Deck 9: Knowledge and Information
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Knowledge and Information
1
In the moral hazard problem,people incur additional risks as a result of being insured.
True
2
Stockholders can use high levels of compensation and substantial severance payments to get their corporate executives to take on higher levels of risk.
True
3
Stock options create the wrong incentive in that they create a principal-agent problem.
False
4
Because of adverse selection,no good used cars ever change hands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Distributing goods equally among consumers would be not only fair but efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A golden parachute is a mechanism that stockholders employ to encourage executives to be more risky than they would be without the parachute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to F.A.Hayek,knowledge is lost as statistics are used to convey information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Most economists believe adverse selection played no role in the 2008 financial crisis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When allocation decision are not made on the basis of price traditional methods of social gain understate the actual gain to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A drafted army can be unnecessarily costly in two ways: it can be the wrong size or it can consist of the wrong people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The use of signals in an economy is both individually rational and socially efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Adverse selection can cause insurance companies to limit the amount of insurance they provide to people who are "poor risks."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the principal-agent problem,the principal is the person performing work and the agent is the one for whom the work is being done.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Whether a good is distributed by a social planner or a market system,the area beneath the demand curve out to the quantity available accurately measures the value consumers receive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Fabian argument that confiscation of rents would not lower social welfare overlooks the costs of resource misallocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An efficiency wage is the wage that maximizes the surplus of the worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If employers had to pay higher than equilibrium wages to their workers,then workers would be better off but employers would be worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A draft is better for society because it is less costly than a volunteer army.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A market price contains no more information about a good than a good social planner would be able to obtain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An unexpected increase in inflation,by diluting the informational content of prices,will lead to an increase in unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In an efficient market,the current price reflects all available information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Fabian socialists argued that there would be no social cost associated with
A) a proportional income tax.
B) the sharp price declines caused when a speculative bubble bursts.
C) limits on employer monitoring imposed to protect employees' privacy.
D) the appropriation of rents by the government.
A) a proportional income tax.
B) the sharp price declines caused when a speculative bubble bursts.
C) limits on employer monitoring imposed to protect employees' privacy.
D) the appropriation of rents by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When a factor of production is in fixed supply,the revenue it earns
A) consists entirely of rent.
B) is an efficiency wage.
C) is independent of how the resource is used.
D) consists entirely of deadweight loss.
A) consists entirely of rent.
B) is an efficiency wage.
C) is independent of how the resource is used.
D) consists entirely of deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Resource Supply/Demand
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.
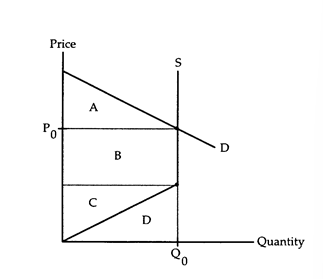
-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.What does area D represent?
A) The value that Q0 units of the resource gives to demanders.
B) The revenue generated from selling Q0 units of the resource.
C) The rent that resource owner earns from providing Q0 units.
D) The minimum payment needed for the resource owner to supply Q0 units.
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.

-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.What does area D represent?
A) The value that Q0 units of the resource gives to demanders.
B) The revenue generated from selling Q0 units of the resource.
C) The rent that resource owner earns from providing Q0 units.
D) The minimum payment needed for the resource owner to supply Q0 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Efficient financial markets are called so because they produce an amount of financial products that maximizes total surplus in the financial industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Resource Supply/Demand
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.

-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.The social gain from this resource being sold is
A) area A
B) area A + B
C) area A + B + C
D) area A + B + C + D
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.

-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.The social gain from this resource being sold is
A) area A
B) area A + B
C) area A + B + C
D) area A + B + C + D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
To make the most accurate predictions about a stock's future price,one must look at both the past pattern of prices and the current price of the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to Hayek,a social planner has no hope of matching the efficiency of a competitive pricing system because
A) no social planner can be completely benevolent in his actions.
B) a social planner cannot have access to the specialized knowledge of individuals.
