Deck 16: Money in the Open Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Money in the Open Economy
1
iPods are less expensive in Canada than the United States,once the exchange rate is taken into account. This is an indication that
A) the nominal exchange rate is equal to one.
B) purchasing power parity does not hold.
C) the law of one price holds.
D) the exchange rate is fixed.
A) the nominal exchange rate is equal to one.
B) purchasing power parity does not hold.
C) the law of one price holds.
D) the exchange rate is fixed.
purchasing power parity does not hold.
2
A devaluation of the exchange rate is a policy action that
A) increases the real exchange rate.
B) decreases the real exchange rate.
C) increases the nominal exchange rate.
D) decreases the nominal exchange rate.
A) increases the real exchange rate.
B) decreases the real exchange rate.
C) increases the nominal exchange rate.
D) decreases the nominal exchange rate.
increases the nominal exchange rate.
3
The nominal exchange rate is the
A) domestic currency price of foreign currency.
B) foreign currency price of domestic currency.
C) price of domestic goods in terms of foreign goods.
D) price of foreign goods in terms of domestic goods.
A) domestic currency price of foreign currency.
B) foreign currency price of domestic currency.
C) price of domestic goods in terms of foreign goods.
D) price of foreign goods in terms of domestic goods.
domestic currency price of foreign currency.
4
Dollarization is a policy action that
A) tries to stabilize the value of the local currency vs. the U.S. dollar.
B) adopts the currency of another country as the national medium of exchange.
C) mimics policy actions taken by the U.S. Federal Reserve.
D) outlaws the holding of foreign currencies other than the U.S. dollar.
A) tries to stabilize the value of the local currency vs. the U.S. dollar.
B) adopts the currency of another country as the national medium of exchange.
C) mimics policy actions taken by the U.S. Federal Reserve.
D) outlaws the holding of foreign currencies other than the U.S. dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A revaluation of the exchange rate is a policy action that
A) increases the real exchange rate.
B) decreases the real exchange rate.
C) increases the nominal exchange rate.
D) decreases the nominal exchange rate.
A) increases the real exchange rate.
B) decreases the real exchange rate.
C) increases the nominal exchange rate.
D) decreases the nominal exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If purchasing power parity holds,the exchange rate (e)can be expressed as a function of the domestic price (P)and the foreign price (P*)as
A) e = P - P*.
B) e = P* - P.
C) e = P* + P.
D) e = P/P*.
A) e = P - P*.
B) e = P* - P.
C) e = P* + P.
D) e = P/P*.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Under purely flexible exchange rates,
A) there is no intervention by the domestic fiscal or monetary authorities to specifically target the nominal exchange rate.
B) there is only occasional intervention by the domestic fiscal or monetary authorities to specifically target the nominal exchange rate.
C) the domestic fiscal and monetary authorities retain considerable flexibility to prevent short-run variability in the nominal exchange rate.
D) the domestic fiscal and monetary authorities retain considerable flexibility to prevent long-run variability in the nominal exchange rate.
A) there is no intervention by the domestic fiscal or monetary authorities to specifically target the nominal exchange rate.
B) there is only occasional intervention by the domestic fiscal or monetary authorities to specifically target the nominal exchange rate.
C) the domestic fiscal and monetary authorities retain considerable flexibility to prevent short-run variability in the nominal exchange rate.
D) the domestic fiscal and monetary authorities retain considerable flexibility to prevent long-run variability in the nominal exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In an open economy,the law of one price implies that
A) the domestic economy may have a comparative advantage in only half the goods it produces.
B) perfect competition holds in all domestic markets.
C) purchasing power parity should hold.
D) the nominal exchange rate should equal one.
A) the domestic economy may have a comparative advantage in only half the goods it produces.
B) perfect competition holds in all domestic markets.
C) purchasing power parity should hold.
D) the nominal exchange rate should equal one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A principal reason that purchasing power parity does not hold exactly in practice is
A) that foreign and domestic assets are not perfect substitutes.
B) the existence of non-traded goods.
C) that consumers in different countries have different preferences.
D) that costs of production are not the same in all countries.
A) that foreign and domestic assets are not perfect substitutes.
B) the existence of non-traded goods.
C) that consumers in different countries have different preferences.
D) that costs of production are not the same in all countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Compared to a fixed exchange rate,a monetary union
A) involves soft pegs.
B) does not allow adjustments to exchange rates.
C) is managed at the International Monetary Fund.
D) has no central bank.
A) involves soft pegs.
B) does not allow adjustments to exchange rates.
C) is managed at the International Monetary Fund.
