Deck 25: Capital Budgeting and Managerial Decisions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/158
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Capital Budgeting and Managerial Decisions
1
The concept of incremental cost is the same as the concept of differential cost.
True
2
Another name for relevant cost is unavoidable cost.
False
3
Relevant benefits refer to the additional or incremental revenue generated by selecting a particular course or action over another.
True
4
If a company has the capacity to produce either 10,000 units of Product A or 10,000 units of Product B;assuming fixed costs are the same,production restrictions are the same for both products,and the markets for both products are unlimited;the company should commit 100% of its capacity to the product that has the higher contribution margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Neither the payback period nor the accounting rate of return methods of evaluating investments considers the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Significant sunk costs are relevant to decisions about the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An out-of-pocket cost requires a future outlay of cash and is relevant for current and future decision making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Incremental costs should be considered in a make or buy decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Capital budgeting decisions are risky because the outcome is uncertain,large amounts of money are usually involved,the investment involves a long-term commitment,and the decision could be difficult or impossible to reverse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the internal rate of return (IRR)of an investment is lower than the hurdle rate,the project should be accepted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Part of the decision to accept additional business should be based on a comparison of the incremental (differential)costs of the added production with the additional revenues to be received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An advantage of the break-even time (BET)method over the payback period method is that it recognizes the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Additional business in the form of a special order of goods or services should be accepted when the incremental revenue equals the incremental costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a make or buy decision,management should focus on costs that are the same under the two alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The decision to accept an additional volume of business should be based on a comparison of the revenue from the additional business with the sunk costs of producing that revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An opportunity cost is the potential benefit lost by taking a specific action when two or more alternative choices are available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Capital budgeting is the process of analyzing alternative long-term investments and deciding which assets to acquire or sell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A sunk cost will change with a future course of action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When computing payback period,the year in which a capital investment is made is year 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In ranking choices with the break-even time (BET)method,the investment with the longest BET gets the highest rank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A shorter payback period reduces the company's ability to respond to unanticipated changes and increases the risk of having to keep an unprofitable investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The payback period method,unlike the net present value method,does not ignore cash flows after the point of cost recovery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The accounting rate of return is based on cash flows rather than net income in its calculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Two investments with exactly the same payback periods are not equally valuable to an investor because the timing of net cash flows may be different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The internal rate of return method of evaluating capital investments cannot be used with uneven cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The time value of money is considered when calculating the payback period of an investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If two projects have the same risks,the same payback periods,and the same initial investments,they are equally attractive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A the company's required rate of return,typically its cost of capital is called the:
A)Internal rate of return.
B)Average rate of return.
C)Hurdle rate.
D)Maximum rate.
E)Payback rate.
A)Internal rate of return.
B)Average rate of return.
C)Hurdle rate.
D)Maximum rate.
E)Payback rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The payback period method of evaluating an investment fails to consider cash inflows after the point where an investment's costs are fully recovered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The process of restating future cash flows in today's dollars is known as:
A)Budgeting.
B)Annualization.
C)Discounting.
D)Payback period.
E)Capitalizing.
A)Budgeting.
B)Annualization.
C)Discounting.
D)Payback period.
E)Capitalizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Capital budgeting decisions are risky because all of the following are true except:
A)The outcome is uncertain.
B)Large amounts of money are usually involved.
C)The investment involves a long-term commitment.
D)The decision could be difficult or impossible to reverse.
E)They rarely produce net cash flows.
A)The outcome is uncertain.
B)Large amounts of money are usually involved.
C)The investment involves a long-term commitment.
D)The decision could be difficult or impossible to reverse.
E)They rarely produce net cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The internal rate of return equals the rate that yields a net present value of zero for an investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The process of analyzing alternative long-term investments and deciding which assets to acquire or sell is known as:
A)Planning and control.
B)Capital budgeting.
C)Variance analysis.
D)Master budgeting.
E)Managerial accounting.
A)Planning and control.
B)Capital budgeting.
C)Variance analysis.
D)Master budgeting.
