Deck 21: International Financial Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/126
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: International Financial Management
1
A multinational corporation may be defined as:
A) a company which owns property in a foreign country.
B) a company which hires foreign labourers.
C) a company which carries on some business activity outside of its own national borders.
D) a company which conducts business with employees and corporations from around the world.
A) a company which owns property in a foreign country.
B) a company which hires foreign labourers.
C) a company which carries on some business activity outside of its own national borders.
D) a company which conducts business with employees and corporations from around the world.
C
2
The value of a country's currency may increase by:
A) continuous excessive government spending.
B) a stock market rally in that country.
C) an increase in that country's money supply.
D) an increase in another countries interest rate.
A) continuous excessive government spending.
B) a stock market rally in that country.
C) an increase in that country's money supply.
D) an increase in another countries interest rate.
B
3
The interplay between interest rate differentials and exchange rates such that each adjusts until the foreign exchange market and the money market reach equilibrium is called the:
A) Purchasing Power Parity Theory.
B) Balance of Payments.
C) Interest Rate Parity Theory.
D) Money Differential Parity.
A) Purchasing Power Parity Theory.
B) Balance of Payments.
C) Interest Rate Parity Theory.
D) Money Differential Parity.
C
4
You are on your way to the beautiful Mexican resort of Zijuatenejo. The current exchange rate is 500 pesos to the dollar. When you arrive, you convert $1,000 for how many pesos?
A) 500,000 peso
B) 5,000 peso
C) 0.05 peso
D) 0.005 peso
A) 500,000 peso
B) 5,000 peso
C) 0.05 peso
D) 0.005 peso

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A form of multinational corporation which exposes the firm to the least amount political risk, and is therefore the preferred arrangement by both business and foreign governments is called a(an):
A) exporter.
B) licensing agreement.
C) joint venture.
D) fully-owned foreign subsidiary.
A) exporter.
B) licensing agreement.
C) joint venture.
D) fully-owned foreign subsidiary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A particular country's pattern of importing more than is being exported is likely to:
A) depress that country's currency.
B) depress other countries' currencies.
C) increase the value of that country's currency.
D) increase the currency relative to the US dollar.
A) depress that country's currency.
B) depress other countries' currencies.
C) increase the value of that country's currency.
D) increase the currency relative to the US dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You are leaving Mexico and have 3,500 pesos to change into dollars. The exchange rate is now 1,500 pesos to the dollar. How many dollars will you receive?
A) $0.43
B) $2.33
C) $23.33
D) $30.00
A) $0.43
B) $2.33
C) $23.33
D) $30.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The possibility of experiencing a drop in revenue or an increase in cost in an international transaction due to a change in foreign exchange rates is called:
A) foreign exchange risk.
B) political risk.
C) credit risk.
D) strategic risk.
A) foreign exchange risk.
B) political risk.
C) credit risk.
D) strategic risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a licensing agreement, the multinational corporation will very likely:
A) be able to compete with the local domestic manufacturers.
B) experience import restrictions imposed by the foreign government.
C) allow a foreign firm to use its technology in exchange for a fee or a royalty.
D) charge a fee for each item sold.
A) be able to compete with the local domestic manufacturers.
B) experience import restrictions imposed by the foreign government.
C) allow a foreign firm to use its technology in exchange for a fee or a royalty.
D) charge a fee for each item sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Multinational corporations are concerned about which of the following exchange rate exposures?
A) Foreign exchange risk and labour rates
B) Economic exposure and translation exposure
C) Political risk and tax rates
D) Foreign exchange risk and strategic risk
A) Foreign exchange risk and labour rates
B) Economic exposure and translation exposure
C) Political risk and tax rates
D) Foreign exchange risk and strategic risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
While shopping in the Mexican market, you find that limes cost 12 pesos each. You remember that back home they cost 60 cents each. If the Purchasing Power Parity Theory holds, the rate of exchange is:
A) 20 pesos/dollar or 5 cents/peso.
B) 80 pesos/dollar or 1.25 cents/peso.
C) 5 pesos/dollar or 20 cents/peso.
D) 1 peso/dollar or 15 cents/peso.
A) 20 pesos/dollar or 5 cents/peso.
B) 80 pesos/dollar or 1.25 cents/peso.
C) 5 pesos/dollar or 20 cents/peso.
