Deck 3: Computing the Tax
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/185
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Computing the Tax
1
An increase in a taxpayer's AGI could decrease the amount of charitable contribution that can be claimed.
False
2
Many taxpayers who previously itemized will start claiming the standard deduction when they purchase a home.
False
3
After Ellie moves out of the apartment she had rented as her personal residence, she recovers her damage deposit of $1,000. The $1,000 is not income to Ellie.
True
4
An "above the line" deduction refers to a deduction for AGI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The additional standard deduction for age and blindness is greater for married taxpayers than for single taxpayers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All exclusions from gross income are reported on Form 1040.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The filing status of a taxpayer (e.g., single, head of household) must be identified before the applicable standard deduction is determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Claude's deductions from AGI exceed the standard deduction allowed for 2014. Under these circumstances, Claude cannot claim the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
As opposed to itemizing deductions from AGI, the majority of individual taxpayers choose the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The basic and additional standard deductions both are subject to an annual adjustment for inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Under the Federal income tax formula for individuals, a choice must be made between claiming deductions for AGI and itemized deductions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Because they appear on page 1 of Form 1040, itemized deductions are also referred to as "page 1 deductions."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Lee, a citizen of Korea, is a resident of the U.S. Any rent income Lee receives from land he owns in Korea is not subject to the U.S. income tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Once they reach age 65, many taxpayers will switch from itemizing their deductions from AGI and start claiming the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Under the Federal income tax formula for individuals, the determination of adjusted gross income (AGI) precedes that of taxable income (TI).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A decrease in a taxpayer's AGI could increase the amount of medical expenses that can be deducted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Jason and Peg are married and file a joint return. Both are over 65 years of age and Jason is blind. Their standard deduction for 2014 is $16,000 ($12,400 + $1,200 + $1,200 + $1,200).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 2014, Ed is 66 and single. If he has itemized deductions of $7,400, he should not claim the standard deduction alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Howard, age 82, dies on January 2, 2014. On Howard's final income tax return, the full amount of the basic and additional standard deductions will be allowed even though Howard lived for only 2 days during the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Under the income tax formula, a taxpayer must choose between deductions for AGI and the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Dan and Donna are husband and wife and file separate returns for the year. If Dan itemizes his deductions from AGI, Donna cannot claim the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Lucas, age 17 and single, earns $6,000 during 2014. Lucas's parents cannot claim him as a dependent if he does not live with them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Buddy and Hazel are ages 72 and 71 and file a joint return. If they have itemized deductions of $14,600 for 2014, they should not claim the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In 2014, Hal furnishes more than half of the support of his ex-wife and her father, both of whom live with him. The divorce occurred in 2013. Hal may claim the father-in-law and the ex-wife as dependents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Clara, age 68, claims head of household filing status. If she has itemized deductions of $10,250 for 2014, she should not claim the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Benjamin, age 16, is claimed as a dependent by his parents. During 2014, he earned $700 at a car wash.
Benjamin's standard deduction is $1,350 ($1,000 + $350).
Benjamin's standard deduction is $1,350 ($1,000 + $350).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A dependent cannot claim a personal exemption on his or her own return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Derek, age 46, is a surviving spouse. If he has itemized deductions of $12,700 for 2014, Derek should not claim the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Debby, age 18, is claimed as a dependent by her mother. During 2014, she earned $1,100 in interest income on a savings account. Debby's standard deduction is $1,450 ($1,100 + $350).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Katrina, age 16, is claimed as a dependent by her parents. During 2014, she earned $5,600 as a checker at a grocery store. Her standard deduction is $5,950 ($5,600 earned income + $350).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Butch and Minerva are divorced in December of 2014. Since they were married for more than one-half of the year, they are considered as married for 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Roy and Linda were divorced in 2013. The divorce decree awards custody of their children to Linda but is silent as to who is entitled to claim them as dependents. If Roy furnished more than half of their support, he can claim them as dependents in 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Monique is a resident of the U.S. and a citizen of France. If she files a U.S. income tax return, Monique cannot claim the standard deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
