Deck 8: Chromosome Mutations: Variation in Number and Arrangement
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Chromosome Mutations: Variation in Number and Arrangement
1
Having a complete set or sets of chromosomes is called____.
A)ploidy
B)diploid
C)euploid
D)monoploid
E)aneuploidy
A)ploidy
B)diploid
C)euploid
D)monoploid
E)aneuploidy
euploid
2
Noninvasive prenatal genetic diagnosis is sometimes preferred to amniocentesis because ____
A)the mother does not have to be present
B)it requires only a blood draw from the mother
C)it requires less technical time of a research lab
D)it gives more precise results
E)it gives quicker results
A)the mother does not have to be present
B)it requires only a blood draw from the mother
C)it requires less technical time of a research lab
D)it gives more precise results
E)it gives quicker results
it requires only a blood draw from the mother
3
Given that a human normally contains 46 chromosomes,give the chromosome number for each of the following conditions: Triploid Trisomy 13
A)69,47
B)138,47
C)69,45
D)138,45
E)96,47
A)69,47
B)138,47
C)69,45
D)138,45
E)96,47
A
4
What is the outcome of nondisjunction in meiosis I?
A)a resultant gamete that is triploid
B)a resultant gamete that may harbor from one chromosome both homologs from one parent or none at all
C)a resultant gamete that is devoid of all chromosomes
D)a resultant gamete that may harbor from one chromosome both sister chromatids or none at all
E)four gametes that are all trisomic
A)a resultant gamete that is triploid
B)a resultant gamete that may harbor from one chromosome both homologs from one parent or none at all
C)a resultant gamete that is devoid of all chromosomes
D)a resultant gamete that may harbor from one chromosome both sister chromatids or none at all
E)four gametes that are all trisomic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Trisomy 21,or Down syndrome,occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement but one extra)chromosome 21.Although fertility is reduced in both sexes,females have higher fertility rates than males.Van Dyke et al.1995; Down Syndrome Research and Practice 32 : 65-69 summarize data involving children born of Down syndrome individuals.Assume that children are born to a female with Down syndrome and a normal 46- chromosome male.What proportion of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome?
A)None of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)One- half of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)One- third of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)Two- thirds of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.
A)None of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)One- half of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)One- third of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)Two- thirds of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What experiment led to the identification of the DSCR Down Syndrome Critical Region ?
A)an extra DSCR was injected into yeast cells
B)transgenic humans were developed that had a duplicated DSCR
C)a mouse model was developed lacking the DSCR
D)cancer cells were sequenced to identify the VEGF gene
E)a mouse model was developed trisomic for the DSCR
A)an extra DSCR was injected into yeast cells
B)transgenic humans were developed that had a duplicated DSCR
C)a mouse model was developed lacking the DSCR
D)cancer cells were sequenced to identify the VEGF gene
E)a mouse model was developed trisomic for the DSCR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
____is viewed as a major cause of aneuploidy.
A)X- ray mutations
B)Heat treatment
C)Segmental deletions
D)Colchicine treatment
E)Nondisjunction
A)X- ray mutations
B)Heat treatment
C)Segmental deletions
D)Colchicine treatment
E)Nondisjunction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Name two methods used in genetic prenatal diagnostic testing in humans.
A)chorionic villus sampling and cellular mitotic analysis
B)whole genome sequencing and PCR
C)amniocentesis and DSCR
D)amniocentesis and NIPGD
E)amniocentesis and fetal uterine physiology compatibility test
A)chorionic villus sampling and cellular mitotic analysis
B)whole genome sequencing and PCR
C)amniocentesis and DSCR
D)amniocentesis and NIPGD
E)amniocentesis and fetal uterine physiology compatibility test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An expected meiotic pairing configuration in a____ would be a trivalent.
A)monoploid
B)diploid
C)monosomic individual
D)trisomic individual
E)triploid
A)monoploid
B)diploid
C)monosomic individual
D)trisomic individual
E)triploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The condition that exists when an organism gains or loses one or more chromosomes but not a complete haploid set is known as____ .
A)polyploidy
B)triploidy
C)euploidy
D)aneuploidy
E)trisomy
A)polyploidy
B)triploidy
C)euploidy
D)aneuploidy
E)trisomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What explanation is generally given for lethality of monosomic individuals?
A)The loss of a single chromosome is not generally lethal,unless the individual is inbred.
B)Cells count the number of chromosomes they have and will undergo apoptosis when the chromosome number is incorrect.
C)Monosomic chromosomes cannot undergo mitosis correctly.
D)The gametes of monosomic individuals cannot undergo meiosis,and this is lethal.
E)Monosomy may unmask recessive lethals that are tolerated in heterozygotes carrying the wild- type allele.
A)The loss of a single chromosome is not generally lethal,unless the individual is inbred.
B)Cells count the number of chromosomes they have and will undergo apoptosis when the chromosome number is incorrect.
C)Monosomic chromosomes cannot undergo mitosis correctly.
D)The gametes of monosomic individuals cannot undergo meiosis,and this is lethal.
E)Monosomy may unmask recessive lethals that are tolerated in heterozygotes carrying the wild- type allele.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Trisomy 21,or Down syndrome,occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement but one extra)chromosome 21.While there is reduced fertility in both sexes,females have higher fertility than males.Van Dyke et al.1995; Down Syndrome Research and Practice 32 : 65- 69 summarize data involving children born of Down syndrome individuals.Given the fact that conceptuses with 48 chromosomes four #21 chromosomes are not likely to survive early development,what percentage of surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome if both parents have Down syndrome?