D) 1 peso/dollar or 15 cents/peso.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following hedging strategies involves a loan without a futures contract?
A) Eurobond market
B) Forward exchange market
C) Money market
D) IMM contract
A) Eurobond market
B) Forward exchange market
C) Money market
D) IMM contract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The current spot exchange rate between the Japanese yen and the Canadian dollar is *105/$. The yen is expected to appreciate by 5% against the dollar over the next six months. What do you expect the spot exchange rate between the yen and the dollar to be six months from now?
A) *94.50/$
B) *99.75/$
C) *110.25/$
D) *115.50/$
A) *94.50/$
B) *99.75/$
C) *110.25/$
D) *115.50/$

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Multinational corporations may take several forms. An exporter could be described as:
A) an multinational corporation which produces a product within its own borders, but sells in a foreign market.
B) the least risky political arrangement.
C) an multinational corporation willing to commit itself to a long-term foreign investment.
D) accepting goods from other countries to sell locally.
A) an multinational corporation which produces a product within its own borders, but sells in a foreign market.
B) the least risky political arrangement.
C) an multinational corporation willing to commit itself to a long-term foreign investment.
D) accepting goods from other countries to sell locally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements about foreign affiliates funding is most accurate?
A) In general, foreign affiliates are more profitable than domestic businesses.
B) Foreign affiliates usually lower the portfolio risk of the parent company.
C) Foreign affiliates may have a significant positive impact on the host company's economic growth, employment, trade, and balance of payments.
D) Bank lending to foreign affiliates is based on some sort of a guarantee by the parent firm.
A) In general, foreign affiliates are more profitable than domestic businesses.
B) Foreign affiliates usually lower the portfolio risk of the parent company.
C) Foreign affiliates may have a significant positive impact on the host company's economic growth, employment, trade, and balance of payments.
D) Bank lending to foreign affiliates is based on some sort of a guarantee by the parent firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A fully owned foreign subsidiary is a form of multinational corporation in which:
A) a local entrepreneur buys the firm in that foreign country.
B) the multinational corporation owns and operates the firm by itself.
C) the foreign government gives its full cooperation.
D) the venture is jointly controlled with a local domestic partner.
A) a local entrepreneur buys the firm in that foreign country.
B) the multinational corporation owns and operates the firm by itself.
C) the foreign government gives its full cooperation.
D) the venture is jointly controlled with a local domestic partner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The following are the prices in the foreign exchange market between the Canadian dollar and another local currency (LC). 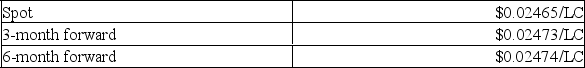 What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward for LC?
What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward for LC?
A) 1.2980% premium
B) 0.0325% premium
C) 0.0325% discount
D) 1.2980% discount
 What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward for LC?
What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward for LC?A) 1.2980% premium
B) 0.0325% premium
C) 0.0325% discount
D) 1.2980% discount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements about forward exchange rates is false?
A) They reduce uncertainty about future value of currencies.
B) They reflect expectations about the future value of currencies.
C) They are usually slightly lower than the spot rate.
D) Interest rate parity theory explains forward exchange rates.
A) They reduce uncertainty about future value of currencies.
B) They reflect expectations about the future value of currencies.
C) They are usually slightly lower than the spot rate.
D) Interest rate parity theory explains forward exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What has motivated Canadian firms to move their operations to foreign countries?
A) Trade barriers, lower production costs, access to skilled workers, Canadian tax deferral.
B) Political stability, large market size, access to advanced technology.
C) Import tariffs, foreign unions, foreign technology, expropriation.
D) Lower production costs, tax deferral, access to natural resources and manufacturing, expropriation.
A) Trade barriers, lower production costs, access to skilled workers, Canadian tax deferral.
B) Political stability, large market size, access to advanced technology.
C) Import tariffs, foreign unions, foreign technology, expropriation.
D) Lower production costs, tax deferral, access to natural resources and manufacturing, expropriation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following hedging strategies is not used to minimize transaction exposure?
A) Eurobond market
B) Forward exchange market
C) Money market
D) Currency futures market
A) Eurobond market
B) Forward exchange market
C) Money market
D) Currency futures market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following factors will not increase the value of a currency in foreign markets?
