Deck 15: International Trade Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/200
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: International Trade Policy
1
The United States decides to follow its comparative advantage and specialize in the production of airplanes. Which of the following will occur?
A) More airplanes will be produced in the United States.
B) There will be no change in the price of airplanes in the United States.
C) The world price of airplanes will increase.
D) The quantity of airplanes demanded in the United States will increase.
A) More airplanes will be produced in the United States.
B) There will be no change in the price of airplanes in the United States.
C) The world price of airplanes will increase.
D) The quantity of airplanes demanded in the United States will increase.
More airplanes will be produced in the United States.
2
The fundamental force that drives international trade is
A) absolute advantage.
B) comparative advantage.
C) law of diminishing returns.
D) law of increasing costs.
A) absolute advantage.
B) comparative advantage.
C) law of diminishing returns.
D) law of increasing costs.
comparative advantage.
3
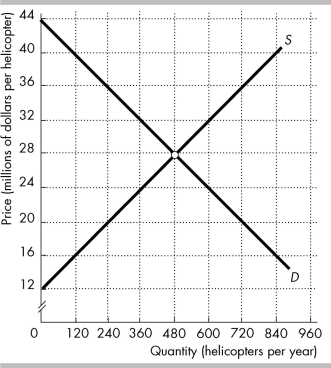
The figure shows the market for helicopters in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The United States trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In the figure above, with international trade U.S. companies buy ________ helicopters per year.
A) 240
B) 480
C) 720
D) 360
240
4
Based on the table below, at what world price would the country import the good?
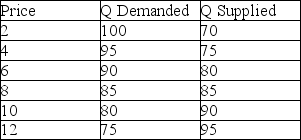
A) all prices below $8
B) at exactly $8
C) all prices above $8
D) it is impossible to say from the information given

A) all prices below $8
B) at exactly $8
C) all prices above $8
D) it is impossible to say from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A country specializes in the production of goods for which it has a comparative advantage. We find that
A) some producers and consumers win, some lose, but overall the gains exceed the losses.
B) all producers win.
C) all consumers win.
D) producers win, consumers lose, but overall the gains exceed the losses.
A) some producers and consumers win, some lose, but overall the gains exceed the losses.
B) all producers win.
C) all consumers win.
D) producers win, consumers lose, but overall the gains exceed the losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a market open to international trade, at the world price the quantity demanded is 150 and quantity supplied is 200. This country will
A) export 50 units.
B) import 50 units.
C) export 200 units.
D) import 150 units.
A) export 50 units.
B) import 50 units.
C) export 200 units.
D) import 150 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider a market that, with no international trade, is initially in equilibrium with quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied at a price of $20. If the world price of the good is $10 and the country opens up to international trade then in this market
A) imports will increase, price will fall, and quantity supplied will fall.
B) exports will increase, price will be unchanged, and quantity supplied will increase.
C) imports will increase, price will decrease, and the supply curve will shift to the left.
D) quantity demanded will decrease, quantity supplied will decrease, and price will decrease.
A) imports will increase, price will fall, and quantity supplied will fall.
B) exports will increase, price will be unchanged, and quantity supplied will increase.
C) imports will increase, price will decrease, and the supply curve will shift to the left.
D) quantity demanded will decrease, quantity supplied will decrease, and price will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Comparative advantage implies that a country will
A) import those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
B) export those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
C) import those goods in which the country has an absolute advantage compared to its trading partner.
D) export those goods in which the country has an absolute advantage compared to its trading partner.
A) import those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
B) export those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
C) import those goods in which the country has an absolute advantage compared to its trading partner.
D) export those goods in which the country has an absolute advantage compared to its trading partner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The fundamental force that drives international trade is
A) comparative advantage.
B) absolute advantage.
C) countries' desire to increase their trade surplus.
D) cheap labor in countries like China or India.
A) comparative advantage.
B) absolute advantage.
