Deck 30: The Labor Market
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: The Labor Market
1
The value of an hour of leisure can best be estimated as
A)Zero since no income is earned.
B)The hourly wage that could have been earned.
C)Total recreational expenditures divided by hours of leisure.
A)Zero since no income is earned.
B)The hourly wage that could have been earned.
C)Total recreational expenditures divided by hours of leisure.
The hourly wage that could have been earned.
2
For an upward-sloping labor supply curve,the quantity of labor supplied varies directly,ceteris paribus,with
A)The wage rate.
B)The value of leisure time.
C)Payroll taxes.
A)The wage rate.
B)The value of leisure time.
C)Payroll taxes.
The wage rate.
3
The labor supply curve starts to bend backward once the
A)Income effect exceeds the substitution effect.
B)Substitution effect exceeds the income effect.
C)Marginal revenue product of labor equals the marginal utility of leisure.
A)Income effect exceeds the substitution effect.
B)Substitution effect exceeds the income effect.
C)Marginal revenue product of labor equals the marginal utility of leisure.
Income effect exceeds the substitution effect.
4
An individual's labor supply curve
A)Slopes upward initially,and then may bend backward.
B)Slopes downward initially,and then may bend upward.
C)Always slopes downward.
A)Slopes upward initially,and then may bend backward.
B)Slopes downward initially,and then may bend upward.
C)Always slopes downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If Reagan's substitution effects outweigh her income effects,her labor supply curve will
A)Appear horizontal.
B)Slope upward.
C)Bend backward.
A)Appear horizontal.
B)Slope upward.
C)Bend backward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
As more hours are worked,the marginal utility of leisure time tends to
A)Increase.
B)Decrease.
C)Stay the same.
A)Increase.
B)Decrease.
C)Stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
As an individual earns additional income,the marginal utility of income tends to
A)Increase.
B)Decrease.
C)Remain constant.
A)Increase.
B)Decrease.
C)Remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The determinants of the market supply of labor include all of the following except
A)Taxes.
B)The market wage rate.
C)Income and wealth.
A)Taxes.
B)The market wage rate.
C)Income and wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Kip will work fewer hours if his salary increases.For Kip,the ___________ effect must outweigh the __________ effect.
A)substitution;income
B)income;substitution
C)income;utility
A)substitution;income
B)income;substitution
C)income;utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The number of hours that a worker is willing to work is determined by the trade-off between the increasing
A)Total utility of income and the decreasing marginal utility of leisure.
B)Marginal utility of leisure and the decreasing marginal utility of income.
C)Total utility of leisure and the decreasing total utility of income.
A)Total utility of income and the decreasing marginal utility of leisure.
B)Marginal utility of leisure and the decreasing marginal utility of income.
C)Total utility of leisure and the decreasing total utility of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If you have an increasing marginal utility for leisure,then as you work more to make greater income,your
A)Total utility for leisure decreases.
B)Marginal utility for income decreases.
C)Marginal utility of income varies positively with the money you earn.
A)Total utility for leisure decreases.
B)Marginal utility for income decreases.
C)Marginal utility of income varies positively with the money you earn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The labor supply curve will be positively sloped if the substitution effect of wages is
A)Equal to the income effect of wages.
B)Stronger than the income effect of wages.
C)Weaker than the income effect of wages.
A)Equal to the income effect of wages.
B)Stronger than the income effect of wages.
C)Weaker than the income effect of wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If wages are relatively high,the individual labor supply curve may
A)Become horizontal.
B)Bend backward.
C)Bend outward.
A)Become horizontal.
B)Bend backward.
C)Bend outward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Higher wage rates allow a person to reduce the hours worked without losing income.This is known as the
A)Substitution effect.
B)Income effect.
C)Law of diminishing marginal utility.
A)Substitution effect.
B)Income effect.
C)Law of diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Workers typically require higher wages in order to work additional hours because of the
A)Increasing opportunity cost of labor.
B)Increasing marginal utility of income.
C)Decreasing value of leisure time forgone.
A)Increasing opportunity cost of labor.
B)Increasing marginal utility of income.