C) the social planner will be unable to fully monitor the activities of his agents.
D) people are selfish and will not be actively altruistic to the social planner.
A) no social planner can be completely benevolent in his actions.
B) a social planner cannot have access to the specialized knowledge of individuals.
C) the social planner will be unable to fully monitor the activities of his agents.
D) people are selfish and will not be actively altruistic to the social planner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When will consumers' surplus overstate the actual gains received by consumers?
A) When allocation decisions are not made on the basis of price.
B) When the commodity is not equally divided among consumers.
C) When all consumers place the same marginal value on the good.
D) When the distribution of goods is Pareto optimal.
A) When allocation decisions are not made on the basis of price.
B) When the commodity is not equally divided among consumers.
C) When all consumers place the same marginal value on the good.
D) When the distribution of goods is Pareto optimal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A Military Draft
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for military service where Q0 represents the quantity provided by a volunteer army and Qd the quantity provided by a draft.
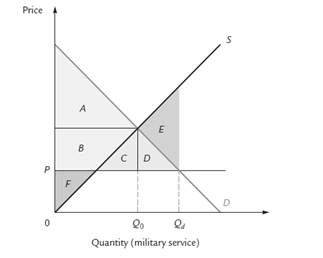
-Refer to Supply and Demand.Deadweight loss
A) is eliminated by a limited draft.
B) occurs only with a volunteer army.
C) occurs only with a draft.
D) Occurs with both a volunteer army and with a draft.
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for military service where Q0 represents the quantity provided by a volunteer army and Qd the quantity provided by a draft.

-Refer to Supply and Demand.Deadweight loss
A) is eliminated by a limited draft.
B) occurs only with a volunteer army.
C) occurs only with a draft.
D) Occurs with both a volunteer army and with a draft.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A speculative bubble is characterized by systematic undervaluing of stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Under competition,the price of a resource reveals
A) information about the past,but not future,uses of a resource.
B) the most valuable way to use the resource.
C) how much the resource is worth in the most valuable of its alternative uses.
D) the value of the labor needed to fully exploit the resource.
A) information about the past,but not future,uses of a resource.
B) the most valuable way to use the resource.
C) how much the resource is worth in the most valuable of its alternative uses.
D) the value of the labor needed to fully exploit the resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A Military Draft
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for military service where Q0 represents the quantity provided by a volunteer army and Qd the quantity provided by a draft.

-Refer to Supply and Demand.The social gain from a draft is represented by
A) areas A + B + F.
B) areas A + B + F - E.
C) areas B + F.
D) Areas A + B + C + D.
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for military service where Q0 represents the quantity provided by a volunteer army and Qd the quantity provided by a draft.

-Refer to Supply and Demand.The social gain from a draft is represented by
A) areas A + B + F.
B) areas A + B + F - E.
C) areas B + F.
D) Areas A + B + C + D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Resource Supply/Demand
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.

-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.The rent earned by the owner of the resource is measured by
A) area A + B + C.
B) area B + C + D.
C) area B + C.
D) area C + D.
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.

-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.The rent earned by the owner of the resource is measured by
A) area A + B + C.
B) area B + C + D.
C) area B + C.
D) area C + D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The past performance of a stock is the best guide to future performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For a fixed resource like land to be allocated to its highest valued use
A) a good social plan is needed.
B) it should be allocated to those who will pay the most.
C) it should be taxed at 100 percent of its rental value.
D) it should be offered to those who promise to put it to its best use.
A) a good social plan is needed.
B) it should be allocated to those who will pay the most.
C) it should be taxed at 100 percent of its rental value.
D) it should be offered to those who promise to put it to its best use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A limited military draft is likely to be inefficient because
A) it transfers wealth from those who are drafted to those who benefit from the army's services.
B) the wage rate paid to army personnel is set by the government,not by the market.
C) more people will be drafted than would have joined a volunteer army.
D) there is no guarantee that young adults with the lowest opportunity costs will be drafted.
A) it transfers wealth from those who are drafted to those who benefit from the army's services.
