Deck 7: Carbohydrates and Glycobiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Carbohydrates and Glycobiology
1
From the abbreviated name of the compound Gal( 1 4)Glc,we know that:
A)C-4 of glucose is joined to C-1 of galactose by a glycosidic bond.
B)the compound is a d-enantiomer.
C)the galactose residue is at the reducing end.
D)the glucose is in its pyranose form.
E)the glucose residue is the anomer.
A)C-4 of glucose is joined to C-1 of galactose by a glycosidic bond.
B)the compound is a d-enantiomer.
C)the galactose residue is at the reducing end.
D)the glucose is in its pyranose form.
E)the glucose residue is the anomer.
C-4 of glucose is joined to C-1 of galactose by a glycosidic bond.
2
Hemoglobin glycation is a process where is attached to hemoglobin.
A)glycerol;covalently
B)glucose;enzymatically
C)glucose;non-enzymatically
D)N-acetyl-galactosamine;enzymatically
E)galactose;non-enzymatically
A)glycerol;covalently
B)glucose;enzymatically
C)glucose;non-enzymatically
D)N-acetyl-galactosamine;enzymatically
E)galactose;non-enzymatically
glucose;non-enzymatically
3
When forming the disaccharide maltose from two glucose monosaccharides:
A)water is eliminated.
B)a hemiacetal is converted to an acetal.
C)the resulting dissacharide is no longer a reducing sugar.
D)Both A and B
E)A,B,and C above
A)water is eliminated.
B)a hemiacetal is converted to an acetal.
C)the resulting dissacharide is no longer a reducing sugar.
D)Both A and B
E)A,B,and C above
Both A and B
4
Following complete hydrolysis of a sample of glycogen and a sample of cellulose,which of the following must be true?
A)The glycogen sample is more soluble than the cellulose sample.
B)The cellulose sample is more soluble than the glycogen sample.
C)Both samples consist of a mixture of -d-glucose and -d-glucose.
D)The glycogen sample has a higher ratio of -d-glucose than the cellulose sample.
E)The cellulose sample contains only -d-glucose.
A)The glycogen sample is more soluble than the cellulose sample.
B)The cellulose sample is more soluble than the glycogen sample.
C)Both samples consist of a mixture of -d-glucose and -d-glucose.
D)The glycogen sample has a higher ratio of -d-glucose than the cellulose sample.
E)The cellulose sample contains only -d-glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an epimeric pair?
A)d-glucose and d-glucosamine
B)d-glucose and d-mannose
C)d-glucose and l-glucose
D)d-lactose and d-sucrose
E)l-mannose and l-fructose
A)d-glucose and d-glucosamine
B)d-glucose and d-mannose
C)d-glucose and l-glucose
D)d-lactose and d-sucrose
E)l-mannose and l-fructose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the linear form of glucose cyclizes,the product is a(n):
A)anhydride.
B)glycoside.
C)hemiacetal.
D)lactone.
E)oligosaccharide.
A)anhydride.
B)glycoside.
C)hemiacetal.
D)lactone.
E)oligosaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To possess optical activity,a compound must be:
A)a carbohydrate.
B)a hexose.
C)asymmetric.
D)colored.
E)D-glucose.
A)a carbohydrate.
B)a hexose.
C)asymmetric.
D)colored.
E)D-glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The reference compound for naming D and L isomers of sugars is:
A)fructose.
B)glucose.
C)glyceraldehyde.
D)ribose.
E)sucrose.
A)fructose.
B)glucose.
C)glyceraldehyde.
D)ribose.
E)sucrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following monosaccharides is not an aldose?
A)Erythrose
B)Fructose
C)Glucose
D)Glyceraldehyde
E)Ribose
A)Erythrose
B)Fructose
C)Glucose
D)Glyceraldehyde
E)Ribose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When two carbohydrates are epimers:
A)one is a pyranose,the other a furanose.
B)one is an aldose,the other a ketose.
C)they differ in length by one carbon.
D)they differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom.
E)they rotate plane-polarized light in the same direction.
A)one is a pyranose,the other a furanose.
B)one is an aldose,the other a ketose.
C)they differ in length by one carbon.
D)they differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom.
E)they rotate plane-polarized light in the same direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a reducing sugar?
A)Fructose
B)Glucose
C)Glyceraldehyde
D)Ribose
E)Sucrose
A)Fructose
B)Glucose
C)Glyceraldehyde
D)Ribose
E)Sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements about hydrogen bonding in glycogen and cellulose is true?
A)Glycogen forms more internal H-bonds than cellulose.
B)Extensive internal hydrogen bonding makes cellulose more water soluble than glycogen.
