Deck 12: Money, Banking, Prices, and Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Money, Banking, Prices, and Monetary Policy
1
As means of payment currency,credit cards,and debit cards differ according to
A) whether they pay interest.
B) whose liability they represent.
C) transactions costs.
D) all of the above.
A) whether they pay interest.
B) whose liability they represent.
C) transactions costs.
D) all of the above.
all of the above.
2
M1 includes all but which of the following?
A) savings deposits.
B) currency in the hands of the public.
C) transactions accounts.
D) travelers checks.
A) savings deposits.
B) currency in the hands of the public.
C) transactions accounts.
D) travelers checks.
savings deposits.
3
The most narrowly defined monetary aggregate is
A) M0.
B) M1.
C) M2.
D) L.
A) M0.
B) M1.
C) M2.
D) L.
M0.
4
Which of the following is included in M0,but not in M1?
A) demand deposits
B) deposits of depository institutions at the Federal Reserve
C) currency held by the U.S. public
D) U.S. currency held by foreigners
A) demand deposits
B) deposits of depository institutions at the Federal Reserve
C) currency held by the U.S. public
D) U.S. currency held by foreigners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The real return on money is
A) 0.
B) -r.
C) -i.
D) -R.
A) 0.
B) -r.
C) -i.
D) -R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The two most common types of money in circulation in the United States today consist of
A) private bank notes and commodity-backed paper currency.
B) commodity-backed paper currency and fiat money.
C) fiat money and transaction deposits at banks.
D) transaction deposits at banks and commodity money.
A) private bank notes and commodity-backed paper currency.
B) commodity-backed paper currency and fiat money.
C) fiat money and transaction deposits at banks.
D) transaction deposits at banks and commodity money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The double coincidence of wants problem is solved by
A) credit markets.
B) government intervention.
C) the use of money.
D) specialization.
A) credit markets.
B) government intervention.
C) the use of money.
D) specialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The supply curve for credit card services is an increasing function of
A) the price of credit card services.
B) bank profitability.
C) the real interest rate.
D) the quantity of money.
A) the price of credit card services.
B) bank profitability.
C) the real interest rate.
D) the quantity of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Price tags attached to goods for purchase at a store would be an example of money's role as a
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) none of the above
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
We want money mostly because
A) it makes us happy.
B) we can buy goods with it.
C) we lengthen the life of our mattress.
D) we trust it.
A) it makes us happy.
B) we can buy goods with it.
C) we lengthen the life of our mattress.
D) we trust it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Money is each of the following except
A) a medium of exchange.
B) a store of value.
C) a means by which the central bank can always, and permanently, affect production.
D) a unit of account.
A) a medium of exchange.
B) a store of value.
C) a means by which the central bank can always, and permanently, affect production.
D) a unit of account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The most distinguishing economic feature of money is its
A) medium of exchange role.
B) store of value role.
C) unit of account role.
D) standard of deferred payment role.
A) medium of exchange role.
B) store of value role.
C) unit of account role.
D) standard of deferred payment role.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The nominal return of money is
A) 0.
B) r.
C) R.
D) i.
A) 0.
B) r.
C) R.
D) i.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The real return on bonds is
A) 0.
B) r.
C) R.
D) i.
A) 0.
B) r.
C) R.
D) i.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The opportunity cost of holding money is
A) zero.
B) the inflation rate.
C) the real interest rate.
D) the nominal interest rate.
A) zero.
B) the inflation rate.
C) the real interest rate.
D) the nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Credit cards are not a form of money because
A) money needs to be tangible (not virtual).
B) credit cards just extend a loan.
C) credit cards just relate to an account.
D) credit card balances are in fact counted as money.
A) money needs to be tangible (not virtual).
B) credit cards just extend a loan.
C) credit cards just relate to an account.
D) credit card balances are in fact counted as money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The most significant problem in trying to empirically measure the real rate of interest is that
A) there are so many different types of bonds.
B) expected inflation is unobservable.
C) interest rates fluctuate so much from day to day.
D) banks infrequently change the prime rate of interest.
A) there are so many different types of bonds.
B) expected inflation is unobservable.
C) interest rates fluctuate so much from day to day.
D) banks infrequently change the prime rate of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To determine the real interest rate in the data,one should take the interest rate on government debt
A) and leave it at that.
B) and add the inflation rate.
C) and subtract the inflation rate.
D) and divide by the inflation rate.
A) and leave it at that.
B) and add the inflation rate.
C) and subtract the inflation rate.
D) and divide by the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Fisher relationship may be described by the following equation in which R is the nominal rate of interest,r is the real rate of interest,and i is the inflation rate.
A) i = r + R
B) 1 + i =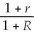
C) 1 + r =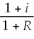
D) 1 + r =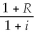
A) i = r + R
B) 1 + i =
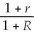
C) 1 + r =
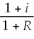
D) 1 + r =
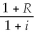

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Going from M0 to M1 and to M2,what is the principle?
