Deck 14: Common Property and Public Goods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Common Property and Public Goods
1
Crowding at a common property site both reduces the benefits of visitors and increases the costs
of being a visitor.
of being a visitor.
False
2
When people have identical tastes,an increase in the demand for a common property's use will increase the social gain it creates.
False
3
If the Open Range Field is currently a common property and the government decides to charge an entrance fee,this would result in an optimal level of activity in the Open Range Field.
False
4
The producer of a public good creates a positive externality,so that such goods tend to be overproduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When people have identical tastes,social gain can be created from a common property by imposing a Pigovian tax on entrants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Each user of a common property imposes a negative externality on its other users.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Whether or not people have identical tastes,free entry to a common property leads to a suboptimal outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An HBO broadcast over cable television is rival in consumption but non-excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When people have identical tastes,nobody has any incentive to maintain or improve a property that is commonly owned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Whether or not people have identical tastes,a commonly owned property creates no social value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Whether or not people have identical tastes,the marginal entrant is indifferent about using a common property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
People use a common property up to the point where the marginal cost of using it equals the social marginal benefit received from it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use of a common property is nonrivalrous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A nonexcludable good,once produced,can be made available to others at no additional cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Once it has been produced,the efficient price for a nonrivalrous good is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The problem with splitting checks is that no one orders as much as they truly want to eat in order to keep the total bill low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When people have identical tastes,the rents created by a common property are totally dissipated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A market failure occurs when the government steps in and failingly attempts to alleviate the tragedy of the commons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The tragedy of the commons is a situation where too much of an input is used by individuals,collectively making each individual worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Private markets tend to undersupply nonrivalrous goods because of free riding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Common Property II
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.
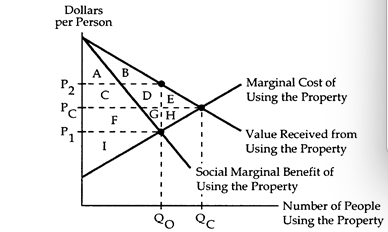
-Refer to Common Property II.If access cannot be prohibited,then users of the common property receive a surplus of
A) zero.
B) area I.
C) area F + G + H + I.
D) area A + C + F + I.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.If access cannot be prohibited,then users of the common property receive a surplus of
A) zero.
B) area I.
C) area F + G + H + I.
D) area A + C + F + I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An economic rent can be created by a common property without any admission fee
A) only if people have identical tastes.
B) if people's tastes differ,but the rent will still be sub-optimal.
C) if people's tastes differ,in which case the rent will be optimal.
D) if people's tastes differ,in which case the rent will be more than optimal.
A) only if people have identical tastes.
B) if people's tastes differ,but the rent will still be sub-optimal.
C) if people's tastes differ,in which case the rent will be optimal.
D) if people's tastes differ,in which case the rent will be more than optimal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Public goods can frequently be provided by private action when the resulting benefits are widespread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Whether or not people have identical tastes,the net value that the marginal user receives from a common property is
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) uncertain.
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
People will continue to use a common property until the marginal cost of using it equals
A) zero.
B) the social marginal benefit from using it.
C) the admission fee that a competitive firm would charge for its use.
D) the value they receive,on average,from using it.
A) zero.
B) the social marginal benefit from using it.
C) the admission fee that a competitive firm would charge for its use.
D) the value they receive,on average,from using it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Common Property I
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.
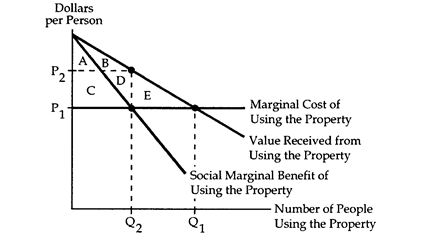
-Refer to Common Property I.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.The owner behaves competitively and charges people an entrance fee for the right to use the property.In this situation,how are the gains from trade divided between the owner and the users of the property?
A) The owner receives area C + D,and the users receive area A + B.
