Deck 8: Political Geography
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Political Geography
1
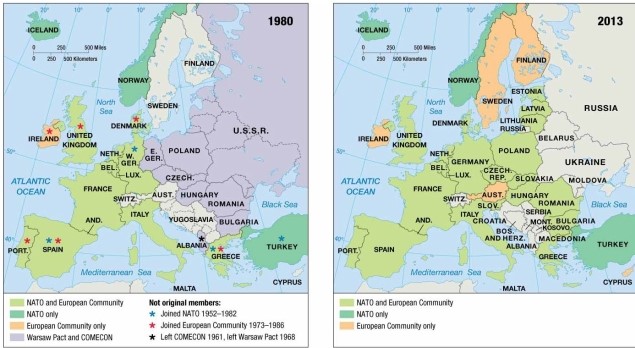
As indicated on the map of European economic and military alliances, in 2013 Ireland
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of COMECON and NATO.
D) was a member of the European Community only.
E) was neither a member of NATO nor of the European Community.
D
2
In 2002 the Organization of African Unity was replaced by
A) the African Union.
B) the African National Party.
C) the African Treaty Organization.
D) the Organization of African OPEC States.
E) the Organization for African Economic Cooperation.
A) the African Union.
B) the African National Party.
C) the African Treaty Organization.
D) the Organization of African OPEC States.
E) the Organization for African Economic Cooperation.
A
3

As indicated on the map of United Nation membership, Namibia joined the United Nations in the
A) early 20th century.
B) early 21st century.
C) mid 20th century.
D) late 20th century.
E) late 19th century.
D
4
The United Nations is primarily what kind of cooperative effort?
A) political
B) military
C) economic
D) cultural
E) environmental
A) political
B) military
C) economic
D) cultural
E) environmental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The most populous country that is not a member of the United Nations is
A) Taiwan.
B) South Korea.
C) Antarctica.
D) Vatican City.
E) Monaco.
A) Taiwan.
B) South Korea.
C) Antarctica.
D) Vatican City.
E) Monaco.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Over the past half century, the number of sovereign states in the world
A) has remained approximately the same.
B) has increased by a couple of dozen.
C) has decreased by a couple of dozen.
D) has increased by more than a hundred.
E) has increased by more than a thousand.
A) has remained approximately the same.
B) has increased by a couple of dozen.
C) has decreased by a couple of dozen.
D) has increased by more than a hundred.
E) has increased by more than a thousand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
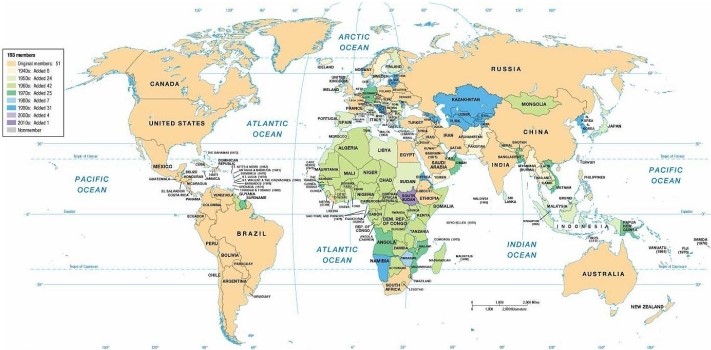
The map concerning United Nations membership indicates that Ethiopia
A) left the UN in the 1990s but joined again in the early 2000s.
B) has not yet joined the United Nations as an independent state.
C) became a UN member in the 1950s.
D) became a UN member in the 1940s.
E) joined the UN in the 1950s but left it in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The historically neutral country that recently joined the United Nations is
A) Switzerland.
B) Australia.
C) France.
D) Canada.
E) Monaco.
A) Switzerland.
B) Australia.
C) France.
D) Canada.
E) Monaco.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The world's largest state is
A) China.
B) Canada.
C) Russia.
D) Alaska.
E) India.
A) China.
B) Canada.
C) Russia.
D) Alaska.
E) India.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
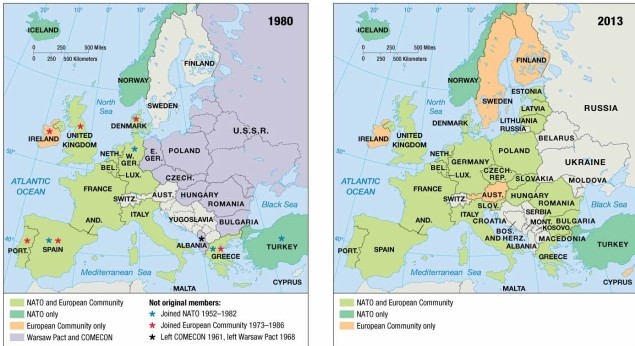
As indicated on the map of European economic and military alliances, in 2013 Austria
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of COMECON and NATO.
D) was a member of the European Community only.
E) was neither a member of NATO nor of the European Community.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
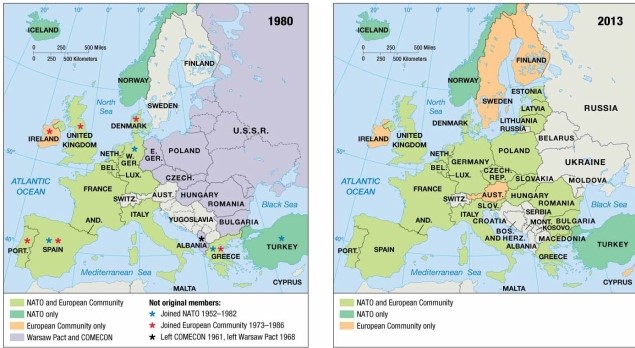
As indicated on the maps of economic and political alliances, in 1980 Sweden
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of the European Community but not NATO.