C)Extensive hydrogen bonding with water makes cellulose more soluble than glycogen.
D)Glycogen primarily forms hydrogen bonds within a single chain.
E)The hydrogen bonding in cellulose favors a helical conformation.
A)Glycogen forms more internal H-bonds than cellulose.
B)Extensive internal hydrogen bonding makes cellulose more water soluble than glycogen.
C)Extensive hydrogen bonding with water makes cellulose more soluble than glycogen.
D)Glycogen primarily forms hydrogen bonds within a single chain.
E)The hydrogen bonding in cellulose favors a helical conformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following monosaccharides is not a carboxylic acid?
A)6-Phospho-gluconate
B)Gluconate
C)Glucose
D)Glucuronate
E)Muramic acid
A)6-Phospho-gluconate
B)Gluconate
C)Glucose
D)Glucuronate
E)Muramic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The basic structure of a proteoglycan consists of a core protein and a:
A)glycolipid.
B)glycosaminoglycan.
C)lectin.
D)lipopolysaccharide.
E)peptidoglycan.
A)glycolipid.
B)glycosaminoglycan.
C)lectin.
D)lipopolysaccharide.
E)peptidoglycan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following pairs is interconverted in the process of mutarotation?
A)d-glucose and d-fructose
B)d-glucose and d-galactose
C)d-glucose and d-glucosamine
D)d-glucose and l-glucose
E)( -d-glucose and -d-glucose)
A)d-glucose and d-fructose
B)d-glucose and d-galactose
C)d-glucose and d-glucosamine
D)d-glucose and l-glucose
E)( -d-glucose and -d-glucose)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Starch and glycogen are both polymers of:
A)fructose.
B)glucose1-phosphate.
C)sucrose.
D)( -d-glucose.)
E)( -d-glucose.)
A)fructose.
B)glucose1-phosphate.
C)sucrose.
D)( -d-glucose.)
E)( -d-glucose.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a heteropolysaccharide?
A)Cellulose
B)Chitin
C)Glycogen
D)Hyaluronate
E)Starch
A)Cellulose
B)Chitin
C)Glycogen
D)Hyaluronate
E)Starch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements about starch and glycogen is false?
A)Amylose is unbranched;amylopectin and glycogen contain many ( 1 6)branches.
B)Both are homopolymers of glucose.
C)Both serve primarily as structural elements in cell walls.
D)Both starch and glycogen are stored intracellularly as insoluble granules.
E)Glycogen is more extensively branched than starch.
A)Amylose is unbranched;amylopectin and glycogen contain many ( 1 6)branches.
B)Both are homopolymers of glucose.
C)Both serve primarily as structural elements in cell walls.
D)Both starch and glycogen are stored intracellularly as insoluble granules.
E)Glycogen is more extensively branched than starch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
d-Glucose is called a reducing sugar because it undergoes an oxidation-reduction reaction at the anomeric carbon.One of the products of this reaction is:
A)d-galactose.
B)d-gluconate.
C)d-glucuronate.
D)d-ribose.
E)muramic acid.
A)d-galactose.
B)d-gluconate.
C)d-glucuronate.
D)d-ribose.
E)muramic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of following is an anomeric pair?
A)d-glucose and d-fructose
B)d-glucose and l-fructose
C)d-glucose and l-glucose
D)( -d-glucose and -d-glucose)
E)( -d-glucose and -l-glucose)
A)d-glucose and d-fructose
B)d-glucose and l-fructose
C)d-glucose and l-glucose
D)( -d-glucose and -d-glucose)
E)( -d-glucose and -l-glucose)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
(a)Define "reducing sugar."
(b)Show the reaction product of glucose after it is used as a reducing sugar.
(c)Explain why fructose is also considered a reducing sugar.(Hint: It must first undergo a chemical conversion. )
(d)Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose
(Glc( 1 2)Fru).Explain why sucrose is not a reducing sugar,even though both glucose and fructose are.
(b)Show the reaction product of glucose after it is used as a reducing sugar.
(c)Explain why fructose is also considered a reducing sugar.(Hint: It must first undergo a chemical conversion. )
(d)Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose
(Glc( 1 2)Fru).Explain why sucrose is not a reducing sugar,even though both glucose and fructose are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements concerning sialic acid residues on glycoproteins is true?
A)Sialic residues on erythrocytes are recognized by lectins,leading to removal of the erythrocytes.
B)Sialic residues on ceruloplasmin are recognized by lectins,leading to removal of ceruloplasmin.
C)Sialic residues are removed by neuraminidases.
D)The anti-viral drug oseltamavir accelerates the removal of sialic acid residues.