E)Managerial accounting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If net present values are used to evaluate two investments that have equal costs and equal total cash flows,the one with more cash flows in the early years has the higher net present value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The net present value decision rule is: When an asset's expected cash flows yield a positive net present value when discounted at the required rate of return,the asset should be acquired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The calculation of annual net cash flow from a particular investment project should include all of the following except:
A)Income taxes.
B)Revenues generated by the investment.
C)Cost of products generated by the investment.
D)Depreciation expense.
E)General and administrative expenses.
A)Income taxes.
B)Revenues generated by the investment.
C)Cost of products generated by the investment.
D)Depreciation expense.
E)General and administrative expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Capital budgeting decisions are generally based on:
A)Tentative and potentially unreliable predictions of future outcomes.
B)Predictions of future outcomes where risk is eliminated.
C)Results from past outcomes only.
D)Results from current outcomes only.
E)Speculation of interest rates and economic performance only.
A)Tentative and potentially unreliable predictions of future outcomes.
B)Predictions of future outcomes where risk is eliminated.
C)Results from past outcomes only.
D)Results from current outcomes only.
E)Speculation of interest rates and economic performance only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Capital budgeting is the process of analyzing:
A)Cash outflows only.
B)Short-term investments.
C)Long-term investments.
D)Investments with certain outcomes only.
E)Operating revenues.
A)Cash outflows only.
B)Short-term investments.
C)Long-term investments.
D)Investments with certain outcomes only.
E)Operating revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the straight-line depreciation method is used,the annual average investment amount used in calculating rate of return is calculated as (beginning book value + ending book value)/2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In business decision-making,managers typically examine the two fundamental factors of:
A)Risk and capital investment.
B)Risk and return.
C)Capital investment and rate of return.
D)Risk and payback.
E)Payback and rate of return.
A)Risk and capital investment.
B)Risk and return.
C)Capital investment and rate of return.
D)Risk and payback.
E)Payback and rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Gordon Corporation inadvertently produced 10,000 defective digital watches.The watches cost $8 each to produce.A salvage company will purchase the defective units as they are for $3 each.Gordon's production manager reports that the defects can be corrected for $5 per unit,enabling them to be sold at their regular market price of $12.50.Gordon should:
A)Sell the watches for $3 per unit.
B)Correct the defects and sell the watches at the regular price.
C)Sell the watches as they are because repairing them will cause their total cost to exceed their selling price.
D)Sell 5,000 watches to the salvage company and repair the remainder.
E)Throw the watches away.
A)Sell the watches for $3 per unit.
B)Correct the defects and sell the watches at the regular price.
C)Sell the watches as they are because repairing them will cause their total cost to exceed their selling price.
D)Sell 5,000 watches to the salvage company and repair the remainder.
E)Throw the watches away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Maxim manufactures a hamster food product called Green Health.Maxim currently has 10,000 bags of Green Health on hand.The variable production costs per bag are $1.80 and total fixed costs are $10,000.The hamster food can be sold as it is for $9.00 per bag or be processed further into Premium Green and Green Deluxe at an additional $2,000 cost.The additional processing will yield 10,000 bags of Premium Green and 3,000 bags of Green Deluxe,which can be sold for $8 and $6 per bag,respectively.The net advantage (incremental income)of processing Green Health further into Premium Green and Green Deluxe would be:
A)$98,000.
B)$96,000.
C)$8,000.
D)$6,000.
E)$2,000.
A)$98,000.
B)$96,000.
C)$8,000.
D)$6,000.
E)$2,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Chang Industries has 2,000 defective units of product that have already cost $14 each to produce.A salvage company will purchase the defective units as they are for $5 each.Chang's production manager reports that the defects can be corrected for $6 per unit,enabling them to be sold at their regular market price of $21.The incremental income or loss on reworking the units is:
A)$20,000 loss.
B)$20,000 income.
C)$12,000 loss.
D)$32,000 income.
E)$30,000 incomE.
A)$20,000 loss.
B)$20,000 income.
C)$12,000 loss.
D)$32,000 income.
E)$30,000 incomE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An additional cost incurred only if a company pursues a particular course of action is a(n):
A)Period cost.
B)Pocket cost.
C)Discount cost.
D)Incremental cost.
E)Sunk cost.
A)Period cost.
B)Pocket cost.
C)Discount cost.
D)Incremental cost.
