Deck 2: Descriptive Statistics and Data Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Descriptive Statistics and Data Analysis
1
________ refers to a collection of quantitative measures and ways of describing data.
A)Statistical inference
B)Descriptive statistics
C)Frequency distribution
D)Categorical data
A)Statistical inference
B)Descriptive statistics
C)Frequency distribution
D)Categorical data
Descriptive statistics
2
The ________ is the sum of all observations divided by the number of observations.
A)arithmetic mean
B)median
C)mode
D)midrange
A)arithmetic mean
B)median
C)mode
D)midrange
arithmetic mean
3
________ is the quartile representing the 50th percentile.
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4
Q2
4
The proportion of the total sample that falls at or below the upper limit value is represented by ________.
A)dispersion
B)cumulative relative frequency
C)median
D)standard deviation
A)dispersion
B)cumulative relative frequency
C)median
D)standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The formula to calculate kth percentile is given by ________.
A)100/Nk + 0.05
B)100/Nk - 0.05
C)Nk/100 + 0.05
D)Nk/100 - 0.05
A)100/Nk + 0.05
B)100/Nk - 0.05
C)Nk/100 + 0.05
D)Nk/100 - 0.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All of the following are examples of measures of dispersion except ________.
A)range
B)variance
C)standard deviation
D)mode
A)range
B)variance
C)standard deviation
D)mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
________ is the quartile representing the 75th percentile.
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In Microsoft Excel 2010,the function that computes the standard deviation of a set of data,assumed to be a population,is ________.
A)STDEV.S(data range)
B)STAND.SNGL(data range)
C)STDEV.P(data range)
D)STAND.MULT(data range)
A)STDEV.S(data range)
B)STAND.SNGL(data range)
C)STDEV.P(data range)
D)STAND.MULT(data range)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All of the following are examples of measures of central tendency except ________.
A)mean
B)median
C)standard deviation
D)mode
A)mean
B)median
C)standard deviation
D)mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
________ is the quartile representing the 25th percentile.
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
________ is the quartile representing the 100th percentile.
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
One-fourth of the data falls below the ________ quartile.
A)fourth
B)second
C)first
D)third
A)fourth
B)second
C)first
D)third

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The sum of relative frequencies will always equal ________.
A)100
B)1.0
C)10
D)0.01
A)100
B)1.0
C)10
D)0.01

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A graphical depiction of a frequency distribution for numerical data in the form of a column chart is called a ________.
A)scatter plot
B)box-and-whisker plot
C)pie chart
D)histogram
A)scatter plot
B)box-and-whisker plot
C)pie chart
D)histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In Microsoft Excel 2010,the function that computes the standard deviation of a set of data,assumed to be a sample,is ________.
A)STDEV.P(data range)
B)MODE.SNGL(data range)
C)STAND.MULT(data range)
D)STDEV.S(data range)
A)STDEV.P(data range)
B)MODE.SNGL(data range)
C)STAND.MULT(data range)
D)STDEV.S(data range)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In Microsoft Excel 2010,the function that computes the single most frequently occurring value in a set of data is ________.
A)MEDIAN(data range)
B)MODE.SNGL(data range)
C)STDEV.P(data range)
D)SKEW(data range)
A)MEDIAN(data range)
B)MODE.SNGL(data range)
C)STDEV.P(data range)
D)SKEW(data range)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The ________ is a value at or below which at least k percent of the observations lie.
A)kth percentile
B)kth ratio
C)kth quartile
D)kth mean
A)kth percentile
B)kth ratio
C)kth quartile
D)kth mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A table that shows the number of observations in each of several nonoverlapping groups is called a ________.
A)frequency distribution
B)scatter plot
C)histogram
D)chart
A)frequency distribution
B)scatter plot
C)histogram
D)chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Three-fourths of the data fall below the ________ quartile.
A)fourth
B)second
C)first
D)third
A)fourth
B)second
C)first
D)third

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Using Microsoft Excel 2010,the function that computes the most frequently occurring values of a set of data is ________.
A)MODE.SNGL(data range)
B)MEDIAN(data range)
C)STDEV.P(data range)
D)MODE.MULT(data range)
A)MODE.SNGL(data range)
B)MEDIAN(data range)
C)STDEV.P(data range)
D)MODE.MULT(data range)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The ________ is the observation that occurs the most frequently in the data set.
A)arithmetic mean
B)median
C)mode
D)midrange
A)arithmetic mean
B)median
C)mode
D)midrange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The sample mean is represented by ________.
A)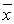
B)α
C)μ
D)η
A)
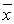
B)α
C)μ
D)η