A) from household money demand to firm money demand
B) from illiquid to liquid
C) from most usable to least usable for transaction purposes
D) from most usable to least usable as a store of value
A) from household money demand to firm money demand
B) from illiquid to liquid
C) from most usable to least usable for transaction purposes
D) from most usable to least usable as a store of value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Seigniorage is government revenue raised by
A) a tax on transactions.
B) issuance of treasury bonds.
C) issuance of money.
D) lump-sum taxation.
A) a tax on transactions.
B) issuance of treasury bonds.
C) issuance of money.
D) lump-sum taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If an increase in the level of the money supply results in a proportionate increase in prices with no effect on any real variables,we say that
A) the Fisher relationship holds.
B) money is neutral.
C) money is superneutral.
D) money is the most preferred store of value.
A) the Fisher relationship holds.
B) money is neutral.
C) money is superneutral.
D) money is the most preferred store of value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a model with money neutrality,how much should the money supply be increased to obtain a 1% increase in real output?
A) -1%
B) between 0 and 1%
C) 1%
D) It cannot be done.
A) -1%
B) between 0 and 1%
C) 1%
D) It cannot be done.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Money neutrality states that
A) with money, one can still use the representative agent.
B) changes in money do not affect real aggregates.
C) changes in inflation do not affect real aggregates.
D) monetary policy is independent from politics.
A) with money, one can still use the representative agent.
B) changes in money do not affect real aggregates.
C) changes in inflation do not affect real aggregates.
D) monetary policy is independent from politics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Inflation tax is
A) the sales tax.
B) a tax on nominal goods.
C) a special tax introduced in the 1970s to fight inflation.
D) the revenue from seigniorage.
A) the sales tax.
B) a tax on nominal goods.
C) a special tax introduced in the 1970s to fight inflation.
D) the revenue from seigniorage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The classical dichotomy states that
A) money is superneutral.
B) goods markets are separated from labor markets.
C) demand is separate from supply.
D) real markets determine nominal outcomes, not the reverse.
A) money is superneutral.
B) goods markets are separated from labor markets.
C) demand is separate from supply.
D) real markets determine nominal outcomes, not the reverse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a model with money neutrality,how much should the money supply be increased to obtain a 1% increase in nominal output?
A) -1%
B) between 0 and 1%
C) 1%
D) It cannot be done.
A) -1%
B) between 0 and 1%
C) 1%
D) It cannot be done.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An increase in the nominal interest rate increases the quantity of credit card services because
A) bank profits go up.
B) of intertemporal substitution.
C) the opportunity cost of making transactions with money has risen.
D) the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
A) bank profits go up.
B) of intertemporal substitution.
C) the opportunity cost of making transactions with money has risen.
D) the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a model with money neutrality,a 10% increase in the money supply leads to an increase of output by
A) more than 10%.
B) 10%.
C) less than 10%, but more than zero.
D) zero.
A) more than 10%.
B) 10%.
C) less than 10%, but more than zero.
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When the nominal interest rate increases,the quantity of credit card services
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) stays constant.
D) moves in unpredictable ways.
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) stays constant.
D) moves in unpredictable ways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the Federal Reserve buys Treasury bonds,it is called
A) a swap.
B) an open market operation.
C) a bond roll-over.
D) bonding.
A) a swap.
B) an open market operation.
C) a bond roll-over.
D) bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The current demand for money increases when
A) current real income decreases.
B) future real income decreases.
C) the nominal rate of interest decreases.
D) none of the above.
A) current real income decreases.
B) future real income decreases.
C) the nominal rate of interest decreases.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The equilibrium price of credit card services is
A) the real quantity of money.
B) determined only by the demand for credit card services.
C) the nominal interest rate.
D) equal to the average cost of credit card services.
A) the real quantity of money.
B) determined only by the demand for credit card services.
C) the nominal interest rate.
D) equal to the average cost of credit card services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Government printing of money to finance government spending is called
A) irresponsible.
B) an open-market purchase.
C) sterilization.
D) seigniorage.
A) irresponsible.
B) an open-market purchase.
C) sterilization.
D) seigniorage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Money is neutral in the model economy we discussed because
A) the money supply is exogenous.
B) the money supply is intertemporal.
C) prices are fully flexible.
D) it is a barter economy.
A) the money supply is exogenous.
B) the money supply is intertemporal.
C) prices are fully flexible.
D) it is a barter economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An open-market operation refers to
A) changing the money supply by changing taxes.
B) changing the money supply by changing government spending.
C) an exchange of money for interest-bearing debt by the monetary authority.
D) an exchange of domestic money for foreign money by the monetary authority.
A) changing the money supply by changing taxes.
B) changing the money supply by changing government spending.
C) an exchange of money for interest-bearing debt by the monetary authority.
D) an exchange of domestic money for foreign money by the monetary authority.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The money supply is vertical because
A) prices are indeterminate.
B) prices have no real impact.
C) the money supply is set by policy.
D) prices are counter-cyclical.
A) prices are indeterminate.
B) prices have no real impact.
C) the money supply is set by policy.
D) prices are counter-cyclical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The current demand for money increases when
A) current real income increases.
B) future real income decreases.
C) the nominal rate of interest increases.
