Deck 23: Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/120
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Competitive Markets
1
The entry of firms into a market
A)Increases the equilibrium price.
B)Reduces the profits of existing firms in the market.
C)Shifts the market supply curve to the left.
A)Increases the equilibrium price.
B)Reduces the profits of existing firms in the market.
C)Shifts the market supply curve to the left.
Reduces the profits of existing firms in the market.
2
The entry of firms into a market,ceteris paribus,
A)Shifts the market supply curve to the left.
B)Reduces the economic profit of each firm already in the market.
C)Decreases the equilibrium output in the market.
A)Shifts the market supply curve to the left.
B)Reduces the economic profit of each firm already in the market.
C)Decreases the equilibrium output in the market.
Reduces the economic profit of each firm already in the market.
3
For a competitive market in the long run,
A)Economic losses induce firms to shut down.
B)Economic profits induce firms to enter until profits are normal.
C)Accounting profit is zero.
A)Economic losses induce firms to shut down.
B)Economic profits induce firms to enter until profits are normal.
C)Accounting profit is zero.
Economic profits induce firms to enter until profits are normal.
4
Which of the following is true about a competitive market supply curve?
A)It is horizontal.
B)It is downward-sloping to the right.
C)It is the sum of the marginal cost curves of all firms.
A)It is horizontal.
B)It is downward-sloping to the right.
C)It is the sum of the marginal cost curves of all firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Marginal cost is the increase in total cost associated with a one-unit
A)Increase in production.
B)Decrease in production.
C)Increase in input usage.
A)Increase in production.
B)Decrease in production.
C)Increase in input usage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The equilibrium price in a competitive market
A)Ensures that anyone who wants the good can get it.
B)Equates the demand for goods with the supply of goods.
C)Remains unchanged forever.
A)Ensures that anyone who wants the good can get it.
B)Equates the demand for goods with the supply of goods.
C)Remains unchanged forever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If someone invents a better way to produce frozen pizzas,then
A)The market supply curve for frozen pizzas will shift to the right.
B)The market supply curve for frozen pizzas will shift to the left.
C)There will be a movement up along the market supply curve for frozen pizzas.
A)The market supply curve for frozen pizzas will shift to the right.
B)The market supply curve for frozen pizzas will shift to the left.
C)There will be a movement up along the market supply curve for frozen pizzas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a competitive market,economic profits will
A)Cause existing firms to expand production.
B)Potentially last a long time.
C)Cause new firms to leave the market.
A)Cause existing firms to expand production.
B)Potentially last a long time.
C)Cause new firms to leave the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an investment decision in a competitive market?
A)The shutdown decision.
B)The rate of output to produce.
C)Entry or exit.
A)The shutdown decision.
B)The rate of output to produce.
C)Entry or exit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a new sushi restaurant opens,then
A)The market supply curve for sushi will shift to the right.
B)The market supply curve for sushi will shift to the left.
C)There will be a movement up along the market supply curve for sushi.
A)The market supply curve for sushi will shift to the right.
B)The market supply curve for sushi will shift to the left.
C)There will be a movement up along the market supply curve for sushi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the price of ricotta cheese,an ingredient in lasagna,increases,then
A)The market supply curve for lasagna will shift to the right.
B)The market supply curve for lasagna will shift to the left.
C)There will be a movement up along the market supply curve for lasagna.
A)The market supply curve for lasagna will shift to the right.
B)The market supply curve for lasagna will shift to the left.
C)There will be a movement up along the market supply curve for lasagna.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)A small number of firms.
B)Exit of small firms when profits are high for large firms.
C)Zero economic profit in the long run.
A)A small number of firms.
B)Exit of small firms when profits are high for large firms.
C)Zero economic profit in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If economic profits are earned in a competitive market,then over time
A)Additional firms will enter the market.
B)The market supply curve will shift to the left.
C)Equilibrium price will rise as more firms enter.
A)Additional firms will enter the market.
B)The market supply curve will shift to the left.
C)Equilibrium price will rise as more firms enter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a competitive market where firms are earning economic losses,which of the following should be expected as the industry moves to long-run equilibrium,ceteris paribus?
A)A higher price and more firms.
B)A higher price and fewer firms.
C)A lower price and more firms.
A)A higher price and more firms.
B)A higher price and fewer firms.
C)A lower price and more firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In making an investment decision,an entrepreneur
A)Makes a decision to exit if price is above marginal cost.
B)Makes a short-run decision.
