Deck 13: Principles of Bioenergetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Principles of Bioenergetics
1
For the following reaction, G'° = +29.7 kJ/mol.
L-Malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+
The reaction as written:
A)can never occur in a cell.
B)can occur in a cell only if it is coupled to another reaction for which G'° is positive.
C)can occur only in a cell in which NADH is converted to NAD+ by electron transport.
D)cannot occur because of its large activation energy.
E)may occur in cells at some concentrations of substrate and product.
L-Malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+
The reaction as written:
A)can never occur in a cell.
B)can occur in a cell only if it is coupled to another reaction for which G'° is positive.
C)can occur only in a cell in which NADH is converted to NAD+ by electron transport.
D)cannot occur because of its large activation energy.
E)may occur in cells at some concentrations of substrate and product.
may occur in cells at some concentrations of substrate and product.
2
For the reaction A B, G'° = -60 kJ/mol.The reaction is started with 10 mmol of A;no B is initially present.After 24 hours,analysis reveals the presence of 2 mmol of B,8 mmol of A.Which is the most likely explanation?
A)A and B have reached equilibrium concentrations.
B)An enzyme has shifted the equilibrium toward A.
C)B formation is kinetically slow;equilibrium has not been reached by 24 hours.
D)Formation of B is thermodynamically unfavorable.
E)The result described is impossible,given the fact that G'° is -60 kJ/mol.
A)A and B have reached equilibrium concentrations.
B)An enzyme has shifted the equilibrium toward A.
C)B formation is kinetically slow;equilibrium has not been reached by 24 hours.
D)Formation of B is thermodynamically unfavorable.
E)The result described is impossible,given the fact that G'° is -60 kJ/mol.
B formation is kinetically slow;equilibrium has not been reached by 24 hours.
3
The G'° values for the two reactions shown below are given.
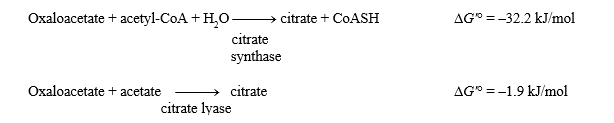
What is the G'° for the hydrolysis of acetyl-CoA?
Acetyl-CoA + H2O acetate + CoASH + H+
A)-34.1 kJ/mol
B)-32.2 kJ/mol
C)-30.3 kJ/mol
D)+61.9 kJ/mol
E)+34.1 kJ/mol

What is the G'° for the hydrolysis of acetyl-CoA?
Acetyl-CoA + H2O acetate + CoASH + H+
A)-34.1 kJ/mol
B)-32.2 kJ/mol
C)-30.3 kJ/mol
D)+61.9 kJ/mol
E)+34.1 kJ/mol
-30.3 kJ/mol
4
Which of the following is true about oxidation-reduction reactions?
A)They usually proceed through homolytic cleavage.
B)During oxidation a compound gains electrons.
C)Dehydrogenases typically remove two electrons and two hydrides.
D)There are four commonly accessed oxidation states of carbon.
E)Every oxidation must be accompanied by a reduction.
A)They usually proceed through homolytic cleavage.
B)During oxidation a compound gains electrons.
C)Dehydrogenases typically remove two electrons and two hydrides.
D)There are four commonly accessed oxidation states of carbon.
E)Every oxidation must be accompanied by a reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When a mixture of glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate is incubated with the enzyme phosphohexose isomerase (which catalyzes the interconversion of these two compounds)until equilibrium is reached,the final mixture contains twice as much glucose 6-phosphate as fructose 6-phosphate.Which one of the following statements is best applied to this reaction outlined below? (R = 8.315 J/mol·K;T = 298 K)
Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6-phosphate
A)( G'° is incalculably large and negative.)
B)( G'° is -1.72 kJ/mol.)
C)( G'° is zero.)
D)( G'° is +1.72 kJ/mol.)
E)( G'° is incalculably large and positive.)
Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6-phosphate
A)( G'° is incalculably large and negative.)
B)( G'° is -1.72 kJ/mol.)
