Deck 14: Magnets and Electromagnetism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Magnets and Electromagnetism
1
An ideal transformer is used to either increase or decrease the voltage in an AC circuit. When the output voltage is greater than the input voltage of a transformer then
A) the power output depends on the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary.
B) the power output is the same as the power input.
C) the power output is larger than the power input.
D) the power output is smaller than the power input.
A) the power output depends on the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary.
B) the power output is the same as the power input.
C) the power output is larger than the power input.
D) the power output is smaller than the power input.
the power output is the same as the power input.
2
A magnetic compass points towards the north geographic pole of the Earth because
A) all magnetic poles, north or south, point that way due to the spin of the Earth.
B) the static electricity in the atmosphere causes the alignment of the compass.
C) there is a north magnetic pole near the north geographic pole.
D) there is a south magnetic pole near the north geographic pole.
A) all magnetic poles, north or south, point that way due to the spin of the Earth.
B) the static electricity in the atmosphere causes the alignment of the compass.
C) there is a north magnetic pole near the north geographic pole.
D) there is a south magnetic pole near the north geographic pole.
there is a south magnetic pole near the north geographic pole.
3
A current flowing through a long, straight wire causes a magnetic field that points
A) along the wire.
B) along concentric circles around the wire.
C) radially inward toward the wire.
D) radially outward from the wire.
A) along the wire.
B) along concentric circles around the wire.
C) radially inward toward the wire.
D) radially outward from the wire.
along concentric circles around the wire.
4
A battery is causing a large current in a solenoid (helical coil of wire). A bar magnet is held at rest nearby, aligned with the axis of the solenoid, with its south pole closest to the solenoid. The bar magnet is being repelled by the solenoid. Which of the following statements is true of the conventional current in the solenoid?
A) The current in the solenoid increases.
B) The current in the solenoid decreases.
C) The current in the solenoid is flowing counterclockwise as seen from the bar magnet.
D) The current in the solenoid is flowing clockwise as seen from the bar magnet.
E) The direction of the current in the solenoid alternates with a constant frequency.
A) The current in the solenoid increases.
B) The current in the solenoid decreases.
C) The current in the solenoid is flowing counterclockwise as seen from the bar magnet.
D) The current in the solenoid is flowing clockwise as seen from the bar magnet.
E) The direction of the current in the solenoid alternates with a constant frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A permanent magnet is produced when
A) magnetic fields of large groups of individual atoms are permanently aligned.
B) electrons become stuck and cease to move.
C) electrical fields exchange electrons with the magnetic fields.
D) current is made to circulate in a clockwise direction in a loop of wire.
A) magnetic fields of large groups of individual atoms are permanently aligned.
B) electrons become stuck and cease to move.
C) electrical fields exchange electrons with the magnetic fields.
D) current is made to circulate in a clockwise direction in a loop of wire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Bar A has one end painted green and the other end red and may or may not be a magnet. A student brings the north pole of a bar magnet M close to the green end of A. He observes that the green end is attracted. He can conclude that
A) A is not a magnet.
B) A is a magnet and the green end is a north pole.
C) A is a magnet and the green end is a south pole.
D) A might be a magnet; this observation does not provide enough information to determine whether or not it is.
A) A is not a magnet.
B) A is a magnet and the green end is a north pole.
C) A is a magnet and the green end is a south pole.
D) A might be a magnet; this observation does not provide enough information to determine whether or not it is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A horizontally moving positive sodium ion enters a magnetic field that points up. The magnetic force pushes the charge out of its original path. 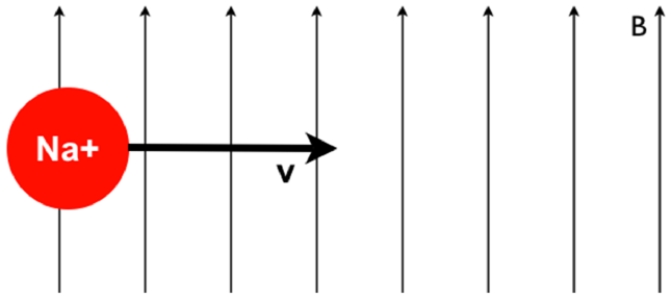 When viewed as shown on this page, what direction will the magnetic force point?