E)Both A and B above
A)Sialic residues on erythrocytes are recognized by lectins,leading to removal of the erythrocytes.
B)Sialic residues on ceruloplasmin are recognized by lectins,leading to removal of ceruloplasmin.
C)Sialic residues are removed by neuraminidases.
D)The anti-viral drug oseltamavir accelerates the removal of sialic acid residues.
E)Both A and B above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The biochemical property of lectins that is the basis for most of their biological effects is their ability to bind to:
A)amphipathic molecules.
B)hydrophobic molecules.
C)specific lipids.
D)specific oligosaccharides.
E)specific peptides.
A)amphipathic molecules.
B)hydrophobic molecules.
C)specific lipids.
D)specific oligosaccharides.
E)specific peptides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In glycoproteins, the carbohydrate moiety is always attached through the amino acid residues:
A)asparagine,serine,or threonine.
B)aspartate or glutamate.
C)glutamine or arginine.
D)glycine,alanine,or aspartate.
E)tryptophan,aspartate,or cysteine.
A)asparagine,serine,or threonine.
B)aspartate or glutamate.
C)glutamine or arginine.
D)glycine,alanine,or aspartate.
E)tryptophan,aspartate,or cysteine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Why is it surprising that the side chains of tryptophan residues in lectins can interact with sugars?
A)Because the side chain of tryptophan is hydrophilic and sugars are hydrophobic
B)Because the side chain of tryptophan is (-)charged and sugars are generally (+)charged or neutral
C)Because the side chain of tryptophan can make hydrogen bonds and sugars cannot.
D)Because the side chain of tryptophan is hydrophobic and sugars are generally hydrophilic
E)None of the above
A)Because the side chain of tryptophan is hydrophilic and sugars are hydrophobic
B)Because the side chain of tryptophan is (-)charged and sugars are generally (+)charged or neutral
C)Because the side chain of tryptophan can make hydrogen bonds and sugars cannot.
D)Because the side chain of tryptophan is hydrophobic and sugars are generally hydrophilic
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is not a reason that it is difficult to study oligosaccharide composition from biological systems?
A)Oligosaccharides are often branched.
B)Oligosaccharides often have a high negative charge density.
C)Oligosaccharides have a variety of linkages .
D)Oligosaccharides have too much conformational flexibility.
E)There are no specific glycosidase enzymes that can be used to selectively digest oligosaccharides.
A)Oligosaccharides are often branched.
B)Oligosaccharides often have a high negative charge density.
C)Oligosaccharides have a variety of linkages .
D)Oligosaccharides have too much conformational flexibility.
E)There are no specific glycosidase enzymes that can be used to selectively digest oligosaccharides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements about heparan sulfate is not true?
A)Sulfation of heparan sulfate to form NS domains is important for its role as an anti-coagulant.
B)Heparan sulfate can promote protein-protein interactions via the NS domains.
C)The secondary structure of heparan sulfate is completely random.
D)The NA domains of heparan sulfate contain no sulfation.
E)The core repeating structure of heparan sulfate is made up of alternating GlcNAc and GlcA.
A)Sulfation of heparan sulfate to form NS domains is important for its role as an anti-coagulant.
B)Heparan sulfate can promote protein-protein interactions via the NS domains.
C)The secondary structure of heparan sulfate is completely random.
D)The NA domains of heparan sulfate contain no sulfation.
E)The core repeating structure of heparan sulfate is made up of alternating GlcNAc and GlcA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Define each in 20 words or fewer:
(a)anomeric carbon
(b)enantiomers
(c)furanose
(d)pyranose
(e)glycoside
(f)epimers
(g)aldose
(h)ketose
(a)anomeric carbon
(b)enantiomers
(c)furanose
(d)pyranose
(e)glycoside
(f)epimers
(g)aldose
(h)ketose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The number of structurally different polysaccharides that can be made with 20 different monosaccharides is far greater than the number of different polypeptides that can be made with 20 different amino acids if both polymers contain an equal number (say 100)of total residues.Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Categorize each of the following as an aldose,a ketose,or neither. 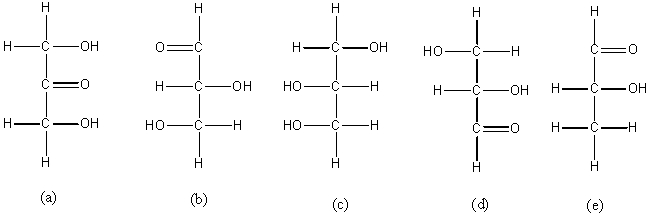


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following techniques is not commonly used to study oligosaccharide structures?