C) countries' desire to increase their trade surplus.
D) cheap labor in countries like China or India.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Who benefits from imports?
A) domestic consumers
B) domestic producers
C) foreign consumers
D) domestic workers in the industry
A) domestic consumers
B) domestic producers
C) foreign consumers
D) domestic workers in the industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider a market that sells some of its goods as exports. Who does NOT benefit?
A) domestic consumers
B) domestic producers
C) workers in the industry
D) foreign consumers
A) domestic consumers
B) domestic producers
C) workers in the industry
D) foreign consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
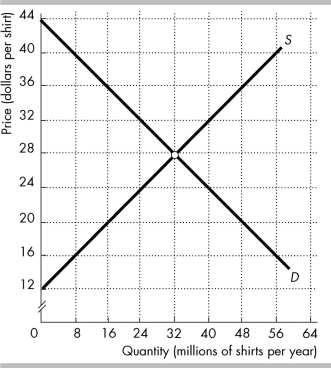
The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In the figure above, with international trade Americans buy ________ million shirts per year.
A) 48
B) 32
C) 16
D) 24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In the figure above, with international trade the United States ________ million shirts per year.
A) imports 32
B) imports 48
C) exports 16
D) exports 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Based on the table below, at what world price would the country export?
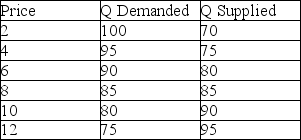
A) all prices above $8
B) at only $8
C) all prices below $8
D) It is impossible to say from the information given.

A) all prices above $8
B) at only $8
C) all prices below $8
D) It is impossible to say from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Prior to international trade, if country A has a lower price of good X than does country B, then we know definitely that
A) country B has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
B) country B has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.
C) country A has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
D) country A has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.
A) country B has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
B) country B has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.
C) country A has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
D) country A has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose the world price of a good is $4. Based on the table below, the country will
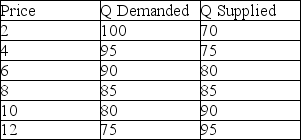
A) import 20 units.
B) export 20 units.
C) import 10 units.
D) export 10 units.

A) import 20 units.
B) export 20 units.
C) import 10 units.
D) export 10 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Comparative advantage implies that a country will
A) import those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
B) export those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
C) find it difficult to conclude free trade agreements with other nations.
D) export goods produced by domestic industries with low wages relative to its trading partners.
A) import those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
B) export those goods in which the country has a comparative advantage.
C) find it difficult to conclude free trade agreements with other nations.
D) export goods produced by domestic industries with low wages relative to its trading partners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When the principle of comparative advantage is used to guide trade, then a country will specialize by producing only
A) goods with the highest opportunity cost.
B) goods with the lowest opportunity costs.
C) goods for which production takes fewer worker-hour than another country.
D) goods for which production costs are more than average total costs.
A) goods with the highest opportunity cost.
B) goods with the lowest opportunity costs.
C) goods for which production takes fewer worker-hour than another country.
D) goods for which production costs are more than average total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In the figure above, with international trade ________ million shirts per year are produced in the United States.
A) 48
B) 32
C) 16
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

The figure shows the market for helicopters in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The United States trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In the figure above, with international trade ________ helicopters per year are produced in the United States.
A) 360
B) 480
C) 720
D) 240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The United States has a comparative advantage in producing cotton if the U.S. price of cotton before international trade is ________ the world price.
A) less than
B) equal to
C) greater than
D) not comparable to
A) less than
B) equal to
C) greater than
D) not comparable to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

The figure shows the market for helicopters in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The United States trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In the figure above, the United States ________ helicopters per year.
A) exports 480
B) exports 720
C) imports 480
D) imports 240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A tariff imposed by the United States on Japanese cars ________ the price of cars in the United States and ________ the quantity of Japanese cars imported into the United States.