A) High interest rates
B) High inflation
C) Positive balance of payments
D) Strong stock market rally
A) High interest rates
B) High inflation
C) Positive balance of payments
D) Strong stock market rally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the Brazilian real is equal to $0.46, a Canadian dollar is equal to how many Brazilian reals?
A) 1.36
B) 1.96
C) 2.17
D) 0.38
A) 1.36
B) 1.96
C) 2.17
D) 0.38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Foreign capital investments are undertaken for reasons that include all of the following except?
A) Broader diversification possibilities
B) Strategic advantages
C) Higher potential returns
D) Reduction of exchange rate exposure
A) Broader diversification possibilities
B) Strategic advantages
C) Higher potential returns
D) Reduction of exchange rate exposure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A portfolio of international stocks in comparison to purely Canadian stocks generally shows:
A) lower percentage risk for a given number of stocks.
B) higher percentage risk for a given number of stocks.
C) the same percentage risk for a given number of stocks.
D) lower percentage return for a given number of stocks.
A) lower percentage risk for a given number of stocks.
B) higher percentage risk for a given number of stocks.
C) the same percentage risk for a given number of stocks.
D) lower percentage return for a given number of stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not an advantage of borrowing on the Eurocurrency market?
A) Greater availability of credit
B) Lower overhead costs for lending banks
C) Absence of compensating balance requirements
D) Constant lending rate over time
A) Greater availability of credit
B) Lower overhead costs for lending banks
C) Absence of compensating balance requirements
D) Constant lending rate over time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is not commonly used to minimize transaction exposure in foreign exchange dealings?
A) Hedging in the foreign exchange market
B) Hedging in the money market
C) Hedging in the stock market
D) Hedging in the currency futures market
A) Hedging in the foreign exchange market
B) Hedging in the money market
C) Hedging in the stock market
D) Hedging in the currency futures market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not a reason for Canadian firms operating in foreign markets?
A) Less expensive labour
B) Better economic and political environment
C) Tax incentives
D) Achieve international diversification
A) Less expensive labour
B) Better economic and political environment
C) Tax incentives
D) Achieve international diversification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A long-term debt issue sold simultaneously in several different national capital markets, but denominated in a currency different than the nation of that issue is called a(an):
A) world bond.
B) international capital bond.
C) floating bond.
D) eurobond.
A) world bond.
B) international capital bond.
C) floating bond.
D) eurobond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements about the International Finance Corporation is not true?
A) The decision to assist a venture depends on both profitability of the project and potential benefit to the host country's economy
B) IFC assumes no managerial responsibility and exercises no voting rights
C) IFC may either buy equity shares or provide long-term loans
D) The IFC is owned by the member countries of the United Nations
A) The decision to assist a venture depends on both profitability of the project and potential benefit to the host country's economy
B) IFC assumes no managerial responsibility and exercises no voting rights
C) IFC may either buy equity shares or provide long-term loans
D) The IFC is owned by the member countries of the United Nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Chinese renminbi is selling for $0.1652 and the British pound is selling for $1.6581. The cross rate between the renminbi and the pound is:
A) 10.0400.
B) 0.1004.
C) 9.9600.
D) 0.0996.
A) 10.0400.
B) 0.1004.
C) 9.9600.
D) 0.0996.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Some multinational corporations may have difficulty raising equity capital in world market for all of the following reasons EXCEPT:
A) language barrier.
B) foreign investors prefer capital gains over dividends.
C) common stock ownership among individuals may be uncommon.
D) the role of commercial banks throughout Europe in the issuing of new securities.
A) language barrier.
B) foreign investors prefer capital gains over dividends.
C) common stock ownership among individuals may be uncommon.
D) the role of commercial banks throughout Europe in the issuing of new securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If prices double in Vancouver while the prices in San Paulo remain the same, the purchasing power of the dollar relative to the real:
A) should increase by 50%.
B) should increase by 100%.
C) should decrease by 50%.
D) should decrease by 100%.
A) should increase by 50%.
B) should increase by 100%.
C) should decrease by 50%.
D) should decrease by 100%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
To minimize exposure to political risk, a multinational firm may establish a joint venture with a local entrepreneur, establish a joint venture with a group of multinationals, or:
A) purchase an insurance policy from the Export Development Corporation.
B) hedge in the Eurodollar market.
C) purchase an insurance policy from the Canada Revenue Agency.