D) has no central bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the European Monetary Union,the supply of euros
A) is managed by the individual central banks of the member countries.
B) is managed by the European Central Bank.
C) is determined by market forces.
D) automatically varied in response to short-run fluctuations in the exchange rates of the member nations.
A) is managed by the individual central banks of the member countries.
B) is managed by the European Central Bank.
C) is determined by market forces.
D) automatically varied in response to short-run fluctuations in the exchange rates of the member nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Purchasing power parity may not hold in practice due to all of the following except
A) transportation costs.
B) cross-country differences in environmental regulations.
C) trade barriers like tariffs and quotas.
D) the existence of non-traded goods.
A) transportation costs.
B) cross-country differences in environmental regulations.
C) trade barriers like tariffs and quotas.
D) the existence of non-traded goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following was specifically instituted to ensure a successful hard peg?
A) the Bretton Woods Agreement
B) the European Monetary System
C) the European Monetary Union
D) the International Monetary Fund
A) the Bretton Woods Agreement
B) the European Monetary System
C) the European Monetary Union
D) the International Monetary Fund

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Adoption of a currency board
A) is one method for achieving a soft peg policy.
B) places responsibility for exchange rate management in the hands of an agency that is independent of political influences.
C) mandates the use of currency in all domestic transactions.
D) requires that a centralized institution holds interest-bearing assets denominated in the currency against which the nominal exchange rate is being fixed.
A) is one method for achieving a soft peg policy.
B) places responsibility for exchange rate management in the hands of an agency that is independent of political influences.
C) mandates the use of currency in all domestic transactions.
D) requires that a centralized institution holds interest-bearing assets denominated in the currency against which the nominal exchange rate is being fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
According to purchasing power parity,the relationship among the domestic price (P),the foreign price (P),and the nominal exchange rate (e),can be written as
A)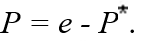
B)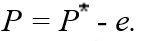
C)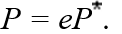
D)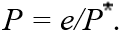
A)
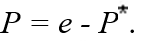
B)
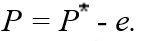
C)
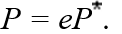
D)
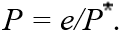

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A hard peg may be achieved by all of the following except
A) following the rules of the Bretton Woods Agreement.
B) dollarization.
C) establishing a currency board.
D) mutual agreements establishing a common currency.
A) following the rules of the Bretton Woods Agreement.
B) dollarization.
C) establishing a currency board.
D) mutual agreements establishing a common currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The supply of euros is managed by
A) the European Monetary Union.
B) the European Monetary System.
C) the European Central Bank.
D) the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development.
A) the European Monetary Union.
B) the European Monetary System.
C) the European Central Bank.
D) the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The real exchange rate is the
A) domestic currency price of foreign currency.
B) foreign currency price of domestic currency.
C) price of domestic goods in terms of foreign goods.
D) price of foreign goods in terms of domestic goods.
A) domestic currency price of foreign currency.
B) foreign currency price of domestic currency.
C) price of domestic goods in terms of foreign goods.
D) price of foreign goods in terms of domestic goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Bretton Woods Agreement
A) fixed the value of the U.S. dollar relative to gold.
B) fixed the value of the U.S. dollar relative to the euro.
C) required foreign central banks to hold certain minimum amounts of gold as foreign exchange reserves.
D) required member nations, other than the United States, to disband their central banks.
A) fixed the value of the U.S. dollar relative to gold.
B) fixed the value of the U.S. dollar relative to the euro.
C) required foreign central banks to hold certain minimum amounts of gold as foreign exchange reserves.
D) required member nations, other than the United States, to disband their central banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Compared to dollarization,a currency board
A) has a flexible exchange rate.
B) has a separate currency.
C) conducts independent monetary policy.
D) is the same institution.
A) has a flexible exchange rate.
B) has a separate currency.
C) conducts independent monetary policy.
D) is the same institution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,the domestic
A) government loses control over the level of domestic government spending.
B) government loses control over the level of domestic taxes.
C) government loses control over the level of domestic government spending and domestic taxes.
D) central bank loses control over the domestic stock of money.
A) government loses control over the level of domestic government spending.
B) government loses control over the level of domestic taxes.
C) government loses control over the level of domestic government spending and domestic taxes.
D) central bank loses control over the domestic stock of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Under a flexible exchange rate,an increase in the domestic money supply leads to
A) a devaluation of the domestic currency.
B) a revaluation of the domestic currency.
C) a depreciation of the domestic currency.
D) an appreciation of the domestic currency.
A) a devaluation of the domestic currency.