C)Decreasing value of leisure time forgone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If we move to the right along the upward-sloping labor supply curve,we observe that the cost of labor
A)Increases due to the increasing opportunity cost.
B)Increases due to the decreasing opportunity cost.
C)Decreases due to the increasing opportunity cost.
A)Increases due to the increasing opportunity cost.
B)Increases due to the decreasing opportunity cost.
C)Decreases due to the increasing opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The willingness to work a certain amount of time at a given wage rate is known as
A)Labor supply.
B)Labor demand.
C)Derived supply.
A)Labor supply.
B)Labor demand.
C)Derived supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The labor supply curve will be negatively sloped if the substitution effect of wages is
A)Weaker than the income effect of wages.
B)Stronger than the income effect of wages.
C)Equal to the income effect of wages.
A)Weaker than the income effect of wages.
B)Stronger than the income effect of wages.
C)Equal to the income effect of wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The opportunity cost of working is the
A)Wage rate.
B)Earnings that could be made in an alternative job.
C)Value of leisure time that must be given up.
A)Wage rate.
B)Earnings that could be made in an alternative job.
C)Value of leisure time that must be given up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
As we work fewer hours and our leisure time increases,the opportunity cost of labor
A)Falls and the marginal utility of income falls.
B)Rises and the marginal utility of income falls.
C)Falls and the marginal utility of income rises.
A)Falls and the marginal utility of income falls.
B)Rises and the marginal utility of income falls.
C)Falls and the marginal utility of income rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If leisure activities become more attractive,there will be a
A)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.
A)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The demand for labor and other factors of production typically decline in a recession because those factors
A)Have become relatively scarcer than before the recession.
B)Are no longer offered for sale in factor markets.
C)Are derived from the demand for final output,which also declines in a recession.
A)Have become relatively scarcer than before the recession.
B)Are no longer offered for sale in factor markets.
C)Are derived from the demand for final output,which also declines in a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
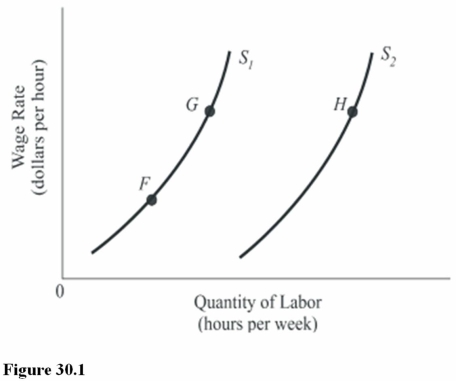
In Figure 30.1,the labor supply could shift from S1 to S2 due to all of the following except
A)Fewer workers preferring to work in this labor market.
B)An increase in the number of workers willing to work in this labor market.
C)A decrease in the payroll tax on workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The marginal revenue product establishes
A)An upper limit to the wage rate an employer is willing and able to pay.
B)A lower limit to profit on the sale of a unit of output.
C)A lower limit to the productivity of a worker.
A)An upper limit to the wage rate an employer is willing and able to pay.
B)A lower limit to profit on the sale of a unit of output.
C)A lower limit to the productivity of a worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following would not shift the market demand for labor,ceteris paribus?
A)The wage paid to labor.
B)The demand for final products.
C)The productivity of labor.
A)The wage paid to labor.
B)The demand for final products.
C)The productivity of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If consumers decide to buy fewer strawberries,then the
A)Demand for strawberry pickers will fall.
B)Demand for strawberry pickers will rise.
C)Quantity demanded of strawberry pickers will fall.
A)Demand for strawberry pickers will fall.
B)Demand for strawberry pickers will rise.
C)Quantity demanded of strawberry pickers will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the wage rate increases,there will be a
A)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.
A)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If there is an increase in the number of workers who want to work as accountants,there will be a
A)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.
A)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The marginal physical product of labor is equal to
A)Total output divided by the quantity of labor.
B)The percentage change in total output divided by the percentage change in quantity of labor.
C)The change in total output divided by the change in quantity of labor.
A)Total output divided by the quantity of labor.
B)The percentage change in total output divided by the percentage change in quantity of labor.