B) The owner receives area C,and the users receive area D.
C) The owner receives area E,and the users receive area A + B + C + D.
D) The owner receives area C + D,and the users receive zero.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property I.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.The owner behaves competitively and charges people an entrance fee for the right to use the property.In this situation,how are the gains from trade divided between the owner and the users of the property?
A) The owner receives area C + D,and the users receive area A + B.
B) The owner receives area C,and the users receive area D.
C) The owner receives area E,and the users receive area A + B + C + D.
D) The owner receives area C + D,and the users receive zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
One problem with a Clarke tax is that although it may not cover the complete cost of a public good,it will never generate more than the cost of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If people have identical tastes,then the economic rent created by a common property is
A) zero.
B) as large as possible.
C) positive,but not as large as possible.
D) negative.
A) zero.
B) as large as possible.
C) positive,but not as large as possible.
D) negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a Clarke tax scheme,the amount of tax that a person pays depends,in part,on his revealed preference for the public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The term "tragedy of the commons" is used to describe
A) overpricing of computer software by Microsoft.
B) an increase in rents when air quality in a community improves.
C) the difficulty in obtaining honest evaluations of public goods.
D) the elimination of social gains due to the overuse of property without a well-defined owner.
A) overpricing of computer software by Microsoft.
B) an increase in rents when air quality in a community improves.
C) the difficulty in obtaining honest evaluations of public goods.
D) the elimination of social gains due to the overuse of property without a well-defined owner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All economists agree that a public good is one the is nonrivalrous and nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Common Property I
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property I.If access to the common property cannot be prohibited,then the resulting social gain equals
A) zero.
B) area E.
C) area A + B.
D) area C + D.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property I.If access to the common property cannot be prohibited,then the resulting social gain equals
A) zero.
B) area E.
C) area A + B.
D) area C + D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Common Property I
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property I.The efficient level of production and consumption on the common property is
A) zero.
B) Q1.
C) Q2
D) cannot be determined from the graph.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property I.The efficient level of production and consumption on the common property is
A) zero.
B) Q1.
C) Q2
D) cannot be determined from the graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A common property is
A) both nonrivalrous and nonexcludable.
B) nonrivalrous,but not nonexcludable.
C) nonexcludable,but not nonrivalrous.
D) either nonrivalrous or nonexcludable,but not both.
A) both nonrivalrous and nonexcludable.
B) nonrivalrous,but not nonexcludable.
C) nonexcludable,but not nonrivalrous.
D) either nonrivalrous or nonexcludable,but not both.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the value that people,on average,receive from a common property exceeds the marginal cost of its use,then
A) more people will use the common property.
B) social gain is as large as possible.
C) the common property creates zero economic rent.
D) demand for the common property will fall.
A) more people will use the common property.
B) social gain is as large as possible.
C) the common property creates zero economic rent.
D) demand for the common property will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is the best example of a common property?
A) The car of a student who is frequently willing to give her friends rides around town.
B) The air that you breathe.
C) Bread that you bake and share.
D) Disney World
A) The car of a student who is frequently willing to give her friends rides around town.
B) The air that you breathe.
C) Bread that you bake and share.
D) Disney World

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a public goods increases the desirability of living in a certain area,benefits tend to be captured entirely by an increase in land values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A non-congested toll road is an example of a good that is excludable,but not rivalrous in consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Common Property I
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property I.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.The owner behaves competitively and charges people an entrance fee for the right to use the property.The fee will be
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P2 - P1.
D) zero.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property I.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.The owner behaves competitively and charges people an entrance fee for the right to use the property.The fee will be
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P2 - P1.
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When a Clarke tax is used,the revenue collected may or may not cover the cost of providing the public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Common Property II
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.If the owner behaves competitively,what entrance fee would he charge for the right to use the property?
A) PC.
B) PC - P1.
C) P2 - PC.
D) P2 - P1.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.If the owner behaves competitively,what entrance fee would he charge for the right to use the property?
A) PC.
B) PC - P1.
