Deck 21: The Costs of Production
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
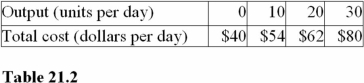
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/127
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: The Costs of Production
1
Which of the following are factors of production?
A)Output in a production function.
B)Productivity.
C)Land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurship.
A)Output in a production function.
B)Productivity.
C)Land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurship.
Land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurship.
2
The change in total output associated with one additional unit of input is the
A)Opportunity cost of the output.
B)Average productivity.
C)Marginal physical product.
A)Opportunity cost of the output.
B)Average productivity.
C)Marginal physical product.
Marginal physical product.
3
Which of the following is the best explanation of why the law of diminishing returns does not apply in the long run?
A)In the long run,firms can increase the availability of space and equipment to keep up with the increase in variable inputs.
B)The MPP does not change in the long run.
C)In the long run,firms have enough time to find the most qualified workers.
A)In the long run,firms can increase the availability of space and equipment to keep up with the increase in variable inputs.
B)The MPP does not change in the long run.
C)In the long run,firms have enough time to find the most qualified workers.
In the long run,firms can increase the availability of space and equipment to keep up with the increase in variable inputs.
4
In the short run,the law of diminishing returns
A)Occurs for only a few economies.
B)Can be observed in every production process.
C)Does not occur in command economies.
A)Occurs for only a few economies.
B)Can be observed in every production process.
C)Does not occur in command economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a factor of production for the Little Biscuit Bread Company?
A)Flour.
B)Bread.
C)Productivity.
A)Flour.
B)Bread.
C)Productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A production function shows the
A)Minimum amount of output that can be obtained from alternative combinations of inputs.
B)Maximum quantity of inputs required to produce a given quantity of output.
C)Maximum output that can be produced with varying combinations of factor inputs.
A)Minimum amount of output that can be obtained from alternative combinations of inputs.
B)Maximum quantity of inputs required to produce a given quantity of output.
C)Maximum output that can be produced with varying combinations of factor inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Labor productivity will increase in response to
A)Lower wages.
B)An increase in the amount of physical capital per worker.
C)Higher resource costs.
A)Lower wages.
B)An increase in the amount of physical capital per worker.
C)Higher resource costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The short-run production function shows how output changes when
A)The quantity of labor changes.
B)The quantity of land changes.
C)Technology changes.
A)The quantity of labor changes.
B)The quantity of land changes.
C)Technology changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements is not true regarding the production function and the production possibilities curve?
A)Both the production function and the production possibilities curve maximize the amount of output attainable.
B)The production function describes the capacity of a single firm,whereas the production function summarizes the output capacity of the entire economy.
C)A production function tells us the maximum amount of output attainable from the use of all resources.
A)Both the production function and the production possibilities curve maximize the amount of output attainable.
B)The production function describes the capacity of a single firm,whereas the production function summarizes the output capacity of the entire economy.
C)A production function tells us the maximum amount of output attainable from the use of all resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Technical efficiency is achieved when a firm produces
A)At an amount indicated by a point on the production function.
B)Below the opportunity cost for the resources it uses.
C)Enough output to cover the opportunity cost of resources.
A)At an amount indicated by a point on the production function.
B)Below the opportunity cost for the resources it uses.
C)Enough output to cover the opportunity cost of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Ceteris paribus,the law of diminishing returns states that beyond some point,the
A)Returns on stocks and bonds diminish with higher security prices.
B)Addition to total utility diminishes as more units of a good are consumed.
C)Marginal physical product of a factor of production diminishes as more of that factor is used.
A)Returns on stocks and bonds diminish with higher security prices.
B)Addition to total utility diminishes as more units of a good are consumed.
C)Marginal physical product of a factor of production diminishes as more of that factor is used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A production function shows
A)How a firm's production increases as it adds more labor.
B)How a firm's costs of production increase as it produces more goods.
C)How production changes as its unit costs go up.
A)How a firm's production increases as it adds more labor.
B)How a firm's costs of production increase as it produces more goods.
C)How production changes as its unit costs go up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Diminishing returns occur because
A)Of inefficiency in the production process.
B)Of the use of inferior factors of production.
C)A firm increases the amount of a variable input without changing a fixed input.