B) a revaluation of the domestic currency.
C) a depreciation of the domestic currency.
D) an appreciation of the domestic currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the monetary small open-economy model with a flexible exchange rate,an increase in the foreign price level has which impact on domestic money demand?
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For a country with a fixed exchange rate,foreign exchange reserves are
A) an asset of the domestic government.
B) a liability of the domestic government.
C) held by private banks.
D) are unnecessary.
A) an asset of the domestic government.
B) a liability of the domestic government.
C) held by private banks.
D) are unnecessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,an increase in the world real interest rate
A) increases domestic output and has no effect on the domestic price level.
B) decreases domestic output and has no effect on the domestic price level.
C) increases the domestic price level and has no effect on domestic output.
D) decreases the domestic price level and has no effect on domestic output.
A) increases domestic output and has no effect on the domestic price level.
B) decreases domestic output and has no effect on the domestic price level.
C) increases the domestic price level and has no effect on domestic output.
D) decreases the domestic price level and has no effect on domestic output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,an increase in the exchange rate has which impact on domestic money demand?
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A key international institution that plays an important role in exchange rate determination is the
A) U.S. Currency Board.
B) European Central Bank.
C) World Bank.
D) International Monetary Fund.
A) U.S. Currency Board.
B) European Central Bank.
C) World Bank.
D) International Monetary Fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the monetary small open-economy model with a flexible exchange rate,an increase in the foreign price level decreases
A) domestic output, but has no effect on the domestic price level or the nominal exchange rate.
B) the domestic price level, but has no effect on domestic output or the nominal exchange rate.
C) the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output or the domestic price level.
D) the domestic price level and the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output.
A) domestic output, but has no effect on the domestic price level or the nominal exchange rate.
B) the domestic price level, but has no effect on domestic output or the nominal exchange rate.
C) the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output or the domestic price level.
D) the domestic price level and the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
To maintain a fixed exchange rate,authorities
A) make laws stipulating the exchange rate.
B) modify money supply.
C) modify government expenses.
D) modify taxes.
A) make laws stipulating the exchange rate.
B) modify money supply.
C) modify government expenses.
D) modify taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following institutions plays the role of an international lender of last resort?
A) the World Bank
B) the International Monetary Fund
C) the European Monetary System
D) the Federal Reserve System
A) the World Bank
B) the International Monetary Fund
C) the European Monetary System
D) the Federal Reserve System

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The International Monetary Fund plays the key role of
A) providing deposit insurance for banks in its member nations.
B) acting as lender of last resort for its member countries' central banks.
C) providing loans to member countries to help finance development projects.
D) enforcing international monetary agreements.
A) providing deposit insurance for banks in its member nations.
B) acting as lender of last resort for its member countries' central banks.
C) providing loans to member countries to help finance development projects.
D) enforcing international monetary agreements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,an increase in the foreign price level has which impact on domestic money demand?
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the monetary small open-economy model with a flexible exchange rate,an increase in the world real interest rate
A) increases domestic output and increases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.
B) increases domestic output and decreases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.
C) decreases domestic output and increases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.
D) decreases domestic output and decreases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.
A) increases domestic output and increases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.
B) increases domestic output and decreases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.
C) decreases domestic output and increases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.
D) decreases domestic output and decreases the nominal exchange rate, as long as real money demand is much more responsive to real income than to the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the monetary small open-economy model with a flexible exchange rate,an increase in the domestic price level has which impact on domestic money demand?
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the monetary small open-economy model with a flexible exchange rate,an increase in the domestic money supply increases
A) domestic output, but has no effect on the domestic price level or the nominal exchange rate.
B) the domestic price level, but has no effect on domestic output or the nominal exchange rate.
C) the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output or the domestic price level.
D) the domestic price level and the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output.
A) domestic output, but has no effect on the domestic price level or the nominal exchange rate.
B) the domestic price level, but has no effect on domestic output or the nominal exchange rate.
C) the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output or the domestic price level.
D) the domestic price level and the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,an increase in the domestic price level has which impact on domestic money demand?
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the monetary small open-economy model with a flexible exchange rate,an increase in the exchange rate has which impact on domestic money demand?
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.
A) It increases it.
B) It decreases it.
C) It has no impact.
D) It depends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,an increase in the foreign price level
A) increases the domestic money supply and increases the domestic price level.
B) increases the domestic money supply and decreases the domestic price level.
C) decreases the domestic money supply and increases the domestic price level.
D) decreases the domestic money supply and decreases the domestic price level.
A) increases the domestic money supply and increases the domestic price level.