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The standard deviation for a sample is denoted as ________.
A)μ
B)Ω
C)s
D)σ
A)μ
B)Ω
C)s
D)σ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The degree of variation in or the numerical spread of the data is known as ________.
A)quartile
B)median
C)dispersion
D)mean
A)quartile
B)median
C)dispersion
D)mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Using Chebyshev's theorem,k = 3 means that ________.
A)at least two-thirds of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
B)at least 89% of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
C)less than 29% of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
D)at least three-fourths of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean
A)at least two-thirds of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
B)at least 89% of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
C)less than 29% of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
D)at least three-fourths of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Using Chebyshev's theorem,k = 2 would mean that ________.
A)at least two-thirds of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean
B)at least 89% of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean
C)less than three-fourths of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
D)at least three-fourths of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean
A)at least two-thirds of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean
B)at least 89% of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean
C)less than three-fourths of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean
D)at least three-fourths of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following provides an estimate that represents "centering" of the entire set of data?
A)range
B)variance
C)midrange
D)standard deviation
A)range
B)variance
C)midrange
D)standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following state(s)that for any set of data,the proportion of values that lie within k standard deviations (k>1)of the mean is at least 1 - 1/k2?
A)empirical rules
B)interquartile range
C)Chebyshev's theorem
D)standard deviation
A)empirical rules
B)interquartile range
C)Chebyshev's theorem
D)standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The ________ is the average of the largest and smallest values in the data set.
A)arithmetic mean
B)median
C)mode
D)midrange
A)arithmetic mean
B)median
C)mode
D)midrange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An observation that is radically different from the rest is called ________.
A)the median
B)the mean
C)an outlier
D)the mode
A)the median
B)the mean
C)an outlier
D)the mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The standard deviation for the population is denoted as ________.
A)μ
B)Ω
C)s
D)σ
A)μ
B)Ω
C)s
D)σ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following can be used to represent dispersion in a data set?
A)proportion
B)range
C)mode
D)median
A)proportion
B)range
C)mode
D)median

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Computing the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value gives the ________ of the data set.
A)variance
B)standard deviation
C)range
D)median
A)variance
B)standard deviation
C)range
D)median

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The range of the middle 50% of the data is called the ________.
A)midrange
B)interquartile range
C)variance
D)mode
A)midrange
B)interquartile range
C)variance
D)mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The population variance is denoted as ________.
A)s2
B)v2
C)σ2
D)α2
A)s2
B)v2
C)σ2
D)α2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The ________ is the middle value when the data are arranged from smallest to largest.
A)mode
B)median
C)midrange
D)arithmetic mean
A)mode
B)median
C)midrange
D)arithmetic mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The population mean is represented by ________.
A)α
B)μ
C)λ
D)π
A)α
B)μ
C)λ
D)π