A)Of inefficiency in the production process.
B)Of the use of inferior factors of production.
C)A firm increases the amount of a variable input without changing a fixed input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is the slope of the production function with respect to an input?
A)The marginal physical product of the input.
B)The average product of the input.
C)The unit cost of the input.
A)The marginal physical product of the input.
B)The average product of the input.
C)The unit cost of the input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The period in which at least one input is fixed in quantity is the
A)Long run.
B)Production run.
C)Short run.
A)Long run.
B)Production run.
C)Short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
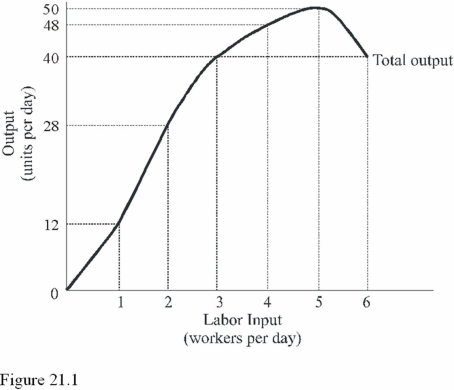 In Figure 21.1,diminishing marginal returns first occur with the
In Figure 21.1,diminishing marginal returns first occur with theA)Fifth worker.
B)Fourth worker.
C)Third worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
As an In and Out Burger restaurant increases the number of employees for a specific restaurant,
A)Total production of hamburgers will fall.
B)Costs of production will fall.
C)Efficiency will suffer as the restaurant becomes too crowded with employees.
A)Total production of hamburgers will fall.
B)Costs of production will fall.
C)Efficiency will suffer as the restaurant becomes too crowded with employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a firm produces at a technically efficient output level,it is
A)Producing the output at the minimum MC curve.
B)Using the fewest resources to produce a good or service.
C)Producing the output where the AVC curve is at a minimum.
A)Producing the output at the minimum MC curve.
B)Using the fewest resources to produce a good or service.
C)Producing the output where the AVC curve is at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a firm could hire all the workers it wanted at a zero wage (i.e. ,the workers are volunteers),the firm should hire
A)Enough workers to produce the output where diminishing returns begin.
B)Enough workers to produce the output where worker productivity is the highest.
C)Enough workers to produce where the MPP equals zero.
A)Enough workers to produce the output where diminishing returns begin.
B)Enough workers to produce the output where worker productivity is the highest.
C)Enough workers to produce where the MPP equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The marginal physical product is the
A)Change in total input required to produce one additional unit of output.
B)Change in total output associated with one additional unit of the variable input.
C)Number of units of output obtained from all units of input employed.
A)Change in total input required to produce one additional unit of output.
B)Change in total output associated with one additional unit of the variable input.
C)Number of units of output obtained from all units of input employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If an additional unit of labor costs $20 and has a MPP of 15 units of output,the marginal cost is
A)$0.75.
B)$1.33.
C)$30.00.
A)$0.75.
B)$1.33.
C)$30.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A U-shaped average total cost curve implies
A)First diminishing returns,and then increasing returns.
B)First marginal cost below average total cost,and then marginal cost above average total cost.
C)That total costs are at a minimum at the minimum of the average cost curve.
A)First diminishing returns,and then increasing returns.
B)First marginal cost below average total cost,and then marginal cost above average total cost.
C)That total costs are at a minimum at the minimum of the average cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The average variable cost curve slopes upward with a higher rate of output in the short run because of
A)The effect of diminishing returns.
B)The shape of the average fixed cost curve.
C)Diseconomies of scale.
A)The effect of diminishing returns.
B)The shape of the average fixed cost curve.
C)Diseconomies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Changes in short-run total costs result from changes in
A)Variable costs.
B)Fixed costs.
C)Profit.
A)Variable costs.
B)Fixed costs.
C)Profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the marginal physical product (MPP)is falling,then the
A)Marginal cost of each unit of output is falling.
B)Marginal cost of each unit of output is rising.
C)Total cost of each unit of output is falling.
A)Marginal cost of each unit of output is falling.
B)Marginal cost of each unit of output is rising.
C)Total cost of each unit of output is falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The most desirable rate of output for a firm is the output that
A)Minimizes total costs.
B)Maximizes total profit.