C)The change in total output divided by the change in quantity of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If payroll taxes are increased,there will be a
A)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.
A)Leftward shift of the labor supply curve.
B)Rightward shift of the labor supply curve.
C)Movement up the labor supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Bill hates to work.He receives a great deal of enjoyment from leisure time.Bill's elasticity of labor supply is
A)High.
B)Low,perhaps even negative.
C)1.
A)High.
B)Low,perhaps even negative.
C)1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The market supply curve for labor curve is upward-sloping because
A)As the wage rises,most workers want to work fewer hours.
B)As the wage falls,most workers want to work more hours.
C)As the wage rises,most workers are willing to work more hours.
A)As the wage rises,most workers want to work fewer hours.
B)As the wage falls,most workers want to work more hours.
C)As the wage rises,most workers are willing to work more hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The determinants of labor demand include
A)Marginal physical productivity.
B)Labor expectations.
C)Labor shortages.
A)Marginal physical productivity.
B)Labor expectations.
C)Labor shortages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
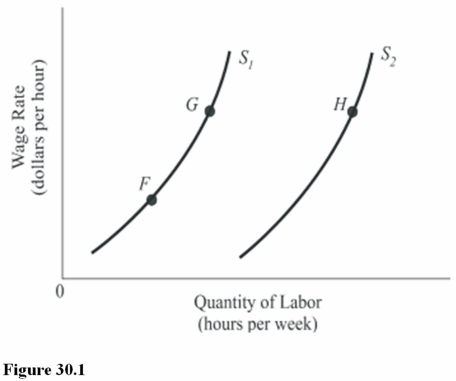
In Figure 30.1,the shift in the labor supply curve from S1 to S2 means that
A)The marginal utility of labor has decreased.
B)Workers are being paid higher wage rates,given their taste for work.
C)The marginal utility of labor relative to leisure has increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a labor supply curve is backward-bending,the elasticity of labor supply in the backward-bending portion is
A)Negative.
B)Positive but less than 1.
C)Greater than 1.
A)Negative.
B)Positive but less than 1.
C)Greater than 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Assume the apple market is competitive.If citizens want wages and the number of available jobs for apple pickers to increase,the best strategy would be to
A)Insist that the government establish a minimum wage for apple pickers.
B)Boycott apples until wages increased.
C)Buy more apples.
A)Insist that the government establish a minimum wage for apple pickers.
B)Boycott apples until wages increased.
C)Buy more apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A firm's demand for labor is referred to as a derived demand because
A)It is derived from the MPP of labor.
B)It is derived from the demand for the product that the labor is producing.
C)The quantity of goods and services labor can purchase is derived from the wages labor receives from the firm.
A)It is derived from the MPP of labor.
B)It is derived from the demand for the product that the labor is producing.
C)The quantity of goods and services labor can purchase is derived from the wages labor receives from the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The elasticity of labor supply does not depend on
A)The demand for labor.
B)The prices of consumer goods.
C)Income and wealth.
A)The demand for labor.
B)The prices of consumer goods.
C)Income and wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If Sara's elasticity of labor supply is 1.5 and she increases her supply of labor by 5 percent,then the wage rate must have
A)Increased by 3.3 percent.
B)Increased by 3.0 percent.
C)Increased by 7.5 percent.
A)Increased by 3.3 percent.
B)Increased by 3.0 percent.
C)Increased by 7.5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When the MPP of labor is zero,ceteris paribus,
A)Employment can be increased only by offering a higher wage rate.
B)No further increases in output can be achieved by using additional units of labor.
C)MRP is at a maximum.
A)Employment can be increased only by offering a higher wage rate.
B)No further increases in output can be achieved by using additional units of labor.
C)MRP is at a maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the price of the output produced by a particular type of labor decreases,which of the following shifts should occur in the labor market for the particular type of labor?
A)Demand for labor should shift to the left.
B)Supply of labor should shift to the left.
C)Demand for labor should shift to the right.
A)Demand for labor should shift to the left.
B)Supply of labor should shift to the left.