C)Must consider only variable costs.
A)Makes a decision to exit if price is above marginal cost.
B)Makes a short-run decision.
C)Must consider only variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a determinant of market supply but not the supply curve of an individual firm?
A)The price of factor inputs.
B)Expectations.
C)The number of firms in the market.
A)The price of factor inputs.
B)Expectations.
C)The number of firms in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Other things being equal,as more firms enter a market,the market supply curve
A)Becomes more inelastic.
B)Shifts to the left.
C)Shifts to the right.
A)Becomes more inelastic.
B)Shifts to the left.
C)Shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If long-run economic losses are being experienced in a competitive market,
A)More firms will enter the market.
B)The market supply curve will shift to the right.
C)Equilibrium price will rise as firms exit.
A)More firms will enter the market.
B)The market supply curve will shift to the right.
C)Equilibrium price will rise as firms exit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The exit of firms from a market,ceteris paribus,
A)Shifts the market supply curve to the right.
B)Reduces the economic losses of remaining firms in the market.
C)Increases the equilibrium output in the market.
A)Shifts the market supply curve to the right.
B)Reduces the economic losses of remaining firms in the market.
C)Increases the equilibrium output in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
To determine the market supply,the quantities
A)Demanded at each price by each demander are added together.
B)Supplied at each price by each supplier are added together.
C)Demanded at each price by each demander and supplied at each price by each supplier are added together.
A)Demanded at each price by each demander are added together.
B)Supplied at each price by each supplier are added together.
C)Demanded at each price by each demander and supplied at each price by each supplier are added together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a firm decides to make the investment decision to expand its capacity,then it must have discovered that
A)P = ATC.
B)P > AVC.
C)P > ATC.
A)P = ATC.
B)P > AVC.
C)P > ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Profit per unit is equal to
A)Price divided by average total cost.
B)Price minus average total cost.
C)Total revenue minus total cost.
A)Price divided by average total cost.
B)Price minus average total cost.
C)Total revenue minus total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a competitive market,
A)Buyers don't have market power but sellers do.
B)Sellers don't have market power but buyers do.
C)Neither buyers nor sellers have market power.
A)Buyers don't have market power but sellers do.
B)Sellers don't have market power but buyers do.
C)Neither buyers nor sellers have market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The behavior expected in a competitive market includes
A)Very little entry and exit.
B)Marginal cost pricing.
C)Aggressive behavior among competitors to control prices.
A)Very little entry and exit.
B)Marginal cost pricing.
C)Aggressive behavior among competitors to control prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
To maximize profits,a competitive firm will seek to expand output until
A)Total revenue equals total cost.
B)The elasticity of demand equals 1.
C)Price equals marginal cost.
A)Total revenue equals total cost.
B)The elasticity of demand equals 1.
C)Price equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the products of two firms are homogeneous,then they
A)Are perfect substitutes.
B)Differ from each other.
C)Must be used together.
A)Are perfect substitutes.
B)Differ from each other.
C)Must be used together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a firm finds that its marginal cost is greater than its price,it
A)Should reduce production.
B)Is maximizing its profit.
C)Should increase production.
A)Should reduce production.
B)Is maximizing its profit.
C)Should increase production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Perfectly competitive firms cannot individually affect market price because
A)There is an infinite demand for their goods.
B)Demand is perfectly inelastic for their goods.
C)There are many firms,none of which has a significant share of total output.
A)There is an infinite demand for their goods.
B)Demand is perfectly inelastic for their goods.
C)There are many firms,none of which has a significant share of total output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)Differentiated products.
B)Price below marginal revenue.
C)A large number of firms.
A)Differentiated products.
B)Price below marginal revenue.
C)A large number of firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The competitive market model is important because
A)It characterizes all the markets in the U.S.economy.
B)It shows how laissez faire can overcome market failures.
C)All industries function much like the competitive model.
A)It characterizes all the markets in the U.S.economy.
B)It shows how laissez faire can overcome market failures.
C)All industries function much like the competitive model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following characterizes a firm that is in long-run perfectly competitive equilibrium where profits are maximized?
A)Price equals minimum ATC.
B)Positive economic profit.
C)Price equals marginal cost.
A)Price equals minimum ATC.
B)Positive economic profit.
C)Price equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Examples of barriers to entry include
A)Price taking.
B)Patents.
C)Standardized products.
A)Price taking.
B)Patents.
C)Standardized products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a production decision?
