Deck 2: Describing Data: Frequency Distributions and Graphic Presentations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Describing Data: Frequency Distributions and Graphic Presentations
1
A pie chart shows the relative frequency in each class.
True
2
A suggested class interval can be determined by the formula: 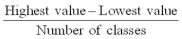
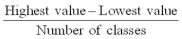
True
3
When constructing a frequency distribution,try to include overlapping stated class limits,such as 100 up to 201,200 up to 301,and 300 up to 401.
False
4
When a frequency distribution is exhaustive,each individual,object,or measurement from a sample or population must appear in at least one category.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A pie chart shows the number of observations in each class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
To construct a histogram,the class frequencies are plotted on the vertical or Y-axis and either the stated limits,the true limits or the midpoints are plotted on the horizontal or X-axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A frequency distribution for qualitative data shows the number of observations in each class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A frequency distribution for quantitative data has class limits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In constructing a frequency distribution,you should try to have open-ended classes such as "Under $100" and "$1,000 and over".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A frequency distribution for qualitative data has class limits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
To construct a pie chart,relative class frequencies are used to graph the "slices" of the pie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In frequency distributions,classes are mutually exclusive if each individual,object,or measurement is included in only one category.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To summarize the gender of students attending a college,the number of classes in a frequency distribution depends on the number of students.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
To convert a frequency distribution to a relative frequency distribution,divide each class frequency by the sum of the class frequencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A class interval,which is the width of a class,can be determined by subtracting the lower limit of a class from the lower limit of the next higher class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A pie chart is similar to a relative frequency distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
To summarize the gender of students attending a college,a frequency distribution groups data into two classes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The midpoint of a class,which is also called a class mark,is halfway between the lower and upper limits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To convert a frequency distribution to a relative frequency distribution,divide each class frequency by the number of classes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A frequency distribution groups data into classes showing the number of observations in each class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For quantitative data,the relative frequency for a class is computed as the
A)class width divided by class interval.
B)class midpoint divided by the class frequency.
C)class frequency divided by the class interval.
D)class frequency divided by the total frequency.
A)class width divided by class interval.
B)class midpoint divided by the class frequency.
C)class frequency divided by the class interval.
D)class frequency divided by the total frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A student was interested in the cigarette smoking habits of college students and collected data from an unbiased random sample of students.The data is summarized in the following table: 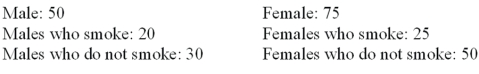 Why is the table NOT a frequency distribution?
Why is the table NOT a frequency distribution?
A)The number of males does not equal the sum of males that smoke and do not smoke.
B)The classes are not mutually exclusive.
C)There are too many classes.
D)Class limits cannot be computed.
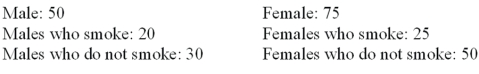 Why is the table NOT a frequency distribution?
Why is the table NOT a frequency distribution?A)The number of males does not equal the sum of males that smoke and do not smoke.
B)The classes are not mutually exclusive.
C)There are too many classes.
D)Class limits cannot be computed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The monthly salaries of a sample of 100 employees were rounded to the nearest ten dollars.They ranged from a low of $1,040 to a high of $1,720.If we want to condense the data into seven classes,what is the most convenient class interval?
A)$50
B)$100
C)$150
D)$200
E)None of the above
A)$50
B)$100
C)$150
D)$200
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Monthly commissions of first-year insurance brokers are $1,270,$1,310,$1,680,$1,380,$1,410,$1,570,$1,180 and $1,420.These figures are referred to as:
A)histogram.
B)raw data.
C)frequency distribution.
D)frequency polygon.
A)histogram.
B)raw data.
C)frequency distribution.
D)frequency polygon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A cumulative frequency distribution is used when we want to determine how many observations lie above or below certain values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A student was studying the political party preferences of a university's student population.The survey instrument asked students to identify themselves as a democrat or a republican.This question is flawed because:
A)Students generally don't know their political preferences.
B)The categories are generally mutually exclusive.
C)The categories are not exhaustive.
D)Political preference is a continuous variable.
A)Students generally don't know their political preferences.
B)The categories are generally mutually exclusive.
C)The categories are not exhaustive.
D)Political preference is a continuous variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a class interval is expressed as: 100 up to 200,
A)Observations with values of 100 are excluded from the class frequency.
B)Observations with values of 200 are included in the class frequency.
C)Observations with values of 200 are excluded from the class frequency.