C)( G'° is zero.)
D)( G'° is +1.72 kJ/mol.)
E)( G'° is incalculably large and positive.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
During glycolysis,glucose 1-phosphate is converted to fructose 6-phosphate in two successive reactions:
Glucose 1-phosphate glucose 6-phosphate G'° = -7.1 kJ/mol
Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6-phosphate G'° = +1.7 kJ/mol
G'° for the overall reaction is:
A)-8.8 kJ/mol.
B)-7.1 kJ/mol.
C)-5.4 kJ/mol.
D)+5.4 kJ/mol.
E)+8.8 kJ/mol.
Glucose 1-phosphate glucose 6-phosphate G'° = -7.1 kJ/mol
Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6-phosphate G'° = +1.7 kJ/mol
G'° for the overall reaction is:
A)-8.8 kJ/mol.
B)-7.1 kJ/mol.
C)-5.4 kJ/mol.
D)+5.4 kJ/mol.
E)+8.8 kJ/mol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is not electrophilic?
A)A proton
B)A sulfhydryl
C)A protonated imine
D)A carbonyl group
E)A phosphoryl group
A)A proton
B)A sulfhydryl
C)A protonated imine
D)A carbonyl group
E)A phosphoryl group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following compounds has the largest negative value for the standard free-energy change ( G'°)upon hydrolysis?
A)Acetic anhydride
B)Glucose 6-phosphate
C)Glutamine
D)Glycerol 3-phosphate
E)Lactose
A)Acetic anhydride
B)Glucose 6-phosphate
C)Glutamine
D)Glycerol 3-phosphate
E)Lactose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not true?
A)The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl can be resonance stabilized to form a carbanion.
B)A carbonyl carbon can be made more electrophilic by a nearby metal ion.
C)The carbon adjacent to an imine can be resonance stabilized to form a carbanion
D)Decarboxylation of an -keto acid goes through a carbocation intermediate.
E)A Claisen ester condensation reaction goes through a carbanion intermediate.
A)The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl can be resonance stabilized to form a carbanion.
B)A carbonyl carbon can be made more electrophilic by a nearby metal ion.
C)The carbon adjacent to an imine can be resonance stabilized to form a carbanion
D)Decarboxylation of an -keto acid goes through a carbocation intermediate.
E)A Claisen ester condensation reaction goes through a carbanion intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not nucleophilic?
A)A proton
B)A carbanion
C)An imidazole
D)A hydroxide
E)A carboxylic acid
A)A proton
B)A carbanion
C)An imidazole
D)A hydroxide
E)A carboxylic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For the reaction A B,the Keq' is 104.If a reaction mixture originally contains 1 mmol of A and no B,which one of the following must be true?
A)At equilibrium,there will be far more B than A.
B)The rate of the reaction is very slow.
C)The reaction requires coupling to an exergonic reaction in order to proceed.
D)The reaction will proceed toward B at a very high rate.
E)( G'° for the reaction will be large and positive.)
A)At equilibrium,there will be far more B than A.
B)The rate of the reaction is very slow.
C)The reaction requires coupling to an exergonic reaction in order to proceed.
D)The reaction will proceed toward B at a very high rate.
E)( G'° for the reaction will be large and positive.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The standard free-energy changes for the reactions below are given.
Phosphocreatine creatine + Pi G'° = -43.0 kJ/mol
ATP ADP + Pi G'° = -30.5 kJ/mol
What is the overall G'° for the following reaction?
Phosphocreatine + ADP creatine + ATP
A)-73.5 kJ/mol
B)-12.5 kJ/mol
C)+12.5 kJ/mol
D)+73.5 kJ/mol
E)( G'° cannot be calculated without Keq'.)
Phosphocreatine creatine + Pi G'° = -43.0 kJ/mol
ATP ADP + Pi G'° = -30.5 kJ/mol
What is the overall G'° for the following reaction?
