Deck 9: Recombinant Dna Technology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Recombinant Dna Technology
1
Certain restriction enzymes produce cohesive (sticky)ends.This means that they:
A)cut both DNA strands at the same base pair.
B)cut in regions of high GC content,leaving ends that can form more hydrogen bonds than ends of high AT content.
C)make a staggered double-strand cut,leaving ends with a few nucleotides of single-stranded DNA protruding.
D)make ends that can anneal to cohesive ends generated by any other restriction enzyme.
E)stick tightly to the ends of the DNA they have cut.
A)cut both DNA strands at the same base pair.
B)cut in regions of high GC content,leaving ends that can form more hydrogen bonds than ends of high AT content.
C)make a staggered double-strand cut,leaving ends with a few nucleotides of single-stranded DNA protruding.
D)make ends that can anneal to cohesive ends generated by any other restriction enzyme.
E)stick tightly to the ends of the DNA they have cut.
make a staggered double-strand cut,leaving ends with a few nucleotides of single-stranded DNA protruding.
2
Restriction enzymes:
A)act at the membrane to restrict the passage of certain molecules into the cell.
B)are highly specialized ribonucleases that degrade mRNA soon after its synthesis.
C)are sequence-specific DNA endonucleases.
D)are very specific proteases that cleave peptides at only certain sequences.
E)catalyze the addition of a certain amino acid to a specific tRNA.
A)act at the membrane to restrict the passage of certain molecules into the cell.
B)are highly specialized ribonucleases that degrade mRNA soon after its synthesis.
C)are sequence-specific DNA endonucleases.
D)are very specific proteases that cleave peptides at only certain sequences.
E)catalyze the addition of a certain amino acid to a specific tRNA.
are sequence-specific DNA endonucleases.
3
Which of the following statements about type II restriction enzymes is false?
A)Many make staggered (off-center)cuts within their recognition sequences.
B)Some cut DNA to generate blunt ends.
C)They are part of a bacterial defense system in which foreign DNA is cleaved.
D)They cleave and ligate DNA.
E)They cleave DNA only at recognition sequences specific to a given restriction enzyme.
A)Many make staggered (off-center)cuts within their recognition sequences.
B)Some cut DNA to generate blunt ends.
C)They are part of a bacterial defense system in which foreign DNA is cleaved.
D)They cleave and ligate DNA.
E)They cleave DNA only at recognition sequences specific to a given restriction enzyme.
They cleave and ligate DNA.
4
Which one of the following analytical techniques does not help illuminate a gene's cellular function?
A)DNA microarray analysis
B)Protein chip analysis
C)Southern blotting
D)Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
E)Two-hybrid analysis
A)DNA microarray analysis
B)Protein chip analysis
C)Southern blotting
D)Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
E)Two-hybrid analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Common features found in a cloning plasmid used for protein expression include all except which of the following?
A)Polylinker
B)Origin of replication.
C)Antibiotic resistance marker(s)
D)Ribosome binding site
E)Telomeric ends
A)Polylinker
B)Origin of replication.
C)Antibiotic resistance marker(s)
D)Ribosome binding site
E)Telomeric ends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not needed in 454 pyrosequencing of DNA?
A)dNTPs
B)Sulfurylase
C)Luciferase
D)ddNTPs
E)Apyrase
A)dNTPs
B)Sulfurylase
C)Luciferase
D)ddNTPs
E)Apyrase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)is false?
A)DNA amplified by PCR can be cloned.
B)DNA amplification is linear in magnitude.
C)Newly synthesized DNA must be heat-denatured before the next round of DNA synthesis begins.
D)The boundaries of the amplified DNA segment are determined by the synthetic oligonucleotides used to prime DNA synthesis.
E)The technique is sufficiently sensitive that DNA sequences can be amplified from a single animal or human hair.
A)DNA amplified by PCR can be cloned.
B)DNA amplification is linear in magnitude.
C)Newly synthesized DNA must be heat-denatured before the next round of DNA synthesis begins.
D)The boundaries of the amplified DNA segment are determined by the synthetic oligonucleotides used to prime DNA synthesis.
E)The technique is sufficiently sensitive that DNA sequences can be amplified from a single animal or human hair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the laboratory,recombinant plasmids are commonly introduced into bacterial cells by:
A)electrophoresis-a gentle low-voltage gradient draws the DNA into the cell.
B)infection with a bacteriophage that carries the plasmid.