When viewed as shown on this page, what direction will the magnetic force point?
A) Into the page
B) Out of the page
C) There is not enough information to answer.
 When viewed as shown on this page, what direction will the magnetic force point?
When viewed as shown on this page, what direction will the magnetic force point?A) Into the page
B) Out of the page
C) There is not enough information to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A bar magnet and an electrically polarized object are placed next to each other on a table. What happens?
A) The positive part of the object turns toward the north pole of the magnet.
B) The positive part of the object turns toward the south pole of the magnet.
C) The object and magnet accelerate toward each other until they touch and then they repel.
D) Nothing happens.
A) The positive part of the object turns toward the north pole of the magnet.
B) The positive part of the object turns toward the south pole of the magnet.
C) The object and magnet accelerate toward each other until they touch and then they repel.
D) Nothing happens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A positive charge is released from rest near a bar magnet. The magnetic force on the charge
A) There is no magnetic force on the charge.
B) Either pole of the magnet will repel the positive charge.
C) can only be attracted toward the S pole of the magnet.
D) can only be attracted toward the N pole of the magnet.
A) There is no magnetic force on the charge.
B) Either pole of the magnet will repel the positive charge.
C) can only be attracted toward the S pole of the magnet.
D) can only be attracted toward the N pole of the magnet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Electrons flow around a circular wire loop in a horizontal plane, in a direction that is clockwise when viewed from above. This causes a magnetic field. Inside the loop, the direction of this field is
A) toward the center of the loop.
B) radially outward from the center of the loop.
C) up, toward the viewer.
D) down, away from the viewer.
A) toward the center of the loop.
B) radially outward from the center of the loop.
C) up, toward the viewer.
D) down, away from the viewer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Magnetic fields affect
A) neither electric charges in motion nor electric charges at rest.
B) both electric charges in motion and electric charges at rest.
C) only electric charges in motion.
D) only electric charges at rest.
A) neither electric charges in motion nor electric charges at rest.
B) both electric charges in motion and electric charges at rest.
C) only electric charges in motion.
D) only electric charges at rest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of these will always produce a magnetic field?
A) A positive charge at rest
B) Another magnetic field
C) A moving charge
D) A negative charge at rest
A) A positive charge at rest
B) Another magnetic field
C) A moving charge
D) A negative charge at rest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A little magnetic compass has a needle whose tips are clearly labeled N and S. The compass is placed next to a single circular loop of wire lying flat on a wooden table. The current in the loop is clockwise. What happens?
A) The S tip of the needle is attracted toward the loop.
B) The N tip of the needle is attracted toward the loop.
C) The needle orients itself with the N tip pointing in the direction of the current in the segment of the loop closest to the needle.
D) The needle orients itself with the S tip pointing in the direction of the current in the segment of the loop closest to the needle.
E) None of these.
A) The S tip of the needle is attracted toward the loop.
B) The N tip of the needle is attracted toward the loop.
C) The needle orients itself with the N tip pointing in the direction of the current in the segment of the loop closest to the needle.
D) The needle orients itself with the S tip pointing in the direction of the current in the segment of the loop closest to the needle.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The south pole of a bar magnet is moved toward an aluminum ring, along the axis of the ring. As the magnet approaches, the changing magnetic flux induces an electric current in the ring that, when seen from the bar magnet, corresponds to positive charge carriers flowing
A) clockwise.
B) counterclockwise.
C) alternating with a fixed frequency.
D) alternating with a frequency proportional to a speed of the bar magnet.
A) clockwise.
B) counterclockwise.
C) alternating with a fixed frequency.
D) alternating with a frequency proportional to a speed of the bar magnet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Two identical coils of wire are placed on a single horizontal wooden broom handle. The coils are separated by a few centimeters. We now run identical currents in the same direction through each coil. The coils experience
A) no forces because the currents are identical.
B) a repulsive magnetic force.
C) an attractive magnetic force.
D) an attractive electrostatic force because one coil is negatively charged and the other positively charged.
E) a repulsive electrostatic force because both coils are identically charged.
A) no forces because the currents are identical.
B) a repulsive magnetic force.
C) an attractive magnetic force.
D) an attractive electrostatic force because one coil is negatively charged and the other positively charged.
