Deck 31: Transport and Exchange 2: Digestion, Nutrition, and Elimination
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 31: Transport and Exchange 2: Digestion, Nutrition, and Elimination
1
The upper throat may be referred to as the:
A) pharynx.
B) epiglottis.
C) larynx.
D) trachea.
A) pharynx.
B) epiglottis.
C) larynx.
D) trachea.
A
2
What problem might result from damage to the epiglottis?
A) A person would no longer be able to taste food.
B) Food would be able to enter the respiratory passageway.
C) Food would not be digested properly.
D) A person would no longer be able to swallow.
A) A person would no longer be able to taste food.
B) Food would be able to enter the respiratory passageway.
C) Food would not be digested properly.
D) A person would no longer be able to swallow.
B
3
In addition to breaking down food, what other valuable function does stomach acid perform?
A) Stomach acid kills bacteria and other pathogens in food.
B) Stomach acid activates enzymes in the small intestine.
C) Stomach acid recycles chlorine.
D) Stomach acid converts waste molecules into bile.
A) Stomach acid kills bacteria and other pathogens in food.
B) Stomach acid activates enzymes in the small intestine.
C) Stomach acid recycles chlorine.
D) Stomach acid converts waste molecules into bile.
A
4
Which of the following is an accessory organ in the digestive system?
A) the skin
B) the lungs
C) the pancreas
D) the kidneys
A) the skin
B) the lungs
C) the pancreas
D) the kidneys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Blood carries most nutrients straight from the small intestine to which organ?
A) the heart
B) the liver
C) the kidneys
D) the stomach
E) the pancreas
A) the heart
B) the liver
C) the kidneys
D) the stomach
E) the pancreas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which structure regulates the passage of food from the stomach into the small intestine?
A) the pharynx
B) the epiglottis
C) the stomach submucosa
D) the pyloric sphincter
A) the pharynx
B) the epiglottis
C) the stomach submucosa
D) the pyloric sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which is the main organic molecule that is digested by the secretions of the stomach?
A) carbohydrate
B) lipid
C) nucleic acid
D) protein
A) carbohydrate
B) lipid
C) nucleic acid
D) protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Chemical digestion begins in the:
A) mouth.
B) stomach.
C) large intestine.
D) small intestine.
A) mouth.
B) stomach.
C) large intestine.
D) small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which layer of the digestive tract is actually in contact with the food?
A) muscularis externa
B) submucosa
C) serosa
D) mucosa
A) muscularis externa
B) submucosa
C) serosa
D) mucosa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which type of muscle is involved in peristalsis in the intestine?
A) cardiac
B) skeletal
C) smooth
D) voluntary
A) cardiac
B) skeletal
C) smooth
D) voluntary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following best describes the stomach's role in absorption?
A) The stomach absorbs most nutrients.
B) The stomach absorbs mostly large proteins.
C) The stomach absorbs some drugs and alcohol but few nutrients.
D) The stomach absorbs acids.
A) The stomach absorbs most nutrients.
B) The stomach absorbs mostly large proteins.
C) The stomach absorbs some drugs and alcohol but few nutrients.
D) The stomach absorbs acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Most of the blood vessels and nerves in the digestive tract are located in the layer of:
A) muscularis externa.
B) submucosa.
C) serosa.
D) mucosa.
A) muscularis externa.
B) submucosa.
C) serosa.
D) mucosa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How does food move from the pharynx to the stomach?
A) Gravity alone pushes food through the trachea.
B) Gravity alone pushes food through the esophagus.
C) Peristalsis and gravity push food through the trachea.
D) Peristalsis and gravity push food through the esophagus.
A) Gravity alone pushes food through the trachea.
B) Gravity alone pushes food through the esophagus.
C) Peristalsis and gravity push food through the trachea.
D) Peristalsis and gravity push food through the esophagus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the function of the rugae, or folds in the stomach?
A) The rugae push food down toward the intestine.
B) The rugae allow the stomach to expand when food enters.
C) The rugae neutralize excess acid.
D) The rugae manufacture bile.
A) The rugae push food down toward the intestine.
B) The rugae allow the stomach to expand when food enters.
C) The rugae neutralize excess acid.
D) The rugae manufacture bile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The outermost layer of the digestive tract is the:
A) muscularis externa.
B) submucosa.
C) serosa.
D) mucosa.
A) muscularis externa.
B) submucosa.
C) serosa.
D) mucosa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Digestion of which organic molecule takes a somewhat more complicated route than most nutrients?