A)One- half of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)Two- thirds of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)None of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)One- third of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.
A)One- half of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)Two- thirds of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)None of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)One- third of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A child is born with Turner's syndrome and she is red green color blind recessive X- linked).Her father is red green color blind as well and her mother is homozygous dominant for color sight.What had to happen in order for this child to be born with this chromosomal complement?
A)nondisjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II of the father
B)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the mother
C)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the father
D)nondisjunction in meiosis I of the father
E)nondisjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II of the mother
A)nondisjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II of the father
B)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the mother
C)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the father
D)nondisjunction in meiosis I of the father
E)nondisjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II of the mother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A son is born with Kleinfelter's syndrome and hemophilia.His father was normal and his mother was a carrier for the recessive X- linked blood clotting disorder.What occurred in meiosis to produce this genetic outcome?
A)nondisjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II of the mother
B)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the father
C)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the mother
D)nondisjunction in meiosis I of the father
E)nondisjunction in meiosis I of the mother
A)nondisjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II of the mother
B)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the father
C)nondisjunction in meiosis II of the mother
D)nondisjunction in meiosis I of the father
E)nondisjunction in meiosis I of the mother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Assume that a species has a diploid chromosome number of 24.The term applied to an individual with 25 chromosomes would be____ .
A)triploid
B)trisomy
C)euploid
D)aneuploidy
E)aneuploidy and trisomy
A)triploid
B)trisomy
C)euploid
D)aneuploidy
E)aneuploidy and trisomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the leading cause of Down syndrome?
A)In men over 25,sperm formation is impaired and produces monosomic children.
B)Aberrant implantation in the uterus leads to developmental problems in the fetus.
C)The nondisjunctional event that produces Down syndrome occurs more frequently during oogenesis in women older than age 35.
D)In older parents,there is egg/sperm incompatibility leading to duplication of chromosome 21.
E)In older females,chromosome 21 is duplicated leading to abnormal egg formation.
A)In men over 25,sperm formation is impaired and produces monosomic children.
B)Aberrant implantation in the uterus leads to developmental problems in the fetus.
C)The nondisjunctional event that produces Down syndrome occurs more frequently during oogenesis in women older than age 35.
D)In older parents,there is egg/sperm incompatibility leading to duplication of chromosome 21.
E)In older females,chromosome 21 is duplicated leading to abnormal egg formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Name the polyploid condition that is formed from the addition of an extra set of chromosomes identical to the normal diploid complement of the same species.
A)autotetraploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is haploid
B)allotetraploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is diploid
C)alloeuploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is diploid
D)autotetraploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is diploid
E)autooctoploidyploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is haploid
A)autotetraploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is haploid
B)allotetraploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is diploid
C)alloeuploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is diploid
D)autotetraploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is diploid
E)autooctoploidyploidy,assuming the normal chromosome complement is haploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An individual with Patau syndrome would be____ .
A)said to have a trisomy
B)termed a triploid
C)said to have a monosomy
D)termed a haploid
E)termed a euploid
A)said to have a trisomy
B)termed a triploid
C)said to have a monosomy
D)termed a haploid
E)termed a euploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Haploinsufficiency refers to____ .
A)the genetic predisposition for some genes to come in only one copy in the genome
B)the process by which a single gene will cause a cascading effect on a genome's phenotype
C)the condition whereby a single cell is insufficient to divide to cause cancer
D)the condition whereby a single chromosome is insufficient to sustain life
E)a state of being whereby a single gene is sufficient to cause several phenotypes
A)the genetic predisposition for some genes to come in only one copy in the genome
B)the process by which a single gene will cause a cascading effect on a genome's phenotype
C)the condition whereby a single cell is insufficient to divide to cause cancer
D)the condition whereby a single chromosome is insufficient to sustain life
E)a state of being whereby a single gene is sufficient to cause several phenotypes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Given that a human normally contains 46 chromosomes,give the chromosome number for each of the following conditions: Turner syndrome female,no Barr bodies Klinefelter syndrome male,one Barr body
A)47,45
B)46,47
C)45,47
D)47,47
E)45,46
A)47,45
B)46,47
C)45,47
D)47,47
E)45,46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An ____may arise when three sperm cells are involved in fertilization of a single egg.
A)allotriploid
B)allotetraploid
C)autotriploid
D)aneuploidy
E)autotetraploid
A)allotriploid
B)allotetraploid
C)autotriploid
D)aneuploidy
E)autotetraploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What error of meiosis leads to both a duplication and a deletion?
A)replication cross formation
B)replication errors
C)X- ray chromosomal breakage
D)D loop formation
E)unequal crossing over
A)replication cross formation
B)replication errors
C)X- ray chromosomal breakage
D)D loop formation
E)unequal crossing over