D) hedge the Canadian dollar.
A) purchase an insurance policy from the Export Development Corporation.
B) hedge in the Eurodollar market.
C) purchase an insurance policy from the Canada Revenue Agency.
D) hedge the Canadian dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A loan arrangement in which a parent company reduces its political risk over a direct transfer of funds is called a(an):
A) parallel loan.
B) EDC direct loan.
C) fronting loan.
D) it depends on the host country
A) parallel loan.
B) EDC direct loan.
C) fronting loan.
D) it depends on the host country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Export Development Corporation (EDC):
A) lends money to foreign purchasers of Canadian goods.
B) issues letters of credit.
C) makes parallel loans.
D) makes fronting loans.
A) lends money to foreign purchasers of Canadian goods.
B) issues letters of credit.
C) makes parallel loans.
D) makes fronting loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The spot rate of the British pound to the dollar is 1.68 ($/ ,). The 180 day forward rate is $1.71, the annualized forward premium is:
A) 1.018%.
B) 3.636%.
C) 7.273%.
D) 2.036%.
A) 1.018%.
B) 3.636%.
C) 7.273%.
D) 2.036%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) The currency of Japan is described in yens.
B) The currency of Mexico is described in pesos.
C) The currency of Italy is described in euros.
D) The currency of Denmark is described in rands.
A) The currency of Japan is described in yens.
B) The currency of Mexico is described in pesos.
C) The currency of Italy is described in euros.
D) The currency of Denmark is described in rands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Foreign business operations are more complex than domestic operations because of all of the following except:
A) the rate of inflation may be higher than that of Canada.
B) the rules of taxation are different.
C) the financial markets vary from country to country.
D) of interprovincial trade barriers.
A) the rate of inflation may be higher than that of Canada.
B) the rules of taxation are different.
C) the financial markets vary from country to country.
D) of interprovincial trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Export Development Corporation (EDC):
A) loans money to multinational firms.
B) does feasibility studies for multinational firms.
C) sells insurance policies to qualified multinational firms.
D) reduces risk by taking an ownership share of exporting companies.
A) loans money to multinational firms.
B) does feasibility studies for multinational firms.
C) sells insurance policies to qualified multinational firms.
D) reduces risk by taking an ownership share of exporting companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A loan arrangement between a parent company and its foreign affiliate which avoids the exchange markets entirely is called a:
A) parallel loan.
B) EDC direct loan.
C) fronting loan.
D) could be any one depending on the circumstances.
A) parallel loan.
B) EDC direct loan.
C) fronting loan.
D) could be any one depending on the circumstances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Assume that you had dollar quotes for the Japanese yen and the British pound. If you want to know the yen/pound exchange rate, you would rely on:
A) forward rates.
B) cross rates.
C) spot rates.
D) hedge ratios.
A) forward rates.
B) cross rates.
C) spot rates.
D) hedge ratios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The belief that shifts in exchange rates result from increasing or decreasing demand for a country's exports (or the corresponding opposite movements in supply of a country's imports) form the basis for the:
A) purchasing power theory of exchange rates.
B) interest rate parity theory of exchange rates.
C) balance of payments theory of exchange rates.
D) government intervention theory of exchange rates.
A) purchasing power theory of exchange rates.
B) interest rate parity theory of exchange rates.
C) balance of payments theory of exchange rates.
D) government intervention theory of exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the Eurobond market:
A) the interest rate is very high.
B) the security is denominated in a currency that is different from that of the nation in which the bonds are issued.
C) the British pound is the most important currency.
D) disclosure requirements are very strict.
A) the interest rate is very high.
B) the security is denominated in a currency that is different from that of the nation in which the bonds are issued.
C) the British pound is the most important currency.
D) disclosure requirements are very strict.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is true about international equity (stock) markets?
A) Japanese households are large investors in common stock.
B) Commercial banks are generally not involved in the international securities business.
C) Some foreign investors are more risk-averse than their counterparts in Canada and prefer dividend income over less certain capital gains.
D) Foreign exchanges never include the listing of Canadian firms.
A) Japanese households are large investors in common stock.
B) Commercial banks are generally not involved in the international securities business.
C) Some foreign investors are more risk-averse than their counterparts in Canada and prefer dividend income over less certain capital gains.