D)The class interval is 99.
A)Observations with values of 100 are excluded from the class frequency.
B)Observations with values of 200 are included in the class frequency.
C)Observations with values of 200 are excluded from the class frequency.
D)The class interval is 99.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For the following distribution of heights,what are the limits for the class with the greatest frequency? 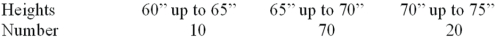
A)64 and up to 70
B)65 and 69
C)65 and up to 70
D)69.5 and 74.5
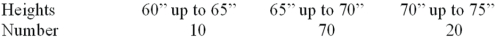
A)64 and up to 70
B)65 and 69
C)65 and up to 70
D)69.5 and 74.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A small sample of computer operators shows monthly incomes of $1,950,$1,775,$2,060,$1,840,$1,795,$1,890,$1,925 and $1,810.What are these ungrouped numbers called?
A)Histogram
B)Class limits
C)Class frequencies
D)Raw data
A)Histogram
B)Class limits
C)Class frequencies
D)Raw data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In general,we should construct a frequency distribution so that there are either 4 or 24 classes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When data is collected using a qualitative,nominal variable,what is true about a frequency distribution that summarizes the data?
A)Upper and lower class limits must be calculated.
B)A pie chart can be used to summarize the data.
C)Number of classes is equal to the number of variable's values plus 2.
D)The "5 to the k rule" can be applied.
A)Upper and lower class limits must be calculated.
B)A pie chart can be used to summarize the data.
C)Number of classes is equal to the number of variable's values plus 2.
D)The "5 to the k rule" can be applied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For qualitative data,the relative frequency for a class is computed as the
A)class width divided by class interval.
B)class midpoint divided by the class frequency.
C)class frequency divided by the class interval.
D)class frequency divided by the total frequency.
A)class width divided by class interval.
B)class midpoint divided by the class frequency.
C)class frequency divided by the class interval.
D)class frequency divided by the total frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The height of a bar in a histogram represents the number of observations for a class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In a frequency distribution,the number of observations in a class is called class
A)midpoint
B)interval
C)array
D)frequency
A)midpoint
B)interval
C)array
D)frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When data is collected using a qualitative,nominal variable,i.e. ,male or female,what is true about a frequency distribution that summarizes the data?
A)Upper and lower class limits must be calculated.
B)Class midpoints can be computed.
C)Number of classes corresponds to number of the variable's values.
D)The "2 to the k rule" can be applied.
A)Upper and lower class limits must be calculated.
B)Class midpoints can be computed.
C)Number of classes corresponds to number of the variable's values.
D)The "2 to the k rule" can be applied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A relative frequency distribution shows the number of observations in each class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A frequency polygon is a very useful graphic technique when comparing two or more distributions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A group of 100 students were surveyed about their interest in a new International Studies program.Interest was measured in terms of high,medium,or low.30 students responded high interest;40 students responded medium interest;30 students responded low interest.What is the relative frequency of students with high interest?
A)30%
B)50%
C)40%
D)Cannot be determined
A)30%
B)50%
C)40%
D)Cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the following table called? 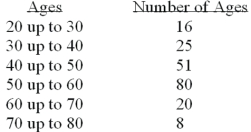
A)Histogram
B)Frequency polygon
C)Cumulative frequency distribution
D)Frequency distribution

A)Histogram
B)Frequency polygon
C)Cumulative frequency distribution
D)Frequency distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When data is collected using a quantitative,ratio variable,what is true about a frequency distribution that summarizes the data?
A)Upper and lower class limits must be calculated.
B)A pie chart can be used to summarize the data.
C)Number of classes is equal to the number of variable's values.
D)The "5 to the k rule" can be applied.
A)Upper and lower class limits must be calculated.
B)A pie chart can be used to summarize the data.
C)Number of classes is equal to the number of variable's values.
D)The "5 to the k rule" can be applied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the following distribution of ages: 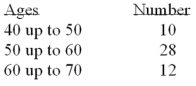 What is the class interval?
What is the class interval?
A)9
B)10
C)10.5
D)11
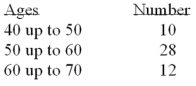 What is the class interval?
What is the class interval?A)9
B)10
C)10.5
D)11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the following distribution of commissions: 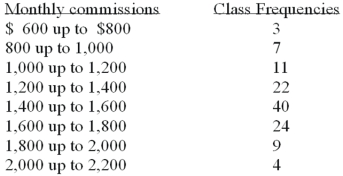 What is the relative frequency for those salespersons that earn from $1,600 up to $1,800?