E) a repulsive electrostatic force because both coils are identically charged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A horizontal straight wire carries a current from east to west. The resulting magnetic field lines are
A) straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
B) parallel to the wire from west to east.
C) parallel to the wire from east to west.
D) closed circles perpendicular to the wire directed counterclockwise as viewed from the east.
E) closed circles perpendicular to the wire directed clockwise as viewed from the east.
A) straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
B) parallel to the wire from west to east.
C) parallel to the wire from east to west.
D) closed circles perpendicular to the wire directed counterclockwise as viewed from the east.
E) closed circles perpendicular to the wire directed clockwise as viewed from the east.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following cannot induce a voltage in a loop of wire?
A) Moving a magnet near the loop.
B) Moving the loop near a magnet.
C) Expanding or contracting the loop in a region where there is no magnetic field.
D) Changing the current in a nearby loop.
A) Moving a magnet near the loop.
B) Moving the loop near a magnet.
C) Expanding or contracting the loop in a region where there is no magnetic field.
D) Changing the current in a nearby loop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a current is induced by a changing magnetic field B1, the current always produces a second magnetic field B2 such that
A) B1 and B2 completely cancel each other out.
B) B1 and B2 combine to give a stronger magnetic field than B1 alone.
C) B1 and B2 combine to give a weaker magnetic field than B1 alone.
D) It is not possible to tell whether the combined field is stronger or weaker than B1 without knowing how B1 is changing.
A) B1 and B2 completely cancel each other out.
B) B1 and B2 combine to give a stronger magnetic field than B1 alone.
C) B1 and B2 combine to give a weaker magnetic field than B1 alone.
D) It is not possible to tell whether the combined field is stronger or weaker than B1 without knowing how B1 is changing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Imagine that this classroom contains a constant magnetic field that points from the front to the back. In front of you a negative charge is slowly moving horizontally to your left. As you watch, the magnetic force on the charge
A) deflects the charge away from you.
B) deflects the charge into a clockwise directed vertical circle.
C) deflects the charge toward you.
D) has no effect on the charge.
E) deflects the charge into a counterclockwise vertical circle.
A) deflects the charge away from you.
B) deflects the charge into a clockwise directed vertical circle.
C) deflects the charge toward you.
D) has no effect on the charge.
E) deflects the charge into a counterclockwise vertical circle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A positively charged ping pong ball is sitting stationary on the floor in the center of a room. There is also a constant, uniform magnetic field in the room that points toward the ceiling. If I now start the ball rolling toward the back of the room, the resultant motion of the ball, as observed from the ceiling, will be
A) a diagonal straight line toward the left back corner of the room.
B) a diagonal straight line toward the right back corner of the room.
C) a horizontal, clockwise circle.
D) a horizontal, counterclockwise circle.
E) a straight line in the original direction of motion.
A) a diagonal straight line toward the left back corner of the room.
B) a diagonal straight line toward the right back corner of the room.
C) a horizontal, clockwise circle.
D) a horizontal, counterclockwise circle.
E) a straight line in the original direction of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A transformer is to be used to step down voltage from an alternating current source from 220 V to 110 V. If the primary has 120 turns, then the number of turns in the secondary is
A) 2.
B) 60.
C) 240.
D) 720.
E) 1320.
A) 2.
B) 60.
C) 240.
D) 720.
E) 1320.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The south pole of a bar magnet is moved toward a short helical coil of wire (solenoid) along the axis of the coil. The coil has 100 turns and the ends of the coil are connected to form a closed circuit. If the coil is replaced with a single loop of the same type of wire, and the magnet is moved exactly as before, the current induced in the loop is
A) the same as in the coil.
B) zero in both cases.
C) 100 times smaller.
D) 100 times larger.
A) the same as in the coil.
B) zero in both cases.
C) 100 times smaller.
D) 100 times larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If an electron is placed at rest near a bar magnet, the electron will
A) accelerate away from the negative pole of the magnet.
B) not move at all.
C) be attracted to the positive pole of the magnet.
D) move in a circular path around the north pole of the magnet.
A) accelerate away from the negative pole of the magnet.
B) not move at all.
C) be attracted to the positive pole of the magnet.
