Deck 18: Fixed Exchange Rates and Foreign Exchange Intervention
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Fixed Exchange Rates and Foreign Exchange Intervention
1
Which of the following is an example of a regional currency arrangement?
A) most-favored nation status
B) free-trade zones
C) exchange rate union
D) currency cartel associations
E) agreement on commercial trade
A) most-favored nation status
B) free-trade zones
C) exchange rate union
D) currency cartel associations
E) agreement on commercial trade
exchange rate union
2
A balance sheet for the central bank of Pecunia is shown below:
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $1,000 Deposits held by private banks $500
Domestic assets $1,500 Currency in circulation $2,000
Please write the new balance sheet if the bank makes a sterilized transaction by selling $100 of foreign assets for domestic currency and then purchasing $100 of domestic assets by writing a check on itself.
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $1,000 Deposits held by private banks $500
Domestic assets $1,500 Currency in circulation $2,000
Please write the new balance sheet if the bank makes a sterilized transaction by selling $100 of foreign assets for domestic currency and then purchasing $100 of domestic assets by writing a check on itself.
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $900 Deposits held by private banks $600
Domestic assets $1,600 Currency in circulation $1,900
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $900 Deposits held by private banks $600
Domestic assets $1,600 Currency in circulation $1,900
3
The liabilities side of a central bank's accounts consists of
A) deposits held by private banks.
B) currency in circulation.
C) deposits held by private banks and currency in circulation.
D) deposits held by foreign banks, domestic assets, and currency in circulation.
E) foreign assets and domestic assets.
A) deposits held by private banks.
B) currency in circulation.
C) deposits held by private banks and currency in circulation.
D) deposits held by foreign banks, domestic assets, and currency in circulation.
E) foreign assets and domestic assets.
deposits held by private banks and currency in circulation.
4
A balance sheet for the central bank of Pecunia is shown below:
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $1,000 Deposits held by private banks $500
Domestic assets $1,500 Currency in circulation $2,000
Please write the new balance sheet if the bank purchased $100 in foreign bonds by writing a check on itself.
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $1,000 Deposits held by private banks $500
Domestic assets $1,500 Currency in circulation $2,000
Please write the new balance sheet if the bank purchased $100 in foreign bonds by writing a check on itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A balance sheet for the central bank of Pecunia is shown below:
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $1,000 Deposits held by private banks $500
Domestic assets $1,500 Currency in circulation $2,000
Please write the new balance sheet if the bank sells $100 worth of foreign bonds for domestic currency.
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets Liabilities
Foreign assets $1,000 Deposits held by private banks $500
Domestic assets $1,500 Currency in circulation $2,000
Please write the new balance sheet if the bank sells $100 worth of foreign bonds for domestic currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Industrialized countries typically ________ their floating exchange rates. Developing countries often ________ their floating exchange rates.
A) fix; allow markets to determine
B) manage; peg
C) allow markets to determine; fix
D) fix; manage
E) peg; manage
A) fix; allow markets to determine
B) manage; peg
C) allow markets to determine; fix
D) fix; manage
E) peg; manage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the central bank does not purchase foreign assets when output increases but instead holds the money stock constant, can it still keep the exchange rate fixed at 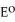 ? Please explain.
? Please explain.
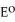 ? Please explain.
? Please explain.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are the factors affecting the demand for foreign currency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the expected dollar rate of return on dollar deposits if today's exchange rate is $1.10 per euro, next year's expected exchange rate is $1.165 per euro, the dollar interest rate is 10%, and the euro interest rate is 5%?
A) 10%
B) 11%
C) -1%
D) 0%
E) 5%
A) 10%
B) 11%
C) -1%
D) 0%
E) 5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following statements is most correct?
A) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money supply.
B) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money demand.
C) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money supply.
D) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments shortage, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money supply.
E) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments shortage, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies an increased domestic money supply.
A) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money supply.
B) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money demand.
C) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money supply.
D) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments shortage, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies a decreased foreign money supply.
E) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments shortage, any associated decrease in a foreign central bank's claims on the home country implies an increased domestic money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the central bank does not purchase foreign assets when output increases but instead holds the money stock constant, can it still keep the exchange rate fixed at 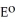 ? Please explain with the aid of a figure.
? Please explain with the aid of a figure.
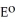 ? Please explain with the aid of a figure.
? Please explain with the aid of a figure.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Under a fixed exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply.
B) Under a flexible exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.
C) Under a fixed exchange rate, fiscal policy tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.
D) Under a fixed exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.
E) Under a dirty float exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.
A) Under a fixed exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply.
B) Under a flexible exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.
C) Under a fixed exchange rate, fiscal policy tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.
D) Under a fixed exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.
E) Under a dirty float exchange rate, central bank monetary tools are powerless to affect the economy's money supply or its output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which one of the following statements is most correct?
A) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in an increase in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets automatically causes the money supply to decline.
B) Any central bank purchase of assets results in an increase in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets causes the money supply to decline.
C) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in a decrease in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets automatically causes the money supply to decline.
D) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in a decrease in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets automatically causes the money supply to increase.
E) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in an increase in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets does not necessarily affect the money supply.
A) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in an increase in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets automatically causes the money supply to decline.
B) Any central bank purchase of assets results in an increase in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets causes the money supply to decline.
C) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in a decrease in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets automatically causes the money supply to decline.
D) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in a decrease in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets automatically causes the money supply to increase.
E) Any central bank purchase of assets automatically results in an increase in the domestic money supply, while any central bank sale of assets does not necessarily affect the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Please define and give an example of sterilized foreign exchange intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Under fixed exchange rate, in general which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: Ms/P = L(R , Y).
, Y).
B) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: Md/P = L(R , Y).
, Y).
C) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: Ms = L(R , Y).
, Y).
D) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: P = L(R , Y).
, Y).
E) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: R*Md/P = L(Y).
A) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: Ms/P = L(R
 , Y).
, Y).B) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: Md/P = L(R
 , Y).
, Y).C) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: Ms = L(R
 , Y).
, Y).D) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: P = L(R
 , Y).
, Y).E) The following condition should hold for domestic money market equilibrium: R*Md/P = L(Y).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which one of the following statements is the most correct?
A) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money supply.
B) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in the home central bank's foreign assets implies a decreased home money supply.
C) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money demand.
D) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated decrease in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money supply.
E) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments shortage, any associated decrease in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money supply.
A) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money supply.
B) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in the home central bank's foreign assets implies a decreased home money supply.
C) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated increase in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money demand.
D) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments surplus, any associated decrease in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money supply.
E) If central banks are not sterilizing and the home country has a balance of payments shortage, any associated decrease in the home central bank's foreign assets implies an increased home money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why is it important to understand fixed exchange rates in the modern global economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A central bank's international reserves consists of its holdings of
A) gold.
B) silver and gold.
C) foreign assets and gold.
D) domestic assets and precious metals.
E) foreign and domestic currency holdings.
A) gold.
B) silver and gold.
C) foreign assets and gold.
D) domestic assets and precious metals.
E) foreign and domestic currency holdings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Central banks often intervene in currency markets. This activity is called
A) super-pegging.
B) flexible floating.
C) currency warfare.
D) fixing exchange rates.
E) managed floating.
A) super-pegging.
B) flexible floating.
C) currency warfare.
D) fixing exchange rates.
E) managed floating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A system of managed floating exchange rates is
A) a system in which governments may attempt to moderate exchange rate movements without keeping exchange rates rigidly fixed.
B) a system in which governments use flexible exchange rates.
C) a system in which governments are forbidden from attempts to moderate exchange rate movements without keeping exchange rates rigidly fixed.
D) a system in which governments need to reach a prior agreement among them before they may attempt to moderate exchange rate movements without keeping exchange rates rigidly fixed.
E) a system in which governments use extensive fiscal policy to discourage exchange rate movements.
A) a system in which governments may attempt to moderate exchange rate movements without keeping exchange rates rigidly fixed.
B) a system in which governments use flexible exchange rates.
