Deck 1: Economics: the Core Issues Appendix: Using Graphs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Economics: the Core Issues Appendix: Using Graphs
1
Which of the following is the best example of land?
A)The ethanol refined from corn.
B)A factory that produces new goods and services.
C)The water used to make a soft drink.
D)A barber's chair.
A)The ethanol refined from corn.
B)A factory that produces new goods and services.
C)The water used to make a soft drink.
D)A barber's chair.
The water used to make a soft drink.
2
In economics,scarcity means that
A)A shortage of a particular good will cause the price to fall.
B)A production possibilities curve cannot accurately represent the trade-off between two goods.
C)Society's desires exceed the want-satisfying capability of the resources available to satisfy those desires.
D) The market mechanism has failed.
A)A shortage of a particular good will cause the price to fall.
B)A production possibilities curve cannot accurately represent the trade-off between two goods.
C)Society's desires exceed the want-satisfying capability of the resources available to satisfy those desires.
D) The market mechanism has failed.
Society's desires exceed the want-satisfying capability of the resources available to satisfy those desires.
3
The opportunity cost of studying for an economics test is
A)Negative because it may improve your grade.
B)Zero because you knew when you registered for the class that studying would be required.
C)The money you spent on tuition for the class.
D)The best alternative use of your time.
A)Negative because it may improve your grade.
B)Zero because you knew when you registered for the class that studying would be required.
C)The money you spent on tuition for the class.
D)The best alternative use of your time.
The best alternative use of your time.
4
Factors of production are
A)Scarce in every society.
B)Scarce only in advanced countries.
C)Scarce only in the poorest countries of the world.
D)Unlimited in quantity.
A)Scarce in every society.
B)Scarce only in advanced countries.
C)Scarce only in the poorest countries of the world.
D)Unlimited in quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The basic factors of production include
A)Land,labor,money,and capital.
B)Land,labor,money,and inputs.
C)Labor and money.
D)Land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurship.
A)Land,labor,money,and capital.
B)Land,labor,money,and inputs.
C)Labor and money.
D)Land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given that resources are scarce,
A)A "free lunch" is possible,but only for a limited number of people.
B)Opportunity costs are experienced whenever choices are made.
C)Poor countries must make choices,but rich countries with abundant resources do not have to make choices.
D)Some choices involve opportunity costs while other choices do not.
A)A "free lunch" is possible,but only for a limited number of people.
B)Opportunity costs are experienced whenever choices are made.
C)Poor countries must make choices,but rich countries with abundant resources do not have to make choices.
D)Some choices involve opportunity costs while other choices do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The role of the entrepreneur in an economy is to
A)Bring the factors of production together and assume the risk of production.
B)Work with government planners to determine what goods are produced.
C)Arrange bank financing for the owners of new businesses.
D)Ensure full employment of labor.
A)Bring the factors of production together and assume the risk of production.
B)Work with government planners to determine what goods are produced.
C)Arrange bank financing for the owners of new businesses.
D)Ensure full employment of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The "guns versus butter" dilemma that all nations confront is that
A)Guns and butter can be produced using the same resources at the same time.
B)An increase in national defense implies more sacrifices of civilian goods and services.
C)An increase in national defense is possible only if we produce more butter.
D)All of the choices are correct.
A)Guns and butter can be produced using the same resources at the same time.
B)An increase in national defense implies more sacrifices of civilian goods and services.
C)An increase in national defense is possible only if we produce more butter.
D)All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Economics can be defined as the study of
A)For whom resources are allocated to increase efficiency.
B)How society spends the income of individuals.
C)How scarce resources are allocated on a macro level to best meet society's goals or on a micro level to best meet an individual's or firm's goals.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)For whom resources are allocated to increase efficiency.
B)How society spends the income of individuals.
C)How scarce resources are allocated on a macro level to best meet society's goals or on a micro level to best meet an individual's or firm's goals.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Opportunity cost is
A)Measured only in dollars and cents.
B)The total dollar cost to society of producing the goods.
C)The difficulty associated with using one good in place of another.
D)The best alternative that must be given up in order to get something else.
A)Measured only in dollars and cents.
B)The total dollar cost to society of producing the goods.
C)The difficulty associated with using one good in place of another.
D)The best alternative that must be given up in order to get something else.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A consequence of the economic problem of scarcity is that
A)Choices have to be made about how resources are used.
B)There is never too much of any good or service produced.
C)The production of goods and services must be controlled by the government.
D)The production possibilities curve is bowed outward.
A)Choices have to be made about how resources are used.