B) the wage rate paid to army personnel is set by the government,not by the market.
C) more people will be drafted than would have joined a volunteer army.
D) there is no guarantee that young adults with the lowest opportunity costs will be drafted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Resource Supply/Demand
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.

-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.If the government confiscates the rent and pays the owner area D to supply Q0 units of the resource at a zero price,then
A) area B + C is transferred from the resource owner to the government with no loss in social gain.
B) area A + B + C overestimates the social gain that will be created.
C) demanders will continue to receive area A + B + C + D in value from the resource.
D) a deadweight loss equal to area B + C will be created.
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.

-Refer to Resource Supply/Demand.If the government confiscates the rent and pays the owner area D to supply Q0 units of the resource at a zero price,then
A) area B + C is transferred from the resource owner to the government with no loss in social gain.
B) area A + B + C overestimates the social gain that will be created.
C) demanders will continue to receive area A + B + C + D in value from the resource.
D) a deadweight loss equal to area B + C will be created.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Payments to a factor of production in excess of the minimum payments necessary to call it into existence constitute
A) consumers' surplus
B) rent
C) a golden parachute
D) an efficiency wage
A) consumers' surplus
B) rent
C) a golden parachute
D) an efficiency wage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Who wrote the book Progress and Poverty,in which the author argued that the payment of rent to landlords serves no economic purpose?
A) George Akerlof.
B) Robert Dorfman.
C) Henry George.
D) Friedrich A.Hayek.
A) George Akerlof.
B) Robert Dorfman.
C) Henry George.
D) Friedrich A.Hayek.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An efficient market is one in which
A) no rents are created.
B) past prices can be used to predict the levels of future prices.
C) the principals can fully monitor the actions of their agents.
D) the price fully reflects all available information.
A) no rents are created.
B) past prices can be used to predict the levels of future prices.
C) the principals can fully monitor the actions of their agents.
D) the price fully reflects all available information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The volatility of stock prices,particularly in the short-run,may,according to Professor S.Grossman,be due to
A) large numbers of stockholders fearful of losing wealth who sell at some predetermined level.
B) some traders being better informed than others about real financial conditions.
C) either or both of the above.
D) the increasing use of stock options as compensation for corporate executives.
A) large numbers of stockholders fearful of losing wealth who sell at some predetermined level.
B) some traders being better informed than others about real financial conditions.
C) either or both of the above.
D) the increasing use of stock options as compensation for corporate executives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The theory of efficient markets suggests that the steep decline the value of stocks traded on the NASDAQ was due to
A) a speculative bubble.
B) a response to new information about firms' expected future profitability..
C) a natural cycle in technology stock prices evidenced by charts of previous prices trends.
D) moral hazard.
A) a speculative bubble.
B) a response to new information about firms' expected future profitability..
C) a natural cycle in technology stock prices evidenced by charts of previous prices trends.
D) moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Technical analysts in the financial markets are those who
A) believe that markets always operate efficiently.
B) look for stocks to buy based on the degree to which the company is investing in technology.
C) argue that a careful study of past prices of a given stock conveys useful information about future prices.
D) base their analyses on the current state of the macroeconomy.
A) believe that markets always operate efficiently.
B) look for stocks to buy based on the degree to which the company is investing in technology.
C) argue that a careful study of past prices of a given stock conveys useful information about future prices.
D) base their analyses on the current state of the macroeconomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The adverse selection process is prevalent in the used car market because
A) only poorer people are likely to purchase used cars.
B) sellers know more about the vehicles being sold than do potential buyers.
C) the price of the car sends a signal about its quality.
D) so many consumers are adverse to buying used cars.
A) only poorer people are likely to purchase used cars.
B) sellers know more about the vehicles being sold than do potential buyers.
C) the price of the car sends a signal about its quality.
D) so many consumers are adverse to buying used cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The option to buy a company's stock at some future time at current prices is often given to CEOs
A) as an incentive to take actions that will raise the share price.
B) because CEOs are often friends of those who hire them.
C) as a means of discouraging the CEO from taking any risky actions.