D) remained nonaligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact.
E) was a member of the Warsaw Pact and COMECON.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
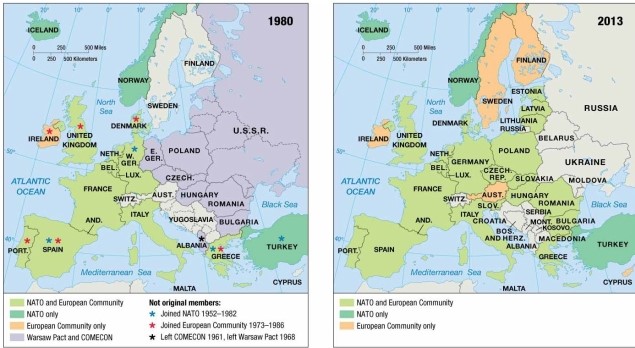
As indicated on the maps of economic and political alliances, in the late 20th century Austria
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of the European Community but not NATO.
D) remained nonaligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact.
E) was a member of the Warsaw Pact and COMECON.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
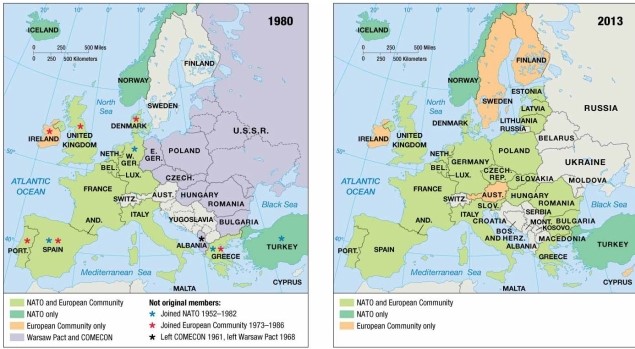
As indicated on the map of European economic and military alliances, in 2013 Latvia
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of COMECON and NATO.
D) was a member of the European Community only.
E) was neither a member of NATO nor of the European Community.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Conflicting claims to the Arctic are mostly due to
A) the potential for energy resources.
B) old Cold War grudges.
C) colonial expansion.
D) shifting sea ice formations.
E) the proximity of South American and African countries.
A) the potential for energy resources.
B) old Cold War grudges.
C) colonial expansion.
D) shifting sea ice formations.
E) the proximity of South American and African countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
During his presentation at the United Nations, then-Secretary of State Colin Powell used what geographic tool to make the case for war?
A) air photos of alleged chemical weapons bunkers
B) documents linking Iran and Afghanistan to yellowcake uranium
C) photos and recordings linking U.S. military leaders to Saddam Hussein
D) air photos showing troop movements and territorial disputes with Kuwait
E) falsified recordings linking Saddam Hussein to al-Qaeda
A) air photos of alleged chemical weapons bunkers
B) documents linking Iran and Afghanistan to yellowcake uranium
C) photos and recordings linking U.S. military leaders to Saddam Hussein
D) air photos showing troop movements and territorial disputes with Kuwait
E) falsified recordings linking Saddam Hussein to al-Qaeda

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
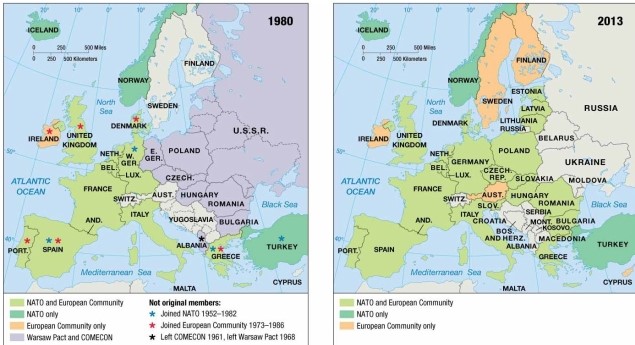
As indicated on the maps of economic and political alliances, in 1980 Ireland
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of the European Community but not NATO.
D) remained nonaligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact.
E) was a member of the Warsaw Pact and COMECON.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

The map concerning United Nations membership indicates that most African countries
A) left the UN in the 1990s but joined again in the early 2000s.
B) have not yet joined the United Nations as independent states.
C) became UN members in the 1940s and 1950s.
D) became UN members in the 1960s and 1970s.
E) joined the UN in the 1950s but left the UN in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
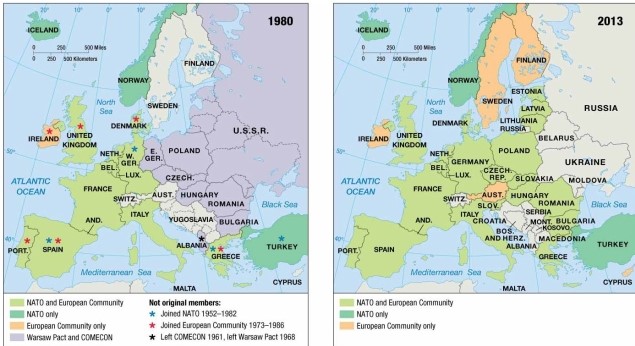
As indicated on the maps of economic and political alliances, in 1980 Belgium
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of the European Community but not NATO.
D) remained nonaligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact.