B)There is never too much of any good or service produced.
C)The production of goods and services must be controlled by the government.
D)The production possibilities curve is bowed outward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not one of the three core economic issues that must be resolved?
A)How to produce the goods and services we select.
B)What to produce with unlimited resources.
C)Who should get the goods and services we produce.
D)What to produce with limited resources.
A)How to produce the goods and services we select.
B)What to produce with unlimited resources.
C)Who should get the goods and services we produce.
D)What to produce with limited resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which economist argued that free markets unleashed the "animal spirits" of entrepreneurs,propelling innovation,technology,and growth?
A)Lord Kelvin.
B)Kenneth Olsen.
C)Irving Fisher.
D)John Maynard Keynes.
A)Lord Kelvin.
B)Kenneth Olsen.
C)Irving Fisher.
D)John Maynard Keynes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Opportunity cost may be defined as the
A)Goods or services that are forgone in order to obtain something else.
B)Dollar prices paid for final goods and services.
C)Dollar cost of producing a particular product.
D)Difference between wholesale and retail prices.
A)Goods or services that are forgone in order to obtain something else.
B)Dollar prices paid for final goods and services.
C)Dollar cost of producing a particular product.
D)Difference between wholesale and retail prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A production possibilities curve indicates the
A)Combinations of goods and services an economy is actually producing.
B)Maximum combinations of goods and services an economy can produce given its available resources and technology.
C)Maximum combinations of goods and services an economy can produce given unlimited resources.
D)Average combinations of goods and services an economy can produce given its available resources and technology.
A)Combinations of goods and services an economy is actually producing.
B)Maximum combinations of goods and services an economy can produce given its available resources and technology.
C)Maximum combinations of goods and services an economy can produce given unlimited resources.
D)Average combinations of goods and services an economy can produce given its available resources and technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not a factor of production?
A)A psychiatrist.
B)The $100,000 used to start a new business.
C)A bulldozer.
D)Six thousand acres of farmland.
A)A psychiatrist.
B)The $100,000 used to start a new business.
C)A bulldozer.
D)Six thousand acres of farmland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The fundamental problem of economics is
A)The law of increasing opportunity costs.
B)The scarcity of resources relative to human wants.
C)How to get government to operate efficiently.
D)How to create employment for everyone.
A)The law of increasing opportunity costs.
B)The scarcity of resources relative to human wants.
C)How to get government to operate efficiently.
D)How to create employment for everyone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Capital,as economists use the term,refers to
A)The money needed to start a new business.
B)The costs of operating a business.
C)Shares of stock issued by businesses.
D)Final goods that are used to produce other goods and services.
A)The money needed to start a new business.
B)The costs of operating a business.
C)Shares of stock issued by businesses.
D)Final goods that are used to produce other goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is an assumption under which the production possibilities curve is drawn?
A)Total unemployment is zero.
B)The supply of resources is fixed.
C)The price level is changing.
D)Technology is changing.
A)Total unemployment is zero.
B)The supply of resources is fixed.
C)The price level is changing.
D)Technology is changing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
With respect to factors of production,which of the following statements is not true?
A)Factors of production are also known as resources.
B)In order to produce any good or service,it is necessary to have factors of production.
C)Factors of production include land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurship.
D)Only those resources that are privately owned are counted as factors of production.
A)Factors of production are also known as resources.
B)In order to produce any good or service,it is necessary to have factors of production.
C)Factors of production include land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurship.
D)Only those resources that are privately owned are counted as factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The production possibilities curve illustrates
A)The limitations that exist because of scarce resources.
B)That there is no limit to what an economy can produce.
C)That there is no limit to the level of output.
D)The existence of unlimited wants and resources.
A)The limitations that exist because of scarce resources.
B)That there is no limit to what an economy can produce.
C)That there is no limit to the level of output.
D)The existence of unlimited wants and resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The production possibilities curve illustrates which two of the following essential principles?
A)Factors of production and price signals.
B)Scarce resources and opportunity cost.
C)Market mechanisms and laissez faire.
D)Economic growth and market failure.
A)Factors of production and price signals.
B)Scarce resources and opportunity cost.
C)Market mechanisms and laissez faire.
D)Economic growth and market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following will cause the production possibilities curve to shift inward?
A)An increase in the working-age population.
B)A decrease in the size of the labor force.
C)A technological advance.
D)An increase in knowledge.
A)An increase in the working-age population.
B)A decrease in the size of the labor force.
C)A technological advance.