C)Demand for labor should shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A competitive firm should continue to hire workers until the MRP is equal to
A)Demand.
B)The number of workers hired.
C)The market wage rate.
A)Demand.
B)The number of workers hired.
C)The market wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the number of employers for a particular type of labor increases,which of the following shifts should occur in the labor market for the particular type of labor?
A)Demand for labor should shift to the left.
B)Supply of labor should shift to the left.
C)Demand for labor should shift to the right.
A)Demand for labor should shift to the left.
B)Supply of labor should shift to the left.
C)Demand for labor should shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The demand for labor is downward-sloping because of
A)Rising MPP.
B)Falling MC.
C)Diminishing returns to labor.
A)Rising MPP.
B)Falling MC.
C)Diminishing returns to labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the MPP of an additional unit of labor is 3 units per hour,product price is constant at $8 per unit,and the wage rate is $26 per hour,then
A)The additional unit of labor should be employed.
B)The additional unit of labor should not be employed because it costs more than it is worth.
C)The employer should lower wages and accept less employment of labor.
A)The additional unit of labor should be employed.
B)The additional unit of labor should not be employed because it costs more than it is worth.
C)The employer should lower wages and accept less employment of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Marginal physical product diminishes as additional workers are hired because
A)Each worker has an increasingly smaller amount of other factors with which to work.
B)Each worker has an increasingly larger amount of other factors with which to work.
C)Later hires are not as skilled as earlier hires.
A)Each worker has an increasingly smaller amount of other factors with which to work.
B)Each worker has an increasingly larger amount of other factors with which to work.
C)Later hires are not as skilled as earlier hires.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the MPP of an additional unit of labor is 4 units per hour,product price is constant at $5 per unit,and the wage rate is $19 per hour,then
A)The additional unit of labor should be employed.
B)The additional unit of labor should not be employed because it costs more than it is worth.
C)The employer should lower wages and accept less employment of labor.
A)The additional unit of labor should be employed.
B)The additional unit of labor should not be employed because it costs more than it is worth.
C)The employer should lower wages and accept less employment of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
As marginal physical product diminishes,marginal revenue product
A)Also diminishes.
B)Is not affected.
C)Rises at a diminishing rate and eventually falls.
A)Also diminishes.
B)Is not affected.
C)Rises at a diminishing rate and eventually falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The marginal revenue product of labor is equal to
A)The marginal physical product multiplied by the marginal revenue of the output.
B)The change in the quantity of labor divided by the change in total revenue.
C)The change in total output divided by the change in the quantity of labor.
A)The marginal physical product multiplied by the marginal revenue of the output.
B)The change in the quantity of labor divided by the change in total revenue.
C)The change in total output divided by the change in the quantity of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
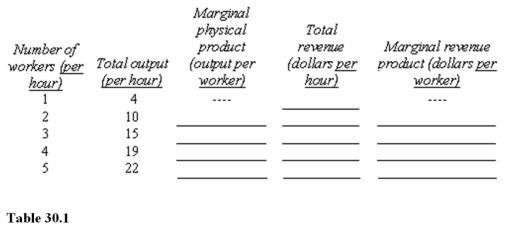
Assume that the product price is $4 per unit and that the hourly wage for workers is $12.Neither price nor wage changes with output.In Table 30.1,the contribution to total revenue of the fourth worker hired is
A)$76 per hour.
B)$16 per hour.
C)$4 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The marginal revenue product of labor curve is the firm's
A)MPP of labor curve divided by the wage rate.
B)Marginal revenue curve.
C)Demand curve for labor.
A)MPP of labor curve divided by the wage rate.
B)Marginal revenue curve.
C)Demand curve for labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
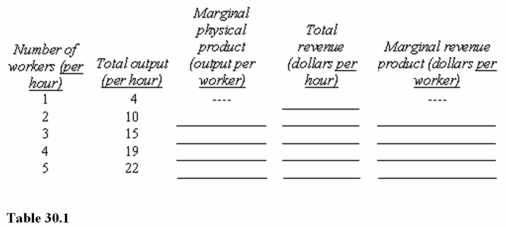
Assume that the product price is $4 per unit and that the hourly wage for workers is $12.Neither price nor wage changes with output.In Table 30.1,the marginal revenue product of the second worker hired is
A)$4 per hour.