D) Foreign exchanges never include the listing of Canadian firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Considerations in a global cash management system include all of the following except:
A) Obtain insurance in advance against such risks when the perceived political risk level is high.
B) deciding how to reallocate cash once it has been centralized.
C) creating the ability to withdraw cash from the subsidiary and centralize it.
D) estimating the levels of local and corporate cash needs at given times.
A) Obtain insurance in advance against such risks when the perceived political risk level is high.
B) deciding how to reallocate cash once it has been centralized.
C) creating the ability to withdraw cash from the subsidiary and centralize it.
D) estimating the levels of local and corporate cash needs at given times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) is:
A) a unit of the world bank charged with the responsibility of providing capital to multinational corporations and others in international trade.
B) a regulatory agency for international trade.
C) a private firm that provides accounts receivable financing to international firms.
D) a foreign affiliate of 10 major banks.
A) a unit of the world bank charged with the responsibility of providing capital to multinational corporations and others in international trade.
B) a regulatory agency for international trade.
C) a private firm that provides accounts receivable financing to international firms.
D) a foreign affiliate of 10 major banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following kinds of risk are NOT uniquely associated with multinational corporations?
A) Exchange rate risk
B) Business risk
C) Political risk
D) Translation risk
A) Exchange rate risk
B) Business risk
C) Political risk
D) Translation risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When Country A's currency strengthens against Country B's, citizens of Country A will:
A) pay less to buy Country B's products.
B) pay more to buy Country B's products.
C) pay more to buy domestically produced products.
D) not be affected by the change in their currency's value.
A) pay less to buy Country B's products.
B) pay more to buy Country B's products.
C) pay more to buy domestically produced products.
D) not be affected by the change in their currency's value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Eurobond market has which of the following characteristics?
A) Eurobond issues are denominated in the currency where the bond is sold.
B) Disclosure requirements in the Eurobond market are much less stringent than those required by Canadian securities commissions.
C) Eurobond issues are underwritten by the European Central Bank.
D) Eurobond issues are denominated in euros.
A) Eurobond issues are denominated in the currency where the bond is sold.
B) Disclosure requirements in the Eurobond market are much less stringent than those required by Canadian securities commissions.
C) Eurobond issues are underwritten by the European Central Bank.
D) Eurobond issues are denominated in euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
As exchange rates change, they:
A) reduce translation exposure for corporations with foreign investment.
B) can not affect imports and exports between countries.
C) will not affect the flow of funds between the countries.
D) change the relative purchasing power between countries.
A) reduce translation exposure for corporations with foreign investment.
B) can not affect imports and exports between countries.
C) will not affect the flow of funds between the countries.
D) change the relative purchasing power between countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In a parallel loan arrangement:
A) the Canadian parent firm lends dollars to the Canadian affiliate while the Dutch parent firm lends euros to the Dutch affiliate.
B) the Canadian parent firm lends dollars to the Dutch affiliate while the Dutch parent lends euros to the Canadian affiliate.
C) the Canadian parent lends euros to the Dutch affiliate while the Dutch parent lends dollars to the Canadian affiliate.
D) the parent firms lend funds to each other while the affiliates lend funds to each other.
A) the Canadian parent firm lends dollars to the Canadian affiliate while the Dutch parent firm lends euros to the Dutch affiliate.
B) the Canadian parent firm lends dollars to the Dutch affiliate while the Dutch parent lends euros to the Canadian affiliate.
C) the Canadian parent lends euros to the Dutch affiliate while the Dutch parent lends dollars to the Canadian affiliate.
D) the parent firms lend funds to each other while the affiliates lend funds to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A particular country's pattern of exporting more than is being imported is likely to:
A) have no effect on that country's currency.
B) depress other countries' currencies.
C) decrease the value of that country's currency.
D) stabilize the relative purchasing power between countries.
A) have no effect on that country's currency.
B) depress other countries' currencies.
C) decrease the value of that country's currency.
D) stabilize the relative purchasing power between countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Eurocurrency are:
A) Canadian dollars deposited in foreign banks.
B) foreign dollars deposited in Canadian banks.
C) investments of common market countries.
D) Euro's converted to US dollars.
A) Canadian dollars deposited in foreign banks.
B) foreign dollars deposited in Canadian banks.
C) investments of common market countries.
D) Euro's converted to US dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The CPA Canada Handbook recommends when a foreign operation is designated as integrated:
A) it causes instability in the currencies in international money and foreign exchange markets.