D)An increase in knowledge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The points on a production possibilities curve show
A)Desired output.
B)Actual output.
C)Potential output.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)Desired output.
B)Actual output.
C)Potential output.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A point on a nation's production possibilities curve represents
A)An undesirable combination of goods and services.
B)Combinations of production that are unattainable,given current technology and resources.
C)Levels of production that will cause both unemployment and inflation.
D)The full employment of resources to achieve a particular combination of goods and services.
A)An undesirable combination of goods and services.
B)Combinations of production that are unattainable,given current technology and resources.
C)Levels of production that will cause both unemployment and inflation.
D)The full employment of resources to achieve a particular combination of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In terms of the production possibilities curve,inefficiency is represented by
A)All points on the curve.
B)All points outside the curve.
C)All points inside the curve.
D)A rightward shift of the curve.
A)All points on the curve.
B)All points outside the curve.
C)All points inside the curve.
D)A rightward shift of the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not a basic decision that all nations must confront?
A)Should we have economic growth?
B)How should we produce goods and services?
C)For whom should goods and services be produced?
D)What goods and services should we produce?
A)Should we have economic growth?
B)How should we produce goods and services?
C)For whom should goods and services be produced?
D)What goods and services should we produce?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the law of increasing opportunity costs,
A)Greater production leads to greater inefficiency.
B)Greater production means factor prices rise.
C)Greater production of one good requires increasingly larger sacrifices of other goods.
D)Higher opportunity costs induce higher output per unit of input.
A)Greater production leads to greater inefficiency.
B)Greater production means factor prices rise.
C)Greater production of one good requires increasingly larger sacrifices of other goods.
D)Higher opportunity costs induce higher output per unit of input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Economic growth would best be represented by a
A)Shift outward of the production possibilities curve.
B)Shift inward of the production possibilities curve.
C)Movement from inside the production possibilities curve to a point on the production possibilities curve.
D)Movement from the production possibilities curve to a point inside the production possibilities curve.
A)Shift outward of the production possibilities curve.
B)Shift inward of the production possibilities curve.
C)Movement from inside the production possibilities curve to a point on the production possibilities curve.
D)Movement from the production possibilities curve to a point inside the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to the law of increasing opportunity costs,
A)The more one is willing to pay for resources,the smaller will be the possible level of production.
B)Increasing the production of a particular good will cause the price of the good to remain constant.
C)In order to produce additional units of a particular good,it is necessary for society to sacrifice increasingly larger amounts of alternative goods.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)The more one is willing to pay for resources,the smaller will be the possible level of production.
B)Increasing the production of a particular good will cause the price of the good to remain constant.
C)In order to produce additional units of a particular good,it is necessary for society to sacrifice increasingly larger amounts of alternative goods.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following correctly characterizes the shape of a constant opportunity cost production possibilities curve?
A)A straight line indicating that the law of increasing opportunity costs applies.
B)A straight line when there is constant opportunity costs.
C)A line that curves outward when resources are perfectly adaptable in the production of different goods.
D)A line that curves inward when resources are perfectly adaptable in the production of different goods.
A)A straight line indicating that the law of increasing opportunity costs applies.
B)A straight line when there is constant opportunity costs.
C)A line that curves outward when resources are perfectly adaptable in the production of different goods.
D)A line that curves inward when resources are perfectly adaptable in the production of different goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If an economy is producing inside the production possibilities curve,then
A)There is full employment of resources.
B)It is operating efficiently.
C)It can produce more of one good without giving up some of another good.
D)There are not enough resources available to produce more output.
A)There is full employment of resources.
B)It is operating efficiently.
C)It can produce more of one good without giving up some of another good.
D)There are not enough resources available to produce more output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the United States decides to convert automobile factories to tank production,as it did during World War II,but finds that some auto manufacturing facilities are not well suited to tank production,then
A)The production possibilities curve between tanks and automobiles will appear as a straight line.
B)The production possibilities curve between tanks and automobiles will shift outward.
C)Decreasing opportunity costs will occur with greater automobile production.
D)Increasing opportunity costs will occur with greater tank production.
A)The production possibilities curve between tanks and automobiles will appear as a straight line.
B)The production possibilities curve between tanks and automobiles will shift outward.
C)Decreasing opportunity costs will occur with greater automobile production.
D)Increasing opportunity costs will occur with greater tank production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If an economy experiences increasing opportunity costs with respect to two goods,then the production possibilities curve between the two goods will be
A)Bowed outward or concave from below.
B)A straight,downward-sloping line.
C)Bowed inward or convex from below.
