Deck 9: The General and Special Senses
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: The General and Special Senses
1
Sensory receptors that monitor the position of joints are called
A) nociceptors.
B) chemoreceptors.
C) thermoreceptors.
D) baroreceptors.
E) proprioceptors.
A) nociceptors.
B) chemoreceptors.
C) thermoreceptors.
D) baroreceptors.
E) proprioceptors.
E
2
Olfactory glands
A) contain the neural receptors for the sense of smell.
B) form the basement membrane of the olfactory epithelium.
C) are sensitive to aromatic molecules in the air.
D) produce a pigmented mucus that covers the olfactory epithelium.
E) form structures called olfactory bulbs.
A) contain the neural receptors for the sense of smell.
B) form the basement membrane of the olfactory epithelium.
C) are sensitive to aromatic molecules in the air.
D) produce a pigmented mucus that covers the olfactory epithelium.
E) form structures called olfactory bulbs.
D
3
Olfactory receptors are examples of
A) pain receptors.
B) thermoreceptors.
C) mechanoreceptors.
D) chemoreceptors.
E) proprioceptors.
A) pain receptors.
B) thermoreceptors.
C) mechanoreceptors.
D) chemoreceptors.
E) proprioceptors.
D
4
Which statement regarding sensory reception is correct?
A) The larger the receptive field, the better is one's ability to localize a stimulus.
B) The CNS can tell the difference between a "true" sensation and a "false" one.
C) Output from higher centers can dampen receptor sensitivity.
D) The CNS interprets the nature of sensory information entirely on the basis of the area of the brain stimulated.
E) In general, the stronger the stimulus, the lower the frequency of action potentials.
A) The larger the receptive field, the better is one's ability to localize a stimulus.
B) The CNS can tell the difference between a "true" sensation and a "false" one.
C) Output from higher centers can dampen receptor sensitivity.
D) The CNS interprets the nature of sensory information entirely on the basis of the area of the brain stimulated.
E) In general, the stronger the stimulus, the lower the frequency of action potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Nociceptors are sensitive to
A) pain.
B) light touch.
C) vibration.
D) osmotic pressure.
E) blood pressure.
A) pain.
B) light touch.
C) vibration.
D) osmotic pressure.
E) blood pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Temperature sensations are relayed along the same pathways that carry sensations of
A) pressure.
B) low frequency vibration.
C) body position.
D) pH.
E) pain.
A) pressure.
B) low frequency vibration.
C) body position.
D) pH.
E) pain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Neurons in the respiratory centers of the brain that respond to pH are examples of
A) baroreceptors.
B) nociceptors.
C) thermoreceptors.
D) mechanoreceptors.
E) chemoreceptors.
A) baroreceptors.
B) nociceptors.
C) thermoreceptors.
D) mechanoreceptors.
E) chemoreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The fading of a dominant odor sometime after one enters a room is an example of experiencing
A) sensory adaptation.
B) damage to receptors.
C) sensory deprivation.
D) a change in concentration of the odor.
E) proprioception.
A) sensory adaptation.
B) damage to receptors.
C) sensory deprivation.
D) a change in concentration of the odor.
E) proprioception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Temperature senses use two types of
A) chemoreceptors.
B) free nerve endings.
C) proprioceptors.
D) tactile corpuscles.
E) lamellated corpuscles.
A) chemoreceptors.
B) free nerve endings.
C) proprioceptors.
D) tactile corpuscles.
E) lamellated corpuscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Axons leaving each olfactory bulb travel along the olfactory tract to reach the olfactory cerebral cortex, portions of the limbic system, and the
A) thalamus.
B) superior colliculus.
C) pineal body.
D) hypothalamus.
E) epithalamus.
A) thalamus.
B) superior colliculus.
C) pineal body.
D) hypothalamus.
E) epithalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Sensory receptors that respond to changes in blood pressure are called
A) thermoreceptors.
B) baroreceptors.
C) proprioceptors.
D) nociceptors.