D) move in a circular path around the north pole of the magnet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A long straight wire carries a current. A positive charge moves toward the wire in a direction perpendicular to the wire. The direction of the force on the charge will be 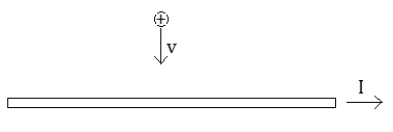
A) parallel to the wire in the direction of the current.
B) parallel to the wire opposite the direction of the current.
C) in the direction of the charge's velocity.
D) opposite the direction of the charge's velocity.
E) There is no force.

A) parallel to the wire in the direction of the current.
B) parallel to the wire opposite the direction of the current.
C) in the direction of the charge's velocity.
D) opposite the direction of the charge's velocity.
E) There is no force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Imagine a magnetic field pointing into the plane of this page. An electron moves across the paper from left to right. The direction of the magnetic force on the electron will be
A) into the plane of the paper.
B) out of the plane of the paper.
C) in the plane of the paper and toward the top of the page.
D) in the plane of the paper and toward the bottom of the page.
E) in the plane of the paper and opposite the electron's velocity.
A) into the plane of the paper.
B) out of the plane of the paper.
C) in the plane of the paper and toward the top of the page.
D) in the plane of the paper and toward the bottom of the page.
E) in the plane of the paper and opposite the electron's velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In outer space, you observe a straight stream of electrons flowing past you at 14.5 miles per second, about the same speed that Mars moves on its orbit around the sun.  You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. Now you fire your rockets and boost your speed so that you are also moving at 14.5 miles per second, exactly at the same speed and direction as the electrons. In what direction does a compass needle point now?
You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. Now you fire your rockets and boost your speed so that you are also moving at 14.5 miles per second, exactly at the same speed and direction as the electrons. In what direction does a compass needle point now?
A) up
B) down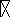
C) left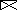
D) right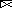
E) You observe no magnetic field.
 You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. Now you fire your rockets and boost your speed so that you are also moving at 14.5 miles per second, exactly at the same speed and direction as the electrons. In what direction does a compass needle point now?
You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. Now you fire your rockets and boost your speed so that you are also moving at 14.5 miles per second, exactly at the same speed and direction as the electrons. In what direction does a compass needle point now?A) up
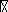
B) down
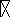
C) left
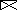
D) right
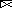
E) You observe no magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two current-carrying wires are parallel to one another and separated by 1 cm. If the distance between them is increased to 2 cm the new force will be what factor times the original force?
A) ¼
B) ½
C) 1
D) 2
E) 4
A) ¼
B) ½
C) 1
D) 2
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The south pole of a bar magnet is moved toward a short helical coil of wire (solenoid) along the axis of the coil. The coil has 100 turns and the ends of the coil are connected to form a closed circuit. If the coil is replaced with a single loop of the same type of wire, and the magnet is moved exactly as before, the magnet experiences a force that is
A) the same as before.
B) attractive and 100 times larger.
C) attractive and 100 times smaller.
D) repulsive and 100 times larger.
E) repulsive and 100 times smaller.
A) the same as before.
B) attractive and 100 times larger.
C) attractive and 100 times smaller.
D) repulsive and 100 times larger.
E) repulsive and 100 times smaller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A bar magnet is broken in half and the magnetic field around one piece is mapped out. What is wrong with this picture? 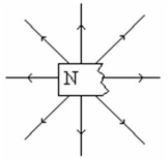
A) The field lines are pointing in the wrong direction.
B) The field lines should converge on the "N."
C) There is no south pole.
D) Nothing; this is how the field looks around a broken magnet.

A) The field lines are pointing in the wrong direction.
B) The field lines should converge on the "N."
C) There is no south pole.
D) Nothing; this is how the field looks around a broken magnet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In outer space, you observe a straight stream of electrons flowing past you at 14.5 miles per second, about the same speed that Mars moves on its orbit around the sun.  You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. In what direction does a compass needle point?
You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. In what direction does a compass needle point?
A) up
B) down
C) left
D) right
E) You observe no magnetic field.
 You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. In what direction does a compass needle point?
You maneuver your spacecraft to face the current so that the electrons are moving from left to right and so that you are 10 m from the stream. In what direction does a compass needle point?A) up
B) down
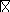
C) left

D) right

E) You observe no magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The magnetic pole near the Earth's north geographic pole actually has to be
A) an N pole because it repels the S pole of your compass needle.