Phosphocreatine + ADP creatine + ATP
A)-73.5 kJ/mol
B)-12.5 kJ/mol
C)+12.5 kJ/mol
D)+73.5 kJ/mol
E)( G'° cannot be calculated without Keq'.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The reaction A + B C has a G'° of -20 kJ/mol at 25° C.Starting under standard conditions,one can predict that:
A)at equilibrium,the concentration of B will exceed the concentration of A.
B)at equilibrium,the concentration of C will be less than the concentration of A.
C)at equilibrium,the concentration of C will be much greater than the concentration of A or B.
D)C will rapidly break down to A + B.
E)when A and B are mixed,the reaction will proceed rapidly toward formation of C.
A)at equilibrium,the concentration of B will exceed the concentration of A.
B)at equilibrium,the concentration of C will be less than the concentration of A.
C)at equilibrium,the concentration of C will be much greater than the concentration of A or B.
D)C will rapidly break down to A + B.
E)when A and B are mixed,the reaction will proceed rapidly toward formation of C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the G'° of the reaction A B is -40 kJ/mol,under standard conditions the reaction:
A)is at equilibrium.
B)will never reach equilibrium.
C)will not occur spontaneously.
D)will proceed at a rapid rate.
E)will proceed spontaneously from A to B.
A)is at equilibrium.
B)will never reach equilibrium.
C)will not occur spontaneously.
D)will proceed at a rapid rate.
E)will proceed spontaneously from A to B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All of the following contribute to the large,negative,free-energy change upon hydrolysis of "high-energy" compounds except:
A)electrostatic repulsion in the reactant.
B)low activation energy of forward reaction.
C)stabilization of products by extra resonance forms.
D)stabilization of products by ionization.
E)stabilization of products by solvation.
A)electrostatic repulsion in the reactant.
B)low activation energy of forward reaction.
C)stabilization of products by extra resonance forms.
D)stabilization of products by ionization.
E)stabilization of products by solvation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In glycolysis,fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is converted to two products with a standard free-energy change ( G'°)of 23.8 kJ/mol.Under what conditions encountered in a normal cell will the free-energy change ( G)be negative,enabling the reaction to proceed spontaneously to the right?
A)Under standard conditions,enough energy is released to drive the reaction to the right.
B)The reaction will not go to the right spontaneously under any conditions because the G'° is positive.
C)The reaction will proceed spontaneously to the right if there is a high concentration of products relative to the concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
D)The reaction will proceed spontaneously to the right if there is a high concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate relative to the concentration of products.
E)None of the above conditions is sufficient.
A)Under standard conditions,enough energy is released to drive the reaction to the right.
B)The reaction will not go to the right spontaneously under any conditions because the G'° is positive.
C)The reaction will proceed spontaneously to the right if there is a high concentration of products relative to the concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
D)The reaction will proceed spontaneously to the right if there is a high concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate relative to the concentration of products.
E)None of the above conditions is sufficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The reaction ATP ADP + Pi is an example of a reaction.
A)homolytic cleavage
B)internal rearrangement
C)free radical
D)group transfer
E)oxidation/reduction
A)homolytic cleavage
B)internal rearrangement
C)free radical
D)group transfer
E)oxidation/reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Hydrolysis of 1 M glucose 6-phosphate catalyzed by glucose 6-phosphatase is 99% complete at equilibrium (i.e. ,only 1% of the substrate remains).Which of the following statements is most nearly correct? (R = 8.315 J/mol·K;T = 298 K)
A)( G'° is -11 kJ/mol.)
B)( G'° is -5 kJ/mol.)
C)( G'° is 0 kJ/mol.)
D)( G'° is +11 kJ/mol.)
E)( G'° cannot be determined from the information given.)
A)( G'° is -11 kJ/mol.)
B)( G'° is -5 kJ/mol.)
C)( G'° is 0 kJ/mol.)
D)( G'° is +11 kJ/mol.)
E)( G'° cannot be determined from the information given.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For the reaction A B,the Keq' is 10-6.If a reaction mixture originally contains 1 mmol of A and 1 mmol of B,which one of the following must be true?
A)At equilibrium,there will be still be equal levels of A and B.
B)The rate of the reaction is very slow.