C)Minimizes marginal costs.
A)Minimizes total costs.
B)Maximizes total profit.
C)Minimizes marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Marginal cost
A)Rises as a direct result of diminishing returns.
B)Falls whenever marginal physical product decreases.
C)Falls in the short run because some resources are fixed.
A)Rises as a direct result of diminishing returns.
B)Falls whenever marginal physical product decreases.
C)Falls in the short run because some resources are fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Average total cost is important to a business because
A)It tells the firm what the profit per unit produced is.
B)It always declines as more output is produced.
C)It tells the firm what its fixed costs are.
A)It tells the firm what the profit per unit produced is.
B)It always declines as more output is produced.
C)It tells the firm what its fixed costs are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the short run,when a firm produces zero output,total cost equals
A)Zero.
B)Variable costs.
C)Fixed costs.
A)Zero.
B)Variable costs.
C)Fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Marginal cost
A)Is the change in total output from hiring one more factor of production.
B)Is the change in total cost from producing one additional unit of output.
C)Falls when there are diminishing returns.
A)Is the change in total output from hiring one more factor of production.
B)Is the change in total cost from producing one additional unit of output.
C)Falls when there are diminishing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is most likely a fixed cost?
A)The material used to make jackets.
B)The labor on an automotive assembly line.
C)The rent for a factory.
A)The material used to make jackets.
B)The labor on an automotive assembly line.
C)The rent for a factory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The shape of the marginal cost curve reflects the
A)Law of diminishing returns.
B)Competitiveness of the firm.
C)Law of diminishing marginal utility.
A)Law of diminishing returns.
B)Competitiveness of the firm.
C)Law of diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the short run,when a firm produces zero output,variable cost equals
A)Zero.
B)Total cost.
C)Fixed cost.
A)Zero.
B)Total cost.
C)Fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Profit is
A)The difference between total cost and variable cost.
B)The difference between total revenue and total cost.
C)Earned at all points along the production function.
A)The difference between total cost and variable cost.
B)The difference between total revenue and total cost.
C)Earned at all points along the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Marginal cost is equal to
A)The change in total costs divided by the change in quantity produced.
B)The change in fixed costs as more units are produced.
C)Total cost divided by quantity produced.
A)The change in total costs divided by the change in quantity produced.
B)The change in fixed costs as more units are produced.
C)Total cost divided by quantity produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An increase in production in the short run definitely results in an increase in
A)Average total costs.
B)Marginal costs.
C)Total costs.
A)Average total costs.
B)Marginal costs.
C)Total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the short run,which of the following is most likely a variable cost?
A)Contractual lease payments.
B)Labor and raw materials costs.
C)Property taxes.
A)Contractual lease payments.
B)Labor and raw materials costs.
C)Property taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The sum of fixed cost and variable cost at any rate of output is
A)Total variable cost.
B)Total cost.
C)Average total cost.
A)Total variable cost.
B)Total cost.
C)Average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The average fixed cost (AFC)curve
A)Is U-shaped as a result of diminishing returns.
B)Declines as long as output increases.
C)Is intersected at its minimum point by marginal cost.
A)Is U-shaped as a result of diminishing returns.
B)Declines as long as output increases.
C)Is intersected at its minimum point by marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Sam's surf shop has total costs of $2,000 when it is not producing any surfboards.This means that
A)Variable costs are $2000.
B)Fixed costs are $2,000.
C)The shop is very inefficient in its production.
A)Variable costs are $2000.
B)Fixed costs are $2,000.
C)The shop is very inefficient in its production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When the size of a factory (and all its associated inputs)doubles and,as a result,output more than doubles,
A)The law of diminishing returns must not apply in the smaller factory.
B)Economies of scale must exist.
C)The short-run ATC curve must be declining.
A)The law of diminishing returns must not apply in the smaller factory.
B)Economies of scale must exist.
C)The short-run ATC curve must be declining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Intel's chief executive says the company might expand the technology it is using in its planned $2.5 billion chip-manufacturing factory in China if the U.S.government allows it,underscoring the technology giant's ambitions in the world's fourth-biggest economy.The Intel executive is making a
A)Long-run decision,and therefore an investment decision.
B)Long-run decision,and therefore a production decision.
C)Decision that would definitely increase costs.