D) none of the above.
A) current real income increases.
B) future real income decreases.
C) the nominal rate of interest increases.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The money supply is
A) endogenous.
B) determined by policy.
C) irrelevant.
D) indeterminate.
A) endogenous.
B) determined by policy.
C) irrelevant.
D) indeterminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a model with money neutrality,a 10% increase in the money supply leads to an increase of prices by
A) more than 10%.
B) 10%.
C) less than 10%, but more than zero.
D) zero.
A) more than 10%.
B) 10%.
C) less than 10%, but more than zero.
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
With money supply shocks in the intertemporal model with money,the price level is
A) procyclical.
B) acyclical.
C) countercyclical.
D) somewhat cyclical.
A) procyclical.
B) acyclical.
C) countercyclical.
D) somewhat cyclical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In practice,money growth targeting was
A) a good idea.
B) a policy introduced in the U.S. in the 1970s, which continues to the present.
C) better than interest rate targeting.
D) a failure.
A) a good idea.
B) a policy introduced in the U.S. in the 1970s, which continues to the present.
C) better than interest rate targeting.
D) a failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Taylor rule
A) is a rule stating that money should grow at a constant rate.
B) is not considered to be a practical policy rule for central banks to follow.
C) dictates that the central bank's target interest rate be responsive to real economic activity and to inflation.
D) dictates that the nominal interest rate stay constant in the long run.
A) is a rule stating that money should grow at a constant rate.
B) is not considered to be a practical policy rule for central banks to follow.
C) dictates that the central bank's target interest rate be responsive to real economic activity and to inflation.
D) dictates that the nominal interest rate stay constant in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The demand for money will fall for each of the following reasons,except
A) more ATMs.
B) higher real GDP.
C) lower interest rates on transactions accounts at banks.
D) more risky banks.
A) more ATMs.
B) higher real GDP.
C) lower interest rates on transactions accounts at banks.
D) more risky banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following increases money demand?
A) Disruptions in the banking system.
B) The introduction of online banking.
C) The wider availability of ATMs.
D) The introduction of deposit insurance.
A) Disruptions in the banking system.
B) The introduction of online banking.
C) The wider availability of ATMs.
D) The introduction of deposit insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The zero lower bound on the nominal interest rate arises because
A) if the nominal interest rate were less than zero, an arbitrage opportunity would exist.
B) bank profits must be zero.
C) the government would not allow it.
D) the economy would crash.
A) if the nominal interest rate were less than zero, an arbitrage opportunity would exist.
B) bank profits must be zero.
C) the government would not allow it.
D) the economy would crash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The introduction of sweep accounts
A) was an open market purchase.
B) was a failure.
C) had no effect.
D) caused a reduction in the demand for money.
A) was an open market purchase.
B) was a failure.
C) had no effect.
D) caused a reduction in the demand for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the intertemporal model with money,the optimal amount of money is
A) equal to total output.
B) equal to consumption and investment.
C) zero.
D) irrelevant as long as it is not zero.
A) equal to total output.
B) equal to consumption and investment.
C) zero.
D) irrelevant as long as it is not zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following decreases money demand?
A) Bonds become more risky.
B) The introduction of online banking.
C) Disruptions in the banking system.
D) An increase in ATM fees.
A) Bonds become more risky.
B) The introduction of online banking.
C) Disruptions in the banking system.
D) An increase in ATM fees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Central banks sometimes attempt quantitative easing when
A) money growth is too high.
B) inflation is too high.
C) there is a liquidity trap.
D) inflation is too low.
A) money growth is too high.
B) inflation is too high.
C) there is a liquidity trap.
D) inflation is too low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If an increase in the level of money supply leads to a proportionate increase in prices with no effect on real variables ,we say that
A) the Fisher relationship holds.
B) money is neutral.
C) money is superneutral.
D) money is a medium of exchange.
A) the Fisher relationship holds.
B) money is neutral.
C) money is superneutral.
D) money is a medium of exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the Friedman-Lucas money surprise model
A) consumers cannot observe all aggregate variables.
B) prices are sticky.
C) money is neutral.
D) credit market frictions matter.
A) consumers cannot observe all aggregate variables.
B) prices are sticky.
C) money is neutral.
D) credit market frictions matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The nominal interest rate cannot fall below
A) the real interest rate.
B) the rate of growth in the money stock.
C) 2%.
D) zero.
A) the real interest rate.
B) the rate of growth in the money stock.
C) 2%.
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An increase in the money supply in the Friedman-Lucas money surprise model
A) reduces aggregate output, raises the price level, and reduces the real interest rate.
B) increases aggregate output, reduces the price level, and reduces the real interest rate.
C) increases aggregate output, raises the price level, and reduces the real interest rate.
D) reduces aggregate output, raises the price level, and raises the real interest rate.
A) reduces aggregate output, raises the price level, and reduces the real interest rate.
B) increases aggregate output, reduces the price level, and reduces the real interest rate.
C) increases aggregate output, raises the price level, and reduces the real interest rate.
D) reduces aggregate output, raises the price level, and raises the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