E)Sunk cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Bannister Co.is thinking about having one of its products manufactured by a subcontractor. Currently,the cost of manufacturing 1,000 units follows:  If Bannister can buy 1,000 units from a subcontractor for $100,000,it should:
If Bannister can buy 1,000 units from a subcontractor for $100,000,it should:
A)Make the product because current factory overhead is less than $100,000.
B)Make the product because the cost of direct material plus direct labor of manufacturing is less than $100,000.
C)Buy the product because the total incremental costs of manufacturing are greater than $100,000.
D)Buy the product because total fixed and variable manufacturing costs are greater than $100,000.
E)Make the product because factory overhead is a sunk cost.
 If Bannister can buy 1,000 units from a subcontractor for $100,000,it should:
If Bannister can buy 1,000 units from a subcontractor for $100,000,it should:A)Make the product because current factory overhead is less than $100,000.
B)Make the product because the cost of direct material plus direct labor of manufacturing is less than $100,000.
C)Buy the product because the total incremental costs of manufacturing are greater than $100,000.
D)Buy the product because total fixed and variable manufacturing costs are greater than $100,000.
E)Make the product because factory overhead is a sunk cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A company is considering a new project that will cost $19,000.This project would result in additional annual revenues of $6,000 for the next 5 years.The $19,000 cost is an example of a(n):
A)Sunk cost.
B)Fixed cost.
C)Incremental cost.
D)Uncontrollable cost.
E)Opportunity cost.
A)Sunk cost.
B)Fixed cost.
C)Incremental cost.
D)Uncontrollable cost.
E)Opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An opportunity cost:
A)Is an unavoidable cost because it remains the same regardless of the alternative chosen.
B)Requires a current outlay of cash.
C)Results from past managerial decisions.
D)Is the potential benefit lost by choosing a specific alternative course of action among two or more.
E)Is irrelevant in decision making because it occurred in the past.
A)Is an unavoidable cost because it remains the same regardless of the alternative chosen.
B)Requires a current outlay of cash.
C)Results from past managerial decisions.
D)Is the potential benefit lost by choosing a specific alternative course of action among two or more.
E)Is irrelevant in decision making because it occurred in the past.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A company paid $200,000 ten years ago for a specialized machine that has no salvage value and is being depreciated at the rate of $10,000 per year.The company is considering using the machine in a new project that will have incremental revenues of $28,000 per year and annual cash expenses of $20,000.In analyzing the new project,the $200,000 original cost of the machine is an example of a(n):
A)Incremental cost.
B)Opportunity cost.
C)Variable cost.
D)Sunk cost.
E)Out-of-pocket cost.
A)Incremental cost.
B)Opportunity cost.
C)Variable cost.
D)Sunk cost.
E)Out-of-pocket cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Minor Electric has received a special one-time order for 1,500 light fixtures (units)at $5 per unit.Minor currently produces and sells 7,500 units at $6.00 each.This level represents 75% of its capacity.Production costs for these units are $4.50 per unit,which includes $3.00 variable cost and $1.50 fixed cost.To produce the special order,a new machine needs to be purchased at a cost of $1,000 with a zero salvage value.Management expects no other changes in costs as a result of the additional production.If Minor wishes to earn $1,250 on the special order,the size of the order would need to be:
A)4,500 units.
B)2,250 units.
C)1,125 units.
D)625 units.
E)300 units.
A)4,500 units.
B)2,250 units.
C)1,125 units.
D)625 units.
E)300 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Listmann Corp.processes four different products that can either be sold as is or processed further. Listed below are sales and additional cost data: 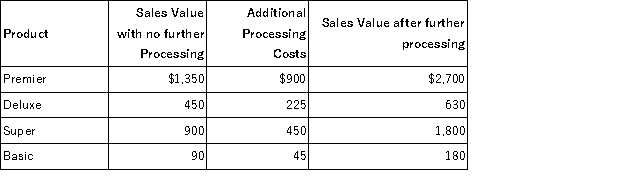 Which product(s)should not be processed further?
Which product(s)should not be processed further?
A)Premier.
B)Deluxe.
C)Super.
D)Basic.
E)Premier and Basic.
 Which product(s)should not be processed further?
Which product(s)should not be processed further?A)Premier.