C)microinjection.
D)mixing plasmids with an extract of broken cells.
E)transformation-heat shock of the cells incubated with plasmid DNA in the presence of CaCl2.
A)electrophoresis-a gentle low-voltage gradient draws the DNA into the cell.
B)infection with a bacteriophage that carries the plasmid.
C)microinjection.
D)mixing plasmids with an extract of broken cells.
E)transformation-heat shock of the cells incubated with plasmid DNA in the presence of CaCl2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The E.coli recombinant plasmid pBR322 has been widely utilized in genetic engineering experiments.pBR322 has all of the following features except:
A)a number of conveniently located recognition sites for restriction enzymes.
B)a number of palindromic sequences near the EcoRI site,which permit the plasmid to assume a conformation that protects newly inserted DNA from nuclease degradation.
C)a replication origin,which permits it to replicate autonomously.
D)resistance to two different antibiotics,which permits rapid screening for recombinant plasmids containing foreign DNA.
E)small overall size,which facilitates entry of the plasmid into host cells.
A)a number of conveniently located recognition sites for restriction enzymes.
B)a number of palindromic sequences near the EcoRI site,which permit the plasmid to assume a conformation that protects newly inserted DNA from nuclease degradation.
C)a replication origin,which permits it to replicate autonomously.
D)resistance to two different antibiotics,which permits rapid screening for recombinant plasmids containing foreign DNA.
E)small overall size,which facilitates entry of the plasmid into host cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements regarding plasmid-cloning vectors is correct?
A)Circular plasmids do not require an origin of replication to be propagated in E.coli.
B)Foreign DNA fragments up to 45,000 base pairs can be cloned in a typical plasmid.
C)Plasmids do not need to contain genes that confer resistance to antibiotics.
D)Plasmid vectors must carry promoters for inserted gene fragments.
E)The copy number of plasmids may vary from a few to several hundred.
A)Circular plasmids do not require an origin of replication to be propagated in E.coli.
B)Foreign DNA fragments up to 45,000 base pairs can be cloned in a typical plasmid.
C)Plasmids do not need to contain genes that confer resistance to antibiotics.
D)Plasmid vectors must carry promoters for inserted gene fragments.
E)The copy number of plasmids may vary from a few to several hundred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The technique known as two hybrid analysis for detecting interacting gene products depend on:
A)activation of DNA polymerase by the nearby binding of hybridizing protein complexes.
B)direct binding of a Gal4p activation domain to a DNA sequence in the promoter region.
C)having a promoter that responds directly to one of the two proteins whose interactions is being measured.
D)hybridization of DNA segments corresponding to the two genes being examined.
E)stimulation of transcription by interaction of two Gal4p domains via fused protein sequences.
A)activation of DNA polymerase by the nearby binding of hybridizing protein complexes.
B)direct binding of a Gal4p activation domain to a DNA sequence in the promoter region.
C)having a promoter that responds directly to one of the two proteins whose interactions is being measured.
D)hybridization of DNA segments corresponding to the two genes being examined.
E)stimulation of transcription by interaction of two Gal4p domains via fused protein sequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not needed to build a cDNA library?
A)Genomic DNA
B)mRNA
C)Reverse transcriptase
D)dNTPs
E)DNA polymerase
A)Genomic DNA
B)mRNA
C)Reverse transcriptase
D)dNTPs
E)DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A convenient cloning vector with which to introduce foreign DNA into E.coli is a(n):
A)E)coli chromosome.
B)messenger RNA.
C)plasmid.
D)yeast "ARS" sequence.
E)yeast transposable element.
A)E)coli chromosome.
B)messenger RNA.
C)plasmid.
D)yeast "ARS" sequence.
E)yeast transposable element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The size of the DNA region specifically recognized by type II restriction enzymes is typically:
A)4 to 6 base pairs.
B)10 to 15 base pairs.
C)50 to 60 base pairs.
D)200 to 300 base pairs.
E)about the size of an average gene.
A)4 to 6 base pairs.
B)10 to 15 base pairs.
C)50 to 60 base pairs.
D)200 to 300 base pairs.
E)about the size of an average gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not used as a heterologous host for the expression of recombinant proteins?
A)Retroviruses
B)Bacteria such as E.coli
C)Eukaryotes such as S.cerevisiae
D)Insect cells
E)Mammalian cells
A)Retroviruses
B)Bacteria such as E.coli
C)Eukaryotes such as S.cerevisiae
D)Insect cells
E)Mammalian cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The PCR reaction mixture does not include:
A)all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
B)DNA containing the sequence to be amplified.