B) increases the domestic money supply and decreases the domestic price level.
C) decreases the domestic money supply and increases the domestic price level.
D) decreases the domestic money supply and decreases the domestic price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,a devaluation of the domestic currency in the absence of any other shocks
A) increases the current account surplus and has no effect on the domestic money supply.
B) decreases the current account surplus and has no effect on the domestic money supply.
C) increases the domestic money supply and has no effect on the current account surplus.
D) decreases the domestic money supply and has no effect on the current account surplus.
A) increases the current account surplus and has no effect on the domestic money supply.
B) decreases the current account surplus and has no effect on the domestic money supply.
C) increases the domestic money supply and has no effect on the current account surplus.
D) decreases the domestic money supply and has no effect on the current account surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the monetary small open-economy model with a fixed exchange rate,a temporary decrease in domestic total factor productivity in the absence of any other shocks
A) increases the current account surplus and increases the domestic money supply.
B) increases the current account surplus and decreases the domestic money supply.
C) increases the domestic money supply and decreases the current account surplus.
D) decreases the domestic money supply and decreases the current account surplus.
A) increases the current account surplus and increases the domestic money supply.
B) increases the current account surplus and decreases the domestic money supply.
C) increases the domestic money supply and decreases the current account surplus.
D) decreases the domestic money supply and decreases the current account surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the monetary small open-economy model,a flexible exchange rate insulates the domestic price level from
A) both real and nominal shocks from abroad.
B) real shocks from abroad, but not from nominal shocks from abroad.
C) nominal shocks from abroad, but not from real shocks from abroad.
D) neither real nor nominal shocks from abroad.
A) both real and nominal shocks from abroad.
B) real shocks from abroad, but not from nominal shocks from abroad.
C) nominal shocks from abroad, but not from real shocks from abroad.
D) neither real nor nominal shocks from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In response to a temporary change in total factor productivity,the adoption of capital controls under a flexible exchange rate
A) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the nominal exchange rate.
B) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and dampens the effect on the nominal exchange rate.
C) dampens the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and amplifies the effect on the nominal exchange rate.
D) dampens the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the nominal exchange rate.
A) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the nominal exchange rate.
B) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and dampens the effect on the nominal exchange rate.
C) dampens the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and amplifies the effect on the nominal exchange rate.
D) dampens the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the nominal exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the New Keynesian open economy model,if the exchange rate is fixed
A) fiscal policy and monetary policy are powerless.
B) fiscal policy is an effective stabilization tool.
C) a change in current total factor productivity increases output.
D) monetary policy is an effective stabilization tool.
A) fiscal policy and monetary policy are powerless.
B) fiscal policy is an effective stabilization tool.
C) a change in current total factor productivity increases output.
D) monetary policy is an effective stabilization tool.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the New Keynesian open economy model,government spending
A) is an effective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an ineffective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate
B) is an ineffective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an effective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate; prices are flexible.
C) is an ineffective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an ineffective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate; net exports depends on the relative price of foreign goods to domestic goods.
D) is an effective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an effective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate.
A) is an effective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an ineffective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate
B) is an ineffective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an effective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate; prices are flexible.
C) is an ineffective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an ineffective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate; net exports depends on the relative price of foreign goods to domestic goods.
D) is an effective stabilization tool with a flexible exchange rate, and an effective stabilization tool with a fixed exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The balance of payments improves
A) when there is an exchange rate appreciation.
B) when there is an exchange rate depreciation.
C) when the interest rate rises.
D) never.
A) when there is an exchange rate appreciation.
B) when there is an exchange rate depreciation.
C) when the interest rate rises.
D) never.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An agreement among countries to adopt a common currency is called a
A) central bank consolidation.
B) currency union.
C) monetary compact.
D) common banking treaty.
A) central bank consolidation.
B) currency union.
C) monetary compact.
D) common banking treaty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The acquisition of a new physical asset by a foreign resident is called
A) foreign direct investment.
B) foreign capital investment.
C) a portfolio inflow.
D) a portfolio outflow.
A) foreign direct investment.
B) foreign capital investment.
C) a portfolio inflow.
D) a portfolio outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the New Keynesian open economy model with a flexible exchange rate,an increase in anticipate future total factor productivity
A) has no effects.
B) increases aggregate output.
C) reduces aggregate consumption.
D) causes an exchange rate appreciation.
A) has no effects.
B) increases aggregate output.
C) reduces aggregate consumption.
D) causes an exchange rate appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A capital outflow occurs when a
A) domestic resident purchases a domestic asset.
B) domestic resident purchases a foreign asset.