B) the market value of assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies is subject to change.
C) it exploits local labour with low wages.
D) its transactions be captured as if they had been performed by the parent company.
A) it causes instability in the currencies in international money and foreign exchange markets.
B) the market value of assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies is subject to change.
C) it exploits local labour with low wages.
D) its transactions be captured as if they had been performed by the parent company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If in 20X2, the Canadian dollar's exchange rate with the Sudanese dinar was.0069 dollars per dinar and in 20X5, the exchange rate was.0062 dollars per dinar, it would indicate that in the period from 20X2 to 20X5, the dollar:
A) strengthened against the dinar.
B) weakened against the dinar.
C) was unrelated to the value of the dinar.
D) the answer cannot be determined without knowing the number of dinars needed to buy a dollar.
A) strengthened against the dinar.
B) weakened against the dinar.
C) was unrelated to the value of the dinar.
D) the answer cannot be determined without knowing the number of dinars needed to buy a dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The lower borrowing costs in the Eurocurrency market as compared to Canada are often attributed to:
A) lower inflation abroad.
B) higher inflation in the Canada.
C) slower money growth in Canada.
D) smaller overhead costs and the absence of reserve requirements abroad.
A) lower inflation abroad.
B) higher inflation in the Canada.
C) slower money growth in Canada.
D) smaller overhead costs and the absence of reserve requirements abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements is not true about American Depositary Receipts (ADRs)?
A) All the American shares owned of a foreign company are placed in trust in a New York bank.
B) Most ADRs trade in the over-the-counter market.
C) ADR prices tend to move parallel with the prices of the underlying security.
D) Most ADRs trade on the New York Stock Exchange.
A) All the American shares owned of a foreign company are placed in trust in a New York bank.
B) Most ADRs trade in the over-the-counter market.
C) ADR prices tend to move parallel with the prices of the underlying security.
D) Most ADRs trade on the New York Stock Exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
For a Canadian company, foreign business operations are more complex because the:
A) host country's economy are consistent with the domestic economy.
B) rules of taxation are similar.
C) operations of financial markets are similar.
D) structure and operations of financial markets vary.
A) host country's economy are consistent with the domestic economy.
B) rules of taxation are similar.
C) operations of financial markets are similar.
D) structure and operations of financial markets vary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Legal, political, and economic factors are most conducive to which form of multinational corporation organization?
A) Exporter/Importer
B) Licensing agreements
C) Joint ventures
D) Fully-owned foreign subsidiaries
A) Exporter/Importer
B) Licensing agreements
C) Joint ventures
D) Fully-owned foreign subsidiaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A firm exposed to exchange rate risk can hedge its risk by all of the following except:
A) using the forward exchange market.
B) borrowing in international money markets.
C) utilizing foreign currency futures markets.
D) speculating in foreign currency.
A) using the forward exchange market.
B) borrowing in international money markets.
C) utilizing foreign currency futures markets.
D) speculating in foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements about foreign affiliates is true?
A) In general, foreign affiliates are less profitable than domestic businesses
B) Foreign affiliates usually raise the portfolio risk of the parent company
C) Foreign affiliates may have a significant positive impact on the host company's economic growth, employment, trade, and balance of payments
D) Foreign affiliates are created only to take advantage of indirect loan arrangements
A) In general, foreign affiliates are less profitable than domestic businesses
B) Foreign affiliates usually raise the portfolio risk of the parent company
C) Foreign affiliates may have a significant positive impact on the host company's economic growth, employment, trade, and balance of payments
D) Foreign affiliates are created only to take advantage of indirect loan arrangements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
You are leaving Mexico and have 3,500 pesos to change into dollars. The exchange rate is now 10 pesos to the dollar. How many dollars will you receive?
A) $35.00
B) $350.00
C) $150.00
D) $35,000.00
A) $35.00
B) $350.00
C) $150.00
D) $35,000.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A joint venture with a local entrepreneur exposes the firm to the least amount of political risk and is a preferred method of investment by foreign governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The surplus which appreciates the value of the currency is known as:
A) Purchasing Power Parity.
B) Balance of Payments.
C) Current Capital.
D) Interest Rate Parity.
A) Purchasing Power Parity.
B) Balance of Payments.
C) Current Capital.