C) P2 - PC.
D) P2 - P1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Computer software is an example of a good that is
A) both nonexcludable and nonrivalrous.
B) nonexcludable,but not nonrivalrous.
C) nonrivalrous,but not nonexcludable.
D) a pure private good.
A) both nonexcludable and nonrivalrous.
B) nonexcludable,but not nonrivalrous.
C) nonrivalrous,but not nonexcludable.
D) a pure private good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Frequently,a public good can be adequately provided by private action when its benefits are
A) concentrated among a small number of people.
B) equally valued by everyone.
C) widespread.
D) greater than its costs.
A) concentrated among a small number of people.
B) equally valued by everyone.
C) widespread.
D) greater than its costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following goods is an example of a good that is nonexcludable but not nonrivalrous?
A) National defense.
B) A fishing lake.
C) A lighthouse.
D) A radio broadcast.
A) National defense.
B) A fishing lake.
C) A lighthouse.
D) A radio broadcast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The nature preservation services supplied by The Nature Conservancy which buys up ecologically important but endangered lands,is
A) nonrivalrous and nonexcludable.
B) nonrivalrous and excludable.
C) rival and nonexcludable.
D) a private service.
A) nonrivalrous and nonexcludable.
B) nonrivalrous and excludable.
C) rival and nonexcludable.
D) a private service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Common Property II
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.If the common property is privately owned,the surplus to the consumers is
A) Area I
B) Area I + F + G
C) Area I + F + G + H
D) zero.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.If the common property is privately owned,the surplus to the consumers is
A) Area I
B) Area I + F + G
C) Area I + F + G + H
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Why is the social marginal benefit of a common property smaller than the value that people,on average,receive from it?
A) Because use of a common property is nonrivalrous.
B) Because when one additional person uses the common property,it lowers the value that others receive from it.
C) Because entrance fees must be taken into account when determining the social benefit derived from a common property.
D) Because "free riders" will use the common property without contributing to its costs.
A) Because use of a common property is nonrivalrous.
B) Because when one additional person uses the common property,it lowers the value that others receive from it.
C) Because entrance fees must be taken into account when determining the social benefit derived from a common property.
D) Because "free riders" will use the common property without contributing to its costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Free riding would be an appropriate description of which of the following behaviors?
A) People who enjoy having nature conserved by The Nature Conservancy but who do not contribute to the organization.
B) People crowding into a public park on a nice summer day.
C) A fisher putting a more powerful motor on her boat so as to get to the fishing grounds before others.
D) Computer software developers who do not charge for their finished programs.
A) People who enjoy having nature conserved by The Nature Conservancy but who do not contribute to the organization.
B) People crowding into a public park on a nice summer day.
C) A fisher putting a more powerful motor on her boat so as to get to the fishing grounds before others.
D) Computer software developers who do not charge for their finished programs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Common Property II
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.If the owner charges a competitive entrance fee for the right to use the property,social gain will equal
A) area C + D + F + G + I.
B) area F + G + H + I.
C) area A + B + C + D + F + G + I.
D) area A + B + C + D + E + F + G + H + I.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.Suppose the common property becomes privately owned.If the owner charges a competitive entrance fee for the right to use the property,social gain will equal
A) area C + D + F + G + I.
B) area F + G + H + I.
C) area A + B + C + D + F + G + I.
D) area A + B + C + D + E + F + G + H + I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When one person consumes a nonexcludable good,
A) others cannot be prevented from also consuming it.
B) it can be provided to others for no additional cost.
C) the amount available for others to consume is reduced.
D) any other users will receive zero economic rent from it.
A) others cannot be prevented from also consuming it.
B) it can be provided to others for no additional cost.
C) the amount available for others to consume is reduced.
D) any other users will receive zero economic rent from it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of a good that is excludable and nonrivalrous?
A) A fishery.
B) Cable television.
C) Over the air television broadcasts.
D) Disney World.
A) A fishery.
B) Cable television.
C) Over the air television broadcasts.