After her divorce, Hope continues to support her exhusband's sister, Cindy, who does not live with her. Hope can claim Cindy as a dependent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For the year a spouse dies, the surviving spouse is considered married for the entire year for income tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Darren, age 20 and not disabled, earns $4,000 during 2014. Darren's parents cannot claim him as a dependent unless he is a full-time student.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When separate income tax returns are filed by married taxpayers, one spouse cannot claim the other spouse as an exemption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In determining whether the gross income test is met for dependency exemption purposes, only the taxable portion of a scholarship is considered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using borrowed funds from a mortgage on her home, Leah provides 52% of her own support, while her sons furnished the rest. Leah can be claimed as a dependent under a multiple support agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Albert buys his mother a TV. For purposes of meeting the support test, Albert cannot include the cost of the TV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Surviving spouse filing status begins in the year in which the deceased spouse died.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When the kiddie tax applies and the parents are divorced, the applicable parent (for determining the parental tax) is the one with the greater taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Currently, the top income tax rate in effect is not the highest it has ever been.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An individual taxpayer uses a fiscal year March 1February 28. The due date of this taxpayer's Federal income tax return is May 15 of each tax year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For tax purposes, married persons filing separate returns are treated the same as single taxpayers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Katelyn is divorced and maintains a household in which she and her daughter, Crissa, live. Crissa, age 22, earns $11,000 during 2014 as a model. Katelyn does not qualify for head of household filing status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Since an abandoned spouse is treated as not married and has one or more dependent children, he or she qualifies for the standard deduction available to head of household.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Kim, a resident of Oregon, supports his parents who are residents of Canada but citizens of Korea. Kim can claim his parents as dependents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In terms of income tax consequences, abandoned spouses are treated the same way as married persons filing separate returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Once a child reaches age 19, the kiddie tax no longer applies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Married taxpayers who file a joint return cannot later (i.e., after the filing due date) switch to separate returns for that year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Married taxpayers who file separately cannot later (i.e., after the due date for filing) change to a joint return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In terms of timing as to any one year, the Tax Tables are available before the Tax Rate Schedules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In January 2014, Jake's wife dies and he does not remarry. For tax year 2014, Jake may not be able to use the filing status available to married persons filing joint returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Ed is divorced and maintains a home in which he and a dependent friend live. Ed does not qualify for head of household filing status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The kiddie tax does not apply to a child whose earned income is more than one-half of his or her support.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Sarah furnishes more than 50% of the support of her son and daughter-in-law who live with her. If the son and daughter-in-law file a joint return, Sarah cannot claim them as dependents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
For dependents who have income, special filing requirements apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A taxpayer who itemizes must use Form 1040, and cannot use Form 1040EZ or Form 1040A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In determining the filing requirement based on gross income received, both additional standard deductions (i.e., age and blindness) are taken into account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In terms of the tax formula applicable to individual taxpayers, which, if any, of the following statements is correct?
A) In arriving at AGI, a taxpayer must elect between claiming deductions for AGI and deductions from AGI.
B) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must elect between claiming deductions for AGI and deductions from AGI.
C) If a taxpayer has deductions for AGI, the standard deduction is not available.
D) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must elect between deductions for AGI and the standard deduction.
E) None of the above.
A) In arriving at AGI, a taxpayer must elect between claiming deductions for AGI and deductions from AGI.
B) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must elect between claiming deductions for AGI and deductions from AGI.
C) If a taxpayer has deductions for AGI, the standard deduction is not available.
D) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must elect between deductions for AGI and the standard deduction.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For 2014, Stuart has a short-term capital loss, a collectible long-term capital gain, and a long-term capital gain from land held as investment. The short-term loss is first applied to the collectible capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
During 2014, Esther had the following transactions:

Esther's AGI is:
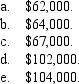

Esther's AGI is:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
During 2014, Marvin had the following transactions:

Marvin's AGI is:
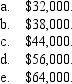

Marvin's AGI is:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Regarding the tax formula and its relationship to Form 1040, which, if any, of the following statements is correct?
A) Most exclusions from gross income are reported on page 2 of Form 1040.
B) An "above the line deduction" refers to a deduction from AGI.
C) A "page 1 deduction" refers to a deduction for AGI.
D) The taxable income (TI) amount appears both at the bottom of page 1 and at the top of page 2 of Form 1040.
E) None of the above.
A) Most exclusions from gross income are reported on page 2 of Form 1040.
B) An "above the line deduction" refers to a deduction from AGI.
C) A "page 1 deduction" refers to a deduction for AGI.
D) The taxable income (TI) amount appears both at the bottom of page 1 and at the top of page 2 of Form 1040.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In 2014, Frank sold his personal use automobile for a loss of $9,000. He also sold a personal coin collection for a gain of $10,000. As a result of these sales, $10,000 is subject to income tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which, if any, of the statements regarding the standard deduction is correct?
A) Some taxpayers may qualify for two types of standard deductions.
B) Not available to taxpayers who choose to deduct their personal and dependency exemptions.
C) May be taken as a for AGI deduction.
D) The basic standard deduction is indexed for inflation but the additional standard deduction is not.
E) None of the above.
A) Some taxpayers may qualify for two types of standard deductions.
B) Not available to taxpayers who choose to deduct their personal and dependency exemptions.
C) May be taken as a for AGI deduction.