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Gene amplification is the basis for____ .
A)formation of the translocation cross
B)the nucleolar organizing region
C)bar- eyed flies
D)interstitial deletions
E)a segmental deletion
A)formation of the translocation cross
B)the nucleolar organizing region
C)bar- eyed flies
D)interstitial deletions
E)a segmental deletion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Inversion heterokaryotypes are often characterized as having reduced crossing over and reduced fertility.Assume that you were examining a strain of organisms you knew to be inversion heterokaryotypes and saw a relatively high number of double chromatid bridges extending between anaphase I nuclei,as indicated in the following drawing.What is the product of this type of inversion loop? 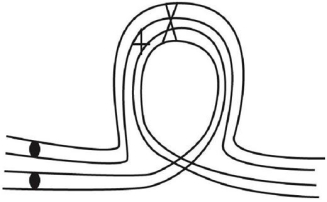
A)two acentric fragments and two dicentric chromosomes
B)two chromosomes with deletions and two acentric fragments
C)one acentric fragment,one dicentric chromosome,and two wild- type chromosomes
D)two chromosomes with deletions and two with duplications
E)four wild- type chromosomes

A)two acentric fragments and two dicentric chromosomes
B)two chromosomes with deletions and two acentric fragments
C)one acentric fragment,one dicentric chromosome,and two wild- type chromosomes
D)two chromosomes with deletions and two with duplications
E)four wild- type chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not a potential outcome of a gene duplication?
A)they may lead to translocation cross formation during synapsis
B)they may result in gene redundancy
C)they may result in providing the raw material for evolution
D)they may produce phenotypic variation
E)they may lead to the development of gene families
A)they may lead to translocation cross formation during synapsis
B)they may result in gene redundancy
C)they may result in providing the raw material for evolution
D)they may produce phenotypic variation
E)they may lead to the development of gene families

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A ____ inversion is one whose breakpoints do not flank the centromere.
A)acentric
B)dicentric
C)pericentric
D)segmental
E)paracentric
A)acentric
B)dicentric
C)pericentric
D)segmental
E)paracentric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is formed when meiosis occurs in an individual who is heterozygous for an intercalary deletion?
A)a trifecta chromosomal cross
B)a terminal loop
C)a compensation loop
D)a translocation
E)a translocation cross
A)a trifecta chromosomal cross
B)a terminal loop
C)a compensation loop
D)a translocation
E)a translocation cross