C) a system in which governments are forbidden from attempts to moderate exchange rate movements without keeping exchange rates rigidly fixed.
D) a system in which governments need to reach a prior agreement among them before they may attempt to moderate exchange rate movements without keeping exchange rates rigidly fixed.
E) a system in which governments use extensive fiscal policy to discourage exchange rate movements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Under fixed exchange rates, which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Devaluation causes a decrease in output, a decrease in official reserves, and a contraction of the money supply.
B) Devaluation causes a rise in output, a rise in official reserves, and an expansion of the money supply.
C) Devaluation causes a rise in output and a rise in official reserves.
D) Devaluation causes a rise in output and an expansion of the money supply.
E) Devaluation causes a rise in official reserves, and an expansion of the money supply.
A) Devaluation causes a decrease in output, a decrease in official reserves, and a contraction of the money supply.
B) Devaluation causes a rise in output, a rise in official reserves, and an expansion of the money supply.
C) Devaluation causes a rise in output and a rise in official reserves.
D) Devaluation causes a rise in output and an expansion of the money supply.
E) Devaluation causes a rise in official reserves, and an expansion of the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Fiscal expansion under fixed exchange rates will have what temporary effect?
A) the money supply will decrease
B) output will decrease
C) the exchange rate will increase
D) the exchange rate will decrease
E) there will be no effect
A) the money supply will decrease
B) output will decrease
C) the exchange rate will increase
D) the exchange rate will decrease
E) there will be no effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Fiscal policy has the same effect on employment under fixed and flexible exchange rate regimes.
B) Fiscal policy affects employment less under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
C) Fiscal policy affects employment more under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
D) Fiscal policy cannot affect employment under fixed exchange rate but does affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.
E) Fiscal policy can affect employment under fixed exchange rate regimes, but does not affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.
A) Fiscal policy has the same effect on employment under fixed and flexible exchange rate regimes.
B) Fiscal policy affects employment less under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
C) Fiscal policy affects employment more under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
D) Fiscal policy cannot affect employment under fixed exchange rate but does affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.
E) Fiscal policy can affect employment under fixed exchange rate regimes, but does not affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Appreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
B) Appreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
C) Appreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed while revaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is flexible.
D) Appreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
E) Appreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
A) Appreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
B) Appreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
C) Appreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed while revaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is flexible.
D) Appreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
E) Appreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while revaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Revaluation reflects an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together while appreciation reflects a deliberate government decision.
B) Revaluation reflects a deliberate government decision while appreciation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.
C) Revaluation reflects a deliberate government decision while appreciation is an outcome of government actions.
D) Revaluation and appreciation have the same meaning and the same causes.
E) Appreciation reflects a deliberate government decision while revaluation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.
A) Revaluation reflects an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together while appreciation reflects a deliberate government decision.
B) Revaluation reflects a deliberate government decision while appreciation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.
C) Revaluation reflects a deliberate government decision while appreciation is an outcome of government actions.
D) Revaluation and appreciation have the same meaning and the same causes.
E) Appreciation reflects a deliberate government decision while revaluation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Under fixed exchange rates, which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Devaluation causes a rise in output.
B) Devaluation causes a decrease in output.
C) Devaluation has no effect on output.
D) Devaluation causes a rise in output and a decrease in official reserves.
E) Devaluation causes a decrease in output and in official reserves.
A) Devaluation causes a rise in output.
B) Devaluation causes a decrease in output.
C) Devaluation has no effect on output.
D) Devaluation causes a rise in output and a decrease in official reserves.
E) Devaluation causes a decrease in output and in official reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
By fixing the exchange rate, the central bank gives up its ability to
A) adjust taxes.
B) increase government spending.
C) influence the economy through fiscal policy.
D) depreciate the domestic currency.
E) influence the economy through monetary policy.
A) adjust taxes.
B) increase government spending.
C) influence the economy through fiscal policy.
D) depreciate the domestic currency.
E) influence the economy through monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use a figure to illustrate the ineffectiveness of monetary policy to spur on an economy under a fixed exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) A devaluation occurs when the central bank lowers the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank raises E.