A) raises; increases
B) raises; decreases
C) lowers; increases
D) lowers; decreases
A) raises; increases
B) raises; decreases
C) lowers; increases
D) lowers; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A tariff is
A) a licensing regulation that limits imports.
B) a tax on an exported good.
C) a tax on an imported good.
D) an agreement to restrict the volume of exports.
A) a licensing regulation that limits imports.
B) a tax on an exported good.
C) a tax on an imported good.
D) an agreement to restrict the volume of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Tariffs and import quotas both result in
A) lower levels of domestic production.
B) the domestic government gaining revenue.
C) lower levels of imports.
D) higher levels of domestic consumption.
A) lower levels of domestic production.
B) the domestic government gaining revenue.
C) lower levels of imports.
D) higher levels of domestic consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A tariff ________ the quantity of the good imported and ________ the domestic price of the imported good.
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; lowers
D) does not change; increases
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; lowers
D) does not change; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a country imposes a tariff on an imported good, the tariff ________ the price in the importing country and ________ the quantity of imports.
A) raises; decreases
B) raises; increases
C) raises; does not change
D) lowers; does not change
A) raises; decreases
B) raises; increases
C) raises; does not change
D) lowers; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Compared to the situation before international trade, after the United States exports a good , then production in the United States ________ and consumption in the United States ________.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose the country of Atlantica imposes a tariff on foreign-produced cars. As a result of the tariff
A) tariff revenue collected by the government in the Atlantica increases.
B) there is an increase in the number of imported cars.
C) the gains from trade rise.
D) there are more efficient trade agreements between Atlantica and its trade partners.
A) tariff revenue collected by the government in the Atlantica increases.
B) there is an increase in the number of imported cars.
C) the gains from trade rise.
D) there are more efficient trade agreements between Atlantica and its trade partners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements concerning tariffs is NOT true?
A) A tariff results in a loss for domestic consumers of the good.
B) A tariff creates revenue for the government.
C) A tariff decreases international trade.
D) A tariff leaves the price of imports unchanged.
A) A tariff results in a loss for domestic consumers of the good.
B) A tariff creates revenue for the government.
C) A tariff decreases international trade.
D) A tariff leaves the price of imports unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Tariffs and import quotas differ in that
A) one is a form of trade restriction, while the other is not.
B) one is a tax, while the other is a limit in quantity.
C) one is imposed by the government, while the other is imposed by the private sector.
D) one is legal, while the other is not.
A) one is a form of trade restriction, while the other is not.
B) one is a tax, while the other is a limit in quantity.
C) one is imposed by the government, while the other is imposed by the private sector.
D) one is legal, while the other is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the United States imposes a tariff on imported cars, the
A) U.S. demand curve shifts rightward.
B) U.S. demand curve shifts leftward.
C) U.S. supply curve shifts rightward.
D) price in the United States rises but neither the U.S. demand curve nor the U.S. supply curve shift.
A) U.S. demand curve shifts rightward.
B) U.S. demand curve shifts leftward.
C) U.S. supply curve shifts rightward.
D) price in the United States rises but neither the U.S. demand curve nor the U.S. supply curve shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A tariff is a
A) tax on an exported good or service.
B) tax on an imported good or service.
C) subsidy on an exported good.
D) subsidy on an imported good.
A) tax on an exported good or service.
B) tax on an imported good or service.
C) subsidy on an exported good.
D) subsidy on an imported good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements about U.S. international trade in 2013 is CORRECT?
A) The value of U.S. exports exceeded the value of U.S. imports.
B) The value of U.S. exports was about 33 percent of the value of total U.S. production.
C) The United States imported only goods.
D) The United States was the world's largest trader.
A) The value of U.S. exports exceeded the value of U.S. imports.
B) The value of U.S. exports was about 33 percent of the value of total U.S. production.
C) The United States imported only goods.
D) The United States was the world's largest trader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A tariff
A) is a tax imposed on imported goods.