D) Interest Rate Parity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In international finance, the chance of experiencing a drop in revenue or an increase in cost in international business transactions is called:
A) credit risk.
B) political risk.
C) economic value exposure.
D) transaction exposure.
A) credit risk.
B) political risk.
C) economic value exposure.
D) transaction exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Since most foreign currency values fluctuate from time to time, the monetary value of an international transaction or investment, measured in either the seller's or the buyer's currency, is likely to change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Canada is the world's major importer and exporter, and has by far the greatest investment in foreign countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A foreign affiliate lowers the portfolio risk of its parent company because the foreign and domestic economies tend to be fairly similar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The current spot exchange rate between the Japanese yen and the Canadian dollar is *75.00/$. The yen is expected to appreciate by 6% against the dollar over the next six months. What do you expect the spot exchange rate between the yen and the dollar to be six months from now?
A) *70.50/$
B) *79.50/$
C) *84.00/$
D) *75.00/$
A) *70.50/$
B) *79.50/$
C) *84.00/$
D) *75.00/$

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is a reason for Canadian firms to operate in foreign markets?
A) More expensive labour
B) Reduce international diversification
C) Tax rate increases
D) Increased savings of production costs
A) More expensive labour
B) Reduce international diversification
C) Tax rate increases
D) Increased savings of production costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Canadian firms expand their operations outside of Canada's borders because the average rate of return for foreign investment is often higher than the rate of return on domestic investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The following are the prices in the foreign exchange market between the Canadian dollar and United States dollar (USD).  What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward and 6 month for United States dollars?
What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward and 6 month for United States dollars?
A) 2.59% premium/6.65% premium
B) 2.59% discount/6.65% discount
C) 1.03% premium/0.73% premium
D) 1.03% discount/0.73% discount
 What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward and 6 month for United States dollars?
What was the discount or premium on 3-month forward and 6 month for United States dollars?A) 2.59% premium/6.65% premium
B) 2.59% discount/6.65% discount
C) 1.03% premium/0.73% premium
D) 1.03% discount/0.73% discount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Government expropriation is an example of:
A) Transaction risk.
B) Business risk.
C) Political risk.
D) Translation risk.
A) Transaction risk.
B) Business risk.
C) Political risk.
D) Translation risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An exporter is able to satisfy foreign demand for a product while avoiding long-term investment although this method is riskier than other alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A joint venture with a private entrepreneur in a host country exposes the multinational corporation to the least amount of political risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements about the International Finance Corporation is true?
A) The decision to assist a venture depends only on potential benefit to the host country's economy.
B) IFC assumes managerial responsibility and exercises no voting rights.
C) IFC may either buy equity shares or provide long-term loans.
D) IFC only provide long-term loans, but not buy equity shares.
A) The decision to assist a venture depends only on potential benefit to the host country's economy.
B) IFC assumes managerial responsibility and exercises no voting rights.
C) IFC may either buy equity shares or provide long-term loans.
D) IFC only provide long-term loans, but not buy equity shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is commonly used to minimize transaction exposure in foreign exchange dealings?
A) Hedging in the interest swap market
B) Hedging in the money market
C) Hedging in the stock market
D) Hedging in the treasury bills market
A) Hedging in the interest swap market
B) Hedging in the money market
C) Hedging in the stock market
D) Hedging in the treasury bills market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A foreign affiliate may be an exporter, a joint venture, or a fully owned foreign subsidiary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
You are on your way to Mexico. The current exchange rate is 12 pesos to the dollar. When you arrive, you convert $1,000 for how many pesos?
A) 12,000
B) 120
C) 83
D) 0.018
A) 12,000
B) 120
C) 83
D) 0.018

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
While shopping in the Mexican market, you find that limes cost 20 pesos each. You remember that back home they cost 80 cents each. If the Purchasing Power Parity Theory holds, the rate of exchange is:
A) 25 pesos/dollar or 4 cents/peso.
B) 80 pesos/dollar or 4 cents/peso.
C) 5 pesos/dollar or 20 cents/peso.
D) 5 pesos/dollar or 4 cents/peso.
A) 25 pesos/dollar or 4 cents/peso.
B) 80 pesos/dollar or 4 cents/peso.
C) 5 pesos/dollar or 20 cents/peso.
D) 5 pesos/dollar or 4 cents/peso.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