A)Whether to enter or exit an industry.
B)Whether to increase or decrease plant capacity.
C)Whether to increase or decrease output.
A)Whether to enter or exit an industry.
B)Whether to increase or decrease plant capacity.
C)Whether to increase or decrease output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If two products are homogeneous,then they
A)Are identical.
B)Differ from each other.
C)Must be used together.
A)Are identical.
B)Differ from each other.
C)Must be used together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is consistent with long-run equilibrium for a perfectly competitive market?
A)Average total costs of production are maximized.
B)Economic profits are positive.
C)Maximum technical efficiency is achieved.
A)Average total costs of production are maximized.
B)Economic profits are positive.
C)Maximum technical efficiency is achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose a perfectly competitive firm is experiencing zero economic profits.In an effort to increase profits,the firm decides to initiate an advertising campaign for its product.The most likely short-run result of this campaign,ceteris paribus,would be
A)Economic losses for the firm.
B)The ability to sell more at the existing market price.
C)The ability to sell more at a lower price.
A)Economic losses for the firm.
B)The ability to sell more at the existing market price.
C)The ability to sell more at a lower price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)Long-run economic profit.
B)High barriers to entry.
C)Identical products.
A)Long-run economic profit.
B)High barriers to entry.
C)Identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The market structure of the computer industry
A)Was originally a monopoly.
B)Was originally perfectly competitive.
C)Has become more competitive over time.
A)Was originally a monopoly.
B)Was originally perfectly competitive.
C)Has become more competitive over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The exit of firms from a market,ceteris paribus,
A)Shifts the market supply curve to the right.
B)Has no effect on the economic losses of remaining firms in the market.
C)Increases the equilibrium price in the market.
A)Shifts the market supply curve to the right.
B)Has no effect on the economic losses of remaining firms in the market.
C)Increases the equilibrium price in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Profit per unit is maximized when the firm produces the output where
A)The ATC is minimized.
B)MC equals MR.
C)The MC is minimized.
A)The ATC is minimized.
B)MC equals MR.
C)The MC is minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In which of the following cases would a firm enter a market?
A)P > short-run ATC.
B)P < short-run ATC.
C)P > long-run ATC.
A)P > short-run ATC.
B)P < short-run ATC.
C)P > long-run ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is least likely to occur during the long run in a perfectly competitive market experiencing economic profits?
A)A rightward shift in the market supply curve.
B)An increase in the market quantity demanded.
C)An increase in marginal revenue.
A)A rightward shift in the market supply curve.
B)An increase in the market quantity demanded.
C)An increase in marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Economic losses are a signal to producers
A)That they are using resources in the most efficient way.
B)That they are not using resources in the best way.
C)That consumer demand is being satisfied.
A)That they are using resources in the most efficient way.
B)That they are not using resources in the best way.
C)That consumer demand is being satisfied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In long-run perfectly competitive equilibrium,marginal cost
A)Is greater than ATC.
B)Is less than ATC.
C)Equals the minimum of the ATC.
A)Is greater than ATC.
B)Is less than ATC.
C)Equals the minimum of the ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
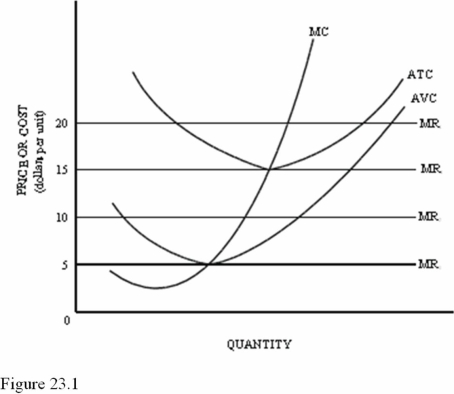
Refer to Figure 23.1 for a perfectly competitive firm.This firm should shut down in the short run if the market price is below
A)$5.
B)$10.
C)$15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When a firm is earning positive economic profits,this is an indication that the firm
A)Should leave this market in the long run.
B)Is using its resources in the best possible way.
C)Is using its resources in one of a number of ways that would yield positive economic profits.
A)Should leave this market in the long run.
B)Is using its resources in the best possible way.
C)Is using its resources in one of a number of ways that would yield positive economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Technological improvements cause
A)ATC to shift down.
B)The supply curve to shift to the left.
C)MC to shift up.
A)ATC to shift down.
B)The supply curve to shift to the left.