B) is a tax imposed on exported goods.
C) encourages worldwide specialization according to the principle of comparative advantage.
D) has no effect on prices paid by domestic consumers even though it increases the revenue collected by domestic producers.
A) is a tax imposed on imported goods.
B) is a tax imposed on exported goods.
C) encourages worldwide specialization according to the principle of comparative advantage.
D) has no effect on prices paid by domestic consumers even though it increases the revenue collected by domestic producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A tax that is imposed by the importing country when an imported good crosses its international boundary is called
A) an import quota.
B) dumping.
C) a voluntary export restraint.
D) a tariff.
A) an import quota.
B) dumping.
C) a voluntary export restraint.
D) a tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a tariff is imposed, the price paid by domestic consumers will ________ and the amount imported will ________.
A) increase; decrease
B) increase; not change
C) not change; increase
D) increase; increase
A) increase; decrease
B) increase; not change
C) not change; increase
D) increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the United States imposes a tariff of $1 per imported shirt, the higher tariff
A) raises the price of a shirt to U.S. consumers.
B) benefits U.S. shirt consumers.
C) increases imports of shirts into the United States.
D) none of the above.
A) raises the price of a shirt to U.S. consumers.
B) benefits U.S. shirt consumers.
C) increases imports of shirts into the United States.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Compared to the situation before international trade, after the United States imports a good, then production in the United States ________ and consumption in the United States ________.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A major purpose of tariffs is to
A) encourage imports.
B) encourage exports.
C) discourage imports.
D) discourage exports.
A) encourage imports.
B) encourage exports.
C) discourage imports.
D) discourage exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
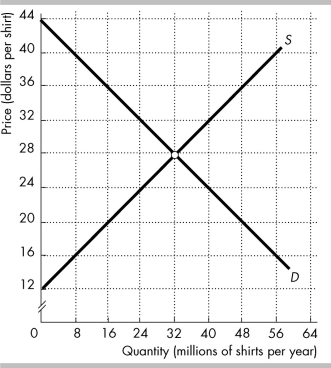
The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. The United States imposes a tariff on imported shirts, $4 per shirt.
In the figure above, the tariff ________ U.S. imports of shirts by ________ million shirts per year.
A) decreases; 16
B) decreases; 8
C) increases; 8
D) increases; 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In 2013 the United States was considering imposing a tariff on solar panels imported from China. Which of the following groups would gain from this tariff?
I. U.S. consumers of solar panels
II. U.S. producers of solar panels
III. Chinese producers of solar panels
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II only
D) I and III only
I. U.S. consumers of solar panels
II. U.S. producers of solar panels
III. Chinese producers of solar panels
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II only
D) I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In 2013 the United States reduced the tariff on ethanol. This tariff reduction ________ the U.S. production of ethanol and ________ the total U.S. consumption of ethanol.
A) increased; increased
B) increased; decreased
C) decreased; increased
D) decreased; decreased
A) increased; increased
B) increased; decreased
C) decreased; increased
D) decreased; decreased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Tariffs
A) generate revenue for consumers.
B) generate revenue for the government.
C) encourage domestic consumers to buy more imports.
D) encourage domestic producers to produce less.
A) generate revenue for consumers.
B) generate revenue for the government.
C) encourage domestic consumers to buy more imports.
D) encourage domestic producers to produce less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Reducing a tariff will ________ the domestic production of the good and ________ the total domestic consumption of the good.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46

The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. The United States imposes a tariff on imported shirts, $4 per shirt.
In the figure above, the U.S. government's revenue from the tariff is ________.
A) $64 million
B) $32 million
C) $128 million
D) $48 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. The United States imposes a tariff on imported shirts, $4 per shirt.
In the figure above, with the tariff Americans buy ________ million shirts per year.
A) 40
B) 48
C) 32
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A tariff is imposed on a good. The tariff will ________ quantity supplied, ________ quantity demanded, and ________ the price of the good in the home country.