A)Long-run decision,and therefore an investment decision.
B)Long-run decision,and therefore a production decision.
C)Decision that would definitely increase costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
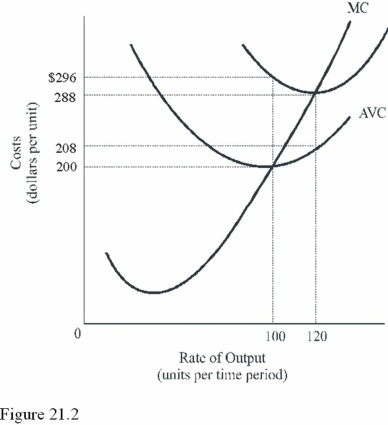
What is the total cost of 120 units in Figure 21.2?
A)$34,560.
B)$9,600.
C)$24,960.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
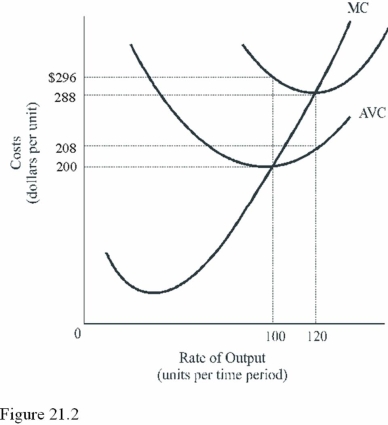
What is the total fixed cost in Figure 21.2?
A)$80.
B)$10,000.
C)$9,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Accounting costs and economic costs differ because
A)Economic costs include implicit costs and accounting costs do not.
B)Accounting costs include implicit costs and economic costs do not.
C)Economic costs include explicit costs and accounting costs do not.
A)Economic costs include implicit costs and accounting costs do not.
B)Accounting costs include implicit costs and economic costs do not.
C)Economic costs include explicit costs and accounting costs do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Economies of scale
A)Exist in both the short run and the long run.
B)Explain why average variable and average total costs decline in the short run.
C)Explain why average total costs decline as output increases in the long run.
A)Exist in both the short run and the long run.
B)Explain why average variable and average total costs decline in the short run.
C)Explain why average total costs decline as output increases in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Explicit costs
A)Include only payments to labor.
B)Are the sum of actual monetary payments made for resources used to produce a good.
C)Include the market value of all resources used to produce a good.
A)Include only payments to labor.
B)Are the sum of actual monetary payments made for resources used to produce a good.
C)Include the market value of all resources used to produce a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Assume a given amount of output can be produced by several small plants or one large plant with identical minimum per-unit costs.This long-run situation reflects the existence of
A)Economies of scale.
B)Diseconomies of scale.
C)Constant returns to scale.
A)Economies of scale.
B)Diseconomies of scale.
C)Constant returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
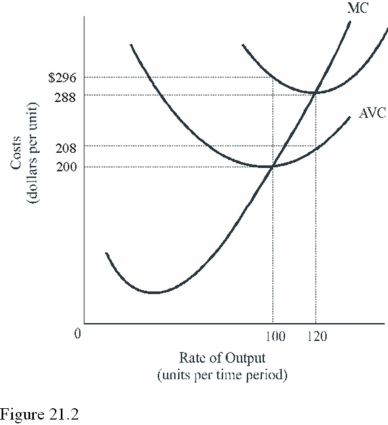
At what output level do diminishing marginal returns begin in Figure 21.2?
A)40 units.
B)100 units.
C)120 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The period in which there are no fixed costs is the
A)Production run.
B)Long run.
C)Short run.
A)Production run.
B)Long run.
C)Short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The marginal cost curve intersects the minimum of the curve representing
A)TC.
B)ATC.
C)AFC.
A)TC.
B)ATC.
C)AFC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The long-run average total cost curve is constructed from the
A)Minimum points of the short-run marginal cost curves.
B)Minimum points of the short-run average variable cost curves.
C)Lowest average total cost for producing each level of output.
A)Minimum points of the short-run marginal cost curves.
B)Minimum points of the short-run average variable cost curves.