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is an example of an endopolyploid?
A)an egg has complete nondisjunction and the resultant offspring is triploid
B)cells lining the gut of mosquito larvae attain 16n ploidy
C)one chromosome is lost during cell division
D)two diploid mate and produce a tetraploid
E)an individual suffers from a trisomy
A)an egg has complete nondisjunction and the resultant offspring is triploid
B)cells lining the gut of mosquito larvae attain 16n ploidy
C)one chromosome is lost during cell division
D)two diploid mate and produce a tetraploid
E)an individual suffers from a trisomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Describe double Bar mutations in Drosophila melanogaster.
A)large deletion in the X chromosome
B)a female fly with only one X chromosome
C)an X chromosome with two duplications of the 16A region
D)duplications in a portion of the X chromosome
E)an inversion heterozygote of the X chromosome
A)large deletion in the X chromosome
B)a female fly with only one X chromosome
C)an X chromosome with two duplications of the 16A region
D)duplications in a portion of the X chromosome
E)an inversion heterozygote of the X chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The chromosomal aberration that causes cri- du- chat syndrome can be referred to as an____.
A)segmental deletion
B)reciprocal translocation
C)simple translocation
D)duplication
E)inversion
A)segmental deletion
B)reciprocal translocation
C)simple translocation
D)duplication
E)inversion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Assume that a species has a diploid chromosome number of 24.The term applied to an individual with 36 chromosomes would be____ .
A)triploid
B)allopolyploid
C)aneuploidy
D)monoploid
E)tetraploid
A)triploid
B)allopolyploid
C)aneuploidy
D)monoploid
E)tetraploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How do deletions and translocations in chromosomes often occur?
A)chromosomes will break and the sticky ends will rejoin
B)during meiosis I,sister chromatid exchange leads to abnormalities
C)colchicine treatment causes chromosomal rearrangements
D)when cells undergo meiosis II,chromosomes naturally break when sister chromatids are being pulled apart
E)chromosomes will fuse telomere to telomere
A)chromosomes will break and the sticky ends will rejoin
B)during meiosis I,sister chromatid exchange leads to abnormalities
C)colchicine treatment causes chromosomal rearrangements
D)when cells undergo meiosis II,chromosomes naturally break when sister chromatids are being pulled apart
E)chromosomes will fuse telomere to telomere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Doubling the chromosomes of a sterile species hybrid with colchicine or cold shock is a method used to produce a fertile species hybrid called a ____.
A)autoploid
B)allopolyploid
C)amphidiploid
D)triploid
E)autoallopolyploid
A)autoploid
B)allopolyploid
C)amphidiploid
D)triploid
E)autoallopolyploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assume that an organism has a haploid chromosome number of 7.There would be ____chromosomes in a monoploid individual of that species.
A)3.5
B)7
C)14
D)28
E)42
A)3.5
B)7
C)14
D)28
E)42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is NOT a potential consequence of a copy number variation?
A)phenotypic consequences that track with the number of each gene
B)none
C)higher protein levels of specific genes
D)phenotypic consequences leading to enhanced ability to fight infection
E)loss of function at multiple loci
A)phenotypic consequences that track with the number of each gene
B)none
C)higher protein levels of specific genes
D)phenotypic consequences leading to enhanced ability to fight infection
E)loss of function at multiple loci

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Provide an example of gene redundancy that occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
A)CNV
B)spindle fiber protein genes
C)rDNA
D)cell wall proteins
E)centromeres
A)CNV
B)spindle fiber protein genes
C)rDNA
D)cell wall proteins
E)centromeres

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The condition known as cri- du- chat syndrome in humans has a genetic constitution designated as ____.
A)trisomy
B)46,5p-
C)45,X
D)heteroplasmy
E)triploidy
A)trisomy
B)46,5p-
C)45,X
D)heteroplasmy
E)triploidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Colchicine is an alkaloid derived from plants.What is its effect on chromosome behavior?
A)By blocking DNA replication,chromosomes fail to migrate to the poles at anaphase; thus,homologous chromosomes end up in the same nucleus.
B)By blocking DNA replication,chromosomes do not undergo meiosis II and instead half the gametes are empty.
C)By blocking DNA replication,chromosomes do not undergo meiosis I and instead all gametes suffer from aneuploidy.
D)By interfering with spindle formation,replicated chromosomes fail to migrate to the poles at anaphase; thus,sister chromatids end up in the same nucleus.
E)By interfering with spindle formation,replicated chromosomes fail to migrate to the poles at anaphase; thus,homologous chromosomes end up in the same nucleus.
A)By blocking DNA replication,chromosomes fail to migrate to the poles at anaphase; thus,homologous chromosomes end up in the same nucleus.
B)By blocking DNA replication,chromosomes do not undergo meiosis II and instead half the gametes are empty.
C)By blocking DNA replication,chromosomes do not undergo meiosis I and instead all gametes suffer from aneuploidy.
D)By interfering with spindle formation,replicated chromosomes fail to migrate to the poles at anaphase; thus,sister chromatids end up in the same nucleus.
E)By interfering with spindle formation,replicated chromosomes fail to migrate to the poles at anaphase; thus,homologous chromosomes end up in the same nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A chromosome without a centromere is ____.
A)segmental
B)paracentric
C)pericentric
D)dicentric
E)acentric
A)segmental
B)paracentric
C)pericentric
D)dicentric
E)acentric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Assume that an organism has a diploid chromosome number of 14.There would be ____chromosomes in a tetraploid.
A)104
B)42
C)56
D)14
E)28
A)104
B)42
C)56
D)14
E)28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Genetic anticipation is best described as____ .
A)the phenomenon by which synapsis is delayed due to translocation cross formation
B)trinucleotide repeats increase in future generations
C)cells stop during the cell cycle to check for DNA damage or acentric fragments
D)trinucleotide repeats form fragile sites
E)the G2 gap before meiosis
A)the phenomenon by which synapsis is delayed due to translocation cross formation
B)trinucleotide repeats increase in future generations
C)cells stop during the cell cycle to check for DNA damage or acentric fragments
D)trinucleotide repeats form fragile sites
E)the G2 gap before meiosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Although the most frequent forms of Down syndrome are caused by a random error,nondisjunction of chromosome 21,Down syndrome occasionally runs in families.The cause of this form of familial Down syndrome is ____.
A)a maternal age effect
B)a chromosomal aberration involving chromosome 1
C)an inversion involving chromosome 21
D)a translocation between chromosome 21 and a member of the D chromosome group
E)too many X chromosomes
A)a maternal age effect
B)a chromosomal aberration involving chromosome 1
C)an inversion involving chromosome 21
D)a translocation between chromosome 21 and a member of the D chromosome group
E)too many X chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A genomic condition that may be responsible for some forms of fragile X syndrome,as well as Huntington disease,involves____ .
A)various lengths of trinucleotide repeats
B)multiple inversions in the X chromosome
C)single translocations in the X chromosome
D)plasmids inserted into the FMR- 1 gene
E)multiple breakpoints fairly evenly dispersed along the X chromosome
A)various lengths of trinucleotide repeats
B)multiple inversions in the X chromosome
C)single translocations in the X chromosome
D)plasmids inserted into the FMR- 1 gene
E)multiple breakpoints fairly evenly dispersed along the X chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What type of chromosomal configuration does the following diagram illustrate? 
A)inversion paracentric.heterozygote
B)reciprocal translocation heterozygote
C)inversion paricentric.heterozygote
D)inversion paracentric.homozygote
E)simple translocation heterozygote