B)$6 per hour.
C)$24 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In competitive markets,the marginal revenue product curve and marginal physical product curve have similar shapes because
A)The demand curve for the product slopes downward in accordance with the law of diminishing returns.
B)MRP = P × MPP.
C)The law of diminishing marginal utility and the law of diminishing returns imply a downward-sloping demand curve in the product market.
A)The demand curve for the product slopes downward in accordance with the law of diminishing returns.
B)MRP = P × MPP.
C)The law of diminishing marginal utility and the law of diminishing returns imply a downward-sloping demand curve in the product market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is true about the equilibrium market wage?
A)All workers are satisfied with the wage.
B)All employers are satisfied with the wage.
C)There is no unemployment in the market at the equilibrium wage.
A)All workers are satisfied with the wage.
B)All employers are satisfied with the wage.
C)There is no unemployment in the market at the equilibrium wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Because of the law of diminishing returns,as additional workers are hired,total output
A)Rises at a constant rate at all output levels.
B)Rises at a diminishing rate initially and eventually falls.
C)Falls at a diminishing rate at all output levels.
A)Rises at a constant rate at all output levels.
B)Rises at a diminishing rate initially and eventually falls.
C)Falls at a diminishing rate at all output levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Other things being equal,which of the following would increase the market demand for labor?
A)A fall in the wage rate.
B)An increase in the marginal productivity of labor.
C)A decrease in the cost-effectiveness of labor relative to other inputs.
A)A fall in the wage rate.
B)An increase in the marginal productivity of labor.
C)A decrease in the cost-effectiveness of labor relative to other inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a chair can be sold for $20 and it takes a worker two hours to make a chair,the marginal revenue product of this worker is
A)$5 per hour.
B)$10 per hour.
C)$20 per hour.
A)$5 per hour.
B)$10 per hour.
C)$20 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
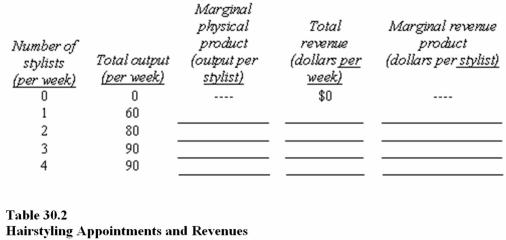
Table 30.2 shows how many hairstyling appointments a hair salon can schedule per week based on the number of stylists.In the spaces provided,compute the marginal physical product (MPP)of the hair stylists,total revenue,and marginal revenue product of the stylists,assuming that a hair stylist charges $60 per appointment.In Table 30.2,as more stylists are hired,
A)There are diminishing returns.
B)There are economies of scale.
C)There are diseconomies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
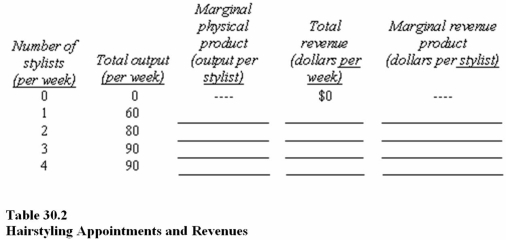
Table 30.2 shows how many hairstyling appointments a hair salon can schedule per week based on the number of stylists.In the spaces provided,compute the marginal physical product (MPP)of the hair stylists,total revenue,and marginal revenue product of the stylists,assuming that a hair stylist charges $60 per appointment.What is the marginal revenue product of the second hairstylist?
A)$80 per week.
B)$1,200 per week.
C)$20 per week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A firm should hire an additional worker as long as the wage rate is
A)Greater than the MRP.
B)Greater than the MPP.
C)Less than the MRP.
A)Greater than the MRP.
B)Greater than the MPP.
C)Less than the MRP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For a minimum wage to have any impact on a labor market,it must be set at a level
A)Higher than the equilibrium wage.
B)Higher than MPP.
C)Higher than MRP.