C)Lowest average total cost for producing each level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
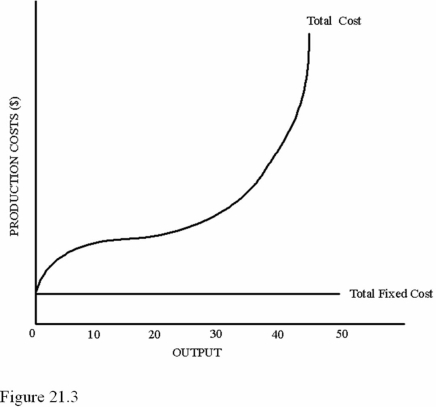 Refer to Figure 21.3.The vertical difference between the total cost curve and the total fixed cost curve represents
Refer to Figure 21.3.The vertical difference between the total cost curve and the total fixed cost curve representsA)Total variable costs.
B)Total marginal costs.
C)Average fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In economics,the long run is considered to be
A)The time period when all costs are variable.
B)The time period when all costs are explicit.
C)One year.
A)The time period when all costs are variable.
B)The time period when all costs are explicit.
C)One year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
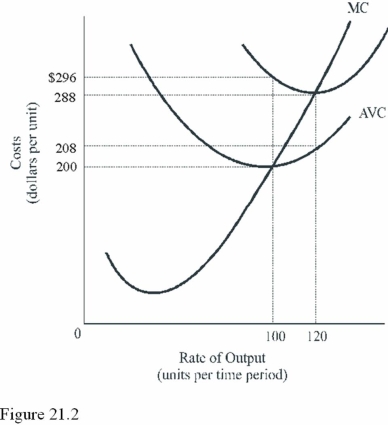
What is the average fixed cost when output is 120 units in Figure 21.2?
A)$0.67.
B)$80.00.
C)$96.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the average total cost curve is rising,the marginal cost curve will be
A)Below the average fixed cost curve.
B)Falling with greater output.
C)Above the average total cost curve.
A)Below the average fixed cost curve.
B)Falling with greater output.
C)Above the average total cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is a long-run concept?
A)Diminishing marginal productivity.
B)Diminishing returns.
C)Diseconomies of scale.
A)Diminishing marginal productivity.
B)Diminishing returns.
C)Diseconomies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements about the relationship between economic costs and accounting costs is true?
A)Accounting costs are always less than or equal to economic costs.
B)Accounting costs must always equal economic costs.
C)Accounting costs are always greater than economic costs.
A)Accounting costs are always less than or equal to economic costs.
B)Accounting costs must always equal economic costs.
C)Accounting costs are always greater than economic costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Economies of scale are reductions in average
A)Total cost that result from declining average fixed costs.
B)Fixed cost that result from reducing the firm's scale of operations.
C)Total cost that result from using operations of larger size.
A)Total cost that result from declining average fixed costs.
B)Fixed cost that result from reducing the firm's scale of operations.
C)Total cost that result from using operations of larger size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Economic cost
A)Includes both implicit and explicit costs.
B)Is the sum of actual monetary payments made for resources used to produce a good.
C)Includes only implicit costs.
A)Includes both implicit and explicit costs.
B)Is the sum of actual monetary payments made for resources used to produce a good.
C)Includes only implicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
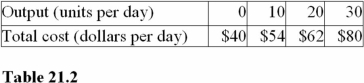
At 10 units of output in Table 21.2,the total fixed cost is
A)$44.
B)$14.
C)$40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62

Complete Table 21.5: The marginal cost of the third unit of output in Table 21.5 is
A)$4.
B)$3.
C)$30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63

Complete Table 21.5: The total variable cost of the first unit of output in Table 21.5 is
A)$15.00.
B)$12.00.
C)$8.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64

Complete Table 21.5: The average variable cost of the second unit of output in Table 21.5 is
A)$6.00.
B)$4.00.
C)$8.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65

Complete Table 21.5: The total cost of 3 units of output in Table 21.5 is
A)$30.
B)$15.
C)$23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
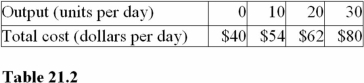
Average fixed cost at 20 units of output in Table 21.2 is
A)$1.00.
B)$2.00.
C)$2.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
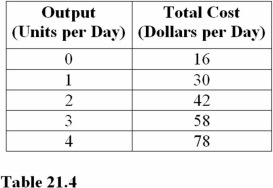
At 2 units of output in Table 20.4,the average variable cost is
A)$13.