B)Deluxe.
C)Super.
D)Basic.
E)Premier and Basic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A cost that requires a future outlay of cash,and is relevant for current and future decision making,is a(n):
A)Out-of-pocket cost.
B)Sunk cost.
C)Opportunity cost.
D)Operating cost.
E)Uncontrollable cost.
A)Out-of-pocket cost.
B)Sunk cost.
C)Opportunity cost.
D)Operating cost.
E)Uncontrollable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Factor Co.can produce a unit of product for the following costs:  An outside supplier offers to provide Factor with all the units it needs at $46 per unit.If Factor buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 60% of its overhead.Factor should choose to:
An outside supplier offers to provide Factor with all the units it needs at $46 per unit.If Factor buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 60% of its overhead.Factor should choose to:
A)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $56.
B)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
C)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
D)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $32.
E)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $32.
 An outside supplier offers to provide Factor with all the units it needs at $46 per unit.If Factor buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 60% of its overhead.Factor should choose to:
An outside supplier offers to provide Factor with all the units it needs at $46 per unit.If Factor buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 60% of its overhead.Factor should choose to:A)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $56.
B)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
C)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
D)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $32.
E)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $32.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Minor Electric has received a special one-time order for 1,500 light fixtures (units)at $5 per unit.Minor currently produces and sells 7,500 units at $6.00 each.This level represents 75% of its capacity.Production costs for these units are $4.50 per unit,which includes $3.00 variable cost and $1.50 fixed cost.To produce the special order,a new machine needs to be purchased at a cost of $1,000 with a zero salvage value.Management expects no other changes in costs as a result of the additional production.Should the company accept the special order?
A)No,because additional production would exceed capacity.
B)No,because incremental costs exceed incremental revenue.
C)Yes,because incremental revenue exceeds incremental costs.
D)Yes,because incremental costs exceed incremental revenues.
E)No,because the incremental revenue is too low.
A)No,because additional production would exceed capacity.
B)No,because incremental costs exceed incremental revenue.
C)Yes,because incremental revenue exceeds incremental costs.
D)Yes,because incremental costs exceed incremental revenues.
E)No,because the incremental revenue is too low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A limitation of the internal rate of return method is that it:
A)Does not consider the time value of money.
B)Measures results in years.
C)Lacks ability to compare dissimilar projects.
D)Ignores varying risks over the life of a project.
E)Measures net income rather than cash flows.
A)Does not consider the time value of money.
B)Measures results in years.
C)Lacks ability to compare dissimilar projects.
D)Ignores varying risks over the life of a project.
E)Measures net income rather than cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Epsilon Co.can produce a unit of product for the following costs:  An outside supplier offers to provide Epsilon with all the units it needs at $60 per unit.If Epsilon buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 40% of its overhead.Epsilon should choose to:
An outside supplier offers to provide Epsilon with all the units it needs at $60 per unit.If Epsilon buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 40% of its overhead.Epsilon should choose to:
A)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $72.
B)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $56.
C)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
D)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
E)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $56.
 An outside supplier offers to provide Epsilon with all the units it needs at $60 per unit.If Epsilon buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 40% of its overhead.Epsilon should choose to:
An outside supplier offers to provide Epsilon with all the units it needs at $60 per unit.If Epsilon buys from the supplier,the company will still incur 40% of its overhead.Epsilon should choose to:A)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $72.
B)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $56.
C)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
D)Make since the relevant cost to make it is $48.
E)Buy since the relevant cost to make it is $56.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Bluebird Mfg.has received a special one-time order for 15,000 bird feeders at $3 per unit.Bluebird currently produces and sells 75,000 units at $7.00 each.This level represents 80% of its capacity.Production costs for these units are $3.50 per unit,which includes $2.25 variable cost and $1.25 fixed cost.If Bluebird accepts this additional business,the effect on net income will be:
A)$45,000 increase.
B)$11,250 increase.
C)$33,750 increase.
D)$7,500 decrease.
E)$33,750 decreasE.
A)$45,000 increase.
B)$11,250 increase.
C)$33,750 increase.
D)$7,500 decrease.