D) because this has become the custom of the business culture.
A) as an incentive to take actions that will raise the share price.
B) because CEOs are often friends of those who hire them.
C) as a means of discouraging the CEO from taking any risky actions.
D) because this has become the custom of the business culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
One theory of unemployment argues that the unemployment rate will rise when
A) people have accurate expectations regarding the inflation rate.
B) unexpected inflation causes people to be "fooled" by high absolute wages.
C) people mistakenly believe their wages have greater purchasing power.
D) people overestimate the rate of inflation.
A) people have accurate expectations regarding the inflation rate.
B) unexpected inflation causes people to be "fooled" by high absolute wages.
C) people mistakenly believe their wages have greater purchasing power.
D) people overestimate the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When do insurance companies encounter the problem of moral hazard?
A) When simply having insurance causes people to take more risks than they would otherwise.
B) When they do not have enough information to distinguish between people who are "good risks" and those who are "bad risks."
C) When the price of insurance premiums fully reflects all available information.
D) When the insurance company suffers large losses because a major catastrophe has affected a large number of people simultaneously.
A) When simply having insurance causes people to take more risks than they would otherwise.
B) When they do not have enough information to distinguish between people who are "good risks" and those who are "bad risks."
C) When the price of insurance premiums fully reflects all available information.
D) When the insurance company suffers large losses because a major catastrophe has affected a large number of people simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The use of signals in a market economy
A) makes everyone better off,even those people who choose not to obtain the signal.
B) prevents the economy from reaching an equilibrium.
C) lowers efficiency because the signals waste resources.
D) is one way that the principal-agent problem can be avoided.
A) makes everyone better off,even those people who choose not to obtain the signal.
B) prevents the economy from reaching an equilibrium.
C) lowers efficiency because the signals waste resources.
D) is one way that the principal-agent problem can be avoided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
People tend to "dress up" for job interviews,even though their clothes do not make them more productive in their positions.This situation is an example of
A) signaling.
B) adverse selection.
C) the principal-agent problem.
D) moral hazard.
A) signaling.
B) adverse selection.
C) the principal-agent problem.
D) moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Recent evidence supports the belief that new information is incorporated into the value of most stocks within
A) one trading day.
B) one week.
C) one month.
D) about 30 seconds.
A) one trading day.
B) one week.
C) one month.
D) about 30 seconds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Firms rarely offer unlimited warranties on their products,because then their customers would be less careful with upkeep and maintenance.This situation is an example of
A) confiscation of rents.
B) a speculative bubble.
C) moral hazard.
D) the principal-agent problem.
A) confiscation of rents.
B) a speculative bubble.
C) moral hazard.
D) the principal-agent problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Employers may choose to pay efficiency wages that are higher than the equilibrium wage because
A) workers will be more willing to accept monitoring by their employers.
B) the threat of unemployment will help prevent workers from shirking.
C) the higher compensation will encourage workers to take more risks.
D) higher wages will attract only the most qualified workers and thus help solve the employer's adverse selection problem 2.
A) workers will be more willing to accept monitoring by their employers.
B) the threat of unemployment will help prevent workers from shirking.
C) the higher compensation will encourage workers to take more risks.
D) higher wages will attract only the most qualified workers and thus help solve the employer's adverse selection problem 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The significant difference between adverse selection problems and moral hazard problems is
A) that adverse selection refers to bad luck,moral hazard refers to bad behaviors.
B) that adverse selection applies to markets for goods,moral hazard applies to markets for services.
C) only identifiable after an action has been taken.
D) that in adverse selection one group of people starts out at a higher risk,while in moral hazard problems,people incur additional risks.
A) that adverse selection refers to bad luck,moral hazard refers to bad behaviors.
B) that adverse selection applies to markets for goods,moral hazard applies to markets for services.
C) only identifiable after an action has been taken.
D) that in adverse selection one group of people starts out at a higher risk,while in moral hazard problems,people incur additional risks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When you hire a company to paint your house,you cannot be sure of the quality of paint that was used.This situation is an example of
A) moral hazard.