A) increase; decrease; increase
B) increase; leave unchanged; leave unchanged
C) increase; increase; increase
D) increase; decrease; decrease
A) increase; decrease; increase
B) increase; leave unchanged; leave unchanged
C) increase; increase; increase
D) increase; decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. The United States imposes a tariff on imported shirts, $4 per shirt.
In the figure above, the tariff ________ the domestic production of shirts in the United States by ________ per year.
A) increases; 8 million
B) decreases; 16 million
C) increases; 4 million
D) decreases; 8 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the United States imposes a tariff on imported steel, the tariff will
A) raise the U.S. price of imported steel.
B) decrease the U.S. production of steel.
C) increase the total U.S. consumption of steel.
D) decrease employment in the U.S. steel industry.
A) raise the U.S. price of imported steel.
B) decrease the U.S. production of steel.
C) increase the total U.S. consumption of steel.
D) decrease employment in the U.S. steel industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Increasing a tariff will ________ the domestic quantity consumed of the good, while ________ the domestic production of the good.
A) increase; increasing
B) increase; decreasing
C) decrease; increasing
D) decrease; decreasing
A) increase; increasing
B) increase; decreasing
C) decrease; increasing
D) decrease; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Lowering the tariff on good X will
A) increase domestic employment in industry X.
B) increase the domestic imports of good X.
C) increase the domestic price of good X.
D) have no effect unless the nation's trading partner also lowers its tariff on good X.
A) increase domestic employment in industry X.
B) increase the domestic imports of good X.
C) increase the domestic price of good X.
D) have no effect unless the nation's trading partner also lowers its tariff on good X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose the country of Mooland imposes tariffs on imported beef from the country of Aqualand. As a result of the tariffs, the
A) price of beef in Mooland falls.
B) quantity of beef exported by Mooland increases.
C) quantity of beef imported by Mooland decreases.
D) quantity of beef imported by Mooland increases.
A) price of beef in Mooland falls.
B) quantity of beef exported by Mooland increases.
C) quantity of beef imported by Mooland decreases.
D) quantity of beef imported by Mooland increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The United States imports cars from Japan. If the United States imposes a tariff on cars imported from Japan, American
A) consumers will lose and Japanese producers will gain.
B) tariff revenue will equal the loss inflicted on American consumers.
C) consumers will lose and American producers will gain.
D) car manufacturers will gain revenue equal to the revenue lost by Japanese car manufacturers.
A) consumers will lose and Japanese producers will gain.
B) tariff revenue will equal the loss inflicted on American consumers.
C) consumers will lose and American producers will gain.
D) car manufacturers will gain revenue equal to the revenue lost by Japanese car manufacturers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
During the Great Depression in the 1930s, the average tariff level in the United States peaked at about
A) zero.
B) 6 percent.
C) 20 percent.
D) 100 percent.
A) zero.
B) 6 percent.
C) 20 percent.
D) 100 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Average tariff levels in the United States in the last decade are
A) about equal to the average since 1930.
B) above the average since 1930.
C) positive, but below the average since 1930.
D) zero, as there are no longer any tariffs in the United States.
A) about equal to the average since 1930.
B) above the average since 1930.
C) positive, but below the average since 1930.
D) zero, as there are no longer any tariffs in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A U.S. tariff on textiles would ________ U.S. prices on clothing and ________ the number of jobs in the U.S. textile industry.
A) reduce; decrease
B) reduce; increase
C) raise; decrease
D) raise; increase
A) reduce; decrease
B) reduce; increase
C) raise; decrease
D) raise; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58

The figure shows the market for shirts in the United States, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. The United States imposes a tariff on imported shirts, $4 per shirt.
In the figure above, with the tariff the United States imports ________ million shirts per year.
A) 24
B) 8
C) 32
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In 2013 the United States reduced the tariff on ethanol. The winners from the tariff reduction are
A) U.S. producers and the U.S. government.