C)MC to shift up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which characteristic of competitive markets permits society to answer the WHAT to produce question efficiently?
A)Marginal cost pricing.
B)Average cost pricing.
C)Minimum cost pricing.
A)Marginal cost pricing.
B)Average cost pricing.
C)Minimum cost pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If price is above the long-run competitive equilibrium level,
A)Firms will enter the market.
B)Firms will shut down.
C)Firms will incur losses.
A)Firms will enter the market.
B)Firms will shut down.
C)Firms will incur losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Marginal cost pricing means that a firm
A)Produces up to the output where P = MC for a given market price.
B)Lowers market price to marginal cost for a given output.
C)Lets marginal cost rise to the market price for a given output.
A)Produces up to the output where P = MC for a given market price.
B)Lowers market price to marginal cost for a given output.
C)Lets marginal cost rise to the market price for a given output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
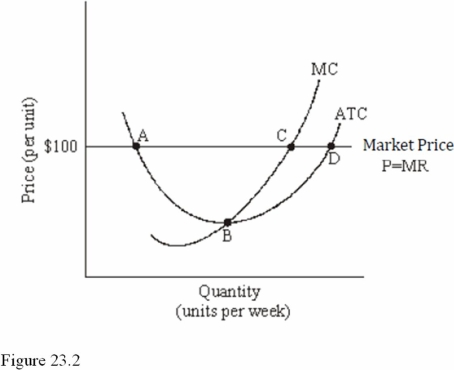
Refer to Figure 23.2 for a perfectly competitive firm.If this firm produces the level of output corresponding to point C in the short run,it will earn
A)Zero profit.
B)The maximum profit possible.
C)A profit,although not the maximum profit possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When firms in a competitive market are experiencing zero economic profits,this is an indication that
A)They should be producing a different product.
B)There is currently no better way to use society's scarce resources.
C)They will eventually go bankrupt.
A)They should be producing a different product.
B)There is currently no better way to use society's scarce resources.
C)They will eventually go bankrupt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is a consequence of competition?
A)An unrelenting squeeze on prices and profit.
B)Positive economic profit in the long run.
C)Elimination of the most efficient firms.
A)An unrelenting squeeze on prices and profit.
B)Positive economic profit in the long run.
C)Elimination of the most efficient firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
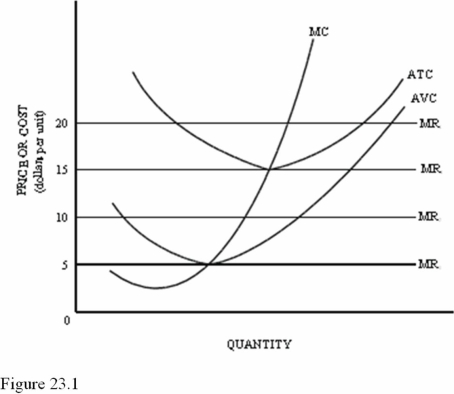
Refer to Figure 23.1.If the market price equaled $10,in the short run this firm should
A)Raise the price.
B)Produce with an economic loss.
C)Shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A firm should shut down production when
A)P < minimum AVC.
B)P > minimum AVC.
C)P = minimum ATC.
A)P < minimum AVC.
B)P > minimum AVC.
C)P = minimum ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
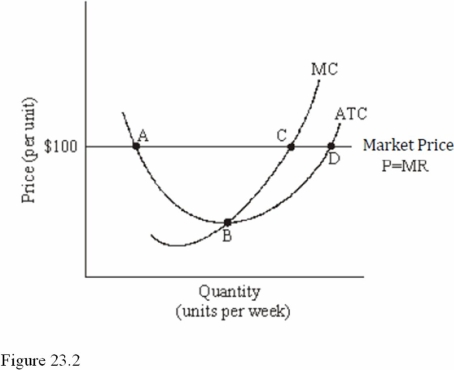
Refer to Figure 23.2 for a perfectly competitive firm.Given the current market price of $100,we expect to see
A)Entry into this industry.
B)Exit from this industry.
C)No change in the number of firms in this industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Technological improvements cause
A)New firms to enter but existing firms to continue producing their old output levels.
B)Some firms to exit but the remaining firms to produce more output.
C)Existing firms to produce more output.
A)New firms to enter but existing firms to continue producing their old output levels.
B)Some firms to exit but the remaining firms to produce more output.