C)At equilibrium,the amount of A will greatly exceed the amount of B.
D)The reaction will proceed toward B at a very high rate.
E)( G'° for the reaction will be large and positive.)
A)At equilibrium,there will be still be equal levels of A and B.
B)The rate of the reaction is very slow.
C)At equilibrium,the amount of A will greatly exceed the amount of B.
D)The reaction will proceed toward B at a very high rate.
E)( G'° for the reaction will be large and positive.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a mixture of 3-phosphoglycerate and 2-phosphoglycerate is incubated at 25 °C with phosphoglycerate mutase until equilibrium is reached,the final mixture contains six times as much 2-phosphoglycerate as 3-phosphoglycerate.Which one of the following statements is most nearly correct,when applied to the reaction as written? (R = 8.315 J/mol·K;T = 298 K)
3-Phosphoglycerate 2-phosphoglycerate
A)( G'° is -4.44 kJ/mol.)
B)( G'° is zero.)
C)( G'°is +12.7 kJ/mol.)
D)( G'°is incalculably large and positive.)
E)( G'° cannot be calculated from the information given.)
3-Phosphoglycerate 2-phosphoglycerate
A)( G'° is -4.44 kJ/mol.)
B)( G'° is zero.)
C)( G'°is +12.7 kJ/mol.)
D)( G'°is incalculably large and positive.)
E)( G'° cannot be calculated from the information given.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Bioenergetics and thermodynamics
What is the difference between G and G'° of a chemical reaction? Describe,quantitatively,the relationship between them.
What is the difference between G and G'° of a chemical reaction? Describe,quantitatively,the relationship between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which one of the following compounds does not have a large negative free energy of hydrolysis?
A)1,3-bis phosphoglycerate
B)3-phosphoglycerate
C)ADP
D)Phosphoenolpyruvate
E)Thioesters (e.g.acetyl-CoA)
A)1,3-bis phosphoglycerate
B)3-phosphoglycerate
C)ADP
D)Phosphoenolpyruvate
E)Thioesters (e.g.acetyl-CoA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Biological oxidation-reduction reactions always involve:
A)direct participation of oxygen.
B)formation of water.
C)mitochondria.
D)transfer of electron(s).
E)transfer of hydrogens.
A)direct participation of oxygen.
B)formation of water.
C)mitochondria.
D)transfer of electron(s).
E)transfer of hydrogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a 0.1 M solution of glucose 1-phosphate is incubated with a catalytic amount of phospho-glucomutase,the glucose 1-phosphate is transformed to glucose 6-phosphate until equilibrium is reached.At equilibrium,the concentration of glucose 1-phosphate is 4.5 x 10-3 M and that of glucose 6-phosphate is 8.6 *10-2 M.Set up the expressions for the calculation of Keq' and G'° for this reaction (in the direction of glucose 6-phosphate formation).(R = 8.315 J/mol·K;T = 298 K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The structure of NAD+ does not include:
A)a flavin nucleotide.
B)a pyrophosphate bond.
C)an adenine nucleotide.
D)nicotinamide.
E)two ribose residues.
A)a flavin nucleotide.
B)a pyrophosphate bond.
C)an adenine nucleotide.
D)nicotinamide.
E)two ribose residues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The hydrolysis of phosphoenolpyruvate proceeds with a G'° of about -62 kJ/mol.The greatest contributing factors to this reaction are the destabilization of the reactants by electostatic repulsion and stabilization of the product pyruvate by:
A)electrostatic attraction.
B)ionization.
C)polarization.
D)resonance.
E)tautomerization.
A)electrostatic attraction.
B)ionization.
C)polarization.
D)resonance.
E)tautomerization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Explain in quantitative terms the circumstances under which the following reaction can proceed.
Citrate isocitrate G'° = +13.3 kJ/mol
Citrate isocitrate G'° = +13.3 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not true for the nicotinamide cofactors?
A)The oxidized form is positively charged.
B)The reduced form has a large extinction coefficient at 340 nm.
C)The oxidized form provides reducing equivalents to other molecules.