B) U.S. producers only.
C) U.S. consumers only.
D) U.S. consumers, U.S. producers, and the U.S. government.
A) U.S. producers and the U.S. government.
B) U.S. producers only.
C) U.S. consumers only.
D) U.S. consumers, U.S. producers, and the U.S. government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The winners from a tariff on imports are
A) producers and government.
B) producers.
C) consumers.
D) consumers, producers, and government.
A) producers and government.
B) producers.
C) consumers.
D) consumers, producers, and government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following best describes the history of tariffs in the United States over the past 70 years?
A) Tariffs were at their highest level in the 1970s and now average just over 10 percent.
B) Tariffs have declined overall since the early 1930s and now average just over 10 percent.
C) Tariffs reached a maximum in the early 1930s and now average less than 5 percent.
D) Average tariff rates have not changed much since the early 1930s and are less than 5 percent.
A) Tariffs were at their highest level in the 1970s and now average just over 10 percent.
B) Tariffs have declined overall since the early 1930s and now average just over 10 percent.
C) Tariffs reached a maximum in the early 1930s and now average less than 5 percent.
D) Average tariff rates have not changed much since the early 1930s and are less than 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An import quota directly restricts ________ and are designed to protect domestic ________.
A) exports; consumers
B) exports; producers
C) imports; consumers
D) imports; producers
A) exports; consumers
B) exports; producers
C) imports; consumers
D) imports; producers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The U.S. government limits the amount of sugar that can be imported into the United States. This policy is
A) an import quota.
B) a tariff.
C) a comparative advantage limitation.
D) None of the above answers are correct.
A) an import quota.
B) a tariff.
C) a comparative advantage limitation.
D) None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Smoot-Hawley Act
A) made most tariffs illegal.
B) greatly raised tariffs.
C) gave the President the right to broker trade deals with other nations.
D) recognized Congress's right to deny trade authorization powers to the President.
A) made most tariffs illegal.
B) greatly raised tariffs.
C) gave the President the right to broker trade deals with other nations.
D) recognized Congress's right to deny trade authorization powers to the President.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
U.S. tariffs peaked in
A) 1992.
B) 1961.
C) 1940.
D) 1933.
A) 1992.
B) 1961.
C) 1940.
D) 1933.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The effect of an import quota is to
A) increase the supply of the good and lower its price.
B) increase the supply of the good and increase its price.
C) increase the demand for the good and increase its price.
D) decrease the supply of the good and raise its price.
A) increase the supply of the good and lower its price.
B) increase the supply of the good and increase its price.
C) increase the demand for the good and increase its price.
D) decrease the supply of the good and raise its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
An import quota specifies the
A) highest price that can be charged for an imported good.
B) per unit tax that must be paid on an imported good.
C) maximum quantity of a good that may be imported during a specified time period.
D) minimum quantity of a good that must be exported during a specified time period.
A) highest price that can be charged for an imported good.
B) per unit tax that must be paid on an imported good.
C) maximum quantity of a good that may be imported during a specified time period.
D) minimum quantity of a good that must be exported during a specified time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The U.S. government imposes an import quota on sugar. This import quota helps ________ and harms ________.
A) U.S. producers of sugar; U.S. consumers of sugar
B) U.S. producers of sugar; the U.S. government
C) the U.S. government; U.S. consumers of sugar
D) U.S. consumers of sugar; U.S. producers of sugar
A) U.S. producers of sugar; U.S. consumers of sugar
B) U.S. producers of sugar; the U.S. government
C) the U.S. government; U.S. consumers of sugar
D) U.S. consumers of sugar; U.S. producers of sugar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Import quotas ________ the price of imported goods and ________ the quantity consumed in the nation imposing the quota.