A) carbohydrate
B) fat
C) protein
D) nucleic acid
A) carbohydrate
B) fat
C) protein
D) nucleic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How do fats leave the digestive system and enter the bloodstream?
A) in the veins
B) in the capillaries
C) in the arteries
D) in the lymphatic vessels
A) in the veins
B) in the capillaries
C) in the arteries
D) in the lymphatic vessels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the digestive system, the villi are:
A) muscles in the digestive system that push the food along.
B) finger-like projections of the mucosa.
C) glands that release digestive enzymes.
D) blood vessels that pick up nutrients from the digestive system.
A) muscles in the digestive system that push the food along.
B) finger-like projections of the mucosa.
C) glands that release digestive enzymes.
D) blood vessels that pick up nutrients from the digestive system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why doesn't the hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach digest its own lining cells?
A) The stomach has a dense connective tissue lining.
B) Lining cells produce a protective mucus layer.
C) The cells make chemicals that quickly neutralize all the acid.
D) The acid is specific to proteins, not cells.
A) The stomach has a dense connective tissue lining.
B) Lining cells produce a protective mucus layer.
C) The cells make chemicals that quickly neutralize all the acid.
D) The acid is specific to proteins, not cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The mixture of food and digestive juices that leaves the stomach is called:
A) cud.
B) chyme.
C) pepsin.
D) trypsin.
A) cud.
B) chyme.
C) pepsin.
D) trypsin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How would blockage of the pancreatic duct affect the digestive system?
A) The food in the small intestine would be more basic (alkaline).
B) It would have little effect because liver enzymes would take over.
C) The small intestine would contain acidic, mostly undigested chyme.
D) The stomach would be unable to function.
A) The food in the small intestine would be more basic (alkaline).
B) It would have little effect because liver enzymes would take over.
C) The small intestine would contain acidic, mostly undigested chyme.
D) The stomach would be unable to function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Deficiency of which nutrient can cause muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, or paralysis?
A) potassium
B) sulfur
C) iron
D) copper
A) potassium
B) sulfur
C) iron
D) copper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a trace mineral?
A) sodium
B) sulfur
C) phosphorus
D) iodine
A) sodium
B) sulfur
C) phosphorus
D) iodine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which category of nutrient would be best described as compounds needed in small amounts in the diet to facilitate chemical reactions in the body?
A) lipids
B) trace minerals
C) vitamins
D) enzymes
A) lipids
B) trace minerals
C) vitamins
D) enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which organ is central to the body's metabolism of nutrients?
A) the stomach
B) the kidneys
C) the liver
D) the small intestine
A) the stomach
B) the kidneys
C) the liver
D) the small intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The main function of the gallbladder is to:
A) make bile.
B) make gallstones.
C) store and concentrate digestive enzymes.
D) store and concentrate bile.
A) make bile.
B) make gallstones.
C) store and concentrate digestive enzymes.
D) store and concentrate bile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a complex carbohydrate that cannot be digested?
A) disaccharides
B) starches
C) high fructose corn syrup
D) fibers
A) disaccharides
B) starches
C) high fructose corn syrup
D) fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The appendix is attached to which portion of the large intestine?
A) the cecum
B) the colon
C) the rectum
D) the ileocecal valve
A) the cecum
B) the colon
C) the rectum
D) the ileocecal valve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In what way are the essential amino acids different from nonessential amino acids?
A) Nonessential amino acids are not necessary for any proteins we make.
B) Nonessential amino acids are not absorbed by the digestive tract.
C) Essential amino acids cannot be made and must be obtained from food.
D) Essential amino acids are the ones exclusively used to make enzymes.
A) Nonessential amino acids are not necessary for any proteins we make.
B) Nonessential amino acids are not absorbed by the digestive tract.
C) Essential amino acids cannot be made and must be obtained from food.
D) Essential amino acids are the ones exclusively used to make enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the main function of the colon?
A) to complete the digestion of lipids
B) to absorb water and vitamin K
C) to control nutrients it will send to the rest of the body
D) to digest and absorb carbohydrates
A) to complete the digestion of lipids
B) to absorb water and vitamin K
C) to control nutrients it will send to the rest of the body
D) to digest and absorb carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following has the most stored energy per gram?
A) minerals
B) proteins
C) carbohydrates
D) lipids
A) minerals
B) proteins
C) carbohydrates
D) lipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the first part of the small intestine that receives food from the stomach?
A) duodenum
B) ileum
C) jejunum
D) cecum
A) duodenum
B) ileum
C) jejunum
D) cecum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Most of the absorption of digested food takes place in the:
A) stomach.