E)$33,750 decreasE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Maxim manufactures a cat food product called Green Health.Maxim currently has 10,000 bags of Green Health on hand.The variable production costs per bag are $1.80 and total fixed costs are $10,000.The cat food can be sold as it is for $9.00 per bag or be processed further into Premium Green and Green Deluxe at an additional $2,000 cost.The additional processing will yield 10,000 bags of Premium Green and 3,000 bags of Green Deluxe,which can be sold for $8 and $6 per bag,respectively.If Green Health is processed further into Premium Green and Green Deluxe,the total gross profit would be:
A)$68,000.
B)$78,000.
C)$96,000.
D)$98,000.
E)$100,000.
A)$68,000.
B)$78,000.
C)$96,000.
D)$98,000.
E)$100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A cost that cannot be avoided or changed because it arises from a past decision,and is irrelevant to future decisions,is called a(n):
A)Uncontrollable cost.
B)Incremental cost.
C)Opportunity cost.
D)Out-of-pocket cost.
E)Sunk cost.
A)Uncontrollable cost.
B)Incremental cost.
C)Opportunity cost.
D)Out-of-pocket cost.
E)Sunk cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Chang Industries has 2,000 defective units of product that have already cost $14 each to produce.A salvage company will purchase the defective units as they are for $5 each.Chang's production manager reports that the defects can be corrected for $6 per unit,enabling them to be sold at their regular market price of $21.Chang should:
A)Throw the units away.
B)Sell the units to the salvage company for $5 per unit.
C)Sell the units as they are because repairing them will cause their total cost to exceed their selling price.
D)Sell 1,000 units to the salvage company and repair the remainder.
E)Correct the defects and sell the units at the regular pricE.
A)Throw the units away.
B)Sell the units to the salvage company for $5 per unit.
C)Sell the units as they are because repairing them will cause their total cost to exceed their selling price.
D)Sell 1,000 units to the salvage company and repair the remainder.
E)Correct the defects and sell the units at the regular pricE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The potential benefits lost by taking a specific action when two or more alternative choices are available is known as a(n):
A)Alternative cost.
B)Sunk cost.
C)Out-of-pocket cost.
D)Differential cost.
E)Opportunity cost.
A)Alternative cost.
B)Sunk cost.
C)Out-of-pocket cost.
D)Differential cost.
E)Opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A company is planning to purchase a machine that will cost $24,000,have a six-year life,and be depreciated over a three-year period with no salvage value.The company expects to sell the machine's output of 3,000 units evenly throughout each year.A projected income statement for each year of the asset's life appears below.What is the accounting rate of return for this machine? 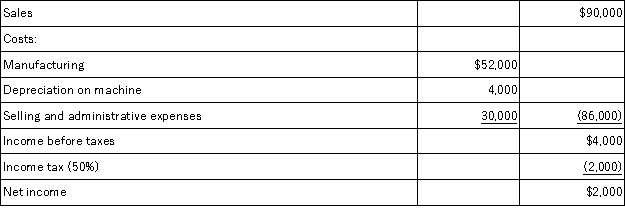
A)33.3%.
B)16.7%.
C)50.0%.
D)8.3%.
E)4%.

A)33.3%.
B)16.7%.
C)50.0%.
D)8.3%.
E)4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
After-tax net income divided by the average amount invested in a project,is the:
A)Net present value rate.
B)Payback rate.
C)Accounting rate of return.
D)Earnings from investment.
E)Profit rate.
A)Net present value rate.
B)Payback rate.
C)Accounting rate of return.
D)Earnings from investment.
E)Profit rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A company buys a machine for $60,000 that has an expected life of 9 years and no salvage value.The company anticipates a yearly net income of $2,850 after taxes of 30%,with the cash flows to be received evenly throughout each year.What is the accounting rate of return?
A)2.85%.
B)4.75%.
C)6.65%.
D)9.50%.
E)42.75%.
A)2.85%.
B)4.75%.
C)6.65%.
D)9.50%.
E)42.75%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Porter Co.is analyzing two projects for the future.Assume that only one project can be selected.  If the company is using the payback period method and it requires a payback of three years or less,which project should be selected?
If the company is using the payback period method and it requires a payback of three years or less,which project should be selected?
A)Project Y.
B)Project X.