C) foreign resident purchases a domestic asset.
D) foreign resident purchases a foreign asset.
A) domestic resident purchases a domestic asset.
B) domestic resident purchases a foreign asset.
C) foreign resident purchases a domestic asset.
D) foreign resident purchases a foreign asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The adoption of capital controls makes
A) everyone in the domestic economy better off.
B) some domestic residents better off and some worse off, although on average welfare increases.
C) some domestic residents better off and some worse off, although on average welfare decreases.
D) everyone in the domestic economy worse off.
A) everyone in the domestic economy better off.
B) some domestic residents better off and some worse off, although on average welfare increases.
C) some domestic residents better off and some worse off, although on average welfare decreases.
D) everyone in the domestic economy worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A natural region over which a single currency dominates as a medium of exchange is called
A) sovereign nation.
B) monetary union area.
C) common currency area.
D) currency union.
A) sovereign nation.
B) monetary union area.
C) common currency area.
D) currency union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In response to a temporary change in total factor productivity,the adoption of capital controls under a fixed exchange rate
A) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the domestic nominal money supply.
B) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and dampens the effect on the domestic nominal money supply.
C) dampens the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and amplifies the effect on domestic nominal money supply.
D) dampens the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the domestic nominal money supply.
A) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the domestic nominal money supply.
B) amplifies the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and dampens the effect on the domestic nominal money supply.
C) dampens the effect of this disturbance on domestic output and amplifies the effect on domestic nominal money supply.
D) dampens the effect of this disturbance on both domestic output and the domestic nominal money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the New Keynesian open economy model,suppose the exchange rate is flexible and there is a decline in total factor productivity
A) expansionary fiscal policy is necessary.
B) contractionary monetary policy is necessary.
C) expansionary monetary policy is necessary.
D) no policy intervention is necessary.
A) expansionary fiscal policy is necessary.
B) contractionary monetary policy is necessary.
C) expansionary monetary policy is necessary.
D) no policy intervention is necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the major problem in a currency union?
A) Money demand becomes more erratic.
B) Participating central banks may not agree on monetary policy.
C) It is akin to dollarization.
D) The capital account becomes difficult to define.
A) Money demand becomes more erratic.
B) Participating central banks may not agree on monetary policy.
C) It is akin to dollarization.
D) The capital account becomes difficult to define.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The balance of payments equals
A) the current account surplus plus the capital account surplus.
B) the current account surplus plus the capital account deficit.
C) the current account deficit plus the capital account surplus.
D) the current account deficit plus the capital account deficit.
A) the current account surplus plus the capital account surplus.
B) the current account surplus plus the capital account deficit.
C) the current account deficit plus the capital account surplus.
D) the current account deficit plus the capital account deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The balance of payments is zero
A) as an accounting identity.
B) because market forces ensure that this is so.
C) only if the current account balance is zero.
D) only if the capital account balance is zero.
A) as an accounting identity.
B) because market forces ensure that this is so.
C) only if the current account balance is zero.
D) only if the capital account balance is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the New Keynesian open economy model
A) the nominal exchange rate is always fixed.
B) prices are flexible.
C) net exports depends on the relative price of foreign goods to domestic goods.
D) the nominal exchange rate is always flexible.
A) the nominal exchange rate is always fixed.
B) prices are flexible.
C) net exports depends on the relative price of foreign goods to domestic goods.
D) the nominal exchange rate is always flexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The acquisition of a domestic financial asset by a foreign resident is called
A) foreign direct investment.
B) foreign capital investment.
C) a portfolio inflow.
D) a portfolio outflow.
A) foreign direct investment.
B) foreign capital investment.
C) a portfolio inflow.
D) a portfolio outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the monetary small open-economy model,a fixed exchange rate insulates the domestic price level from
A) both real and nominal shocks from abroad.
B) real shocks from abroad, but not nominal shocks from abroad.
C) nominal shocks from abroad, but not from real shocks from abroad.
D) neither real nor nominal shocks from abroad.
A) both real and nominal shocks from abroad.
B) real shocks from abroad, but not nominal shocks from abroad.
C) nominal shocks from abroad, but not from real shocks from abroad.
D) neither real nor nominal shocks from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A capital inflow occurs when a
A) domestic resident purchases a domestic asset.
B) domestic resident purchases a foreign asset.
C) foreign resident purchases a domestic asset.
D) foreign resident purchases a foreign asset.
A) domestic resident purchases a domestic asset.
B) domestic resident purchases a foreign asset.
C) foreign resident purchases a domestic asset.
D) foreign resident purchases a foreign asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