C)Existing firms to produce more output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
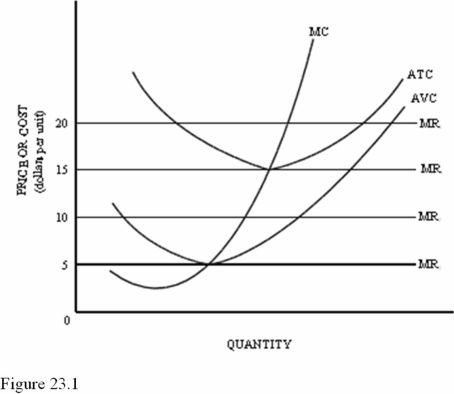
Refer to Figure 23.1 for a perfectly competitive firm.In the long run,this firm would stay in this market only if the market price was equal to or higher than
A)$5.
B)$10.
C)$15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a competitive market,if the market price is equal to the minimum point of the firm's ATC curve,the firm may seek to earn economic profits by
A)Producing at the rate of output where price equals demand.
B)Decreasing production costs through technological improvements.
C)Decreasing price.
A)Producing at the rate of output where price equals demand.
B)Decreasing production costs through technological improvements.
C)Decreasing price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In which of the following cases would entry and exit cease?
A)P > short-run ATC.
B)P = long-run ATC.
C)P > long-run ATC.
A)P > short-run ATC.
B)P = long-run ATC.
C)P > long-run ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A perfectly competitive market results in efficiency because
A)Price is driven down to minimum ATC.
B)Price rises high enough to equal marginal cost.
C)Zero economic profit is achieved.
A)Price is driven down to minimum ATC.
B)Price rises high enough to equal marginal cost.
C)Zero economic profit is achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
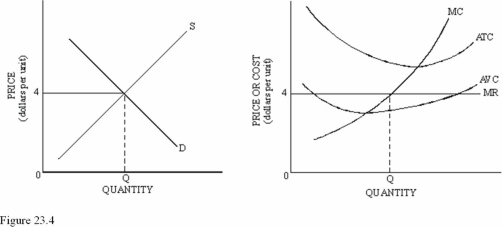
If the firm in Figure 23.4 raised the price of its product above $4,the firm would
A)Increase its profits.
B)Reduce its total revenue to zero.
C)Increase its total revenue but not its profits because costs would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The price signal the consumer gets in a competitive market
A)In no way reflects opportunity cost.
B)Is an accurate reflection of opportunity cost.
C)Is not reliable for making choices about the allocation of resources.
A)In no way reflects opportunity cost.
B)Is an accurate reflection of opportunity cost.
C)Is not reliable for making choices about the allocation of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Bib's Soccer Ball Company produces 800 soccer balls per week.If the firm used marginal cost pricing to determine soccer ball output,it would produce 600 soccer balls.Consumers do not receive the most desirable quantity of soccer balls from Bib's because
A)Economic losses are occurring.
B)The firm must be earning higher than normal economic profits.
C)The cost of producing the additional 200 soccer balls is greater than the amount that consumers are willing to pay for the additional soccer balls.
A)Economic losses are occurring.
B)The firm must be earning higher than normal economic profits.
C)The cost of producing the additional 200 soccer balls is greater than the amount that consumers are willing to pay for the additional soccer balls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
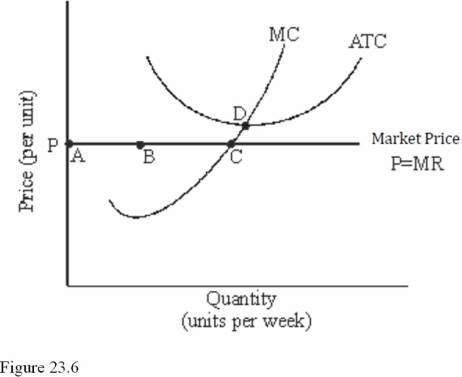
Refer to Figure 23.6 for a perfectly competitive firm.Given the current market price,we expect to see
A)Entry into this industry.
B)Exit from this industry.
C)No change in the number of firms in this industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
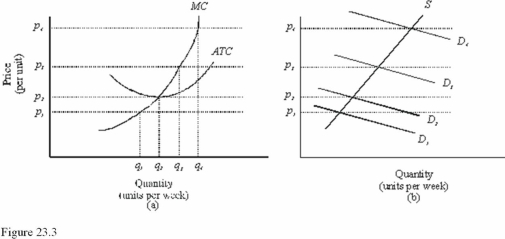
In Figure 23.3,diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision,and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.Use both diagrams to answer the following question: In Figure 23.3,at a price of p3 in the long run
A)Firms will enter the market.