E) was a member of the Warsaw Pact and COMECON.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
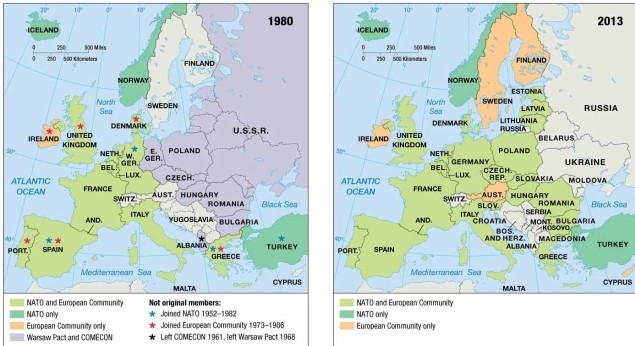
As indicated on the maps of economic and political alliances, in 1980 Bulgaria
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of the European Community but not NATO.
D) remained nonaligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact.
E) was a member of the Warsaw Pact and COMECON.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
As indicated on the maps of economic and political alliances, in 1980 Hungary
A) was a member of NATO and the European Community.
B) was a member of NATO but not the European Community.
C) was a member of the European Community but not NATO.
D) remained nonaligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact.
E) was a member of the Warsaw Pact and COMECON.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Commonwealth is primarily
A) an economic and cultural alliance of states once part of the British Empire.
B) an organization of culturally homogenous nations that opposed the Warsaw Pact.
C) organized to increase availability of mineral resources in perforated states that are NATO allies.
D) a religious entity that sends missionaries to Africa from the United Kingdom.
E) an association of countries that were once members of COMECON and the Warsaw Pact.
A) an economic and cultural alliance of states once part of the British Empire.
B) an organization of culturally homogenous nations that opposed the Warsaw Pact.
C) organized to increase availability of mineral resources in perforated states that are NATO allies.
D) a religious entity that sends missionaries to Africa from the United Kingdom.
E) an association of countries that were once members of COMECON and the Warsaw Pact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The attempt by one country to impose political control over another territory is
A) colonialism.
B) constitutionality.
C) self-determination.
D) sovereignty.
E) suffrage.
A) colonialism.
B) constitutionality.
C) self-determination.
D) sovereignty.
E) suffrage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
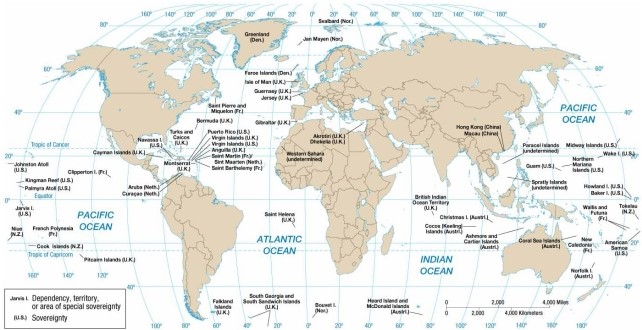
According to the map of present-day colonial possessions, the U.S. colony located east of the Philippines is
A) Palmyra.
B) Guam.
C) Jarvis Island.
D) Puerto Rico.
E) the U.S. Virgin Islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The most populous remaining colony is ruled by
A) the United States.
B) the United Kingdom.
C) France.
D) China.
E) the Netherlands.
A) the United States.
B) the United Kingdom.
C) France.
D) China.
E) the Netherlands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Fertile Crescent
A) followed the Nile and Euphrates rivers.
B) was the key to the Roman Empire in classical times.
C) was the location of the first city-states in the Middle East and the first large-scale agricultural projects of Sub-Saharan Africa.
D) is sometimes considered to have extended from the Nile Valley to the Atlas Mountains.
E) extended from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea and was the location of the first city-states in the Middle East.
A) followed the Nile and Euphrates rivers.
B) was the key to the Roman Empire in classical times.
C) was the location of the first city-states in the Middle East and the first large-scale agricultural projects of Sub-Saharan Africa.
D) is sometimes considered to have extended from the Nile Valley to the Atlas Mountains.
E) extended from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea and was the location of the first city-states in the Middle East.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
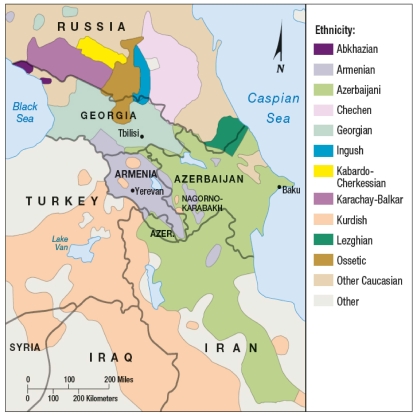
The Kurds are
A) a multinational state.
B) divided among more than one state.
C) a religious minority in the Middle East.
D) trying to unite with Turkey.
E) the majority population of Iraq.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A territory tied to a state rather than being completely independent is a
A) nation.
B) state.
C) nation-state.
D) colony.
E) patron-state.
A) nation.
B) state.
C) nation-state.
D) colony.
E) patron-state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An area organized into an independent political unit is a
A) colony.
B) nationality.
C) nation.
D) state.
E) territory.
A) colony.
B) nationality.
C) nation.
D) state.
E) territory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Examples of major nation-states are
A) Germany and Denmark.
B) Australia and New Zealand.
C) Russia and the United States.
D) Mexico and Russia.
E) Mexico and Germany.
A) Germany and Denmark.
B) Australia and New Zealand.
C) Russia and the United States.
D) Mexico and Russia.