B) A devaluation occurs when the central bank raises the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank lowers E.
C) Devaluation occurs when the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, raises and a revaluation occurs when E is lowered.
D) A devaluation occurs when the central bank of the foreign country raises the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank of the foreign country lowers E.
E) A devaluation occurs when the central bank raises the foreign currency price of domestic currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank lowers E.
A) A devaluation occurs when the central bank lowers the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank raises E.
B) A devaluation occurs when the central bank raises the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank lowers E.
C) Devaluation occurs when the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, raises and a revaluation occurs when E is lowered.
D) A devaluation occurs when the central bank of the foreign country raises the domestic currency price of foreign currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank of the foreign country lowers E.
E) A devaluation occurs when the central bank raises the foreign currency price of domestic currency, E, and a revaluation occurs when the central bank lowers E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Fiscal policy has the same effect on output under fixed and flexible exchange rate regimes.
B) Fiscal policy affects output more under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
C) Fiscal policy affects output less under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
D) Fiscal policy cannot affect output under fixed exchange rate but does affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.
E) Fiscal policy can affect output under fixed exchange rate but does not affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.
A) Fiscal policy has the same effect on output under fixed and flexible exchange rate regimes.
B) Fiscal policy affects output more under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
C) Fiscal policy affects output less under fixed than under flexible exchange rate regimes.
D) Fiscal policy cannot affect output under fixed exchange rate but does affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.
E) Fiscal policy can affect output under fixed exchange rate but does not affect output under flexible exchange rate regimes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Under fixed rates, which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Fiscal policy can affect output, employment and international reserves at the same time.
B) Fiscal policy can affect only employment.
C) Fiscal policy can affect only international reserves.
D) Fiscal policy can affect only output and employment.
E) Fiscal employment can affect only output and international reserves.
A) Fiscal policy can affect output, employment and international reserves at the same time.
B) Fiscal policy can affect only employment.
C) Fiscal policy can affect only international reserves.
D) Fiscal policy can affect only output and employment.
E) Fiscal employment can affect only output and international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The main reason(s) why governments sometimes choose to devalue their currencies is (are)
A) devaluation makes domestic goods more expensive in relation to foreign goods.
B) devaluation makes domestic services more expensive in relation to foreign services.
C) devaluation increases foreign reserves held by the central bank.
D) devaluation improves the current account and increases foreign reserves held by the central bank.
E) devaluation hurts foreign currencies.
A) devaluation makes domestic goods more expensive in relation to foreign goods.
B) devaluation makes domestic services more expensive in relation to foreign services.
C) devaluation increases foreign reserves held by the central bank.
D) devaluation improves the current account and increases foreign reserves held by the central bank.
E) devaluation hurts foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Devaluation reflects a deliberate government decision.
B) Depreciation reflects a deliberate government decision.
C) Devaluation reflects a deliberate government decision while depreciation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.
D) Depreciation reflects a deliberate government decision while devaluation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.
E) Devaluation and depreciation have the same meaning and the same causes.
A) Devaluation reflects a deliberate government decision.
B) Depreciation reflects a deliberate government decision.
C) Devaluation reflects a deliberate government decision while depreciation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.
D) Depreciation reflects a deliberate government decision while devaluation is an outcome of government actions and market forces acting together.
E) Devaluation and depreciation have the same meaning and the same causes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Depreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed while devaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats.
B) Depreciation is a decrease in E when the exchange rate floats while devaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
C) Depreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while devaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
D) Depreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while devaluation is a decrease in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
E) Depreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed while devaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate floats.
A) Depreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed while devaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats.
B) Depreciation is a decrease in E when the exchange rate floats while devaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
C) Depreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while devaluation is a rise in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
D) Depreciation is a rise in E when the exchange rate floats while devaluation is a decrease in E when the exchange rate is fixed.
E) Depreciation is a fall in E when the exchange rate is fixed while devaluation is a fall in E when the exchange rate floats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Please discuss the difference between the terms devaluation and depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When a country's currency is devalued
A) output decreases.