B)Economic profits equal zero.
C)Firms will exit the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When economic profits exist in the market for a particular product,this is a signal to producers that
A)Consumers would like more scarce resources devoted to the production of this product.
B)The market is oversupplied with this product.
C)The best mix of goods and services is being produced with society's scarce resources.
A)Consumers would like more scarce resources devoted to the production of this product.
B)The market is oversupplied with this product.
C)The best mix of goods and services is being produced with society's scarce resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In a perfectly competitive market economy,business failures can benefit society by causing
A)A reallocation of resources to better uses.
B)An increase in market power for the remaining firms.
C)A decline in market prices as remaining firms attempt to increase sales and stay in business.
A)A reallocation of resources to better uses.
B)An increase in market power for the remaining firms.
C)A decline in market prices as remaining firms attempt to increase sales and stay in business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
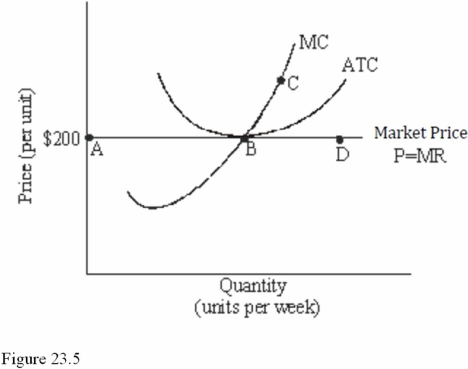
Refer to Figure 23.5 for a perfectly competitive firm.Given the current market price of $200,we expect to see
A)Firms exit from the industry,driving up the market price.
B)Firms exit from the industry,driving down the market price.
C)No change in the number of firms in the industry and no change in the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
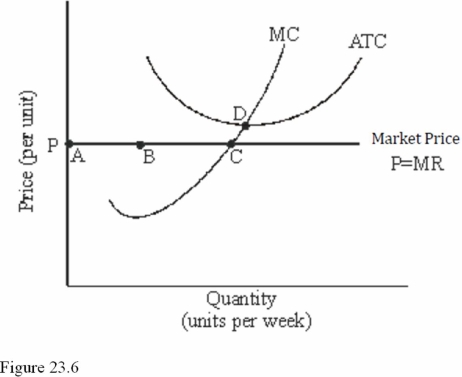
Refer to Figure 23.6 for a perfectly competitive firm.Given the current market price,we expect to see
A)Firms exit from the industry,driving up the market price.
B)Firms exit from the industry,driving down the market price.
C)No change in the number of firms in the industry and no change in the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
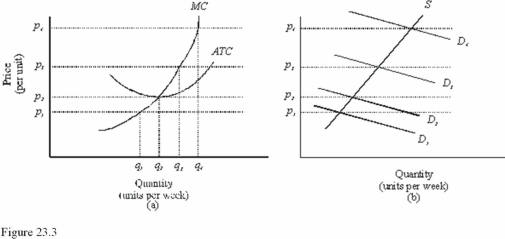
In Figure 23.3,diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision,and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.Use both diagrams to answer the following question: In Figure 23.3,the price at which a firm makes zero economic profits is
A)p1.
B)p2.
C)p3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When economic losses exist in the cereal market,for example,this is an indication that
A)The goods and services that society is giving up (the opportunity cost)are more valuable than the cereal being produced.
B)Society's scarce resources are being used in the best way.
C)Not enough firms are producing cereal (assuming that the market is perfectly competitive).
A)The goods and services that society is giving up (the opportunity cost)are more valuable than the cereal being produced.
B)Society's scarce resources are being used in the best way.
C)Not enough firms are producing cereal (assuming that the market is perfectly competitive).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
High profits in a particular industry indicate that
A)Consumers want less of that industry's goods.
B)Consumers are satisfied with the level of production of that industry's goods.
C)Consumers want more of that industry's goods.
A)Consumers want less of that industry's goods.
B)Consumers are satisfied with the level of production of that industry's goods.