B) an S pole, because it attracts the N pole of your compass needle.
C) either an N or an S pole, but scientists have not determined which one yet.
A) an N pole because it repels the S pole of your compass needle.
B) an S pole, because it attracts the N pole of your compass needle.
C) either an N or an S pole, but scientists have not determined which one yet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A loop of wire is oriented in the magnetic field as shown below (the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field). Which of the following is true? 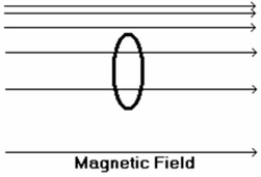
A) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved to the left.
B) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved to the right.
C) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved upward.
D) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved downward.
E) There will be an induced current if the loop is moved either up or down.

A) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved to the left.
B) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved to the right.
C) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved upward.
D) There will be an induced current only if the loop is moved downward.
E) There will be an induced current if the loop is moved either up or down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Two long bar magnets are aligned so that north poles face each other. The magnets are separated by 1 cm, and a repulsive force between the north poles is 0.04 N. When the separation is increased to 2 cm the force will be
A) 0.010 N.
B) 0.020 N.
C) 0.025 N.
D) 0.40 N.
E) 0.050 N.
A) 0.010 N.
B) 0.020 N.
C) 0.025 N.
D) 0.40 N.
E) 0.050 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two particles move into a magnetic field. They enter moving at the same speed and direction. The magnitude of the charge on each is known to be the same. One particle curls to the right and the other to the left upon entering the field, the one on the left moving in a larger circle than the one on the right. From this we can say that
A) the leftward moving particle has more mass and is positively charged.
B) the rightward moving particle has less mass and is positively charged.
C) the leftward moving particle has more mass and its charge is opposite the other particle.
D) the rightward moving particle has positive charge but we cannot say anything about its mass.
A) the leftward moving particle has more mass and is positively charged.
B) the rightward moving particle has less mass and is positively charged.
C) the leftward moving particle has more mass and its charge is opposite the other particle.
D) the rightward moving particle has positive charge but we cannot say anything about its mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the southern hemisphere, the north pole of a compass needle
A) points toward the south geographic pole because there is a south magnetic pole there.
B) points toward the south geographic pole because that is the nearest magnetic pole.
C) points away from the south geographic pole because there is a north magnetic pole there.
D) spins aimlessly because the north geographic pole is beyond the horizon.
A) points toward the south geographic pole because there is a south magnetic pole there.
B) points toward the south geographic pole because that is the nearest magnetic pole.
C) points away from the south geographic pole because there is a north magnetic pole there.
D) spins aimlessly because the north geographic pole is beyond the horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A transformer has 200 turns on the primary and 20 turns on the secondary. The primary is connected to a direct current source of 100 millivolts. The voltage in the secondary coil will be
A) zero.
B) 10 millivolts.
C) 20 millivolts.
D) 1000 millivolts.
E) 4000 millivolts.
A) zero.
B) 10 millivolts.
C) 20 millivolts.
D) 1000 millivolts.
E) 4000 millivolts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The scientist credited with discovering that electric currents produce magnetic fields was
A) Oersted.
B) Ampere.
C) Coulomb.
D) Tesla.
E) Faraday.
A) Oersted.
B) Ampere.
C) Coulomb.
D) Tesla.
E) Faraday.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Think of a closed rectangular loop of wire around the edge of this page. A magnetic field perpendicular to the page points upward and increases in strength in a certain time. During this time the conventional current induced in the loop will be
A) clockwise.
B) counterclockwise.
C) zero.
D) continually changing direction.
A) clockwise.
B) counterclockwise.
C) zero.
D) continually changing direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The sketch below shows a bar magnet in a loop of wire with the bar perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The left-hand side shows the magnet being spun around its long axis while on the right side the magnet is turned end-over-end. Which case creates a larger induced current in the loop? 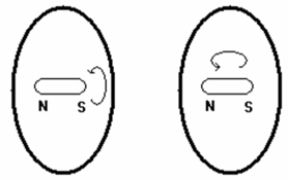
A) The right-hand side.
B) The left-hand side.
C) Neither situation produces an induced current.
D) The induced current is the same in each case and is not zero.

A) The right-hand side.