B)$6.
C)$12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
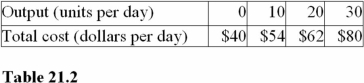
The marginal cost between 20 and 30 units of output in Table 21.2 is
A)$1.60.
B)$4.00.
C)$1.80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
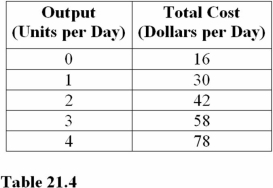
The marginal cost of the fourth unit of output in Table 21.4 is
A)$4.00.
B)$20.00.
C)$16.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

At 30 units of output in Table 21.2,the total variable cost is
A)$30.
B)$40.
C)$50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
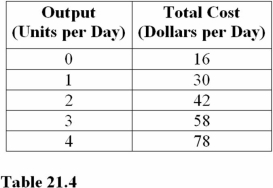
For the output levels in Table 21.4,the minimum of the average variable cost curve occurs at a production rate of
A)3 units per day.
B)2 units per day.
C)4 units per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
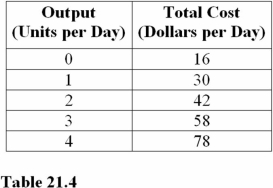
For the output levels in Table 21.4,the minimum of the average total cost curve occurs at a production rate of
A)2 units per day.
B)3 units per day.
C)4 units per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
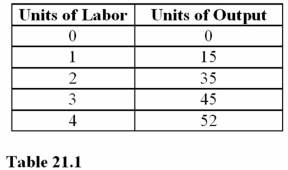
If workers are paid $10,what is the labor cost per unit of output in Table 21.1 when output is increased from 15 to 35 units of output?
A)$0.28 per unit.
B)$0.50 per unit.
C)$10 per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
At 20 units of output in Table 21.2,the average variable cost is
A)$1.10 per unit.
B)$1.75 per unit.
C)$2.00 per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
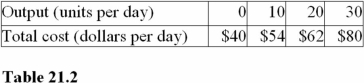
For the output levels in Table 21.2,the minimum of the average variable cost curve occurs at a production rate of
A)Zero units per day.
B)10 units per day.
C)20 units per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Complete Table 21.3 below: 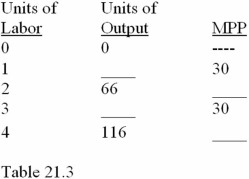 What is the unit labor cost in Table 21.3 for the second unit of labor if the MPP represents daily output and the wage rate is $72 per day?
What is the unit labor cost in Table 21.3 for the second unit of labor if the MPP represents daily output and the wage rate is $72 per day?
A)$0.50 per unit of output.
B)$2.00 per unit of output.
C)$36.00 per unit of output.
 What is the unit labor cost in Table 21.3 for the second unit of labor if the MPP represents daily output and the wage rate is $72 per day?
What is the unit labor cost in Table 21.3 for the second unit of labor if the MPP represents daily output and the wage rate is $72 per day?A)$0.50 per unit of output.
B)$2.00 per unit of output.
C)$36.00 per unit of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77

Complete Table 21.5: Total fixed costs in Table 21.5 are equal to
A)$0 because the problem involves the long run.
B)$15.
C)$30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
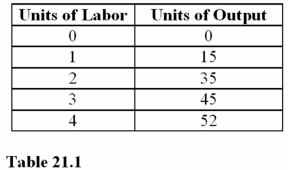
With which unit of labor do diminishing marginal returns first appear in Table 21.1?
A)The first.
B)The second.
C)The third.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
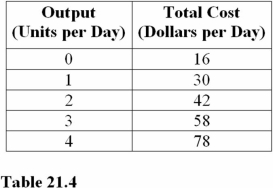
At 4 units of output in Table 21.4,total fixed costs are
A)$78.00.
B)$19.50.
C)$16.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
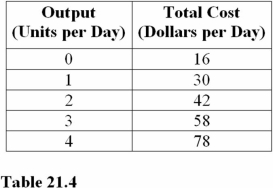
At 3 units of output in Table 21.4,average fixed costs are
A)$16.00.
B)$19.50.
C)$5.33.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