E) chemoreceptors.
A) thermoreceptors.
B) baroreceptors.
C) proprioceptors.
D) nociceptors.
E) chemoreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Proprioceptors
A) do not adapt to constant stimulation.
B) for the most part produce information that is processed consciously.
C) do not send information continuously to the CNS.
D) are free nerve endings that branch within the walls of a distensible organ.
E) are exemplified by receptors in the carotid and aortic sinus.
A) do not adapt to constant stimulation.
B) for the most part produce information that is processed consciously.
C) do not send information continuously to the CNS.
D) are free nerve endings that branch within the walls of a distensible organ.
E) are exemplified by receptors in the carotid and aortic sinus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Golgi tendon organs are examples of which of the following?
A) mechanoreceptors
B) proprioceptors
C) baroreceptors
D) chemoreceptors
E) nociceptors
A) mechanoreceptors
B) proprioceptors
C) baroreceptors
D) chemoreceptors
E) nociceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Lamellated corpuscles (Pacinian corpuscles) are
A) tactile receptors.
B) baroreceptors.
C) nociceptors.
D) thermoreceptors.
E) proprioceptors.
A) tactile receptors.
B) baroreceptors.
C) nociceptors.
D) thermoreceptors.
E) proprioceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Nociceptors
A) are rare in joint capsules.
B) increase in sensitivity in the presence of a constant stimulus.
C) have large receptive fields.
D) carry fast pain sensations through unmyelinated fibers.
E) are widely distributed in all tissues.
A) are rare in joint capsules.
B) increase in sensitivity in the presence of a constant stimulus.
C) have large receptive fields.
D) carry fast pain sensations through unmyelinated fibers.
E) are widely distributed in all tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Ruffini corpuscles are examples of
A) tactile receptors.
B) baroreceptors.
C) chemoreceptors.
D) proprioceptors.
E) nociceptors.
A) tactile receptors.
B) baroreceptors.
C) chemoreceptors.
D) proprioceptors.
E) nociceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The conscious awareness of a sensation is called
A) reception.
B) perception.
C) proprioception.
D) adaptation.
E) desensitization.
A) reception.
B) perception.
C) proprioception.
D) adaptation.
E) desensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following arrives at the primary sensory cortex?
A) olfactory sensations
B) visual sensations
C) auditory sensations
D) motor efferents
E) touch sensations
A) olfactory sensations
B) visual sensations
C) auditory sensations
D) motor efferents
E) touch sensations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Gustation refers to the special sense of
A) balance.
B) touch.
C) equilibrium.
D) vision.
E) taste.
A) balance.
B) touch.
C) equilibrium.
D) vision.
E) taste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The perception of pain coming from parts of the body that are not actually stimulated is called
A) preferential pain.
B) recalcitrant pain.
C) actual pain.
D) referred pain.
E) slow pain.
A) preferential pain.
B) recalcitrant pain.
C) actual pain.
D) referred pain.
E) slow pain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Each gustatory cell extends a ________ into the surrounding fluids through a narrow taste pore.
A) taste bud
B) papilla
C) taste hair
D) basal cell
E) neuron
A) taste bud
B) papilla
C) taste hair
D) basal cell
E) neuron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Normal eye focusing is termed
A) hyperopia.
B) myopia.
C) presbyopia.
D) emmetropia.
E) refraction.
A) hyperopia.
B) myopia.
C) presbyopia.
D) emmetropia.
E) refraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which structure of the eye contains blood vessels and lymphatic vessels?
A) retina
B) fibrous layer
C) sclera
D) vascular layer
E) neural layer
A) retina
B) fibrous layer
C) sclera
D) vascular layer
E) neural layer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following concerning olfaction is true?
A) Olfactory receptors are highly modified neurons.
B) Molecules to be smelled cannot be dissolved first in mucus.
C) Humans have fewer than 10,000 olfactory receptors.
D) Human power of olfaction is as powerful as that of most other mammals.