D)Oxidation-reduction reactions with nicotinamides usually involve hydride transfer.
E)Enzymes transfer hydrides stereospecifically to one or the other side of the nicotinamide ring.
A)The oxidized form is positively charged.
B)The reduced form has a large extinction coefficient at 340 nm.
C)The oxidized form provides reducing equivalents to other molecules.
D)Oxidation-reduction reactions with nicotinamides usually involve hydride transfer.
E)Enzymes transfer hydrides stereospecifically to one or the other side of the nicotinamide ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The hydrolysis of ATP has a large negative G'°;nevertheless it is stable in solution due to:
A)entropy stabilization.
B)ionization of the phosphates.
C)resonance stabilization.
D)the hydrolysis reaction being endergonic.
E)the hydrolysis reaction having a large activation energy.
A)entropy stabilization.
B)ionization of the phosphates.
C)resonance stabilization.
D)the hydrolysis reaction being endergonic.
E)the hydrolysis reaction having a large activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The immediate precursors of DNA and RNA synthesis in the cell all contain:
A)3' triphosphates.
B)5' triphosphates.
C)adenine.
D)deoxyribose.
E)ribose.
A)3' triphosphates.
B)5' triphosphates.
C)adenine.
D)deoxyribose.
E)ribose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Explain the relationships among the change in the degree of order,the change in entropy,and the change in free energy that occur during a chemical reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
E'° of the NAD+/NADH half reaction is -0.32 V.The E'° of the oxaloacetate/malate half reaction is
-0)175 V.When the concentrations of NAD+,NADH,oxaloacetate,and malate are all 10-5 M,the "spontaneous" reaction is:
A)malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+.
B)malate + NADH + H+ oxaloacetate + NAD+.
C)NAD+ + NADH + H+ malate + oxaloacetate.
D)NAD+ + oxaloacetate NADH + H+ + malate.
E)oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ malate + NAD+.
-0)175 V.When the concentrations of NAD+,NADH,oxaloacetate,and malate are all 10-5 M,the "spontaneous" reaction is:
A)malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+.
B)malate + NADH + H+ oxaloacetate + NAD+.
C)NAD+ + NADH + H+ malate + oxaloacetate.
D)NAD+ + oxaloacetate NADH + H+ + malate.
E)oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ malate + NAD+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Biological oxidation-reduction reactions never involve:
A)transfer of e- from one molecule to another.
B)formation of free e-.
C)transfer of H+ (or H3O+)from one molecule to another.
D)formation of free H+ (or H3O+).
E)none of the above.
A)transfer of e- from one molecule to another.
B)formation of free e-.
C)transfer of H+ (or H3O+)from one molecule to another.
D)formation of free H+ (or H3O+).
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The expression G = G'° + RT ln Keq' for the actual free-energy change for the reaction A + B C + D is incorrect.Why is it wrong,and what is the correct expression for the real free-energy change of this reaction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Muscle contraction involves the conversion of:
A)chemical energy to kinetic energy.
B)chemical energy to potential energy.
C)kinetic energy to chemical energy.
D)potential energy to chemical energy.
E)potential energy to kinetic energy.
A)chemical energy to kinetic energy.
B)chemical energy to potential energy.
C)kinetic energy to chemical energy.
D)potential energy to chemical energy.
E)potential energy to kinetic energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the reaction: A + B C + D.If the equilibrium constant for this reaction is a large number (say,10,000),what do we know about the standard free-energy change ( G'°)for the reaction? Describe the relationship between Keq' and G'°.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The standard free energy change ( G'°)for ATP hydrolysis is -30.5 kJ/mol.ATP,ADP,and Pi are mixed together at initial concentrations of 1 M of each,then left alone until the reaction ADP + Pi ATP has come to equilibrium.For each species (i.e. ,ATP,ADP,and Pi),indicate whether the concentration will be equal to 1 M,less than 1 M,or greater than 1 M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The standard reduction potentials (E'°)for the following half reactions are given.