C)Both X and Y are acceptable projects.
D)Neither X nor Y is an acceptable project.
E)Project Y because it has a lower initial investment.
 If the company is using the payback period method and it requires a payback of three years or less,which project should be selected?
If the company is using the payback period method and it requires a payback of three years or less,which project should be selected?A)Project Y.
B)Project X.
C)Both X and Y are acceptable projects.
D)Neither X nor Y is an acceptable project.
E)Project Y because it has a lower initial investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A company is considering purchasing a machine for $21,000.The machine will generate an after-tax net income of $2,000 per year.Annual depreciation expense would be $1,500.What is the payback period for the new machine?
A)4 years.
B)6 years.
C)10.5 years.
D)14 years.
E)42 years.
A)4 years.
B)6 years.
C)10.5 years.
D)14 years.
E)42 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The break-even time (BET)method is a variation of the:
A)Payback method.
B)Internal rate of return method.
C)Accounting rate of return method.
D)Net present value method.
E)Present value method.
A)Payback method.
B)Internal rate of return method.
C)Accounting rate of return method.
D)Net present value method.
E)Present value method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Ahngram Corp.has 1,000 defective units of a product that cost $3 per unit in direct costs and $6.50 per unit in indirect cost when produced last year.The units can be sold as scrap for $4 per unit or reworked at an additional cost of $2.50 and sold at full price of $12.The incremental net income (loss)from the choice of reworking the units would be:
A)$5,500.
B)$0.
C)($2,500).
D)$10,500.
E)$2,500.
A)$5,500.
B)$0.
C)($2,500).
D)$10,500.
E)$2,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The expected amount of time to recover the initial amount of an investment is called the:
A)Amortization period.
B)Payback period.
C)Interest period.
D)Budgeting period.
E)Discounted cash flow period.
A)Amortization period.
B)Payback period.
C)Interest period.
D)Budgeting period.
E)Discounted cash flow period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The calculation of the payback period for an investment when net cash flow is even (equal)is:
A)Cost of investment/Annual net cash flow
B)Cost of investment/Total net cash flow
C)Annual net cash flow/Cost of investment
D)Total net cash flow/Cost of investment
E)Total net cash flow/Annual net cash flow
A)Cost of investment/Annual net cash flow
B)Cost of investment/Total net cash flow
C)Annual net cash flow/Cost of investment
D)Total net cash flow/Cost of investment
E)Total net cash flow/Annual net cash flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Markson Company had the following results of operations for the past year: 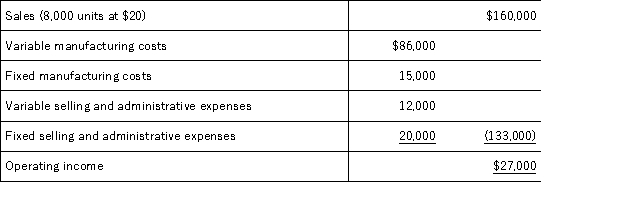 A foreign company whose sales will not affect Markson's market offers to buy 2,000 units at $14 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $1,600 for the purchase of special tools.If Markson accepts this additional business,its profits will:
A foreign company whose sales will not affect Markson's market offers to buy 2,000 units at $14 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $1,600 for the purchase of special tools.If Markson accepts this additional business,its profits will:
A)Increase by $3,500.
B)Decrease by $5,650.
C)Decrease by $1,600.
D)Increase by $1,900.
E)Decrease by $5,100.
 A foreign company whose sales will not affect Markson's market offers to buy 2,000 units at $14 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $1,600 for the purchase of special tools.If Markson accepts this additional business,its profits will:
A foreign company whose sales will not affect Markson's market offers to buy 2,000 units at $14 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $1,600 for the purchase of special tools.If Markson accepts this additional business,its profits will:A)Increase by $3,500.
B)Decrease by $5,650.
C)Decrease by $1,600.
D)Increase by $1,900.
E)Decrease by $5,100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A company has the choice of either selling 600 defective units as scrap or rebuilding them.The company could sell the defective units as they are for $2.00 per unit.Alternatively,it could rebuild them with incremental costs of $0.60 per unit for materials,$1.00 per unit for labor,and $0.80 per unit for overhead,and then sell the rebuilt units for $5.00 each.What should the company do?