A) raise; increase
B) raise; decrease
C) lower; increase
D) lower; decrease
A) raise; increase
B) raise; decrease
C) lower; increase
D) lower; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An import quota is
A) a tariff that is a fixed percentage of the price of a good.
B) a tariff that is a fixed dollar amount per unit of a good.
C) an agreed upon price for a good to be imported at a specified future date.
D) a restriction that specifies the maximum amount of a good that may be imported.
A) a tariff that is a fixed percentage of the price of a good.
B) a tariff that is a fixed dollar amount per unit of a good.
C) an agreed upon price for a good to be imported at a specified future date.
D) a restriction that specifies the maximum amount of a good that may be imported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An import quota is a
A) tariff imposed on goods that are dumped in the country.
B) law that prevents ecologically damaging goods from being imported into a country.
C) market-imposed balancing factor that keeps prices of imports and exports in equilibrium.
D) government-imposed restriction on the quantity of a specific good that can be imported.
A) tariff imposed on goods that are dumped in the country.
B) law that prevents ecologically damaging goods from being imported into a country.
C) market-imposed balancing factor that keeps prices of imports and exports in equilibrium.
D) government-imposed restriction on the quantity of a specific good that can be imported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An import quota protects domestic producers by
A) setting a limit on the amount of imports.
B) placing a prohibitive tax on imports.
C) encouraging competition among domestic producers.
D) increasing the total supply of the product.
A) setting a limit on the amount of imports.
B) placing a prohibitive tax on imports.
C) encouraging competition among domestic producers.
D) increasing the total supply of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The Smoot-Hawley Act was enacted in
A) 1980.
B) 2000.
C) 1930.
D) 1950.
A) 1980.
B) 2000.
C) 1930.
D) 1950.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Import quotas
A) encourage freer trade.
B) are a tax on an imported good.
C) set the number of units of a good that can be imported.
D) set the minimum percentage of the value of a good that can consist of imported components.
A) encourage freer trade.
B) are a tax on an imported good.
C) set the number of units of a good that can be imported.
D) set the minimum percentage of the value of a good that can consist of imported components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Of the following, in which decade were U.S. tariffs at their lowest level?
A) 2000s
B) 1970s
C) 1950s
D) 1930s
A) 2000s
B) 1970s
C) 1950s
D) 1930s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Import quotas
A) are the same as tariffs.
B) set the maximum number of units of a good that can be imported.
C) are not used by the United States.
D) set the minimum percentage of the value of a product that must consist of imported components.
A) are the same as tariffs.
B) set the maximum number of units of a good that can be imported.
C) are not used by the United States.
D) set the minimum percentage of the value of a product that must consist of imported components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The Smoot-Hawley Act introduced
A) opportunities for expanding U.S. foreign trade.
B) the highest tariffs set by the United States in the last 80 years.
C) a framework promoting international free trade.
D) revenue tariffs as a major source of U.S. government revenues.
A) opportunities for expanding U.S. foreign trade.
B) the highest tariffs set by the United States in the last 80 years.
C) a framework promoting international free trade.
D) revenue tariffs as a major source of U.S. government revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Since the 1930s, tariff levels in the United States have
A) declined overall.
B) steadily risen.
C) increased during expansions.
D) decreased during recessions.
A) declined overall.
B) steadily risen.
C) increased during expansions.
D) decreased during recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In 2012 the United States government tightened the import quota on sugar by decreasing the quantity of sugar that could be imported. Which of the following groups would gain from this change?
I.U.S. consumers of sugar
II.U.S. producers of sugar
III.Foreign producers of sugar
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II only
D) I and III only
I.U.S. consumers of sugar
II.U.S. producers of sugar
III.Foreign producers of sugar
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II only
D) I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The current U.S. average tariff rate
A) less than 5 percent.
B) greater than 10 percent.
C) approximately 20 percent.
D) over 50 percent.
A) less than 5 percent.
B) greater than 10 percent.
C) approximately 20 percent.
D) over 50 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