E) Mexico and Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
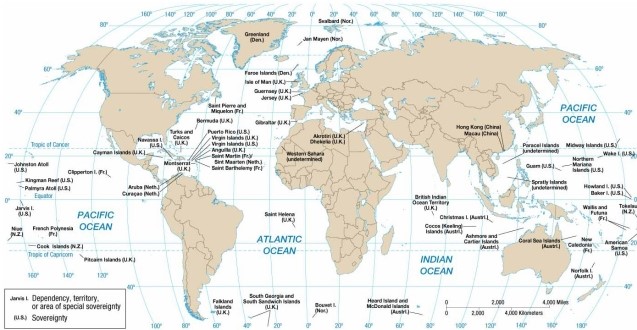
According to the map of present-day colonial possessions, the U.S. colony located west of the British Virgin Islands is
A) Palmyra.
B) Guam.
C) Jarvis Island.
D) Puerto Rico.
E) the U.S. Virgin Islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
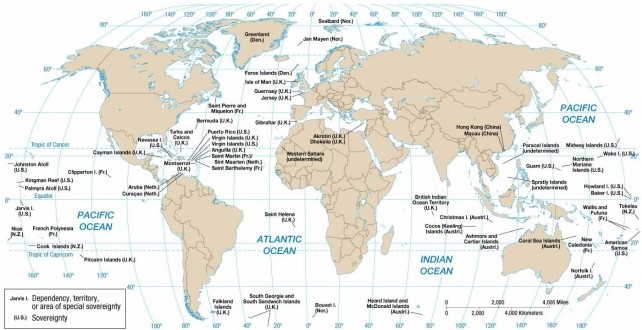
Which of the following is a small British colony in the Pacific Ocean?
A) Hong Kong.
B) Pitcairn.
C) Puerto Rico.
D) San Marino.
E) St. Lucia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The motives of European states in establishing colonies can be summarized as all but which of the following?
A) God
B) glory
C) guilt
D) gold
E) power
A) God
B) glory
C) guilt
D) gold
E) power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The first states in ancient Mesopotamia were
A) city-states, which incorporated cities as well as their countryside.
B) colonies, which incorporated cities as well as their countryside.
C) empires, which incorporated dozens of unified colonies.
D) nation-states, which incorporated city-states, colonies, and empires.
E) patron-states ruled by sheiks.
A) city-states, which incorporated cities as well as their countryside.
B) colonies, which incorporated cities as well as their countryside.
C) empires, which incorporated dozens of unified colonies.
D) nation-states, which incorporated city-states, colonies, and empires.
E) patron-states ruled by sheiks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Korea is a good example of a(n)
A) sovereign state.
B) nation-state existing in a unified condition.
C) ethnicity divided between more than one state.
D) colony divided between more than one ethnicity.
E) patron-state.
A) sovereign state.
B) nation-state existing in a unified condition.
C) ethnicity divided between more than one state.
D) colony divided between more than one ethnicity.
E) patron-state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Political unity in the ancient Mediterranean world reached its height in
A) the Fertile Crescent.
B) Egypt.
C) the Roman Empire.
D) Western Europe.
E) the Alexandrian Empire.
A) the Fertile Crescent.
B) Egypt.
C) the Roman Empire.
D) Western Europe.
E) the Alexandrian Empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The best example of a state among the following is
A) an island with a long history of self-rule and a homogeneous ethnic identity, although the island has been under the control of a colonial power for the last 30 years.
B) a group of islands inhabited by a homogeneous ethnicity, although the westernmost islands pertain to the territory of one country whereas the easternmost islands pertain to another country.
C) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities and divided up administratively among various independent countries.
D) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities which share responsibility for maintaining an independent government and a standing army.
E) a mountainous region inhabited by a mixture of peoples but recently colonized by a European nation-state.
A) an island with a long history of self-rule and a homogeneous ethnic identity, although the island has been under the control of a colonial power for the last 30 years.
B) a group of islands inhabited by a homogeneous ethnicity, although the westernmost islands pertain to the territory of one country whereas the easternmost islands pertain to another country.
C) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities and divided up administratively among various independent countries.
D) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities which share responsibility for maintaining an independent government and a standing army.
E) a mountainous region inhabited by a mixture of peoples but recently colonized by a European nation-state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The best example of a nation among the following is
A) an island with a long history of self-rule and a homogeneous ethnic identity, although the island has been under the control of a colonial power for the last 30 years.
B) a group of islands inhabited by a homogeneous ethnicity, although the westernmost islands pertain to the territory of one country whereas the easternmost islands pertain to another country.
C) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities and divided up administratively among various independent countries.
D) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities which share responsibility for maintaining an independent government and a standing army.
E) a mountainous region inhabited by a mixture of peoples but recently colonized by a European nation-state.
A) an island with a long history of self-rule and a homogeneous ethnic identity, although the island has been under the control of a colonial power for the last 30 years.
B) a group of islands inhabited by a homogeneous ethnicity, although the westernmost islands pertain to the territory of one country whereas the easternmost islands pertain to another country.
C) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities and divided up administratively among various independent countries.
D) a mountainous region inhabited by heterogeneous ethnicities which share responsibility for maintaining an independent government and a standing army.
E) a mountainous region inhabited by a mixture of peoples but recently colonized by a European nation-state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Among the world's largest multinational states are
A) Russia and the United States.
B) Australia and New Zealand.
C) Japan and Denmark.
D) Mexico and Russia.
E) Mexico and Japan.
A) Russia and the United States.
B) Australia and New Zealand.
C) Japan and Denmark.
D) Mexico and Russia.
E) Mexico and Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The problems experienced by Cyprus during the past four decades include all but which of the following?
A) a Greek-inspired military coup
B) a Turkish army invasion
C) a partition of the island by the British as part of independence
D) an increasing spatial segregation of Greeks and Turks
E) division of the capital city by a buffer zone patrolled by UN soldiers
A) a Greek-inspired military coup
B) a Turkish army invasion
C) a partition of the island by the British as part of independence
D) an increasing spatial segregation of Greeks and Turks
E) division of the capital city by a buffer zone patrolled by UN soldiers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The first widespread use of the nation-state concept came in
A) Mesopotamia.