E) Olfactory stimuli must pass through the thalamus before journeying to the olfactory cortex.
A) Olfactory receptors are highly modified neurons.
B) Molecules to be smelled cannot be dissolved first in mucus.
C) Humans have fewer than 10,000 olfactory receptors.
D) Human power of olfaction is as powerful as that of most other mammals.
E) Olfactory stimuli must pass through the thalamus before journeying to the olfactory cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The transparent portion of the fibrous layer of the eye is the
A) conjunctiva.
B) cornea.
C) iris.
D) pupil.
E) canthus.
A) conjunctiva.
B) cornea.
C) iris.
D) pupil.
E) canthus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The space between the suspensory ligaments and the iris is the
A) anterior chamber.
B) posterior chamber.
C) pupil.
D) vitreous body.
E) posterior cavity.
A) anterior chamber.
B) posterior chamber.
C) pupil.
D) vitreous body.
E) posterior cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Nearsightedness is more properly called
A) emmetropia.
B) myopia.
C) retinal detachment.
D) hyperopia.
E) glaucoma.
A) emmetropia.
B) myopia.
C) retinal detachment.
D) hyperopia.
E) glaucoma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Humans are most sensitive to which taste?
A) sweet
B) bitter
C) sour
D) salty
E) umami
A) sweet
B) bitter
C) sour
D) salty
E) umami

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is a primary taste sensation?
A) sweet
B) putrid
C) pungent
D) metallic
E) fruity
A) sweet
B) putrid
C) pungent
D) metallic
E) fruity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The mechanism of gustatory reception seems to parallel that of
A) light receptors.
B) mechanoreceptors.
C) olfactory receptors.
D) nociceptors.
E) baroreceptors.
A) light receptors.
B) mechanoreceptors.
C) olfactory receptors.
D) nociceptors.
E) baroreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The portion of the eye that contains blood vessels, pigment cells, loose connective tissue, and intrinsic muscle fibers is the
A) conjunctiva.
B) cornea.
C) iris.
D) pupil.
E) canthus.
A) conjunctiva.
B) cornea.
C) iris.
D) pupil.
E) canthus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The space between the iris and the cornea is the
A) anterior chamber.
B) posterior chamber.
C) pupil.
D) aqueous humor.
E) vitreous body.
A) anterior chamber.
B) posterior chamber.
C) pupil.
D) aqueous humor.
E) vitreous body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Taste buds are monitored by cranial nerves
A) IX, X, and XI.
B) VII, VIII, and IX.
C) VII, IX, and X.
D) V, VII, and IX.
E) IX, XI, and XII.
A) IX, X, and XI.
B) VII, VIII, and IX.
C) VII, IX, and X.
D) V, VII, and IX.
E) IX, XI, and XII.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Loss of lens transparency is referred to as
A) a cataract.
B) glaucoma.
C) myopia.
D) accommodation.
E) corneal scarring.
A) a cataract.
B) glaucoma.
C) myopia.
D) accommodation.
E) corneal scarring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The anterior cavity is
A) hollow.
B) filled with aqueous humor.
C) filled by the vitreous body.
D) filled with perilymph.
E) filled with endolymph.
A) hollow.
B) filled with aqueous humor.
C) filled by the vitreous body.
D) filled with perilymph.
E) filled with endolymph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is part of the inner layer of the wall of the eye?
A) lateral rectus muscle
B) iris
C) retina
D) sclera
E) conjunctiva
A) lateral rectus muscle
B) iris
C) retina
D) sclera
E) conjunctiva

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Changing the shape of the lens to keep the focal length constant is a process called
A) nearsightedness.
B) farsightedness.
C) myopia.
D) astigmatism.
E) accommodation.
A) nearsightedness.
B) farsightedness.
C) myopia.
D) astigmatism.
E) accommodation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Taste receptors are
A) found only on the tongue.
B) unable to divide.
C) modified neural cells.
D) specialized epithelial cells.
E) sensitive to pain.