B) output increases and the money supply decreases.
C) the money supply decreases.
D) output decreases and the money supply increases.
E) both the output and the money supply increases.
A) output decreases.
B) output increases and the money supply decreases.
C) the money supply decreases.
D) output decreases and the money supply increases.
E) both the output and the money supply increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Under fixed exchange rates, which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Devaluation causes a reduction of the money supply.
B) Devaluation has no effect on the stock of money.
C) Devaluation causes an expansion of the money supply.
D) Devaluation causes a reduction in output.
E) Devaluation causes a reduction in official reserves.
A) Devaluation causes a reduction of the money supply.
B) Devaluation has no effect on the stock of money.
C) Devaluation causes an expansion of the money supply.
D) Devaluation causes a reduction in output.
E) Devaluation causes a reduction in official reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use a figure to explain the potential effectiveness of fiscal policy to spur on the economy under a fixed exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Under fixed rates, which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Monetary policy can affect only output.
B) Monetary policy can affect only employment.
C) Monetary policy can affect only international reserves.
D) Monetary policy can not affect international reserves.
E) Monetary policy can only affect money supply.
A) Monetary policy can affect only output.
B) Monetary policy can affect only employment.
C) Monetary policy can affect only international reserves.
D) Monetary policy can not affect international reserves.
E) Monetary policy can only affect money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following best describes a deliberate government decision to lower the exchange rate, E?
A) appreciation
B) depreciation
C) revaluation
D) devaluation
E) accumulation
A) appreciation
B) depreciation
C) revaluation
D) devaluation
E) accumulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Define devaluation and use a figure to show the effect of a currency devaluation on the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Imperfect asset substitutability assumes
A) the returns on foreign and domestic currency bonds are identical.
B) the returns on foreign and domestic currency are unrelated.
C) the risks of holding foreign and domestic currency are identical.
D) the risks of holding foreign and domestic currency are unrelated to returns.
E) the returns on foreign and domestic currency differ and are influenced by risk.
A) the returns on foreign and domestic currency bonds are identical.
B) the returns on foreign and domestic currency are unrelated.
C) the risks of holding foreign and domestic currency are identical.
D) the risks of holding foreign and domestic currency are unrelated to returns.
E) the returns on foreign and domestic currency differ and are influenced by risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Please describe in detail a self-fulfilling currency crisis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A balance of payments crisis is best described as
A) a sharp change in interest rates sparked by a change in expectations about the level of imports.
B) a sharp change in foreign reserves sparked by a change in expectations about the future exchange rate.
C) a sharp change in interest rates sparked by a change in expectations about the level of exports.
D) a sharp change in foreign reserves sparked by a change in expectations about the level of imports.
E) a sharp change in foreign reserves sparked by a change in expectations about domestic production.
A) a sharp change in interest rates sparked by a change in expectations about the level of imports.
B) a sharp change in foreign reserves sparked by a change in expectations about the future exchange rate.
C) a sharp change in interest rates sparked by a change in expectations about the level of exports.
D) a sharp change in foreign reserves sparked by a change in expectations about the level of imports.
E) a sharp change in foreign reserves sparked by a change in expectations about domestic production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Imperfect asset substitutability exists
A) when it is possible for the expected returns on two assets to be different.
B) when the expected returns on two assets are the same.
C) only when one asset is foreign and the other is domestic.
D) when there is risk in the foreign exchange market.
E) when assets are liquid.
A) when it is possible for the expected returns on two assets to be different.
B) when the expected returns on two assets are the same.
C) only when one asset is foreign and the other is domestic.
D) when there is risk in the foreign exchange market.
E) when assets are liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The expectation of future revaluation causes a balance of payments crisis marked by
A) a sharp rise in reserves and a fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
B) a sharp fall in reserves and an even bigger fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
C) a sharp fall in reserves and a rise in the home interest rate above the world interest rate.
D) a sharp rise in reserves and an even greater rise in the home interest rate above the world interest.
E) a sharp fall in reserves and an unchanged home interest rate.
A) a sharp rise in reserves and a fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
B) a sharp fall in reserves and an even bigger fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
C) a sharp fall in reserves and a rise in the home interest rate above the world interest rate.