C)Consumers want more of that industry's goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
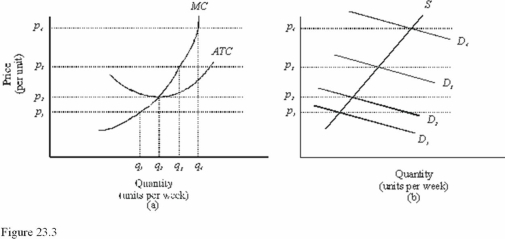
In Figure 23.3,diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision,and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.Use both diagrams to answer the following question: If the market demand curve is D2 in Figure 23.3,then in the long run,
A)Economic profit is less than zero,and firms will exit.
B)Economic profit is greater than zero,and firms will expand production.
C)There are zero economic profits,so there will be no entry or exit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
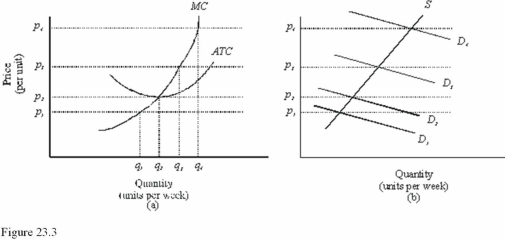
In Figure 23.3,diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision,and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.Use both diagrams to answer the following question: In Figure 23.3,at a price of p2 in the long run
A)Firms will enter the market.
B)Economic profits equal zero.
C)Firms will exit the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The equilibrium price of a good or service in a competitive market is
A)Higher than it should be because profits are included in the price.
B)A reflection of the opportunity cost of producing the product.
C)Lower than it should be because bankruptcies are common in competitive markets.
A)Higher than it should be because profits are included in the price.
B)A reflection of the opportunity cost of producing the product.
C)Lower than it should be because bankruptcies are common in competitive markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
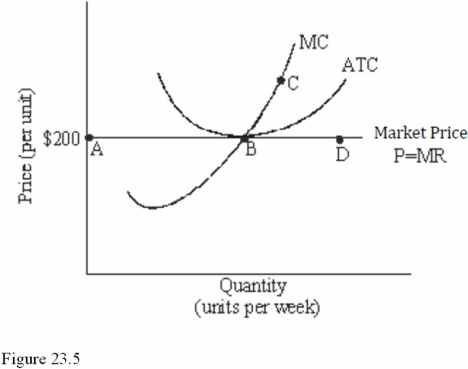
Refer to Figure 23.5 for a perfectly competitive firm.If this firm produces the level of output corresponding to point B in the short run,it will earn
A)Zero economic profit.
B)The maximum profit possible.
C)A profit,although not the maximum profit possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When a computer firm is producing a level of output at which MC is greater than price,from society's standpoint the firm is producing too
A)Much because society is giving up more to produce additional computers than the computers are worth.
B)Much because society would be willing to give up more alternative goods in order to get additional computers.
C)Little because society is giving up more to produce additional computers than the computers are worth.
A)Much because society is giving up more to produce additional computers than the computers are worth.
B)Much because society would be willing to give up more alternative goods in order to get additional computers.
C)Little because society is giving up more to produce additional computers than the computers are worth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
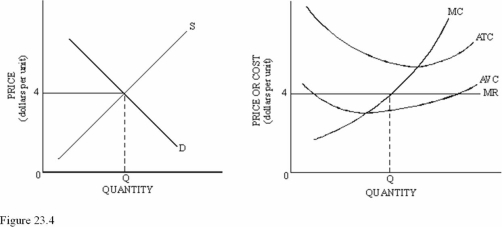
Refer to Figure 23.4 for a perfectly competitive market and firm.Which of the following is most likely to occur,ceteris paribus?
A)The firm will exit in the long run.
B)The firm will increase output.
C)The firm will shut down in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
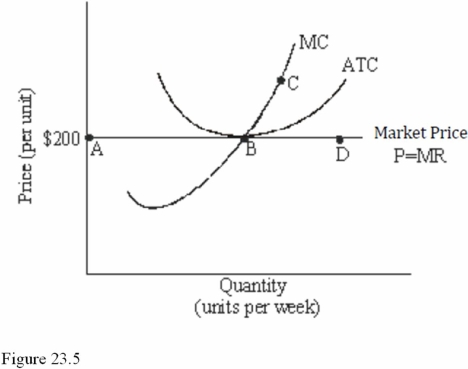
Refer to Figure 23.5 for a perfectly competitive firm.If more efficient production techniques were developed in this market,which of the following changes would we expect to occur,ceteris paribus?
A)The ATC,MC,and market price would all decrease.
B)The ATC alone would decrease.
C)The ATC,MC,and market price would all increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