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The midrange for a data set containing all the values between 50 and 67 is ________.
A)67
B)58.5
C)50
D)-17
A)67
B)58.5
C)50
D)-17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The square root of the variance is called the ________.
A)mean
B)standard deviation
C)median
D)interquartile range
A)mean
B)standard deviation
C)median
D)interquartile range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The sample variance is denoted as ________.
A)s2
B)v2
C)σ2
D)α2
A)s2
B)v2
C)σ2
D)α2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A histogram with only one peak ________.
A)does not have a mode value
B)is unimodal
C)is bimodal
D)has a high degree of kurtosis
A)does not have a mode value
B)is unimodal
C)is bimodal
D)has a high degree of kurtosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is included in the empirical rules?
A)Approximately 59% of the observations will fall within two standard deviations of the mean,or within x ± 2s.
B)Approximately 68% of the observations will fall within one standard deviation of the mean,or between x - s and x + s.
C)Approximately 89% of the observations will fall within three standard deviations of the mean,or within x ± 3s.
D)Approximately 28% of the observations will fall within three standard deviations of the mean,or within x ± 3s.
A)Approximately 59% of the observations will fall within two standard deviations of the mean,or within x ± 2s.
B)Approximately 68% of the observations will fall within one standard deviation of the mean,or between x - s and x + s.
C)Approximately 89% of the observations will fall within three standard deviations of the mean,or within x ± 3s.
D)Approximately 28% of the observations will fall within three standard deviations of the mean,or within x ± 3s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
According to the empirical rules,approximately 95% of the observations will fall within ________.
A)one standard deviation of the mean
B)two standard deviations of the mean
C)three standard deviations of the mean
D)four standard deviations of the mean
A)one standard deviation of the mean
B)two standard deviations of the mean
C)three standard deviations of the mean
D)four standard deviations of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A distribution that is relatively flat with a wide degree of dispersion has a coefficient of kurtosis that is ________.
A)more than 3
B)less than 3
C)less than 6
D)more than 6
A)more than 3
B)less than 3
C)less than 6
D)more than 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A distribution that is relatively peaked with a low degree of dispersion has a coefficient of kurtosis that is ________.
A)equal to 0
B)less than 0
C)more than 3
D)equal to 3
A)equal to 0
B)less than 0
C)more than 3
D)equal to 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A histogram with exactly two peaks ________.
A)is unimodal
B)has a low degree of kurtosis
C)has the same values for mean and mode
D)is bimodal
A)is unimodal
B)has a low degree of kurtosis
C)has the same values for mean and mode
D)is bimodal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The coefficient of variation (CV)is calculated as ________.
A)mode/standard deviation
B)standard deviation/mean
C)standard deviation/variance
D)range/standard deviation
A)mode/standard deviation
B)standard deviation/mean
C)standard deviation/variance
D)range/standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following coefficients of skewness values has the lowest degree of skewness?
A)1
B)1.1
C)0.5
D)0.05
A)1
B)1.1
C)0.5
D)0.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
________ is a measure of a linear relationship between two variables.
A)Variance
B)Proportion
C)Correlation
D)Kurtosis
A)Variance
B)Proportion
C)Correlation
D)Kurtosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The degree of asymmetry of observations around the mean is measured by the ________.
A)coefficient of correlation
B)coefficient of symmetry
C)coefficient of skewness
D)coefficient of deviation
A)coefficient of correlation
B)coefficient of symmetry
C)coefficient of skewness
D)coefficient of deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A coefficient of skewness that indicates relative symmetry would lie between ________.
A)0.5 and -0.5
B)5 and -5
C)1 and -1
D)0.95 and 1
A)0.5 and -0.5
B)5 and -5
C)1 and -1
D)0.95 and 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A coefficient of skewness that indicates moderate skewness would lie between ________.
A)1 and 2
B)0.5 and 1
C)0 and 1
D)0.5 and -0.5
A)1 and 2
B)0.5 and 1
C)0 and 1
D)0.5 and -0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When a histogram is positively skewed,it ________.
A)tails off to the right
B)is symmetrical
C)tails off to the left
D)has a slope greater than one
A)tails off to the right
B)is symmetrical
C)tails off to the left
D)has a slope greater than one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The degree of flatness or peakedness of a population is measured by the ________.
A)coefficient of kurtosis
B)coefficient of skewness
C)coefficient of variation
D)coefficient of deviation
A)coefficient of kurtosis
B)coefficient of skewness
C)coefficient of variation
D)coefficient of deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the distribution of observations were perfectly symmetrical and unimodal,________.
A)the mean would be greater than the mode
B)the mean,median,and mode would be the same
C)the mode would be lesser than the median
D)the median would be greater than the mean
A)the mean would be greater than the mode
B)the mean,median,and mode would be the same
C)the mode would be lesser than the median
D)the median would be greater than the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When more of the mass of the data is concentrated on one side and the distribution of values tails off to the other side,the histogram is said to be ________.
A)symmetric
B)skewed
C)curved
D)positively sloped
A)symmetric
B)skewed
C)curved
D)positively sloped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Given that the standard deviation is equal to 0.568,the median equals 5,and the mean value is 3.5,what is the value of the coefficient of variation?
A)0.1136
B)0.162
C)6.16
D)0.7
A)0.1136
B)0.162
C)6.16
D)0.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
According to the empirical rules,approximately 99.7% of the observations will fall within ________.