C)DNA ligase.
D)heat-stable DNA polymerase.
E)oligonucleotide primer(s).
A)all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
B)DNA containing the sequence to be amplified.
C)DNA ligase.
D)heat-stable DNA polymerase.
E)oligonucleotide primer(s).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a commonly used tag for affinity purification of cloned proteins?
A)Glutathione-S-transferase
B)Maltose binding protein
C)Nickel
D)Protein A
E)Chitin-binding domain
A)Glutathione-S-transferase
B)Maltose binding protein
C)Nickel
D)Protein A
E)Chitin-binding domain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The biological role of restriction enzymes is to:
A)aid recombinant DNA research.
B)degrade foreign DNA that enters a bacterium.
C)make bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
D)restrict the damage to DNA by ultraviolet light.
E)restrict the size of DNA in certain bacteria.
A)aid recombinant DNA research.
B)degrade foreign DNA that enters a bacterium.
C)make bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
D)restrict the damage to DNA by ultraviolet light.
E)restrict the size of DNA in certain bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following does not apply to the construction or use of a DNA library?
A)Determining the location of a particular DNA sequence in a DNA library requires a suitable hybridization probe.
B)Genomic libraries are better for expressing gene products than cDNA libraries.
C)Many segments of DNA from a cellular genome are cloned.
D)Specialized DNA libraries can be made by cloning DNA copies of mRNAs.
E)The DNA copies of mRNA found in a cDNA library are made by reverse transcriptase.
A)Determining the location of a particular DNA sequence in a DNA library requires a suitable hybridization probe.
B)Genomic libraries are better for expressing gene products than cDNA libraries.
C)Many segments of DNA from a cellular genome are cloned.
D)Specialized DNA libraries can be made by cloning DNA copies of mRNAs.
E)The DNA copies of mRNA found in a cDNA library are made by reverse transcriptase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following tags is not used to study protein function?
A)Green fluorescent protein (GFP)
B)Synteny tag
C)Tandem affinity purification (TAP)
D)Gal4p DNA binding domain
E)Gal4p activation domain
A)Green fluorescent protein (GFP)
B)Synteny tag
C)Tandem affinity purification (TAP)
D)Gal4p DNA binding domain
E)Gal4p activation domain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Explain briefly the properties of the plasmid pBR322 that make it so convenient as a vector for cloning fragments of foreign DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A scientist wishes to produce a mammalian protein in E.coli.The protein is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 40,000.Approximately 20% of its mass is polysaccharide.The isolated protein is usually phosphorylated and contains three disulfide bonds.The cloned gene contains no introns.
(a)What sequences or sites will be required in the vector to get this gene regulated,transcribed,and translated in E.coli?
(b)List two problems that might arise in producing a protein identical to that isolated from mammalian cells and describe each problem in no more than two sentences.
(a)What sequences or sites will be required in the vector to get this gene regulated,transcribed,and translated in E.coli?
(b)List two problems that might arise in producing a protein identical to that isolated from mammalian cells and describe each problem in no more than two sentences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Current estimates indicate that humans have about ________ genes.
A)3,000
B)10,000
C)30,000
D)100,000
E)300,000
A)3,000
B)10,000
C)30,000
D)100,000
E)300,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs)are used as cloning vectors,what size of DNA fragment can be cloned?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A DNA sequence that may be present as only a single copy in a large mammalian genome can be amplified and cloned using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).Describe the steps and reaction components required in a PCR experiment.Illustrate the steps in just one round.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Name two different methods by which protein-protein interactions can be discovered and probed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Explain how each of the following is used in cloning in a plasmid: (a)antibiotic-resistance genes
(b)origin of replication
(c)polylinker region.
(b)origin of replication
(c)polylinker region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Match each feature of the plasmid pBR322 (at left)with one appropriate description presented (at right)(see illustration of pBR322 below).Descriptions may be used more than once. 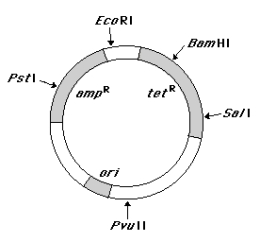 ____ ampR sequence (a)Permits selection of bacteria containing the plasmid.