What is the relative frequency for those salespersons that earn from $1,600 up to $1,800?
A)2%
B)2.4%
C)20%
D)24%
E)None of the above
 What is the relative frequency for those salespersons that earn from $1,600 up to $1,800?
What is the relative frequency for those salespersons that earn from $1,600 up to $1,800?A)2%
B)2.4%
C)20%
D)24%
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the following information from a frequency distribution for "heights of college women" recorded to the nearest inch: The first two class midpoints are 62.5" and 65.5".
What are the class limits for the lowest class?
A)61 and up to 64
B)62 and up to 64
C)62 and 65
D)62 and 63
What are the class limits for the lowest class?
A)61 and up to 64
B)62 and up to 64
C)62 and 65
D)62 and 63

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the following distribution: 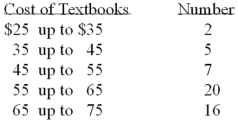 What is the relative class frequency for the $25 up to $35 class?
What is the relative class frequency for the $25 up to $35 class?
A)2%
B)4%
C)5%
D)10%
 What is the relative class frequency for the $25 up to $35 class?
What is the relative class frequency for the $25 up to $35 class?A)2%
B)4%
C)5%
D)10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the following information from a frequency distribution for "heights of college women" recorded to the nearest inch: The first two class midpoints are 62.5" and 65.5".
What is the class interval?
A)1"
B)2"
C)2.5"
D)3"
What is the class interval?
A)1"
B)2"
C)2.5"
D)3"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the following wage breakdown for a garment factory. 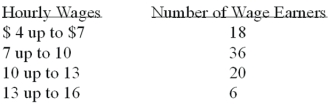 What is the class midpoint for the class with the greatest frequency?
What is the class midpoint for the class with the greatest frequency?
A)$5.50
B)$8.50
C)$11.50
D)$14.50
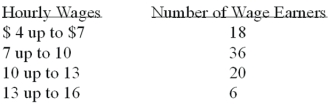 What is the class midpoint for the class with the greatest frequency?
What is the class midpoint for the class with the greatest frequency?A)$5.50
B)$8.50
C)$11.50
D)$14.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A sample distribution of hourly earnings in Paul's Cookie Factory is: 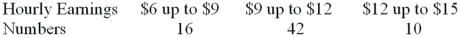 The limits of the class with the smallest frequency are:
The limits of the class with the smallest frequency are:
A)$6.00 and $9.00
B)$12.00 and up to $14.00
C)$11.75 and $14.25
D)$12.00 and up to $15.00
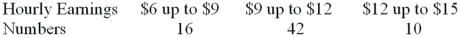 The limits of the class with the smallest frequency are:
The limits of the class with the smallest frequency are:A)$6.00 and $9.00
B)$12.00 and up to $14.00
C)$11.75 and $14.25
D)$12.00 and up to $15.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the following distribution of commissions: 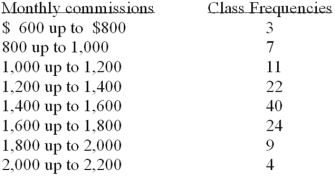 What is the relative frequency of those salespersons that earn more than $1,599?
What is the relative frequency of those salespersons that earn more than $1,599?
A)25.5%
B)27.5%
C)29.5%
D)30.8%
 What is the relative frequency of those salespersons that earn more than $1,599?
What is the relative frequency of those salespersons that earn more than $1,599?A)25.5%
B)27.5%
C)29.5%
D)30.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the following distribution: 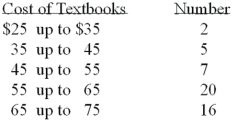 What are the class limits for class with the highest frequency?
What are the class limits for class with the highest frequency?
A)55 and 64
B)54 and 64
C)55 and up to 65
D)55 and 64.5
 What are the class limits for class with the highest frequency?
What are the class limits for class with the highest frequency?A)55 and 64
B)54 and 64
C)55 and up to 65
D)55 and 64.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the following distribution of ages: 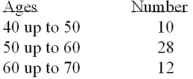 What is the class midpoint of the highest class?
What is the class midpoint of the highest class?
A)54
B)55
C)64
D)65
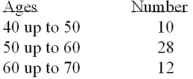 What is the class midpoint of the highest class?
What is the class midpoint of the highest class?A)54
B)55
C)64
D)65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why are unequal class intervals sometimes used in a frequency distribution?