D) a sharp rise in reserves and an even greater rise in the home interest rate above the world interest.
E) a sharp fall in reserves and an unchanged home interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Perfect asset substitutability is the assumption that
A) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on domestic assets are greater than returns on foreign currency bonds.
B) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on foreign currency bonds are greater than returns on domestic assets.
C) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on all assets are negative.
D) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on domestic assets are equal to returns on foreign currency bonds.
E) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when domestic assets are risk-free.
A) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on domestic assets are greater than returns on foreign currency bonds.
B) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on foreign currency bonds are greater than returns on domestic assets.
C) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on all assets are negative.
D) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when expected returns on domestic assets are equal to returns on foreign currency bonds.
E) the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium only when domestic assets are risk-free.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Capital flight
A) increases reserves.
B) is never associated with the expectation of devaluation.
C) may undo expected devaluation.
D) reduces losses during a devaluation scare.
E) decreases reserves and may induce devaluation.
A) increases reserves.
B) is never associated with the expectation of devaluation.
C) may undo expected devaluation.
D) reduces losses during a devaluation scare.
E) decreases reserves and may induce devaluation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The global financial crisis of 2007-2008 resulted in a(n) ________ of the Swiss franc. In 2011, the Swiss central bank intervened in order to cause a(n) ________ of the franc.
A) appreciation; appreciation
B) depreciation; depreciation
C) appreciation; revaluation
D) depreciation; appreciation
E) appreciation; depreciation
A) appreciation; appreciation
B) depreciation; depreciation
C) appreciation; revaluation
D) depreciation; appreciation
E) appreciation; depreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Assuming perfect asset substitutability, can sterilized intervention by the central bank be effective? Please discuss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Currency crises may result from
A) central bank balance sheets with higher liabilities than assets.
B) political upheaval leading to lowering exports.
C) a reconfiguration of central bank balance sheets.
D) speculative attacks on the currency or central banks purchasing excessive amounts of government bonds.
E) depreciation of foreign reserves.
A) central bank balance sheets with higher liabilities than assets.
B) political upheaval leading to lowering exports.
C) a reconfiguration of central bank balance sheets.
D) speculative attacks on the currency or central banks purchasing excessive amounts of government bonds.
E) depreciation of foreign reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use a figure to explain how a balance of payments crisis occurs and its hand in capital flight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The signaling effect of foreign exchange intervention
A) never has any effect on exchange rates.
B) can alter the market's view of exchange rates independent from the stance of monetary and fiscal policies.
C) cannot cause an immediate exchange rate change when bonds denominated in different currencies are perfect substitutes.
D) never leads to actual changes in monetary or fiscal policy.
E) can alter the market's view of future monetary policies and cause an immediate exchange rate change.
A) never has any effect on exchange rates.
B) can alter the market's view of exchange rates independent from the stance of monetary and fiscal policies.
C) cannot cause an immediate exchange rate change when bonds denominated in different currencies are perfect substitutes.
D) never leads to actual changes in monetary or fiscal policy.
E) can alter the market's view of future monetary policies and cause an immediate exchange rate change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Please draw a figure illustrating the actions the central bank must take to maintain a fixed exchange rate following an increase in output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The global financial crisis of 2007-2008 resulted in a(n) ________ of the Swiss franc as foreign currency flowed ________ the country. As a result, Swiss products became ________ competitive in world markets.
A) depreciation; out of; more
B) depreciation; into; more
C) appreciation; out of; less
D) depreciation; out of; less
E) appreciation; into; less
A) depreciation; out of; more
B) depreciation; into; more
C) appreciation; out of; less
D) depreciation; out of; less
E) appreciation; into; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Describe the effect of the 2008-2009 global financial crisis on the Swiss franc and the central bank's efforts to respond to the resulting problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The expectation of future devaluation causes a balance of payments crisis marked by
A) a sharp rise in reserves and a fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
B) a sharp fall in reserves and an even bigger fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
C) a sharp fall in reserves and a rise in the home interest rate above the world interest rate.