Fumarate + 2H+ + 2e- succinate E'° = +0.031 V
FAD + 2H+ + 2e- FADH2 E'° = -0.219 V
If you mixed succinate,fumarate,FAD,and FADH2 together,all at l M concentrations and in the presence of succinate dehydrogenase,which of the following would happen initially?
A)Fumarate and succinate would become oxidized;FAD and FADH2 would become reduced.
B)Fumarate would become reduced;FADH2 would become oxidized.
C)No reaction would occur because all reactants and products are already at their standard concentrations.
D)Succinate would become oxidized;FAD would become reduced.
E)Succinate would become oxidized;FADH2 would be unchanged because it is a cofactor.
Fumarate + 2H+ + 2e- succinate E'° = +0.031 V
FAD + 2H+ + 2e- FADH2 E'° = -0.219 V
If you mixed succinate,fumarate,FAD,and FADH2 together,all at l M concentrations and in the presence of succinate dehydrogenase,which of the following would happen initially?
A)Fumarate and succinate would become oxidized;FAD and FADH2 would become reduced.
B)Fumarate would become reduced;FADH2 would become oxidized.
C)No reaction would occur because all reactants and products are already at their standard concentrations.
D)Succinate would become oxidized;FAD would become reduced.
E)Succinate would become oxidized;FADH2 would be unchanged because it is a cofactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In glycolysis,the enzyme pyruvate kinase catalyzes this reaction:
Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP pyruvate + ATP
Given the information below,show how you would calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.(R = 8.315 J/mol·K;T = 298 K)
Reaction 1)ATP ADP + Pi G'° = -30.5 kJ/mol
Reaction 2)phosphoenolpyruvate pyruvate + Pi G'° = -61.9 kJ/mol
Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP pyruvate + ATP
Given the information below,show how you would calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.(R = 8.315 J/mol·K;T = 298 K)
Reaction 1)ATP ADP + Pi G'° = -30.5 kJ/mol
Reaction 2)phosphoenolpyruvate pyruvate + Pi G'° = -61.9 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Explain why each of the following statements is false.
(a)In a reaction under standard conditions,only the reactants are fixed at 1 M.
(b)When G'° is positive,Keq' > 1.
(c) G and G'° mean the same thing.
(d)When G'° = 1.0 kJ/mol,Keq' = 1.
(a)In a reaction under standard conditions,only the reactants are fixed at 1 M.
(b)When G'° is positive,Keq' > 1.
(c) G and G'° mean the same thing.
(d)When G'° = 1.0 kJ/mol,Keq' = 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The free energy of hydrolysis of phosphoenolpyruvate is -61.9 kJ/mol.Rationalize this large,negative value for G'° in chemical terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why is the actual free energy ( G)of hydrolysis of ATP in the cell different from the standard free energy ( G'°)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If E'° for an oxidation-reduction reaction is positive,will G'° be positive or negative? What is the equation that relates G'° and E'°?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For each pair of ions or compounds below,indicate which is the more highly reduced species.
(a)Co2+/Co+
(b)Glucose/CO2
(c)Fe3+/Fe2+
(d)Acetate/CO2
(e)Ethanol/acetic acid
(f)Acetic acid/acetaldehyde
(a)Co2+/Co+
(b)Glucose/CO2
(c)Fe3+/Fe2+
(d)Acetate/CO2
(e)Ethanol/acetic acid
(f)Acetic acid/acetaldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The first law of thermodynamics states that the amount of energy in the universe is constant,but that the various forms of energy can be interconverted.Describe four different types of such energy transduction that occur in living organisms and provide one example for each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
During transfer of two electrons through the mitochondrial respiratory chain,the overall reaction is:
NADH + 1/2 O2 + H+ NAD+ + H2O
For this reaction,the difference in reduction potentials for the two half-reactions ( E'°)is +1.14 V.Show how you would calculate the standard free-energy change, G'°,for the reaction.(The Faraday constant,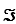 ,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. )
,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. )
NADH + 1/2 O2 + H+ NAD+ + H2O
For this reaction,the difference in reduction potentials for the two half-reactions ( E'°)is +1.14 V.Show how you would calculate the standard free-energy change, G'°,for the reaction.(The Faraday constant,
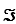 ,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. )
,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. ) 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the following reversible reaction:
Acetaldehyde + NADH + H+ Ethanol + NAD+
Use the following information to answer the questions below:
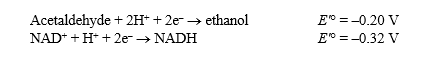
The Faraday constant,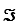 ,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol.