B) esophagus.
C) large intestine.
D) small intestine.
A) stomach.
B) esophagus.
C) large intestine.
D) small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Most digestion occurs in the:
A) large intestine.
B) mouth.
C) stomach.
D) small intestine.
A) large intestine.
B) mouth.
C) stomach.
D) small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is an example of a nutrient that helps to regulate bodily processes?
A) protein
B) water
C) lipid
D) potassium
A) protein
B) water
C) lipid
D) potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Gallstones are a problem when they:
A) get stuck in the folds of the small intestine.
B) block the cystic duct or common bile duct.
C) break and release enzymes.
D) break and release cholesterol.
A) get stuck in the folds of the small intestine.
B) block the cystic duct or common bile duct.
C) break and release enzymes.
D) break and release cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is unusual about soy protein as opposed to other plant protein sources?
A) Soy protein has all essential amino acids in the proper proportions.
B) Soy protein has the same saturated fat levels as animal fat.
C) Soy protein has more energy per gram than lipids.
D) Soy protein has only one-tenth the energy per gram of other proteins.
A) Soy protein has all essential amino acids in the proper proportions.
B) Soy protein has the same saturated fat levels as animal fat.
C) Soy protein has more energy per gram than lipids.
D) Soy protein has only one-tenth the energy per gram of other proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Roughly how long is the small intestine?
A) 6 feet
B) 14 feet
C) 20 feet
D) 30 feet
A) 6 feet
B) 14 feet
C) 20 feet
D) 30 feet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Calories are a measure of the:
A) nutritional value of food.
B) amount of energy the food contains.
C) weight of the food.
D) amount of minerals and vitamins a food contains.
A) nutritional value of food.
B) amount of energy the food contains.
C) weight of the food.
D) amount of minerals and vitamins a food contains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The measure of how blood glucose levels are affected by a given amount of carbohydrate is:
A) sugar input.
B) glycemic load.
C) monosaccharide ratio.
D) insulin index.
A) sugar input.
B) glycemic load.
C) monosaccharide ratio.
D) insulin index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The urethra is different lengths in men and women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the difference between fats and oils?
A) Oils are mostly made of saturated fat.
B) Fats are mostly made of unsaturated fat.
C) Oils are liquids and fats are solid at room temperature.
D) Fats are always healthier as long as they are mostly saturated.
A) Oils are mostly made of saturated fat.
B) Fats are mostly made of unsaturated fat.
C) Oils are liquids and fats are solid at room temperature.
D) Fats are always healthier as long as they are mostly saturated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
About 99 percent of the fluid the kidney processes is recycled back into the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Sodium is a nutrient because it provides us with energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why are saturated fats considered a less healthy nutrient?
A) Because saturated fats are from animal sources, they can produce allergic reactions.
B) Saturated fats cannot be used for energy as the other fats can.
C) Saturated fats raise HDL levels, which contributes to heart disease.
D) Saturated fats raise LDL levels, which contributes to heart disease.
A) Because saturated fats are from animal sources, they can produce allergic reactions.
B) Saturated fats cannot be used for energy as the other fats can.
C) Saturated fats raise HDL levels, which contributes to heart disease.
D) Saturated fats raise LDL levels, which contributes to heart disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why does alcohol ingestion increase urine output?
A) The alcohol increases blood pressure.
B) The alcohol suppresses ADH production.
C) The alcohol stimulates ADH production.
D) The alcohol redirects blood flow away from the skin and to the kidneys.
E) The alcohol is converted to excess water by the liver.
A) The alcohol increases blood pressure.
B) The alcohol suppresses ADH production.
C) The alcohol stimulates ADH production.
D) The alcohol redirects blood flow away from the skin and to the kidneys.
E) The alcohol is converted to excess water by the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Place the following in order of the movement of urine through the urinary system: (1) urethra, (2) ureter, (3) kidney, (4) urinary bladder.
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 3, 4, 1, 2
C) 1, 3, 2, 4
D) 2, 3, 4, 1
E) 3, 2, 4, 1
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 3, 4, 1, 2
C) 1, 3, 2, 4
D) 2, 3, 4, 1
E) 3, 2, 4, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Soy protein and nearly all animal protein sources provide all the essential amino acids needed in the diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following types of fat are the least healthy?
A) trans fat
B) polyunsaturated fat
C) saturated fat
D) monounsaturated fat
A) trans fat
B) polyunsaturated fat
C) saturated fat
D) monounsaturated fat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a traditional food pyramid, which type of food would be closest to the base?