A)Higher than the equilibrium wage.
B)Higher than MPP.
C)Higher than MRP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
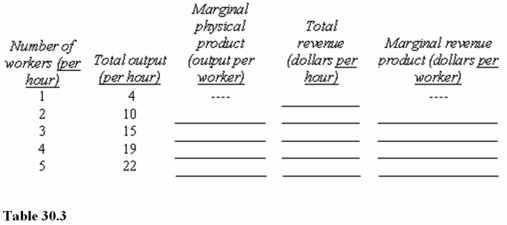
Assume that the product price is $4 per unit and that the hourly wage for workers is $12.Neither price nor wage changes with output.In Table 30.3,the contribution to total revenue of the fourth worker hired is
A)$76 per hour.
B)$16 per hour.
C)$4 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
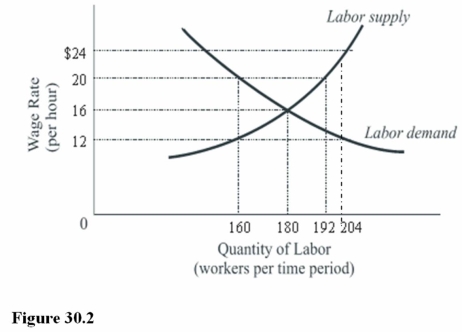
In Figure 30.2,unemployed labor at the equilibrium wage is equal to
A)34 workers.
B)28 workers.
C)Zero workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When people are standing in line for jobs and there are more applicants than jobs,then the labor market is characterized by a
A)Shortage of jobs from the point of view of the buyer in the labor market.
B)Surplus of jobs from the point of view of the seller in the labor market.
C)Surplus of labor.
A)Shortage of jobs from the point of view of the buyer in the labor market.
B)Surplus of jobs from the point of view of the seller in the labor market.
C)Surplus of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If the demand for alarm clocks decreases,the effect on the alarm clock job market will be to
A)Increase the demand for labor and increase equilibrium wages.
B)Reduce the supply of labor and increase equilibrium wages.
C)Decrease the demand for labor and reduce equilibrium wages.
A)Increase the demand for labor and increase equilibrium wages.
B)Reduce the supply of labor and increase equilibrium wages.
C)Decrease the demand for labor and reduce equilibrium wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Ceteris paribus,all of the following result when the minimum wage is raised in a competitive market,except
A)Some workers lose their jobs.
B)There are fewer workers available to work.
C)Workers with a marginal revenue product below the minimum wage are worse off.
A)Some workers lose their jobs.
B)There are fewer workers available to work.
C)Workers with a marginal revenue product below the minimum wage are worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
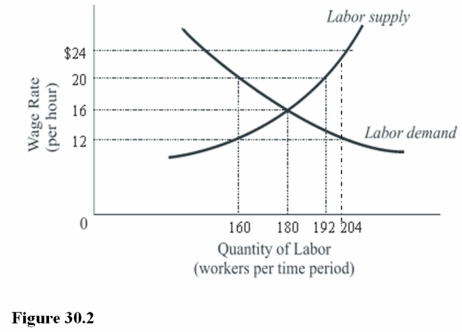
In Figure 30.2,a minimum wage of $20 will result in a
A)Shortage of 160 workers.
B)Shortage of 180 hours.
C)Surplus of 32 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Democrats argue that labor demand is _______,so ________ jobs will be lost when the minimum wage is raised.
A)inelastic;few
B)inelastic;many
C)elastic;few
A)inelastic;few
B)inelastic;many
C)elastic;few

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
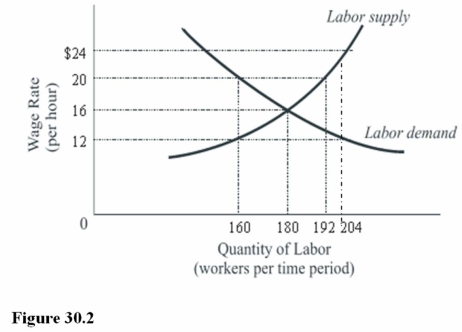
In Figure 30.2,the equilibrium wage rate is
A)$24 per hour.