,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol.
(a)Calculate G'° for the reaction as written.Show your work.
(b)Given your answer to (a),what is the G'° for the reaction occurring in the reverse direction?
(c)Which reaction (forward or reverse)will tend to occur spontaneously under standard conditions?
(d)In the cell,the reaction actually proceeds in the direction that has a positive G'°.Explain how this could be possible.
Acetaldehyde + NADH + H+ Ethanol + NAD+
Use the following information to answer the questions below:

The Faraday constant,
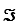 ,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol.
,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol.(a)Calculate G'° for the reaction as written.Show your work.
(b)Given your answer to (a),what is the G'° for the reaction occurring in the reverse direction?
(c)Which reaction (forward or reverse)will tend to occur spontaneously under standard conditions?
(d)In the cell,the reaction actually proceeds in the direction that has a positive G'°.Explain how this could be possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In general,when ATP hydrolysis is coupled to an energy-requiring reaction,the actual reaction often consists of the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to another substrate,rather than an actual hydrolysis of the ATP.Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Classify each of the *ed atoms as an electrophile or a nucleophile: 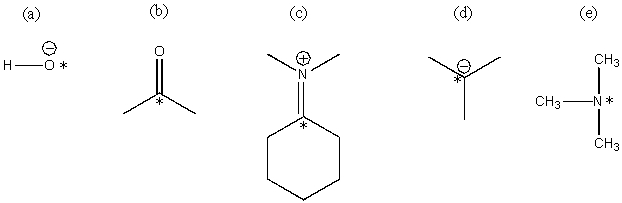


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is an oxidation? What is a reduction? Can an oxidation occur without a simultaneous reduction? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain what is meant by the statement: "Standard free-energy changes are additive." Give an example of the usefulness of this additive property in understanding how cells carry out thermodynamically unfavorable chemical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase catalyzes the following reversible reaction:
Glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD+ NADH + H+ + dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Given the standard reduction potentials below,calculate G'° for the glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction,proceeding from left to right as shown.Show your work.(The Faraday constant,F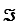 ,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. )
,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. )
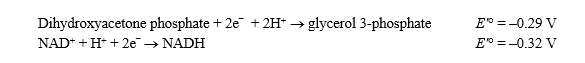
Glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD+ NADH + H+ + dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Given the standard reduction potentials below,calculate G'° for the glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction,proceeding from left to right as shown.Show your work.(The Faraday constant,F
 ,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. )
,is 96.48 kJ/V·mol. )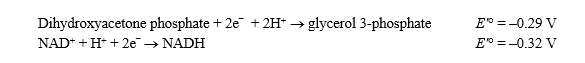

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reversible reaction:
Pyruvate + NADH + H+ Lactate + NAD+
Given the following facts
(a)tell in which direction the reaction will tend to go if NAD+,NADH,pyruvate,and lactate were mixed,all at 1 M concentrations,in the presence of lactate dehydrogenase at pH 7; (b)calculate G'° for this reaction.Show your work.
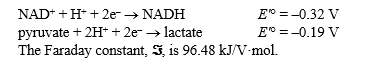
Pyruvate + NADH + H+ Lactate + NAD+
Given the following facts
(a)tell in which direction the reaction will tend to go if NAD+,NADH,pyruvate,and lactate were mixed,all at 1 M concentrations,in the presence of lactate dehydrogenase at pH 7; (b)calculate G'° for this reaction.Show your work.
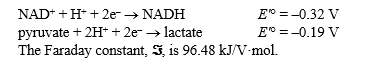

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