A)Sell the units as scrap.
B)Rebuild the units.
C)It does not matter because both alternatives have the same result.
D)Since both alternatives produce a loss,store the units in hopes of a better price later.
E)Throw the units away.
A)Sell the units as scrap.
B)Rebuild the units.
C)It does not matter because both alternatives have the same result.
D)Since both alternatives produce a loss,store the units in hopes of a better price later.
E)Throw the units away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Frederick Co.is thinking about having one of its products manufactured by a subcontractor. Currently,the cost of manufacturing 5,000 units follows:  If Frederick can buy 5,000 units from a subcontractor for $130,000,it should:
If Frederick can buy 5,000 units from a subcontractor for $130,000,it should:
A)Make the product because current factory overhead is less than $130,000.
B)Make the product because the cost of direct material plus direct labor of manufacturing is less than $130,000.
C)Make the product because factory overhead is a sunk cost.
D)Buy the product because total fixed and variable manufacturing costs are greater than $130,000.
E)Buy the product because the total incremental costs of manufacturing are greater than $130,000.
 If Frederick can buy 5,000 units from a subcontractor for $130,000,it should:
If Frederick can buy 5,000 units from a subcontractor for $130,000,it should:A)Make the product because current factory overhead is less than $130,000.
B)Make the product because the cost of direct material plus direct labor of manufacturing is less than $130,000.
C)Make the product because factory overhead is a sunk cost.
D)Buy the product because total fixed and variable manufacturing costs are greater than $130,000.
E)Buy the product because the total incremental costs of manufacturing are greater than $130,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Porter Co.is analyzing two projects for the future.Assume that only one project can be selected.  The payback period in years for Project X is:
The payback period in years for Project X is:
A)2.00.
B)3.83.
C)3.50.
D)2.83.
E)4.00.
 The payback period in years for Project X is:
The payback period in years for Project X is:A)2.00.
B)3.83.
C)3.50.
D)2.83.
E)4.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A company is considering the purchase of a new piece of equipment for $90,000.Predicted annual cash inflows from this investment are $36,000 (year 1),$30,000 (year 2),$18,000 (year 3),$12,000 (year 4)and $6,000 (year 5).The payback period is:
A)4.50 years.
B)4.25 years.
C)3.50 years.
D)3.00 years.
E)2.50 years.
A)4.50 years.
B)4.25 years.
C)3.50 years.
D)3.00 years.
E)2.50 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A company is planning to purchase a machine that will cost $24,000,have a six-year life,and be depreciated over a three-year period with no salvage value.The company expects to sell the machine's output of 3,000 units evenly throughout each year.A projected income statement for each year of the asset's life appears below.What is the payback period for this machine? 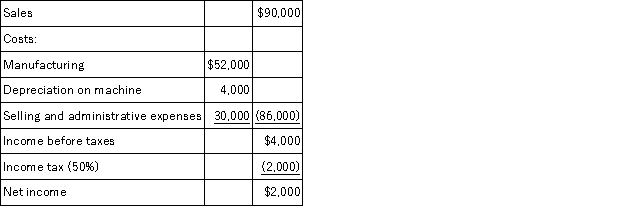
A)24 years.
B)12 years.
C)6 years.
D)4 years.
E)1 year.
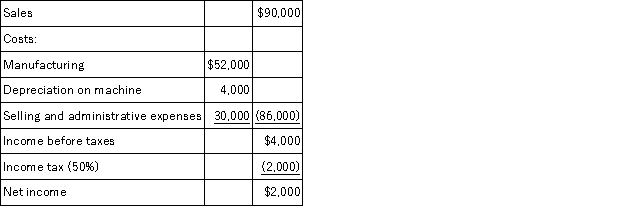
A)24 years.
B)12 years.
C)6 years.
D)4 years.
E)1 year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Benjamin Company had the following results of operations for the past year:  A foreign company (whose sales will not affect Benjamin's market)offers to buy 4,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $600 and selling and administrative costs by $300.If Benjamin accepts the offer,its profits will:
A foreign company (whose sales will not affect Benjamin's market)offers to buy 4,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $600 and selling and administrative costs by $300.If Benjamin accepts the offer,its profits will:
A)Increase by $30,000.