B)$20 per hour.
C)$16 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the price for a box of kiwis is $40,the wage rate for kiwi laborers is $10 per hour,and a laborer can pick 3 boxes of kiwis per hour,the
A)MRP is $30 per hour.
B)MPP is $30 per hour.
C)Cost efficiency is 3/10 of a box per dollar.
A)MRP is $30 per hour.
B)MPP is $30 per hour.
C)Cost efficiency is 3/10 of a box per dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The cost efficiency of labor is equal to the
A)Marginal cost of output.
B)MPP of labor times the wage rate.
C)MPP of labor divided by the wage rate.
A)Marginal cost of output.
B)MPP of labor times the wage rate.
C)MPP of labor divided by the wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that Silvia's Dance Studio uses both labor and capital to teach dance lessons.Given her current mix of labor and capital,the cost efficiency of labor is 1 dance lesson per dollar,and the cost efficiency of capital is 5 dance lessons per dollar.Silvia should
A)Hire less labor and use more capital.
B)Use only capital to produce the lessons.
C)Use less capital and hire more labor.
A)Hire less labor and use more capital.
B)Use only capital to produce the lessons.
C)Use less capital and hire more labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The efficiency decision involves choosing the input combination or process that
A)Produces the greatest output.
B)Results in the lowest output per dollar of input.
C)Results in the least cost for a given output.
A)Produces the greatest output.
B)Results in the lowest output per dollar of input.
C)Results in the least cost for a given output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the minimum wage is raised in a competitive market,ceteris paribus,
A)All workers are better off.
B)All workers are worse off.
C)Some workers are better off and some are worse off.
A)All workers are better off.
B)All workers are worse off.
C)Some workers are better off and some are worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If the demand for hair gel increases,the effect on the hair gel manufacturing job market will be to
A)Increase the demand for labor and increase equilibrium wages.
B)Reduce the supply of labor and increase equilibrium wages.
C)Decrease the demand for labor and reduce equilibrium wages.
A)Increase the demand for labor and increase equilibrium wages.
B)Reduce the supply of labor and increase equilibrium wages.
C)Decrease the demand for labor and reduce equilibrium wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When there are more qualified applicants than job openings,this indicates that the
A)Economy must be in a recession.
B)Labor supply curve must be backward-bending.
C)Wages being offered are too high.
A)Economy must be in a recession.
B)Labor supply curve must be backward-bending.
C)Wages being offered are too high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the cost efficiency of labor equals 2,then
A)Labor costs 100 percent more than the revenue it generates.
B)The wage rate is 100 percent more than the product price.
C)Each extra dollar spent on wages returns 2 units of additional output.
A)Labor costs 100 percent more than the revenue it generates.
B)The wage rate is 100 percent more than the product price.
C)Each extra dollar spent on wages returns 2 units of additional output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A production process is defined as
A)The manufacturing of goods and services.
B)The mix of resources used to produce output.
C)A means by which labor generates revenue.
A)The manufacturing of goods and services.
B)The mix of resources used to produce output.
C)A means by which labor generates revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Cost efficiency refers to the
A)Amount of output associated with an additional dollar spent on input.
B)Effectiveness of labor in reducing production costs.
C)MPP of labor divided by the product price.
A)Amount of output associated with an additional dollar spent on input.
B)Effectiveness of labor in reducing production costs.
C)MPP of labor divided by the product price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
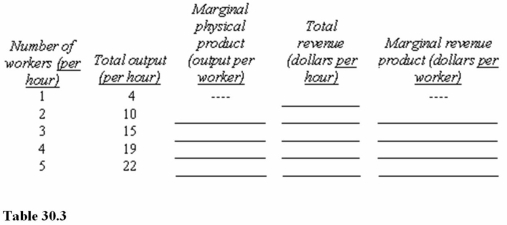
Assume that the product price is $4 per unit and that the hourly wage for workers is $12.Neither price nor wage changes with output.In Table 30.3,the marginal revenue product of the second worker hired is
A)$4 per hour.
B)$6 per hour.
C)$24 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