A)To avoid a large number of empty classes
B)For the sake of variety in presenting the data
C)To make the class frequencies smaller
D)To avoid the need for midpoints
A)To avoid a large number of empty classes
B)For the sake of variety in presenting the data
C)To make the class frequencies smaller
D)To avoid the need for midpoints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Refer to the following distribution of ages: 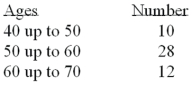 For the distribution of ages above,what is the relative class frequency for the lowest class?
For the distribution of ages above,what is the relative class frequency for the lowest class?
A)50%
B)18%
C)20%
D)10%
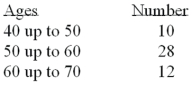 For the distribution of ages above,what is the relative class frequency for the lowest class?
For the distribution of ages above,what is the relative class frequency for the lowest class?A)50%
B)18%
C)20%
D)10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Refer to the following distribution of commissions: 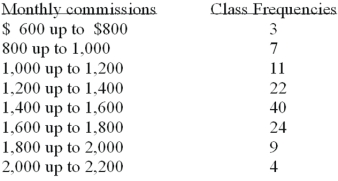 The first plot for a cumulative frequency distribution would be:
The first plot for a cumulative frequency distribution would be:
A)X = 0,Y = 600.
B)X = 600,Y = 3.
C)X = 3,Y = 600.
D)X = 600,Y = 0.
 The first plot for a cumulative frequency distribution would be:
The first plot for a cumulative frequency distribution would be:A)X = 0,Y = 600.
B)X = 600,Y = 3.
C)X = 3,Y = 600.
D)X = 600,Y = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the following distribution: 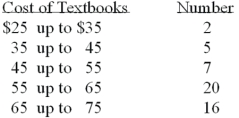 What is the class midpoint for the $45 up to $55 class?
What is the class midpoint for the $45 up to $55 class?
A)49
B)49.5
C)50
D)50.5
 What is the class midpoint for the $45 up to $55 class?
What is the class midpoint for the $45 up to $55 class?A)49
B)49.5
C)50
D)50.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Refer to the following wage breakdown for a garment factory. 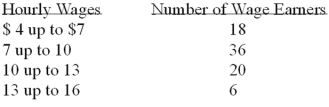 What is the class interval for the table of wages above?
What is the class interval for the table of wages above?
A)$2
B)$3
C)$4
D)$5
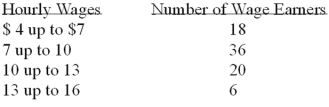 What is the class interval for the table of wages above?
What is the class interval for the table of wages above?A)$2
B)$3
C)$4
D)$5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The age distribution of a sample of part-time employees at Lloyd's Fast Food Emporium is:  What type of chart should be drawn to present this data?
What type of chart should be drawn to present this data?
A)Histogram
B)Simple line chart
C)Cumulative Frequency Distribution
D)Pie chart
E)Frequency polygon
 What type of chart should be drawn to present this data?
What type of chart should be drawn to present this data?A)Histogram
B)Simple line chart
C)Cumulative Frequency Distribution
D)Pie chart
E)Frequency polygon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to the following information from a frequency distribution for "heights of college women" recorded to the nearest inch: The first two class midpoints are 62.5" and 65.5".
What are the class limits for the third class?
A)64 and up to 67
B)67 and 69
C)67 and up to 70
D)66 and 68
What are the class limits for the third class?
A)64 and up to 67
B)67 and 69
C)67 and up to 70
D)66 and 68

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the following wage breakdown for a garment factory. 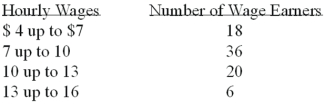 What are the class limits for the class with the smallest frequencies?
What are the class limits for the class with the smallest frequencies?
A)3.5 and 6.5
B)4 and up to 7
C)13 and up to 16
D)12.5 and 15.5
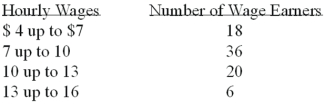 What are the class limits for the class with the smallest frequencies?
What are the class limits for the class with the smallest frequencies?A)3.5 and 6.5
B)4 and up to 7
C)13 and up to 16
D)12.5 and 15.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the following distribution of commissions: 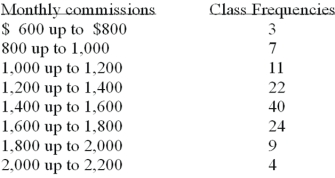 For the distribution above,what is the midpoint of the class with the greatest frequency?
