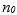 such that
such that 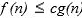 For all
For all 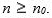
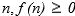 and
and 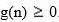 We say that
We say that 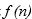 is of g(n). written
is of g(n). written 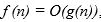
if there exist positive constants c and
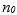 such that
such that 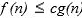 For all
For all 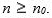

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When working with the unsorted portion of a list,the second step in a selection sort is to ____.
A) divide the list into two parts
B) move the smallest element to the top of the list (position 0)
C) move the smallest element to the beginning of the unsorted list
D) find the smallest element
A) divide the list into two parts
B) move the smallest element to the top of the list (position 0)
C) move the smallest element to the beginning of the unsorted list
D) find the smallest element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If n = 1000,to sort the list,bubble sort makes about ____ item assignments.
A) 10,000
B) 100,000
C) 250,000
D) 500,000
A) 10,000
B) 100,000
C) 250,000
D) 500,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the bubble sort algorithm,the following code accomplishes swapping values in elements at positions index and index + 1.
A) list[index] = list[index + 1]
List[index + 1] = list[index]
B) list[index + 1] = list[index]
List[index] = list[index + 1]
C) list[index] = temp;
List[index] = list[index + 1];
Temp = list[index + 1];
D) temp = list[index];
List[index] = list[index + 1];
List[index + 1] = temp;
A) list[index] = list[index + 1]
List[index + 1] = list[index]
B) list[index + 1] = list[index]
List[index] = list[index + 1]
C) list[index] = temp;
List[index] = list[index + 1];
Temp = list[index + 1];
D) temp = list[index];
List[index] = list[index + 1];
List[index + 1] = temp;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For a list of length n,selection sort makes ____ item assignments.
A) n(n - 1)/2
B) 3(n - 1)
C) 3(n)
D) 4(n + 1)
A) n(n - 1)/2
B) 3(n - 1)
C) 3(n)
D) 4(n + 1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The ____________________ search algorithm is the optimal worst-case algorithm for solving search problems by using the comparison method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Let f be a function of n.By the term ____________________,we mean the study of the function f as n becomes larger and larger without bound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a list of eight elements is sorted using selection sort,the unsorted list is ____ after the second iteration.
A) list[0] ... list[1]
B) list[0] ... list[6]
C) list[1] ... list[7]
D) list[2] ... list[7]
A) list[0] ... list[1]
B) list[0] ... list[6]
C) list[1] ... list[7]
D) list[2] ... list[7]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The behavior of quick sort is ____ in the worst case and ____ in the average case.
A) O(nlog2n), O(nlog2n)
B) O(n2), O(n)
C) O(nlog2n), O(n2)
D) O(n2), O(nlog2n)
A) O(nlog2n), O(nlog2n)
B) O(n2), O(n)
C) O(nlog2n), O(n2)
D) O(n2), O(nlog2n)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
____ sort requires knowing where the middle element of the list is.
A) Merge
B) Bubble
C) Insertion
D) Selection
A) Merge
B) Bubble
C) Insertion
D) Selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assuming the following list declaration,which element is at the position 0 after the first iteration of selection sort? int list[] = {16,30,24,7,62,45,5,55}
A) 5
B) 7
C) 16
D) 62
A) 5
B) 7
C) 16
D) 62

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The behavior of merge sort is ____ in the worst case and ____ in the average case.
A) O(nlog2n), O(nlog2n)
B) O(n2), O(n)
C) O(nlog2n), O(n2)
D) O(n2), O(nlog2n)
A) O(nlog2n), O(nlog2n)
B) O(n2), O(n)
C) O(nlog2n), O(n2)
D) O(n2), O(nlog2n)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
We can trace the execution of a comparison-based algorithm by using a graph called a ____.
A) pivot table
B) partition table
C) comparison tree
D) merge tree
A) pivot table
B) partition table
C) comparison tree
D) merge tree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a list of length n,insertion sort makes ____ key comparisons,in the worst case.
A) n(n - 1)/4
B) n(n - 1)/2
C) n2
D) n3
A) n(n - 1)/4
B) n(n - 1)/2
C) n2
D) n3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the case of an unsuccessful search,it can be shown that for a list of length n,a binary search makes approximately ____________________ key comparisons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When moving array values for insertion sort,to move list[4] into list[2],first ____.
A) move list[2] to list[3]
B) delete list[2]
C) move list[4] to list[3]
D) copy list[4] into temp
A) move list[2] to list[3]
B) delete list[2]
C) move list[4] to list[3]
D) copy list[4] into temp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To construct a search algorithm of the order less than log?n,it cannot be ____________________ based.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For a list of length n,the bubble sort makes exactly ____________________ key comparisons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The quick sort algorithm uses the ____________________ technique to sort a list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The top node of a comparison tree is call the ____________________ node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In general,the selection sort algorithm is good only for small lists because ____________________ grows rapidly as n grows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a quick sort,all of the sorting work is done by the function ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The first step in the quick sort partition algorithm is to determine the ____________________ and swap it with the first element in the list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The following C++ function implements the ____________________ sort algorithm.
template
void Sort(elemType list[],int length)
{
for (int iteration = 1; iteration < length; iteration++)
{
for (int index = 0; index < length - iteration;
index++)
{
if (list[index] > list[index + 1])
{
elemType temp = list[index];
list[index] = list[index + 1];
list[index + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
template
void Sort(elemType list[],int length)
{
for (int iteration = 1; iteration < length; iteration++)
{
for (int index = 0; index < length - iteration;
index++)
{
if (list[index] > list[index + 1])
{
elemType temp = list[index];
list[index] = list[index + 1];
list[index + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Any sorting algorithm that sorts a list of n distinct elements by comparison of the keys only,in its worst case,makes at least ____________________ key comparisons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A sequence of branches in a comparison tree is called a(n)____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A comparison tree is a(n)____________________ tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