B) The left-hand side.
C) Neither situation produces an induced current.
D) The induced current is the same in each case and is not zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If an electron moves in a magnetic field,
A) it always feels a force.
B) it only feels a force if its velocity vector is parallel (or antiparallel) to the direction of the magnetic field.
C) it only feels a force if its velocity vector is not parallel (or antiparallel) to the direction of the magnetic field.
D) it does not feel a force if it is in motion, only if stationary.
A) it always feels a force.
B) it only feels a force if its velocity vector is parallel (or antiparallel) to the direction of the magnetic field.
C) it only feels a force if its velocity vector is not parallel (or antiparallel) to the direction of the magnetic field.
D) it does not feel a force if it is in motion, only if stationary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a switch is closed allowing current to flow in coil A, the current induced in a nearby coaxial but unconnected coil B will flow
A) only momentarily and then stop
B) steadily until the current flow in A is shutoff
C) will not flow at all since the coils are not connected
D) will keep flowing long after the current in A is shut off
A) only momentarily and then stop
B) steadily until the current flow in A is shutoff
C) will not flow at all since the coils are not connected
D) will keep flowing long after the current in A is shut off

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When there is a changing magnetic flux through an electric circuit, the direction of the induced current in the circuit is determined by _____________ Law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The unit used in expressing magnetic field strength is the __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A step-up transformer that doubles the input voltage is designed to work with an input voltage that varies at 60 Hz. The frequency with which the output voltage varies is ____________ Hz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If a current of negative charge flows in a circle in the direction of one's curled fingers of the right hand, the resulting magnetic field would be in the direction
A) of the right index finger.
B) of the thumb of the right hand.
C) opposite to the thumb of the right hand.
D) of due north.
Fill in the Blank Questions
A) of the right index finger.
B) of the thumb of the right hand.
C) opposite to the thumb of the right hand.
D) of due north.
Fill in the Blank Questions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A bar magnet is held near a single closed loop of wire. The magnet is aligned with the loop axis, and the north pole is facing the loop. If the magnet is moved away, the current induced in the loop will be in a ______________ direction as viewed from the side the magnet is on.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A solenoid carrying an electric current, if free to rotate when placed in a magnetic field, will tend to orient its axis _________________________________ (parallel, perpendicular, anti-parallel) to the magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Faraday's Law states that a voltage is induced in a circuit when there is a changing ___________________ passing through the circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Two parallel wires each carrying a current in opposite directions will __________________ one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What would happen if you had a car made completely of plastic, with no metal parts, and you drove over a vehicle sensor embedded in the road surface?
A) You would overload the sensor, so this is an excellent method for forcing all lights to turn green.
B) The circuit would detect the absence of magnetic flux, thereby working normally.
C) The sensor would signal with the opposite polarity, indicating you've already gone through the intersection.
D) The sensor would not notice you or your vehicle, and you'd be stuck at the red light.
A) You would overload the sensor, so this is an excellent method for forcing all lights to turn green.
B) The circuit would detect the absence of magnetic flux, thereby working normally.
C) The sensor would signal with the opposite polarity, indicating you've already gone through the intersection.
D) The sensor would not notice you or your vehicle, and you'd be stuck at the red light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The north pole of a bar magnet is moved away from a single closed loop of wire along the axis of the loop. The induced current in the loop produces an effective ____________ pole toward the bar magnet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
You could use two parallel wires to move objects 1 and 2 apart if each wire is embedded in its own object and if 
A) the currents in the wires are in opposite directions.
B) the currents in the wires are in the same direction.
C) one wire carries a current and the other wire has zero current.

A) the currents in the wires are in opposite directions.
B) the currents in the wires are in the same direction.
C) one wire carries a current and the other wire has zero current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
You see a positively charged helium ion in space, and it is at rest with respect to your spacecraft. Since you are studying for the final exam, you decide to experiment. You slowly push the N pole of a bar magnet closer to the helium ion. What happens to the helium ion?
A) It experiences a magnetic force and moves off.
B) It depends on whether it is a positive ion or a negative ion.
C) Nothing happens, because the ion is not moving.
A) It experiences a magnetic force and moves off.
B) It depends on whether it is a positive ion or a negative ion.
C) Nothing happens, because the ion is not moving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