B) the Roman Empire.
C) Western Europe.
D) the United States.
E) Southeast Asia.
A) Mesopotamia.
B) the Roman Empire.
C) Western Europe.
D) the United States.
E) Southeast Asia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A feature of the physical environment commonly used to separate states includes all but which of the following?
A) deserts
B) geometry
C) mountains
D) lakes
E) rivers
A) deserts
B) geometry
C) mountains
D) lakes
E) rivers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Swaziland makes ________ into a perforated state.
A) Madagascar
B) the United Kingdom
C) Italy
D) South Africa
E) Zimbabwe
A) Madagascar
B) the United Kingdom
C) Italy
D) South Africa
E) Zimbabwe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
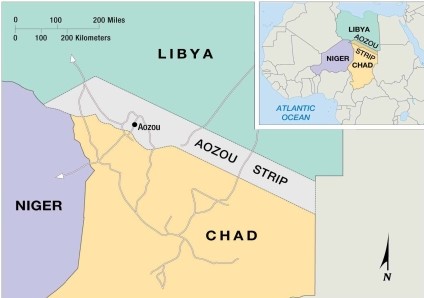
As indicated on the maps in this chapter, the shape and size of the Aozou Strip make it an example of a
A) prorupted boundary.
B) physical boundary.
C) geometric boundary.
D) mathematical frontier.
E) perforated frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
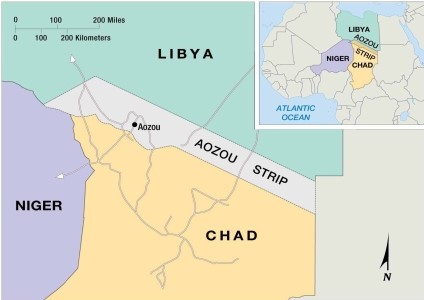
As shown on this map, the Aozou Strip
A) is a zone of conflict between Russia and its neighbors in the Caucasus region.
B) exists because of Egypt's past invasions of the Sinai Peninsula.
C) disappeared when the disputed border between Egypt and Libya was overrun.
D) is a disputed zone that abuts Niger on the west and Sudan on the east.
E) forms an elongated strip of disputed land between Chad and Egypt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
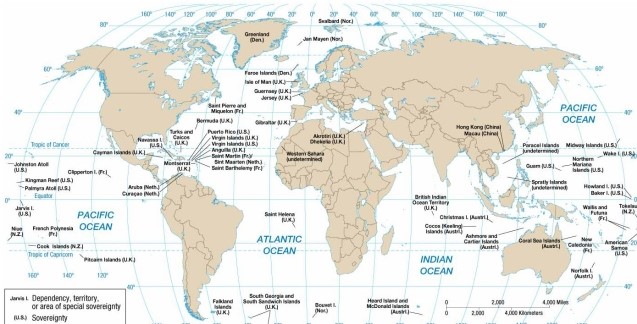
According to the map of present-day colonial possessions, the British colony east of Argentina is
A) Gibraltar.
B) Saint Helena.
C) the British Virgin Islands.
D) the Falkland Islands.
E) Anguila.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The most fragmented Southeast Asian state is
A) Brunei.
B) Malaysia.
C) East Timor.
D) Indonesia.
E) Thailand.
A) Brunei.
B) Malaysia.
C) East Timor.
D) Indonesia.
E) Thailand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A South American country with an elongated shape is
A) Bolivia.
B) Colombia.
C) Brazil.
D) Chile.
E) Ecuador
A) Bolivia.
B) Colombia.
C) Brazil.
D) Chile.
E) Ecuador

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
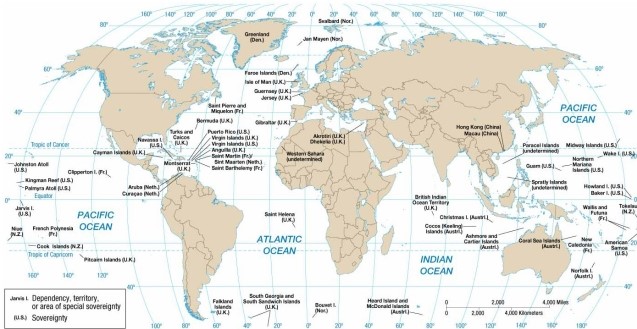
According to the map of present-day colonial possessions, the British colony to the west of Angola is
A) Anguila.
B) the Falkland Islands.
C) Gibraltar.
D) Saint Helena.
E) the British Virgin Islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A Southeast Asian country with a partly elongated or prorupted shape is
A) Pakistan.
B) China.
C) Cambodia.
D) Thailand.
E) Indonesia.
A) Pakistan.
B) China.
C) Cambodia.
D) Thailand.
E) Indonesia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Germans established the ________ known as the Caprivi Strip in present-day Namibia to access resources in central Africa, including the Zambezi River.