D) Disney World.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Who tends to receive the benefits from a public good that increases the desirability of living in a certain area?
A) Government.
B) Residents.
C) Landlords.
D) No one.
A) Government.
B) Residents.
C) Landlords.
D) No one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Common Property II
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.If the common property is privately owned,the owner earns revenue equal to
A) Area C + D.
B) Area F + G.
C) Area C + D + F + G.
D) zero.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.If the common property is privately owned,the owner earns revenue equal to
A) Area C + D.
B) Area F + G.
C) Area C + D + F + G.
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 100 acre wood used by four people for collecting firewood is common property.The socially efficient use of the wood could be achieved by assigning property rights
A) only if they go to whichever of the four most values the wood.
B) only if they are divided equally among all four users.
C) only if the are divided according to those who have been using it the longest.
D) to any of all of the four.
A) only if they go to whichever of the four most values the wood.
B) only if they are divided equally among all four users.
C) only if the are divided according to those who have been using it the longest.
D) to any of all of the four.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose that when one person consumes a good,it is possible to provide it to others at no additional cost.Such a good is called
A) nonexcludable.
B) nonrivalrous.
C) a free good.
D) a Clarke good.
A) nonexcludable.
B) nonrivalrous.
C) a free good.
D) a Clarke good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Why do private markets tend to undersupply nonrivalrous goods?
A) Because free riders will refuse to pay for these goods.
B) Because the tragedy of the commons will reduce their value to zero.
C) Because people have an incentive to understate their preferences for these goods.
D) Because the efficient price for these goods is zero.
A) Because free riders will refuse to pay for these goods.
B) Because the tragedy of the commons will reduce their value to zero.
C) Because people have an incentive to understate their preferences for these goods.
D) Because the efficient price for these goods is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A market failure occurs when
A) shortages or surpluses of some good cannot be eliminated.
B) a private market cannot provide a good in socially efficient quantities.
C) consumers' surplus falls to zero.
D) property is privately owned and people behave competitively.
A) shortages or surpluses of some good cannot be eliminated.
B) a private market cannot provide a good in socially efficient quantities.
C) consumers' surplus falls to zero.
D) property is privately owned and people behave competitively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Private markets tend to undersupply nonexcludable goods because of
A) individuals' incentives to be untruthful.
B) overcrowding.
C) free riding.
D) dissipated rents.
A) individuals' incentives to be untruthful.
B) overcrowding.
C) free riding.
D) dissipated rents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the government conducts a survey asking it citizens how much they value having potholes filled in,we can expect
A) an accurate evaluation of the work.
B) citizens to understate the value of the work.
C) citizens to exaggerate the value of the work.
D) most citizens to refuse to answer.
A) an accurate evaluation of the work.
B) citizens to understate the value of the work.
C) citizens to exaggerate the value of the work.
D) most citizens to refuse to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Common Property II
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.If the common property is privately owned,the amount of the good supplied equals
A) QO
B) QC
C) zero.
D) none of the above.
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.

-Refer to Common Property II.If the common property is privately owned,the amount of the good supplied equals
A) QO
B) QC
C) zero.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When a Clarke tax is used to finance a public good,each person's tax equals
A) the amount that he is willing to pay for the good.
B) the difference between the value he places on the public good and its cost.
C) the cost of the public good minus the value that other people claim to receive from it.
D) everyone else's tax,with the sum equaling the cost of producing the public good.
A) the amount that he is willing to pay for the good.
B) the difference between the value he places on the public good and its cost.
C) the cost of the public good minus the value that other people claim to receive from it.
D) everyone else's tax,with the sum equaling the cost of producing the public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is excludable but not rivalrous in consumption?
A) Cable television
B) Non congested toll roads
C) Near empty gold courses.
D) All of the above.
A) Cable television
B) Non congested toll roads
C) Near empty gold courses.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider the following:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
GA 400 is a state highway that runs through part of Atlanta,GA.In order to travel on one portion of GA 400,drivers are required to pay a toll.It follows that section of GA 400 will exhibit non-rivalry in consumption if
A) the road is congested.