____ ampR sequence (a)Permits selection of bacteria containing the plasmid.
____ ori sequence (b)A sequence required for packaging recombinant plasmids
____ tetR into bacteriophage.
____ BamHI sequence (c)Origin of replication.
____ PstI sequence (d)Cleavage of the plasmid here does not affect antibiotic
sequence resistance genes.
(e)Insertion of foreign DNA here permits identification of
bacteria containing recombinant plasmids .
 ____ ampR sequence (a)Permits selection of bacteria containing the plasmid.
____ ampR sequence (a)Permits selection of bacteria containing the plasmid.____ ori sequence (b)A sequence required for packaging recombinant plasmids
____ tetR into bacteriophage.
____ BamHI sequence (c)Origin of replication.
____ PstI sequence (d)Cleavage of the plasmid here does not affect antibiotic
sequence resistance genes.
(e)Insertion of foreign DNA here permits identification of
bacteria containing recombinant plasmids .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Explain why a probe designed to detect a gene encoding a particular amino acid sequence must usually consist of a mixture of different DNA sequences rather than only one sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Rank the following organisms in order from smallest genome (number of base pairs of DNA)to largest genome.
A)Human,fruit fly,E.coli bacterium
B)E)coli bacterium,human,fruit fly
C)E)coli bacterium,fruit fly,human
D)Fruit fly,E.coli bacterium,human
E)Fruit fly,human,E.coli bacterium
A)Human,fruit fly,E.coli bacterium
B)E)coli bacterium,human,fruit fly
C)E)coli bacterium,fruit fly,human
D)Fruit fly,E.coli bacterium,human
E)Fruit fly,human,E.coli bacterium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What sequences are required in an expression vector (for use with E.coli)that are not essential in a cloning plasmid?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What happens in PCR if you use DNA polymerase derived from E.coli instead of from a thermostable source?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Distinguish between protein function at the molecular,cellular,and phenotypic level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Name one enzyme that is always used to make a cDNA library but is generally not used to make a genomic DNA library.Describe its function briefly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is(are)the distinguishing feature(s)of a shuttle vector?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following methods is not used in linkage analysis?
A)Compare densely spaced polymorphisms.
B)Collect DNA from a family affected by the disease of interest.
C)Sequence selected parts of the genome.
D)Introduce retroviruses at the mutated locus.
E)Look for SNP variants.
A)Compare densely spaced polymorphisms.
B)Collect DNA from a family affected by the disease of interest.
C)Sequence selected parts of the genome.
D)Introduce retroviruses at the mutated locus.
E)Look for SNP variants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the essential difference between a genomic library and a cDNA library?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How does a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC)differ from a plasmid?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A plasmid that encodes resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline is digested with the restriction enzyme PstI,which cuts the plasmid at a single site in the ampicillin-resistance gene.The DNA is then annealed with a PstI digest of human DNA,ligated,and used to transform E.coli cells.
(a)What antibiotic would you put in an agar plate to ensure that the cells of a bacterial colony contain the plasmid?
(b)What antibiotic-resistance phenotypes will be found on the plate?
(c)Which phenotype will indicate the presence of plasmids that contain human DNA fragments?
(a)What antibiotic would you put in an agar plate to ensure that the cells of a bacterial colony contain the plasmid?
(b)What antibiotic-resistance phenotypes will be found on the plate?
(c)Which phenotype will indicate the presence of plasmids that contain human DNA fragments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Current estimates indicate that ________ % of the human genome is translated into protein.
A)less than 0.5%
B)roughly 1.5%
C)roughly 10%
D)roughly 25%
E)more than 50%
A)less than 0.5%
B)roughly 1.5%
C)roughly 10%
D)roughly 25%
E)more than 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which type of DNA sequence is not found in the human genome?
A)Long repetitive repeats
B)Introns
C)Retro-palindromes
D)Simple sequence repeats
E)Transposons
A)Long repetitive repeats
B)Introns
C)Retro-palindromes
D)Simple sequence repeats
E)Transposons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which would you expect to be larger,the percentage of the human genome that is translated into protein or the percentage of the genome of a bacterium that is translated into protein? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Briefly explain the procedure used in next-generation pyrosequencing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is a DNA microarray? How does it resemble and how does it differ from a DNA library?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain the importance of outgroups for understanding genomic lineages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
As the cost of sequencing your personal human genome rapidly approaches $1,000,consider the benefits and risks of having every fetus' DNA sequenced before birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