B) the adverse selection problem.
C) the market for lemons.
D) the principal-agent problem.
A) moral hazard.
B) the adverse selection problem.
C) the market for lemons.
D) the principal-agent problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Insurance companies are not permitted to require AIDS tests as a precondition for coverage,so they do not know whether or not the people they insure have already contracted HIV (the virus that causes AIDS).This situation is an example of
A) signaling.
B) adverse selection.
C) the principal-agent problem.
D) moral hazard.
A) signaling.
B) adverse selection.
C) the principal-agent problem.
D) moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A principal-agent problem occurs when
A) people are "fooled" by high absolute wages offered by employers.
B) insurance increases people's willingness to take risks.
C) an employer cannot fully monitor the employee's work.
D) a highly productive worker is unable to earn any rent.
A) people are "fooled" by high absolute wages offered by employers.
B) insurance increases people's willingness to take risks.
C) an employer cannot fully monitor the employee's work.
D) a highly productive worker is unable to earn any rent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is meant by a speculative bubble?
A) A pattern in past stock prices that,according to technical analysts,indicates higher future prices.
B) A circumstance where everyone expects higher prices,which in turn causes higher prices.
C) An occasional occurrence in program trading in which many investors simultaneously receive instructions to sell.
D) A situation where poorly informed traders exacerbate any upturns or downturns in the market.
A) A pattern in past stock prices that,according to technical analysts,indicates higher future prices.
B) A circumstance where everyone expects higher prices,which in turn causes higher prices.
C) An occasional occurrence in program trading in which many investors simultaneously receive instructions to sell.
D) A situation where poorly informed traders exacerbate any upturns or downturns in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The fact that employees often take longer lunch breaks than they are supposed to is an example of
A) the principal-agent problem.
B) moral hazard.
C) adverse selection.
D) a golden parachute.
A) the principal-agent problem.
B) moral hazard.
C) adverse selection.
D) a golden parachute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Why are corporate executives are often guaranteed "golden parachutes" if they should be fired?
A) To give them the incentive to take the higher levels of risk desired by stockholders.
B) To ensure that they exercise great caution in spending stockholders' money.
C) To encourage the most experienced people to apply for the executive positions.
D) To provide a signal to the public that the firm is on solid financial ground.
A) To give them the incentive to take the higher levels of risk desired by stockholders.
B) To ensure that they exercise great caution in spending stockholders' money.
C) To encourage the most experienced people to apply for the executive positions.
D) To provide a signal to the public that the firm is on solid financial ground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Assume that the supply curve is horizontal because marginal cost is constant at $10.John,Robert,and Jimmy each value one compact disc at $20 but only Jimmy and John value a second compact disc (Jimmy at $5 and John at $15).If a social planner dictates that five compact discs be produced and distributed to John,Robert,and Jimmy,then even if the compact discs are allocated based on demand,this market will lose out on $___ of value.
A) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) There will be no lost value as five compact discs is the efficient level..
A) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) There will be no lost value as five compact discs is the efficient level..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Assume that the supply curve is horizontal because marginal cost is constant at $10.John,Robert,and Jimmy each value one compact disc at $20 but only Jimmy and John value a second compact disc (Jimmy at $5 and John at $15).If a social planner dictates that two compact discs be produced and distributed to John,Robert,and Jimmy,then even if the compact discs are allocated based on demand,this market will lose out on $___ of value.
A) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) There will be no lost value as five compact discs is the efficient level.
A) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) There will be no lost value as five compact discs is the efficient level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider two individuals,Jay and Randy,and their decision to serve in the military.The accompanying tables show their opportunity costs of supplying military service.The government has determined that it needs 12 total hours of military service per week from these two individuals.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Define the term rent.Explain why confiscation of rents would cause more than a simple transfer of income from resource owners to the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Assume that the supply curve is horizontal because marginal cost is constant at $10.John,Robert,and Jimmy each value one compact disc at $20 but only Jimmy and John value a second compact disc (Jimmy at $5 and John at $15).It follows that the optimal number of compact discs sold in this market is
A) two.