A) found only on the tongue.
B) unable to divide.
C) modified neural cells.
D) specialized epithelial cells.
E) sensitive to pain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
There are ________ primary taste sensations.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 12
D) 20
E) more than 50
A) 2
B) 4
C) 12
D) 20
E) more than 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Within the olfactory epithelium, which of the following are regenerative stem cells?
A) olfactory bulbs
B) olfactory glands
C) odorant-binding proteins
D) basal cells
E) olfactory tracts
A) olfactory bulbs
B) olfactory glands
C) odorant-binding proteins
D) basal cells
E) olfactory tracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following extrinsic eye muscles is responsible for the eye looking down?
A) lateral rectus
B) inferior oblique
C) inferior rectus
D) medial rectus
E) superior rectus
A) lateral rectus
B) inferior oblique
C) inferior rectus
D) medial rectus
E) superior rectus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The highest concentration of cones is in the
A) fibrous layer.
B) blind spot.
C) choroid.
D) optic disc.
E) fovea centralis.
A) fibrous layer.
B) blind spot.
C) choroid.
D) optic disc.
E) fovea centralis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement is correct?
A) For distant vision, the ciliary muscle is relaxed and the lens is rounded.
B) For close vision, the ciliary muscle is relaxed and the lens is flattened.
C) For distant vision, the ciliary muscle is contracted and the lens is flattened.
D) The closer the light source, the shorter the focal distance.
E) For close vision, the ciliary muscle is contracted and the lens is rounded.
A) For distant vision, the ciliary muscle is relaxed and the lens is rounded.
B) For close vision, the ciliary muscle is relaxed and the lens is flattened.
C) For distant vision, the ciliary muscle is contracted and the lens is flattened.
D) The closer the light source, the shorter the focal distance.
E) For close vision, the ciliary muscle is contracted and the lens is rounded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
You have been diagnosed with glaucoma. The doctor is worried that the pressure within the anterior cavity will damage the corneal cells, even with treatment. How is this explained?
A) The cornea is the location of the photoreceptor cells.
B) The damaged lens will stick to the cornea, affecting light refraction.
C) The glaucoma will cause the pupils to get smaller, allowing less light through the cornea.
D) The cornea cannot easily get nutrients and oxygen.
E) The cornea will be pushed inward toward the back of the eyeball, causing pressure increases on the retina.
A) The cornea is the location of the photoreceptor cells.
B) The damaged lens will stick to the cornea, affecting light refraction.
C) The glaucoma will cause the pupils to get smaller, allowing less light through the cornea.
D) The cornea cannot easily get nutrients and oxygen.
E) The cornea will be pushed inward toward the back of the eyeball, causing pressure increases on the retina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A person suffering from ________ can see distant objects more clearly than those that are close.
A) myopia
B) hyperopia
C) glaucoma
D) emmetropia
E) cataracts
A) myopia
B) hyperopia
C) glaucoma
D) emmetropia
E) cataracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The fibrous layer of the eye
A) consists of the sclera and the cornea.
B) contains the intrinsic eye muscles.
C) regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
D) consists of the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
E) consists of the retina.
A) consists of the sclera and the cornea.
B) contains the intrinsic eye muscles.
C) regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
D) consists of the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
E) consists of the retina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
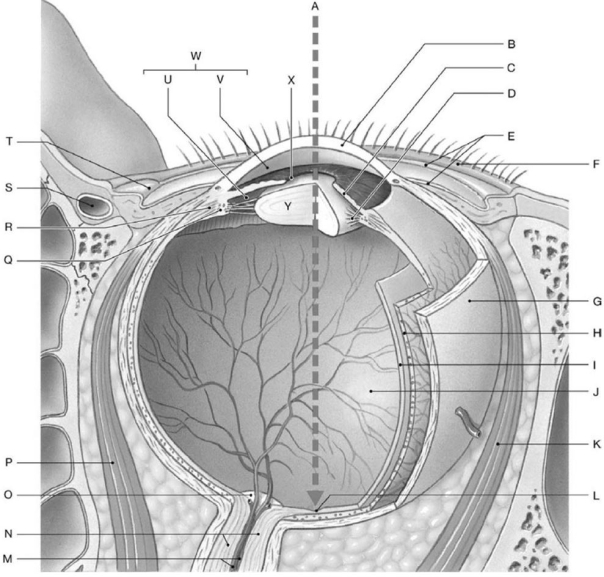 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure D is the
A) ciliary muscle.