A)X-ray crystallography
B)Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectroscopy (MALDI-MS)
C)Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
D)Complete chemical synthesis
E)Oligosaccharide microarrays
A)X-ray crystallography
B)Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectroscopy (MALDI-MS)
C)Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
D)Complete chemical synthesis
E)Oligosaccharide microarrays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the following structure: 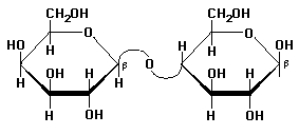 (a)How many of the monosaccharide units are furanoses and how may are pyranoses?
(a)How many of the monosaccharide units are furanoses and how may are pyranoses?
(b)What is the linkage between the two monosaccharide units?
(c)Is this a reducing sugar?
 (a)How many of the monosaccharide units are furanoses and how may are pyranoses?
(a)How many of the monosaccharide units are furanoses and how may are pyranoses? (b)What is the linkage between the two monosaccharide units?
(c)Is this a reducing sugar?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
This compound is l-glyceraldehyde.Draw a stereochemically correct representation of C-1 and C-2 of d-glucose.
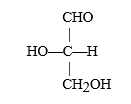


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Explain why all mono- and disaccharides are soluble in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is a dominant feature of the outer membrane of the cell wall of gram negative bacteria?
A)Amylose
B)Cellulose
C)Glycoproteins
D)Lipopolysaccharides
E)Lipoproteins
A)Amylose
B)Cellulose
C)Glycoproteins
D)Lipopolysaccharides
E)Lipoproteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Explain how it is possible that a polysaccharide molecule,such as glycogen,may have only one reducing end,and yet have many nonreducing ends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Describe one biological advantage of storing glucose units in branched polymers (glycogen,amylopectin)rather than in linear polymers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
(a)Draw the structures of both anomers of glucose in the pyranose ring form.
(b)How many asymmetric carbons (chiral centers)does each of these structures have?
(c)How many stereoisomers of the glucose are theoretically possible?
(b)How many asymmetric carbons (chiral centers)does each of these structures have?
(c)How many stereoisomers of the glucose are theoretically possible?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Match these molecules with their biological roles.
(a)glycogen __ viscosity,lubrication of extracellular secretions
(b)starch __ carbohydrate storage in plants
(c)trehalose __ transport/storage in insects
(d)chitin __ exoskeleton of insects
(e)cellulose __ structural component of bacterial cell wall
(f)peptidoglycan __ structural component of plant cell walls
(g)hyaluronate __ extracellular matrix of animal tissues
(h)proteoglycan __ carbohydrate storage in animal liver
(a)glycogen __ viscosity,lubrication of extracellular secretions
(b)starch __ carbohydrate storage in plants
(c)trehalose __ transport/storage in insects
(d)chitin __ exoskeleton of insects
(e)cellulose __ structural component of bacterial cell wall
(f)peptidoglycan __ structural component of plant cell walls
(g)hyaluronate __ extracellular matrix of animal tissues
(h)proteoglycan __ carbohydrate storage in animal liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In measuring long-term glucose levels in the bloodstream,glycated hemoglobin must be separated from unmodified hemoglobin to determine the percentage of glycated hemoglobin.Suggest a simple chromatographic method by which this separation can be performed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Identify all the epimeric pairs in the structures shown below. 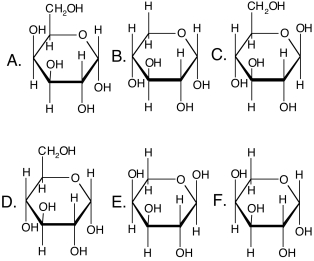


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Briefly explain the procedure involved in using an oligosaccharide microarray to identify the binding specificity for a potential lectin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe the process by which "old" serum glycoproteins are removed from the mammalian circulatory system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sketch the principal components of a typical proteoglycan,showing their relationships and connections to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How do oligosaccharide portions of glycoproteins change the properties of the proteins?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What are lectins? What are some biological processes that involve lectins?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the structure of a proteoglycan aggregate such as is found in the extracellular matrix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the biological advantage to an organism that stores its carbohydrate reserves as starch or glycogen rather than as an equivalent amount of free glucose?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain in molecular terms why humans cannot use cellulose as a nutrient,but goats and cattle can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Briefly explain how the drugs Tamiflu and Relenza work to prevent the flu.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Draw the structure of the repeating basic unit of (a)amylose and (b)cellulose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Describe the differences between a proteoglycan and a glycoprotein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The glycosaminoglycans are negatively charged at neutral pH.What components of these polymers confer the negative charge?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