D) a sharp rise in reserves and an even greater rise in the home interest rate above the world interest.
E) a sharp rise in reserves and a rise in the home interest rate to the level of the world interest.
A) a sharp rise in reserves and a fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
B) a sharp fall in reserves and an even bigger fall in the home interest rate below the world interest rate.
C) a sharp fall in reserves and a rise in the home interest rate above the world interest rate.
D) a sharp rise in reserves and an even greater rise in the home interest rate above the world interest.
E) a sharp rise in reserves and a rise in the home interest rate to the level of the world interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Please use a figure to discuss whether or not a devaluation under a fixed exchange rate has the same long-run effect as a proportional increase in the money supply under a floating rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the interest rate parity condition with imperfect substitutes and a risk premium of ρ
A) an increased stock of domestic government debt will raise the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
B) a decreased stock of domestic government debt will raise the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
C) an increased stock of domestic government debt will reduce the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
D) an increased stock of domestic government debt will have no effect on the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
E) a decreased stock of domestic government debt will have no effect on the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
A) an increased stock of domestic government debt will raise the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
B) a decreased stock of domestic government debt will raise the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
C) an increased stock of domestic government debt will reduce the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
D) an increased stock of domestic government debt will have no effect on the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.
E) a decreased stock of domestic government debt will have no effect on the difference between the expected returns on domestic and foreign currency bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Briefly describe two systems for fixing the exchange rates of all currencies against each other and the time periods in which they were used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A balance of payments crises under fixed exchange rates occurs when
A) marginal returns on foreign exchange investments approach zero.
B) a country runs out of foreign reserves.
C) a country is in a liquidity trap.
D) forward currency markets undergo high volatility.
E) exports and imports expand beyond some point.
A) marginal returns on foreign exchange investments approach zero.
B) a country runs out of foreign reserves.
C) a country is in a liquidity trap.
D) forward currency markets undergo high volatility.
E) exports and imports expand beyond some point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Under the gold standard, if the dollar price of gold is pegged at $35 per ounce and the dollar/euro exchange rate is set at $2.40 per euro, what must the euro price of gold be pegged at?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
List the drawbacks of the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain how a country whose currency is the reserve currency can use monetary policy for macroeconomic stabilization. In particular, explain the result if that country doubled its domestic money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
From the figure below, please provide an explanation for the large decline in the growth rate of international reserves held by developing countries in the 2008-2009 period. 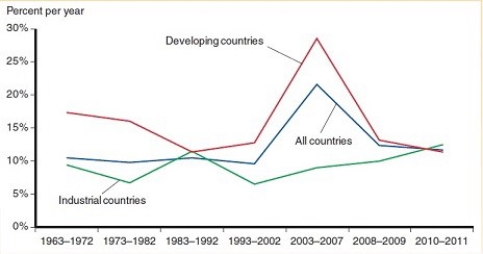


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If assets are imperfect substitutes, then a decrease in the amount of domestic currency bonds held by the public will ________ the risk premium and ________ the amount of domestic currency bonds held by the central bank.
A) decrease; leave unchanged
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) leave unchanged; decrease
A) decrease; leave unchanged
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) leave unchanged; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Balance of payments crises under fixed exchange rates occur because of
A) government policies that are inconsistent with fixed exchange rates.
B) punitive currency wars.
C) global inflation and trade imbalances due to war.
D) excessive exports and imports that overload the global system.
E) monotonic expansion in global currency volume.
A) government policies that are inconsistent with fixed exchange rates.
B) punitive currency wars.
C) global inflation and trade imbalances due to war.
D) excessive exports and imports that overload the global system.
E) monotonic expansion in global currency volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume that initially, the risk premium, ρ = 0 and that the domestic and foreign interest rates are given by R = .06, R* = .05. Suppose that the risk premium depends linearly on the difference between domestic government debt, B, and domestic assets of the central bank, A, i.e.,
ρ =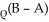 How much will the central bank have to reduce domestic assets A s.t. the domestic interest rate will increase by (a) 1% (b) 4%?