A) causeway
B) disruption zone
C) railroad
D) protraction
E) proruption
A) causeway
B) disruption zone
C) railroad
D) protraction
E) proruption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
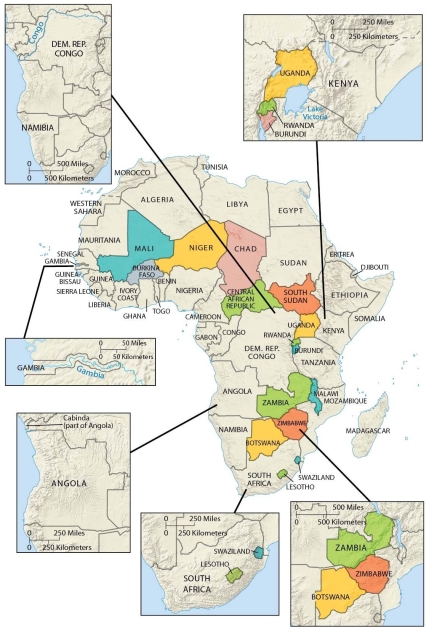
As shown on this map, an African country with an elongated shape is
A) Libya.
B) Central African Republic.
C) Algeria.
D) Malawi.
E) Sudan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Extremely small island-states in the world, many of which are former European colonies, are called
A) island nations.
B) macrostates.
C) microstates.
D) small nation-states.
E) island-colonies.
A) island nations.
B) macrostates.
C) microstates.
D) small nation-states.
E) island-colonies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The only large land mass not part of a sovereign state is
A) Antarctica.
B) the Arctic.
C) Greenland.
D) Siberia.
E) Borneo.
A) Antarctica.
B) the Arctic.
C) Greenland.
D) Siberia.
E) Borneo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A frontier, in contrast to a boundary,
A) separates two states.
B) is an area rather than a line.
C) has become a more common means to separate states.
D) is a region of ethnic conflict.
E) is the westernmost part of a state.
A) separates two states.
B) is an area rather than a line.
C) has become a more common means to separate states.
D) is a region of ethnic conflict.
E) is the westernmost part of a state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The eastern part of the border between the United States and Mexico is delineated by
A) the Rio Grande.
B) the Gulf of Mexico.
C) the Mojave desert.
D) the Mississippi River.
E) the Rocky Mountains.
A) the Rio Grande.
B) the Gulf of Mexico.
C) the Mojave desert.
D) the Mississippi River.
E) the Rocky Mountains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
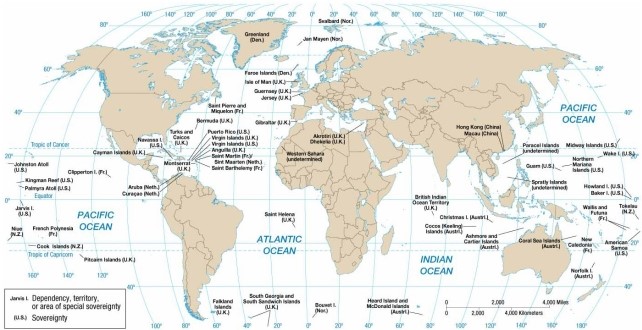
According to the map of present-day colonial possessions, the French colony northwest of the Pitcairn Islands is
A) Aruba.
B) the Cook Islands.
C) Kingman Reef.
D) French Polynesia.
E) Clipperton Island.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Cultural boundaries include all but which of the following?
A) ethnic
B) geometric
C) religious
D) linguistic
E) geomorphic
A) ethnic
B) geometric
C) religious
D) linguistic
E) geomorphic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The boundary between Argentina and Chile is an example of a
A) prorupted boundary.
B) geometric boundary.
C) physical boundary.
D) cultural frontier.
E) perforated frontier.
A) prorupted boundary.
B) geometric boundary.
C) physical boundary.
D) cultural frontier.
E) perforated frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The boundary between the United States and Canada is best described by which of the following?
A) geometric only
B) linguistic and religious
C) water and linguistic
D) mountain and water
E) water and geometric
A) geometric only
B) linguistic and religious
C) water and linguistic
D) mountain and water
E) water and geometric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The conflict over the Aozou Strip involves
A) centripetal forces acting in the absence of any centrifugal forces.
B) a disputed border and Egypt's claims of sovereignty over the zone.
C) a disagreement regarding suffrage and a disputed border.
D) a disputed border and Libya's claims of sovereignty over the zone.
E) Aozou attempts to join the United Nations as a sovereign nation-state.
A) centripetal forces acting in the absence of any centrifugal forces.
B) a disputed border and Egypt's claims of sovereignty over the zone.
C) a disagreement regarding suffrage and a disputed border.
D) a disputed border and Libya's claims of sovereignty over the zone.
E) Aozou attempts to join the United Nations as a sovereign nation-state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
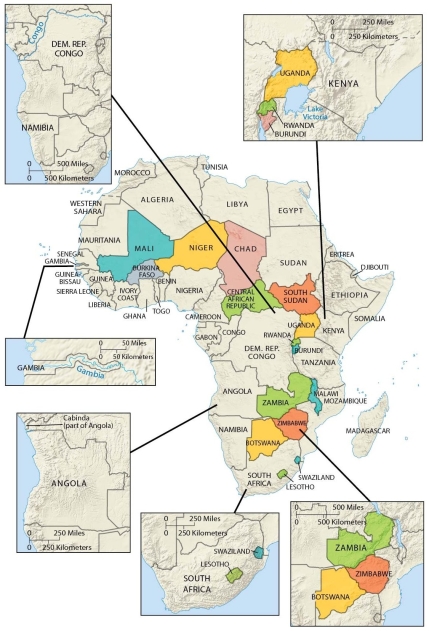
Elongated states may suffer from poor internal communication and difficulty defending borders. Which of the following is not an elongated state?