B) the road is not congested.
C) the toll is decreased.
D) the the toll is completely removed.
A) the road is congested.
B) the road is not congested.
C) the toll is decreased.
D) the the toll is completely removed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Cleantown and Grimyville are identical except for the inferior air quality in Grimyville.All potential residents have identical tastes.Apartments in Cleantown rent for $400 per month.The cost of breathing Grimyville air is $75 per month.The quantity of apartments in each town is fixed.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe how a Clarke tax is designed and explain how it leads a person to correctly reveal his preferences for a public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The purpose of a Clarke tax is to
A) give people an incentive to truthfully reveal their preferences for a public good.
B) raise enough revenue to pay for a public good.
C) give producers an incentive to supply nonrivalrous public goods in socially efficient quantities.
D) prevent the dissipation of rents that would occur with a nonexcludable public good.
A) give people an incentive to truthfully reveal their preferences for a public good.
B) raise enough revenue to pay for a public good.
C) give producers an incentive to supply nonrivalrous public goods in socially efficient quantities.
D) prevent the dissipation of rents that would occur with a nonexcludable public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consider a lake stocked with fish.The total value of fish caught at the lake depends on the number of fishers,as shown in the accompanying table.As the table indicates,1 fisher can catch $36 worth of fish in a day,2 fishers can catch a total of $66 worth of fish,3 fishers can catch a total of $90 worth of fish,and so forth.The fishers are identical,and the opportunity cost of a day at the lake is $18 for each fisher.
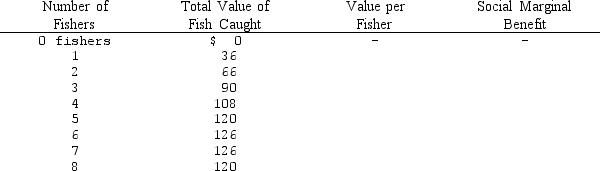




Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is one problem with using a Clarke tax to finance government provision of a public good?
A) People tend to overstate their preferences for the public good when a Clarke tax is imposed.
B) The government may decide against providing the public good,even when it would be efficient to do so.
C) The Clarke tax is not a fair tax,because everyone pays the same amount regardless of income.
D) The revenues collected from the Clarke tax may not cover the cost of the public good.
A) People tend to overstate their preferences for the public good when a Clarke tax is imposed.
B) The government may decide against providing the public good,even when it would be efficient to do so.
C) The Clarke tax is not a fair tax,because everyone pays the same amount regardless of income.
D) The revenues collected from the Clarke tax may not cover the cost of the public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following would be the most accurate means for the government to obtain information about the value of irrigation water for farmers to be supplied by the construction of a new dam?
A) Survey the farmers.
B) Hire experts to provide an estimate.
C) Use the current cost to farmers of withdrawing water from underground sources.
D) Conduct an economic study of how an increase in water supply would affect farmer income.
A) Survey the farmers.
B) Hire experts to provide an estimate.
C) Use the current cost to farmers of withdrawing water from underground sources.
D) Conduct an economic study of how an increase in water supply would affect farmer income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When access to a common property is unrestricted,why does the resulting social gain fail to be as large as possible? How can an entrance fee increase social gain in this situation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Free-riding is a problem associated with
A) nonrivalrous goods.
B) nonexclusive goods.
C) both nonrivalrous and nonexclusive goods.
D) neither nonrivalrous nor nonexclusive goods.
A) nonrivalrous goods.
B) nonexclusive goods.
C) both nonrivalrous and nonexclusive goods.
D) neither nonrivalrous nor nonexclusive goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider the following:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
There are two people in an economy.Person A's demand for a public good is Q = 10 - P and person B's demand is Q = 20 - 2P.The highest total that A and B will be willing to pay for six units of the public good is
A) $3
B) $4
C) $7
D) $11
A) $3
B) $4
C) $7
D) $11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