B)Increase by $6,000.
C)Decrease by $6,000.
D)Increase by $5,200.
E)Increase by $4,300.
 A foreign company (whose sales will not affect Benjamin's market)offers to buy 4,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $600 and selling and administrative costs by $300.If Benjamin accepts the offer,its profits will:
A foreign company (whose sales will not affect Benjamin's market)offers to buy 4,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to variable manufacturing costs,selling these units would increase fixed overhead by $600 and selling and administrative costs by $300.If Benjamin accepts the offer,its profits will:A)Increase by $30,000.
B)Increase by $6,000.
C)Decrease by $6,000.
D)Increase by $5,200.
E)Increase by $4,300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A company is considering the purchase of a new machine for $48,000.Management predicts that the machine can produce sales of $16,000 each year for the next 10 years.Expenses are expected to include direct materials,direct labor,and factory overhead totaling $12,000 per year including depreciation of $3,000 per year.The company's tax rate is 40%.What is the payback period for the new machine?
A)20.0 years.
B)6.0 years.
C)7.5 years.
D)12.0 years.
E)8.9 years.
A)20.0 years.
B)6.0 years.
C)7.5 years.
D)12.0 years.
E)8.9 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Lattimer Company had the following results of operations for the past year: 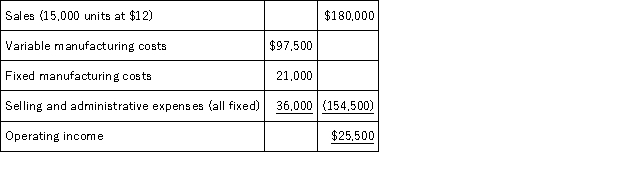 A foreign company whose sales will not affect Lattimer's market offers to buy 5,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to existing costs,selling these units would add a $0.25 selling cost for export fees.If Lattimer accepts this additional business,the special order will yield a:
A foreign company whose sales will not affect Lattimer's market offers to buy 5,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to existing costs,selling these units would add a $0.25 selling cost for export fees.If Lattimer accepts this additional business,the special order will yield a:
A)$2,000 loss.
B)$8,250 loss.
C)$3,750 profit.
D)$3,250 loss.
E)$5,000 profit.
 A foreign company whose sales will not affect Lattimer's market offers to buy 5,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to existing costs,selling these units would add a $0.25 selling cost for export fees.If Lattimer accepts this additional business,the special order will yield a:
A foreign company whose sales will not affect Lattimer's market offers to buy 5,000 units at $7.50 per unit.In addition to existing costs,selling these units would add a $0.25 selling cost for export fees.If Lattimer accepts this additional business,the special order will yield a:A)$2,000 loss.
B)$8,250 loss.
C)$3,750 profit.
D)$3,250 loss.
E)$5,000 profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A company has the choice of either selling 1,000 defective units as scrap or rebuilding them.The company could sell the defective units as they are for $4.00 per unit.Alternatively,it could rebuild them with incremental costs of $1.00 per unit for materials,$2.00 per unit for labor,and $1.50 per unit for overhead,and then sell the rebuilt units for $8.00 each.What should the company do?
A)Sell the units as scrap.
B)Rebuild the units.
C)It does not matter because both alternatives have the same result.
D)Neither sell nor rebuild because both alternatives produce a loss.Instead,the company should store the units permanently.
E)Throw the units away.
A)Sell the units as scrap.
B)Rebuild the units.
C)It does not matter because both alternatives have the same result.
D)Neither sell nor rebuild because both alternatives produce a loss.Instead,the company should store the units permanently.
E)Throw the units away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A disadvantage of using the payback period to compare investment alternatives is that:
A)It ignores cash flows beyond the payback period.
B)It includes the time value of money.
C)It cannot be used when cash flows are not uniform.
D)It cannot be used if a company records depreciation.
E)It cannot be used to compare investments with different initial investments.
A)It ignores cash flows beyond the payback period.
B)It includes the time value of money.
C)It cannot be used when cash flows are not uniform.
D)It cannot be used if a company records depreciation.
E)It cannot be used to compare investments with different initial investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