A) Malawi
B) Gambia
C) Namibia
D) Chile
E) Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
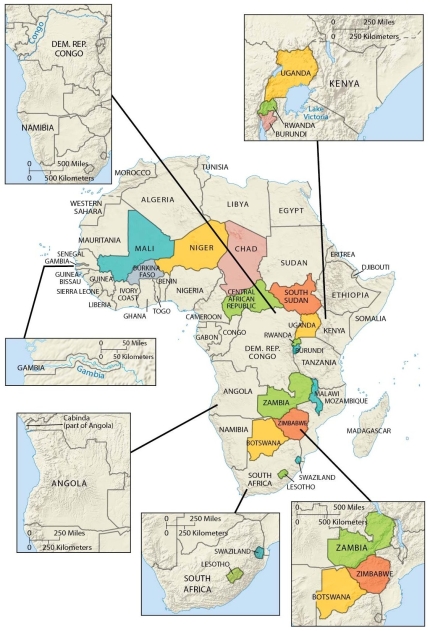
As shown on our maps, an example of a perforated state is
A) South Africa.
B) Sudan.
C) Slovenia.
D) Malaysia.
E) Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An increasing number of states have adopted a federal form of government primarily to
A) grant different ethnicities or nationalities more effective representation.
B) encourage the breakup of the superpower alliances.
C) govern compact states more effectively.
D) deploy scarce resources efficiently.
E) accommodate rightwing political parties and their demands for more representation in national elections.
A) grant different ethnicities or nationalities more effective representation.
B) encourage the breakup of the superpower alliances.
C) govern compact states more effectively.
D) deploy scarce resources efficiently.
E) accommodate rightwing political parties and their demands for more representation in national elections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A state which places most power in the hands of a central government is a(n)
A) federal state.
B) anocratic state.
C) fragmented state.
D) unitary state.
E) compact state.
A) federal state.
B) anocratic state.
C) fragmented state.
D) unitary state.
E) compact state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
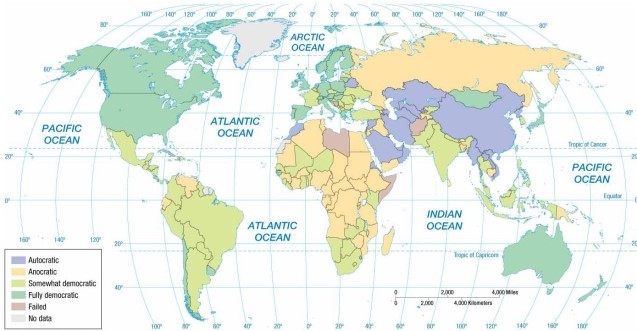
According to the map of regime types, Iraq is now an example of a(n)
A) autocracy.
B) partial democracy.
C) full democracy.
D) anocracy.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
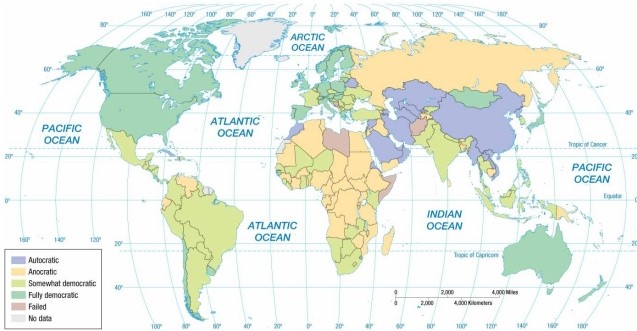
According to the map of regime types, Zimbabwe is an example of a(n)
A) autocracy.
B) partial democracy.
C) full democracy.
D) anocracy.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which shape most easily fosters the establishment of effective internal communications for a smaller state?
A) compact
B) elongated
C) fragmented
D) prorupted
E) prolonged
A) compact
B) elongated
C) fragmented
D) prorupted
E) prolonged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When gerrymandering takes place, the kind of redistricting that concentrates opposition voters into a small number of districts, allowing the party in power to gain control of numerous other districts, is termed a(n) ________ strategy.
A) excess vote
B) red-state rigged
C) stacked vote
D) wasted vote
E) inexcess vote
A) excess vote
B) red-state rigged
C) stacked vote
D) wasted vote
E) inexcess vote

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
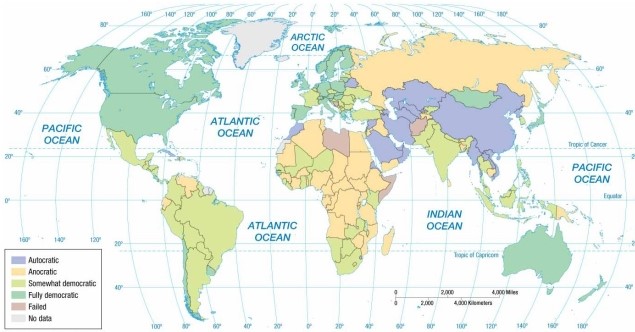
According to the map of regime types, Belarus is an example of a(n)
A) anocracy.
B) partial democracy.
C) full democracy.
D) autocracy.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
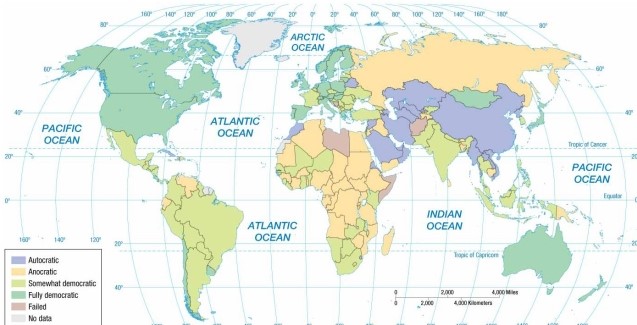
According to the map of regime types, Chile is now an example of a(n)
A) autocracy.
B) anocracy.
C) partial democracy.