B) ciliary body.
C) vitreous humor.
D) medial rectus muscle.
E) ciliary zonule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Light rays refract or bend when they go through
A) J.
B) L.
C) B.
D) X.
E) R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The lens focuses the visual image on the photoreceptors by
A) moving up and down.
B) moving in and out.
C) changing shape.
D) opening and closing.
E) dilating and constricting.
A) moving up and down.
B) moving in and out.
C) changing shape.
D) opening and closing.
E) dilating and constricting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The shape of the lens is controlled by the
A) pupillary constrictor muscles.
B) pupillary dilator muscles.
C) ciliary muscle.
D) conjunctiva.
E) aqueous body.
A) pupillary constrictor muscles.
B) pupillary dilator muscles.
C) ciliary muscle.
D) conjunctiva.
E) aqueous body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The vitreous body
A) contains the lens.
B) helps to stabilize the eye shape.
C) contains blood vessels that nourish the retina.
D) is located between the lens and the iris.
E) is found in the posterior chamber.
A) contains the lens.
B) helps to stabilize the eye shape.
C) contains blood vessels that nourish the retina.
D) is located between the lens and the iris.
E) is found in the posterior chamber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following extrinsic eye muscles is responsible for enabling the eye to roll, look up, and look laterally?
A) inferior rectus
B) superior oblique
C) inferior oblique
D) superior rectus
E) medial rectus
A) inferior rectus
B) superior oblique
C) inferior oblique
D) superior rectus
E) medial rectus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The lacrimal glands
A) are located in pockets in the lacrimal bones.
B) produce only about 20% of the volume of tears.
C) produce a slightly acidic secretion that contains lysozyme.
D) have a dozen or more ducts.
E) function only intermittently.
A) are located in pockets in the lacrimal bones.
B) produce only about 20% of the volume of tears.
C) produce a slightly acidic secretion that contains lysozyme.
D) have a dozen or more ducts.
E) function only intermittently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The ciliary muscle helps to
A) control the amount of light reaching the retina.
B) pull the lens into a more rounded shape.
C) control the production of aqueous humor.
D) move the eyeball.
E) produce the vitreous body.
A) control the amount of light reaching the retina.
B) pull the lens into a more rounded shape.
C) control the production of aqueous humor.
D) move the eyeball.
E) produce the vitreous body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When viewing an object in close distance, the lens should be more
A) rounded.
B) flattened.
C) convex.
D) lateral.
E) medial.
A) rounded.
B) flattened.
C) convex.
D) lateral.
E) medial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The transparent anterior portion of the eye is called the
A) cornea.
B) retina.
C) conjunctiva.
D) lens.
E) choroid.
A) cornea.
B) retina.
C) conjunctiva.
D) lens.
E) choroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The abducens nerve innervates which extrinsic eye muscle?
A) superior oblique
B) medial rectus
C) inferior oblique
D) superior rectus
E) lateral rectus
A) superior oblique
B) medial rectus
C) inferior oblique
D) superior rectus
E) lateral rectus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure C is the
A) choroid.
B) iris.
C) sclera.
D) ciliary body.
E) lens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A blind spot in the retina occurs
A) at the fovea.
B) where ganglion cells synapse with bipolar cells.
C) at the optic disc.
D) where rod cells are clustered to form the macula.
E) where amacrine cells are located.
A) at the fovea.
B) where ganglion cells synapse with bipolar cells.
C) at the optic disc.