A)one standard deviation of the mean
B)two standard deviations of the mean
C)three standard deviations of the mean
D)four standard deviations of the mean
A)one standard deviation of the mean
B)two standard deviations of the mean
C)three standard deviations of the mean
D)four standard deviations of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When a histogram is negatively skewed,it ________.
A)is symmetrical
B)tails off to the left
C)has a slope lesser than one
D)tails off to the right
A)is symmetrical
B)tails off to the left
C)has a slope lesser than one
D)tails off to the right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The ________ is used to compare the variability of two or more data sets with different scales.
A)coefficient of variation
B)variance
C)median
D)coefficient of skewness
A)coefficient of variation
B)variance
C)median
D)coefficient of skewness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Pivot tables can be used to create ________.
A)dot-scale diagrams.
B)box-and-whisker plots.
C)cross-tabulations for categorical data.
D)scatter plots.
A)dot-scale diagrams.
B)box-and-whisker plots.
C)cross-tabulations for categorical data.
D)scatter plots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The cumulative relative frequency represents the proportion of the total sample that falls at or below the upper limit value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is true of outliers in a data set?
A)All outliers should be eliminated in order to portray accurate information.
B)Outliers that are within 1 standard deviation of the mean must be eliminated.
C)The mean and range are sensitive to outliers in the data.
D)Outliers do not make any difference in the results obtained from statistical analyses.
A)All outliers should be eliminated in order to portray accurate information.
B)Outliers that are within 1 standard deviation of the mean must be eliminated.
C)The mean and range are sensitive to outliers in the data.
D)Outliers do not make any difference in the results obtained from statistical analyses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The formal statistical measure for categorical data is called the ________.
A)sample mean
B)sample median
C)sample mode
D)sample proportion
A)sample mean
B)sample median
C)sample mode
D)sample proportion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In a box plot,the outer boundaries of the box represent the ________.
A)interquartile range
B)median and mode
C)minimum and maximum
D)outlier values
A)interquartile range
B)median and mode
C)minimum and maximum
D)outlier values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What does a negative correlation coefficient indicate?
A)When one variable increases,the other variable decreases.
B)There is a nonlinear relationship between the two variables.
C)When one variable increases,the other variable increases by a smaller proportion.
D)A change in one variable does not lead to a change in the other variable.
A)When one variable increases,the other variable decreases.
B)There is a nonlinear relationship between the two variables.
C)When one variable increases,the other variable increases by a smaller proportion.
D)A change in one variable does not lead to a change in the other variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The sum of relative frequencies must equal 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A ________ displays the minimum,first quartile,median,third quartile,and maximum of a data set.
A)scatter plot
B)contingency table
C)box plot
D)stacked column chart
A)scatter plot
B)contingency table
C)box plot
D)stacked column chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Outliers defined as being more than 3*IQR away from Q1 and Q3 are considered ________.
A)mild
B)extreme
C)weak
D)irrelevant
A)mild
B)extreme
C)weak
D)irrelevant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The subcategories of the variables in a contingency table must ________.
A)be mutually exclusive
B)sum up to a total of 1
C)be arranged in ascending order
D)lie between 0 and 1
A)be mutually exclusive
B)sum up to a total of 1
C)be arranged in ascending order
D)lie between 0 and 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In a box plot,the line inside the box represents the ________.
A)mean
B)median
C)mode
D)range
A)mean
B)median
C)mode
D)range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Frequency distributions can only be constructed for numerical data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What does a positive correlation coefficient indicate?
A)When one variable increases,the other variable decreases.
B)When one variable increases,the other variable also increases.
C)When one variable decreases,the other variable remains constant.
D)Both the variables are not linearly related.
A)When one variable increases,the other variable decreases.
B)When one variable increases,the other variable also increases.
C)When one variable decreases,the other variable remains constant.
D)Both the variables are not linearly related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Point estimates that accurately represent population parameters are called outliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Sample proportion is usually denoted as ________.
A)sp
B)p
C)p2
D)s
A)sp
B)p
C)p2
D)s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The standard deviation is the square root of the variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Outliers defined as being between 1.5*IQR and 3*IQR to the left of Q1 or to the right of Q3 are considered ________.
A)weak
B)extreme
C)mild
D)statistically significant
A)weak
B)extreme
C)mild
D)statistically significant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In a box-and-whisker plot,the whiskers represent the ________.
A)Q1 and Q3
B)minimum and maximum values
C)median and mode
D)cumulative frequencies
A)Q1 and Q3
B)minimum and maximum values
C)median and mode
D)cumulative frequencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The correlation coefficient for two variables that are not linearly related will be equal to ________.
A)1
B)2
C)0
D)3
A)1
B)2
C)0
D)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The correlation coefficient is a number between ________.
A)0 and +1
B)-1 and 0
C)-1 and +1
D)-2 and +2
A)0 and +1
B)-1 and 0
C)-1 and +1
D)-2 and +2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