D) full democracy.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
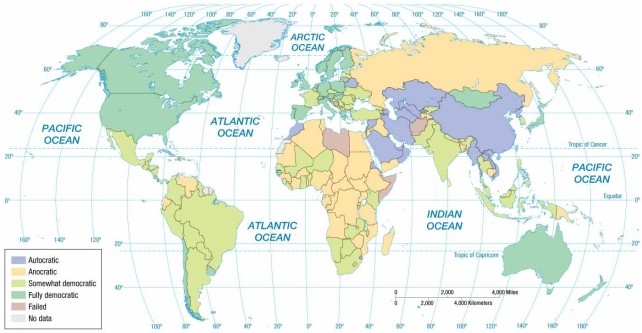
According to the map of regime types, Spain is an example of a(n)
A) autocracy.
B) anocracy.
C) partial democracy.
D) full democracy.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
After the fall of communism, Poland
A) adopted a unitary form of government.
B) became a nation-state.
C) delegated more authority to local governments.
D) gave most of its federal power to its ethnic minorities.
E) annexed land from Germany.
A) adopted a unitary form of government.
B) became a nation-state.
C) delegated more authority to local governments.
D) gave most of its federal power to its ethnic minorities.
E) annexed land from Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A state with control over its internal affairs has
A) centripetal forces.
B) nationality.
C) suffrage.
D) sovereignty.
E) ethnicity.
A) centripetal forces.
B) nationality.
C) suffrage.
D) sovereignty.
E) ethnicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The concept that ethnicities have the right to govern themselves is known as
A) centripetal determination.
B) nationalism.
C) universal suffrage.
D) self determination.
E) sovereignty.
A) centripetal determination.
B) nationalism.
C) universal suffrage.
D) self determination.
E) sovereignty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
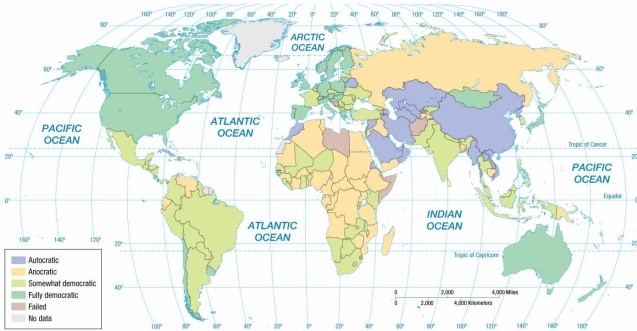
According to the map of regime types, Brazil is an example of a(n)
A) autocracy.
B) anocracy.
C) fully democratic and sovereign state.
D) somewhat democratic state.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The process of redrawing legislative boundaries to benefit the party in power is called
A) gerrymandering.
B) stacking votes.
C) hanging chads.
D) redlining.
E) blockbusting.
A) gerrymandering.
B) stacking votes.
C) hanging chads.
D) redlining.
E) blockbusting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When gerrymandering takes place, the kind of redistricting so that the opposition is spread across many districts as a minority is termed a(n) ________ strategy.
A) wasted vote
B) rightwing
C) stacked vote
D) districting
E) excess vote
A) wasted vote
B) rightwing
C) stacked vote
D) districting
E) excess vote

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
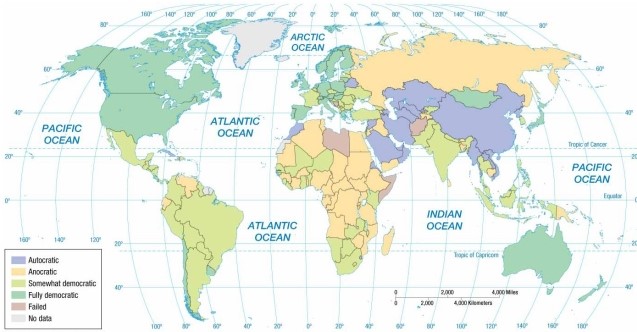
According to the map of regime types, Russia is an example of a(n)
A) autocracy.
B) partial democracy.
C) full democracy.
D) anocracy.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
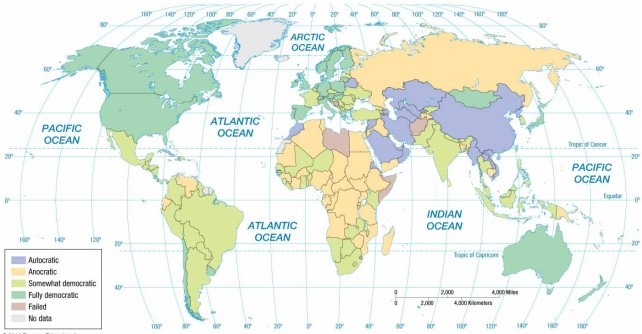
According to the map of regime types, Saudi Arabia is an example of a(n)
A) anocracy.
B) partial democracy.
C) full democracy.
D) autocracy.
E) failed state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The European Union has
A) replaced COMECON as the main organization for regional cooperation in Eastern Europe.
B) protected Western Europe from a Soviet invasion and improved Europe's environmental protections.
C) promoted economic growth and integration in Western Europe.
D) closed NATO military bases around the Mediterranean Sea in order to save money since the end of the Cold War.
E) protected Southwestern Asia and North Africa from Muslim incursions.
A) replaced COMECON as the main organization for regional cooperation in Eastern Europe.
B) protected Western Europe from a Soviet invasion and improved Europe's environmental protections.
C) promoted economic growth and integration in Western Europe.
D) closed NATO military bases around the Mediterranean Sea in order to save money since the end of the Cold War.
E) protected Southwestern Asia and North Africa from Muslim incursions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