B) three.
C) four.
D) five.
A) two.
B) three.
C) four.
D) five.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain how incomplete information causes each of the following situations and why the equilibrium in each of these situations is not Pareto optimal:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Assume that the supply curve is horizontal because marginal cost is constant at $10.John,Robert,and Jimmy each value one compact disc at $20 but only Jimmy and John value a second compact disc (Jimmy at $5 and John at $15).The maximum possible value achieved in this market is
A) $35.
B) $60.
C) $75.
D) $80.
A) $35.
B) $60.
C) $75.
D) $80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume that the supply curve is horizontal because marginal cost is constant at $10.If John,Robert,and Jimmy each value one compact disc at $20 but only Jimmy values a second compact disc,then the total value in this market is $35 if
A) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $0.
B) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $5.
C) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $10.
D) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $35.
A) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $0.
B) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $5.
C) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $10.
D) Jimmy's value for a second compact disc is $35.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following are attempts to ease the principal-agent problem?
A) Stock Options.
B) Golden Parachutes.
C) Efficiency Wages.
D) All of the above.
A) Stock Options.
B) Golden Parachutes.
C) Efficiency Wages.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A speculative bubble causes
A) current prices to sink artificially low.
B) current prices to rise artificially high.
C) no current price changes,only possible future changes.
D) undervaluing of stock prices.
A) current prices to sink artificially low.
B) current prices to rise artificially high.
C) no current price changes,only possible future changes.
D) undervaluing of stock prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The accompany diagram shows the market for gasoline,in which there are 1,000 consumers.Gasoline can be produced at a constant marginal cost of $2 per gallon.When the market is in equilibrium,the average consumer uses 15 gallons of gasoline per week. 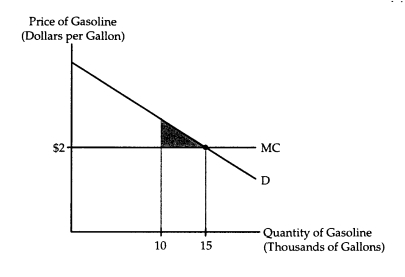 Suppose a war breaks out,temporarily limiting the amount of gasoline available for civilian use to 10,000 gallons per week.In the interest of fairness,the government allocates 10 gallons per week to each consumer,taxes each consumer $20 per week,and forbids barter in gasoline.Will the shaded area in the diagram accurately measure the loss in consumers' surplus? Why or why not?
Suppose a war breaks out,temporarily limiting the amount of gasoline available for civilian use to 10,000 gallons per week.In the interest of fairness,the government allocates 10 gallons per week to each consumer,taxes each consumer $20 per week,and forbids barter in gasoline.Will the shaded area in the diagram accurately measure the loss in consumers' surplus? Why or why not?
 Suppose a war breaks out,temporarily limiting the amount of gasoline available for civilian use to 10,000 gallons per week.In the interest of fairness,the government allocates 10 gallons per week to each consumer,taxes each consumer $20 per week,and forbids barter in gasoline.Will the shaded area in the diagram accurately measure the loss in consumers' surplus? Why or why not?
Suppose a war breaks out,temporarily limiting the amount of gasoline available for civilian use to 10,000 gallons per week.In the interest of fairness,the government allocates 10 gallons per week to each consumer,taxes each consumer $20 per week,and forbids barter in gasoline.Will the shaded area in the diagram accurately measure the loss in consumers' surplus? Why or why not?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Demand in the apricot market can be expressed as P=100-Q.Further,the supply function in the apricot industry is P=10+Q.If a social planner specifies that 30 units be produced,is that level of production efficient? Can you propose a more efficient level of production? Explain why your proposed level is better than that of the social planner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What is a principal-agent problem and why does it create inefficiency? What are efficiency wages and how can they help correct principal-agent problems?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How does the adverse selection problem faced by insurance companies differ from the moral hazard problem they face? How might an insurance company deal with each problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