A)inversion paracentric.heterozygote
B)reciprocal translocation heterozygote
C)inversion paricentric.heterozygote
D)inversion paracentric.homozygote
E)simple translocation heterozygote

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is a fragile site?
A)a site in a chromosome prone to duplication,such as the bar gene
B)a structural component of a chromosome due to proteins bound to it that leads to a high percentage of chromosomal breakage
C)the telomere of a chromosome can fall off due to spindle malfunctions during meiosis
D)a structural component of a chromosome due to the nucleotide sequence to it that leads to a high percentage of chromosomal breakage
E)an area around the centromere prone to inversion due to gene duplications
A)a site in a chromosome prone to duplication,such as the bar gene
B)a structural component of a chromosome due to proteins bound to it that leads to a high percentage of chromosomal breakage
C)the telomere of a chromosome can fall off due to spindle malfunctions during meiosis
D)a structural component of a chromosome due to the nucleotide sequence to it that leads to a high percentage of chromosomal breakage
E)an area around the centromere prone to inversion due to gene duplications

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is a potentially evolutionary advantage of inversion heterozygosity?
A)inversion loops stimulate favorable allele combinations
B)haploinsufficiency does not occur in inversion heterozygotes
C)if a favorable complement of alleles occurs in an inversion heterozygote,they will not be disrupted by crossing over
D)enhanced genetic variation in the offspring
E)there is none
A)inversion loops stimulate favorable allele combinations
B)haploinsufficiency does not occur in inversion heterozygotes
C)if a favorable complement of alleles occurs in an inversion heterozygote,they will not be disrupted by crossing over
D)enhanced genetic variation in the offspring
E)there is none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Recently,a gene located on chromosome 3 in humans,FHIT,has been shown to be associated with the significant human malady known as ____ .
A)XYY/XY mosaicism
B)Klinefelter syndrome
C)Huntington disease
D)cancer
E)"mad- cow" disease
A)XYY/XY mosaicism
B)Klinefelter syndrome
C)Huntington disease
D)cancer
E)"mad- cow" disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)In general,inversion and translocation heterozygotes are as fertile as organisms whose chromosomes are in the standard arrangement.
B)Inversions and translocations are without evolutionary significance.
C)Translocations may be pericentric or paracentric.
D)Individuals with familial Down syndrome are trisomic and have 47 chromosomes.
E)Familial Down syndrome is caused by a translocation involving chromosome 21.
A)In general,inversion and translocation heterozygotes are as fertile as organisms whose chromosomes are in the standard arrangement.
B)Inversions and translocations are without evolutionary significance.
C)Translocations may be pericentric or paracentric.
D)Individuals with familial Down syndrome are trisomic and have 47 chromosomes.
E)Familial Down syndrome is caused by a translocation involving chromosome 21.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