D) where rod cells are clustered to form the macula.
E) where amacrine cells are located.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Treatment of a cataract usually involves removal of the
A) cornea.
B) iris.
C) lens.
D) sclera.
E) vitreous humor.
A) cornea.
B) iris.
C) lens.
D) sclera.
E) vitreous humor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Structure S is the
A) nasolacrimal duct.
B) lacrimal pore.
C) lacrimal sac.
D) lacrimal gland.
E) lacrimal canal.
A) nasolacrimal duct.
B) lacrimal pore.
C) lacrimal sac.
D) lacrimal gland.
E) lacrimal canal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which structure contains neurons?
A) G
B) H
C) B
D) Y
E) N
A) G
B) H
C) B
D) Y
E) N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Structure L is the
A) ciliary body.
B) pupil.
C) lacrimal canal.
D) macula.
E) optic disc.
A) ciliary body.
B) pupil.
C) lacrimal canal.
D) macula.
E) optic disc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Structure O is the
A) optic disc.
B) fovea.
C) blood vessels.
D) ocular muscle.
E) optic nerve.
A) optic disc.
B) fovea.
C) blood vessels.
D) ocular muscle.
E) optic nerve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure H is the
A) retina.
B) sclera.
C) choroid.
D) ciliary body.
E) cornea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Structure Q is the
A) lacrimal sac.
B) iris.
C) ciliary zonule.
D) ciliary muscle.
E) ciliary body.
A) lacrimal sac.
B) iris.
C) ciliary zonule.
D) ciliary muscle.
E) ciliary body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure L is the
A) optic nerve.
B) optic disc.
C) choroid.
D) fovea.
E) lacrimal pore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure G is the
A) retina.
B) sclera.
C) choroid.
D) ciliary body.
E) cornea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Aqueous humor fluid is produced at
A) Q.
B) V.
C) D.
D) I.
E) O.
A) Q.
B) V.
C) D.
D) I.
E) O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is located within this chamber marked U?
A) vitreous humor
B) aqueous humor
C) plasma
D) lymph
E) saline
A) vitreous humor
B) aqueous humor
C) plasma
D) lymph
E) saline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which structure focuses light rays?
A) Y
B) D
C) L
D) O
E) X
A) Y
B) D
C) L
D) O
E) X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Structure P is the
A) medial rectus muscle.
B) lateral rectus muscle.
C) retina.
D) choroid.
E) superior oblique muscle.
A) medial rectus muscle.
B) lateral rectus muscle.
C) retina.
D) choroid.
E) superior oblique muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
When the muscle labeled P contracts, the eye moves
A) superiorly.
B) laterally.
C) medially.
D) inferiorly.
E) in a circular fashion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure E is the
A) iris.
B) fovea.
C) cornea.
D) conjunctiva.
E) sclera.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure I is the
A) choroid.
B) sclera.
C) ciliary layer.
D) retina.
E) fovea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
What is located within the chamber marked J?
A) saline
B) aqueous humor
C) plasma
D) vitreous humor
E) lymph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Structure Y is the
A) lens.
B) cornea.
C) pupil.
D) choroid.
E) optic canal.
A) lens.
B) cornea.
C) pupil.
D) choroid.
E) optic canal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
 Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right Eye
Figure 9-1 Horizontal Dissection of the Right EyeUse Figure 9-1 to identify the labeled part.
Structure K is the
A) lateral rectus muscle.
B) medial rectus muscle.
C) lateral oblique muscle.
D) medial oblique muscle.
E) lacrimal caruncle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Photoreceptors are located in
A) G.
B) H.
C) I.
D) N.
E) O.
A) G.
B) H.
C) I.
D) N.
E) O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Structure R is the
A) lacrimal sac.
B) iris.
C) ciliary zonule.
D) ciliary muscle.
E) ciliary body.
A) lacrimal sac.
B) iris.
C) ciliary zonule.
D) ciliary muscle.
E) ciliary body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