How much will the central bank have to reduce domestic assets A s.t. the domestic interest rate will increase by (a) 1% (b) 4%?
ρ =
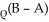 How much will the central bank have to reduce domestic assets A s.t. the domestic interest rate will increase by (a) 1% (b) 4%?
How much will the central bank have to reduce domestic assets A s.t. the domestic interest rate will increase by (a) 1% (b) 4%?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If assets are imperfect substitutes, then an increase in the amount of domestic currency bonds held by the public will ________ the risk premium and ________ the amount of domestic currency bonds held by the central bank.
A) increase; leave unchanged
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) leave unchanged; decrease
A) increase; leave unchanged
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) leave unchanged; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Please briefly describe what is meant by a gold exchange standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
From 1837 and up until the Civil War, the United States adhered to a
A) gold standard.
B) silver standard.
C) bimetallic standard.
D) bronze standard.
E) copper standard.
A) gold standard.
B) silver standard.
C) bimetallic standard.
D) bronze standard.
E) copper standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use a figure to show the effect of a sterilized central bank purchase of foreign assets under the imperfect asset substitutability assumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Under the gold standard, if the dollar price of gold is pegged at $35 per ounce and the euro price of gold is pegged at 12 euro per ounce, what is the dollar/euro exchange rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Briefly discuss the main advantage of the bimetallic standard over the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
This question concerns the mechanism of a reserve currency standard.
Two countries, X and Y, have two currencies, x and y, fixed to the reserve currency, the U.S. dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between x and the U.S. dollar is 3x per dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between y and the U.S. dollar is 5y per dollar. Explain (using numbers) the mechanism if the x-y exchange rate was 0.5 x per y.
Two countries, X and Y, have two currencies, x and y, fixed to the reserve currency, the U.S. dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between x and the U.S. dollar is 3x per dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between y and the U.S. dollar is 5y per dollar. Explain (using numbers) the mechanism if the x-y exchange rate was 0.5 x per y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Describe the mechanism which would take place if the Bank of England decides to increase its money supply by purchasing domestic assets under the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
This question concerns the mechanism of a reserve currency standard.
Two countries, X and Y, have two currencies, x and y, fixed to the reserve currency, the U.S. dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between x and the U.S. dollar is 3x per dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between y and the U.S. dollar is 5y per dollar. Explain (using numbers) the mechanism if the x-y exchange rate was 0.8 x per y.
Two countries, X and Y, have two currencies, x and y, fixed to the reserve currency, the U.S. dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between x and the U.S. dollar is 3x per dollar. Suppose the exchange rate between y and the U.S. dollar is 5y per dollar. Explain (using numbers) the mechanism if the x-y exchange rate was 0.8 x per y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
From the Civil War up to 1914, the United States adhered to a
A) gold standard.
B) silver standard.
C) bimetallic standard.
D) bronze standard.
E) copper standard.
A) gold standard.
B) silver standard.
C) bimetallic standard.
D) bronze standard.
E) copper standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Does the signalling effect of foreign exchange intervention support or refute the claim that assets cannot be perfect substitutes if sterilized intervention is going to have any effect? Please explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Assume that initially, the risk premium, ρ = 0 and that the domestic and foreign interest rates are given by R = .06, R* = .05. Suppose that the risk premium depends linearly on the difference between domestic government debt, B, and domestic assets of the central bank, A, i.e.,
ρ =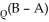 Find the new domestic interest rate if a sterilized purchase of foreign assets adjusts A s.t.
Find the new domestic interest rate if a sterilized purchase of foreign assets adjusts A s.t.
(a) B - A = -.01/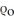 (b) B - A = .01/
(b) B - A = .01/ 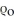 (c) B - A = .03/
(c) B - A = .03/ 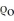
ρ =
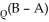 Find the new domestic interest rate if a sterilized purchase of foreign assets adjusts A s.t.
Find the new domestic interest rate if a sterilized purchase of foreign assets adjusts A s.t.(a) B - A = -.01/
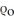 (b) B - A = .01/
(b) B - A = .01/ 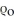 (c) B - A = .03/
(c) B - A = .03/ 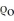

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