D) The basic standard deduction is indexed for inflation but the additional standard deduction is not.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In 2014, Cindy had the following transactions:
Cindy's AGI is:
Cindy's AGI is:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In terms of the tax formula applicable to individual taxpayers, which, if any, of the following statements is correct?
A) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must choose between the standard deduction and deductions from AGI.
B) In arriving at AGI, personal and dependency exemptions must be subtracted from gross income.
C) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must choose between the standard deduction and claiming personal and dependency exemptions.
D) The formula does not apply if a taxpayer elects to claim the standard deduction.
E) None of the above.
A) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must choose between the standard deduction and deductions from AGI.
B) In arriving at AGI, personal and dependency exemptions must be subtracted from gross income.
C) In arriving at taxable income, a taxpayer must choose between the standard deduction and claiming personal and dependency exemptions.
D) The formula does not apply if a taxpayer elects to claim the standard deduction.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
During 2014, Sarah had the following transactions:
Sarah's AGI is:
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
Sarah's AGI is:
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Gain on the sale of collectibles held for more than 12 months always is subject to a tax rate of 28%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the kiddie tax applies, the child need not file an income tax return because the child's income will be reported on the parents' return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A child who has unearned income of $2,000 or less cannot be subject to the kiddie tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which, if any, of the following is a deduction for AGI?
A) State and local sales taxes.
B) Interest on home mortgage.
C) Charitable contributions.
D) Unreimbursed moving expenses of an employee.
E) None of the above.
A) State and local sales taxes.
B) Interest on home mortgage.
C) Charitable contributions.
D) Unreimbursed moving expenses of an employee.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following items, if any, is deductible?
A) Parking expenses incurred in connection with jury duty-taxpayer is a dentist.
B) Substantiated gambling losses (not in excess of gambling winnings) from state lottery.
C) Contributions to mayor's reelection campaign.
D) Speeding ticket incurred while on business.
E) Premiums paid on personal life insurance policy.
A) Parking expenses incurred in connection with jury duty-taxpayer is a dentist.
B) Substantiated gambling losses (not in excess of gambling winnings) from state lottery.
C) Contributions to mayor's reelection campaign.
D) Speeding ticket incurred while on business.
E) Premiums paid on personal life insurance policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Sylvia, age 17, is claimed by her parents as a dependent. During 2014, she had interest income from a bank savings account of $2,000 and income from a parttime job of $4,200. Sylvia's taxable income is:
A) $4,200 - $4,550 = $0.
B) $6,200 - $5,700 = $500.
C) $6,200 - $4,550 = $1,650.
D) $6,200 - $1,000 = $5,200.
E) None of the above.
A) $4,200 - $4,550 = $0.
B) $6,200 - $5,700 = $500.
C) $6,200 - $4,550 = $1,650.
D) $6,200 - $1,000 = $5,200.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Tony, age 15, is claimed as a dependent by his grandmother. During 2014, Tony had interest income from Boeing Corporation bonds of $1,000 and earnings from a parttime job of $700. Tony's taxable income is:
A) $1,700.
B) $1,700 - $700 - $1,000 = $0.
C) $1,700 - $1,050 = $650.
D) $1,700 - $1,000 = $700.
E) None of the above.
A) $1,700.
B) $1,700 - $700 - $1,000 = $0.
C) $1,700 - $1,050 = $650.
D) $1,700 - $1,000 = $700.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A child who is married cannot be subject to the kiddie tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which, if any, of the following statements relating to the standard deduction is correct?
A) If a taxpayer dies during the year, his (or her) standard deduction must be prorated.
B) If a taxpayer is claimed as a dependent of another, his (or her) additional standard deduction is allowed in full (i.e., no adjustment is necessary).
C) If spouses file separate returns, both spouses must claim the standard deduction (rather than itemize their deductions from AGI).
D) If a taxpayer is claimed as a dependent of another, no basic standard deduction is allowed.
E) None of the above.
A) If a taxpayer dies during the year, his (or her) standard deduction must be prorated.
B) If a taxpayer is claimed as a dependent of another, his (or her) additional standard deduction is allowed in full (i.e., no adjustment is necessary).
C) If spouses file separate returns, both spouses must claim the standard deduction (rather than itemize their deductions from AGI).
D) If a taxpayer is claimed as a dependent of another, no basic standard deduction is allowed.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which, if any, of the following is a deduction for AGI?
A) Contributions to a traditional Individual Retirement Account.
B) Child support payments.
C) Funeral expenses.
D) Loss on the sale of a personal residence.
E) Medical expenses.
A) Contributions to a traditional Individual Retirement Account.
B) Child support payments.
C) Funeral expenses.
D) Loss on the sale of a personal residence.
E) Medical expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