A) dairy products
B) fish and poultry
C) whole grain foods
D) vegetables
E) fruits
A) dairy products
B) fish and poultry
C) whole grain foods
D) vegetables
E) fruits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Fiber is defined as a complex carbohydrate that is digestible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Why are large amounts of red meat and butter not healthy choices in the diet?
A) They contain too much protein.
B) They contain a lot of saturated fat.
C) Most people cannot digest them.
D) They contain excessive amounts of fiber.
A) They contain too much protein.
B) They contain a lot of saturated fat.
C) Most people cannot digest them.
D) They contain excessive amounts of fiber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Voluntary control of urination is accomplished by:
A) an external sphincter made of skeletal muscle.
B) an internal sphincter of smooth muscle.
C) the skeletal muscle of the bladder.
D) contraction of the ureters.
A) an external sphincter made of skeletal muscle.
B) an internal sphincter of smooth muscle.
C) the skeletal muscle of the bladder.
D) contraction of the ureters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The tube leading from the bladder that carries urine out of the body is the ureter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Digestion is a process of mechanical and chemical breakdown of larger food molecules into smaller ones that can be absorbed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What affect does ADH secretion have on the kidneys?
A) Water stays trapped in the kidney tubules.
B) Urine output increases.
C) The filtration rate increases.
D) Water moves out of the kidney tubules.
E) Blood pressure to the kidneys decreases.
A) Water stays trapped in the kidney tubules.
B) Urine output increases.
C) The filtration rate increases.
D) Water moves out of the kidney tubules.
E) Blood pressure to the kidneys decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A "nutritional" calorie is actually 1,000 of the energy unit calories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Most digested food is absorbed into the blood by the villi of the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Minerals are always chemical elements, not compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The knot of capillaries in a nephron, where filtration of blood occurs, is the:
A) glomerulus.
B) bowman's capsule.
C) proximal tubule.
D) distal tubule.
E) collecting duct.
A) glomerulus.
B) bowman's capsule.
C) proximal tubule.
D) distal tubule.
E) collecting duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Formulate reasons in support of why the duodenum could be described both structurally and functionally as the "crossroads" of the digestive tract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows. 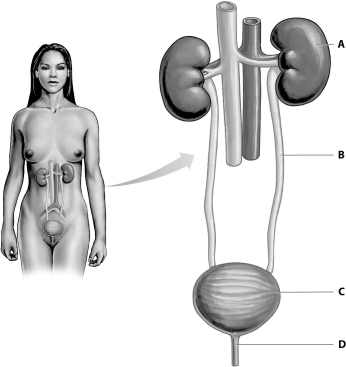
Which structure, A, B, C, or D, transports urine using peristalsis?

Which structure, A, B, C, or D, transports urine using peristalsis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A classmate tells you that his mother had her gallbladder removed, and he says she wants to cut down on fat in her diet. He comments that he's not sure why because lipase is the enzyme that breaks down fats, and bile stored in the gallbladder isn't an enzyme. Although his last statement is factually true, how would you help your classmate understand this connection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The functional units of the kidneys are the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A friend tells you that she wants to try to be a strict vegetarian or vegan, but her parents are discouraging her from doing so. Her parents say she will not get enough protein or vitamins. What advice can you offer your friend to help her convince her parents she will get enough protein and vitamins on a vegetarian or vegan diet?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which nutrient has the highest caloric content?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Chemical elements that are needed to help form bodily structures and to facilitate chemical reactions in the body are ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which part of the brain is responsible for producing and controlling the release of the hormone ADH?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Could someone add body fat by eating a diet low in fat but high in carbohydrates? Defend your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Propose an argument for why the urinary system is much more than just a waste filtration site and is also a major player in the game of homeostasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What are the two main chemicals secreted by the gastric pits in the stomach?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Complex carbohydrates that are digestible are known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The layer of the digestive tract that contains smooth muscle is the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows. 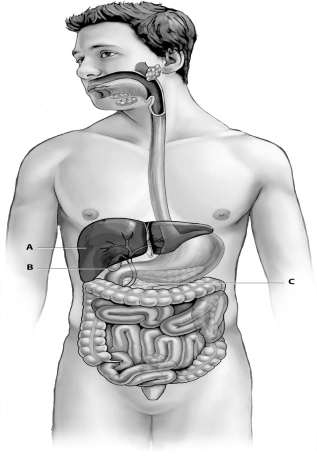
Which organ, A, B, or C, produces digestive enzymes and chemical buffers?

Which organ, A, B, or C, produces digestive enzymes and chemical buffers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