For the distribution above,what is the midpoint of the class with the greatest frequency?
A)1400
B)1500
C)1700
D)The midpoint cannot be determined
 For the distribution above,what is the midpoint of the class with the greatest frequency?
For the distribution above,what is the midpoint of the class with the greatest frequency?A)1400
B)1500
C)1700
D)The midpoint cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the following distribution of commissions: 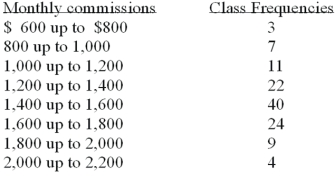 What is the class interval?
What is the class interval?
A)200
B)300
C)3.500
D)400
 What is the class interval?
What is the class interval?A)200
B)300
C)3.500
D)400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A frequency distribution for nominal data requires that the categories be ___________________ and _______________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Draw a bar graph that illustrates the frequency table above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Refer to the following breakdown of responses to a survey of room cleanliness in a hotel.  What is the class interval for the frequency table above?
What is the class interval for the frequency table above?
A)10
B)20
C)40
D)None of the above
 What is the class interval for the frequency table above?
What is the class interval for the frequency table above?A)10
B)20
C)40
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the following class marks or midpoints for a frequency distribution of "weights of college men" recorded to the nearest pound:
The first three class marks are 105,115,and 125.
What is the upper limit for the third class? _______
The first three class marks are 105,115,and 125.
What is the upper limit for the third class? _______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the number of observations in each class of a frequency distribution called?__________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the following frequency distribution on days absent during a calendar year by employees of a manufacturing company: 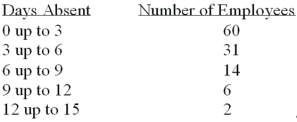 How many employees were absent more than six days or more?
How many employees were absent more than six days or more?
A)8
B)4
C)22
D)31
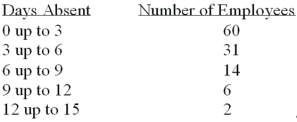 How many employees were absent more than six days or more?
How many employees were absent more than six days or more?A)8
B)4
C)22
D)31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In constructing a frequency polygon,class frequencies are scaled on which axis? ______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The midpoint of a class interval is also called a __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Refer to the following frequency distribution on days absent during a calendar year by employees of a manufacturing company:  How many employees were absent from 6 up to 12 days?
How many employees were absent from 6 up to 12 days?
A)20
B)8
C)12
D)17
 How many employees were absent from 6 up to 12 days?
How many employees were absent from 6 up to 12 days?A)20
B)8
C)12
D)17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Refer to the following breakdown of responses to a survey of room cleanliness in a hotel.  What percent of the responses indicated that customers were satisfied?
What percent of the responses indicated that customers were satisfied?
A)20
B)25%
C)50%
D)100%
 What percent of the responses indicated that customers were satisfied?
What percent of the responses indicated that customers were satisfied?A)20
B)25%
C)50%
D)100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For a frequency distribution of quantitative data,if every individual,object or measurement can be assigned to a class,the frequency distribution is ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What chart or graph is useful to display a relative frequency distribution for a nominal variable? _______________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the following breakdown of responses to a survey of room cleanliness in a hotel.  What is the class with the greatest frequency?
What is the class with the greatest frequency?
A)Not satisfied
B)Satisfied
C)Highly satisfied
D)None of the above
 What is the class with the greatest frequency?
What is the class with the greatest frequency?A)Not satisfied
B)Satisfied
C)Highly satisfied
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For a frequency distribution of qualitative data,if the observations can be assigned to only one class,the classes are ____________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When classes in a frequency table are constructed so that each observation will fit into only one class,the categories are ________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Unorganized data is referred to as ________ data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A table showing the number of observations that have been grouped into each of several classes is called a _____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the following frequency distribution on days absent during a calendar year by employees of a manufacturing company:  How many employees were absent between 3 up to 6 days?
How many employees were absent between 3 up to 6 days?
A)31
B)29
C)14
D)2
 How many employees were absent between 3 up to 6 days?
How many employees were absent between 3 up to 6 days?A)31
B)29
C)14
D)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Draw a bar graph that illustrates the relative frequencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the following frequency distribution on days absent during a calendar year by employees of a manufacturing company:  How many employees were absent fewer than six days?
How many employees were absent fewer than six days?
A)60
B)31
C)91
D)46
 How many employees were absent fewer than six days?
How many employees were absent fewer than six days?A)60
B)31
C)91
D)46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