D)Bowed outward until the two goods are equal, and then bowed inward.
A)Bowed outward or concave from below.
B)A straight,downward-sloping line.
C)Bowed inward or convex from below.
D)Bowed outward until the two goods are equal, and then bowed inward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is true when an economy is producing efficiently?
A)The economy is producing on the production possibilities curve.
B)The economy is producing outside the production possibilities curve.
C)The economy is getting the fewest goods and services from the available resources.
D)Everyone in the economy is happy.
A)The economy is producing on the production possibilities curve.
B)The economy is producing outside the production possibilities curve.
C)The economy is getting the fewest goods and services from the available resources.
D)Everyone in the economy is happy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If North Korea is currently producing at efficiency,and it proceeds to increase the size of its military,then,as long as nothing else changes,its
A)Production possibilities curve will shift outward.
B)Production possibilities curve will shift inward.
C)Production of nonmilitary goods will increase.
D)Production of nonmilitary goods will decrease.
A)Production possibilities curve will shift outward.
B)Production possibilities curve will shift inward.
C)Production of nonmilitary goods will increase.
D)Production of nonmilitary goods will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A technological advance would best be represented by
A)A shift outward of the production possibilities curve.
B)A shift inward of the production possibilities curve.
C)A movement from inside the production possibilities curve to a point on the production possibilities curve.
D)A movement from the production possibilities curve to a point inside the production possibilities curve.
A)A shift outward of the production possibilities curve.
B)A shift inward of the production possibilities curve.
C)A movement from inside the production possibilities curve to a point on the production possibilities curve.
D)A movement from the production possibilities curve to a point inside the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a market economy,the people who receive the goods and services that are produced are those who
A)Need the goods and services the most.
B)Have the most political power.
C)Want the goods and services the most.
D)Are willing to pay the highest price.
A)Need the goods and services the most.
B)Have the most political power.
C)Want the goods and services the most.
D)Are willing to pay the highest price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When an economy is producing efficiently,it is
A)Producing a combination of goods and services beyond the production possibilities curve.
B)Getting the most goods and services from the available resources.
C)Experiencing decreasing opportunity costs.
D)Producing equal amounts of all goods.
A)Producing a combination of goods and services beyond the production possibilities curve.
B)Getting the most goods and services from the available resources.
C)Experiencing decreasing opportunity costs.
D)Producing equal amounts of all goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following events would allow the production possibilities curve to shift outward?
A)The economy's capital stock declines.
B)More teenagers enter the labor force.
C)Technology is lost.
D)People begin to retire at earlier ages.
A)The economy's capital stock declines.
B)More teenagers enter the labor force.
C)Technology is lost.
D)People begin to retire at earlier ages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When the invisible hand does not produce optimal outcomes for the economy,there is evidence of
A)Market failure.
B)Government failure.
C)Macroeconomic failure.
D)Scarcity.
A)Market failure.
B)Government failure.
C)Macroeconomic failure.
D)Scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Government intervention may achieve a more optimal outcome than the market mechanism when addressing
A)Inefficient bureaucracy.
B)Consumption of cigarettes.
C)Theme park construction.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)Inefficient bureaucracy.
B)Consumption of cigarettes.
C)Theme park construction.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Latin phrase ceteris paribus means
A)The production possibilities curve never shifts.
B)Laissez faire.
C)Other things remain equal.
D)The invisible hand.
A)The production possibilities curve never shifts.
B)Laissez faire.
C)Other things remain equal.
D)The invisible hand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following can be used to correct market failure?
A)The market mechanism.
B)Laws and regulations.
C)Laissez faire price policies.
D)Government failure.
A)The market mechanism.
B)Laws and regulations.
C)Laissez faire price policies.
D)Government failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is not a macroeconomic statement?
A)The unemployment rate for the United States rose to 5 percent in the last quarter.
B)The Federal Reserve lowered interest rates at its last meeting.
C)Congress increased the minimum wage rate in January.
D)Jenny's wage rate rose,and in response,she decided to work more hours.
A)The unemployment rate for the United States rose to 5 percent in the last quarter.
B)The Federal Reserve lowered interest rates at its last meeting.
C)Congress increased the minimum wage rate in January.
D)Jenny's wage rate rose,and in response,she decided to work more hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Microeconomics is concerned with issues such as
A)The demand for bottled water by individuals.
B)The level of inflation in the economy.
C)Maintaining a strong level of economic growth.
D)All of the choices are correct.
A)The demand for bottled water by individuals.
B)The level of inflation in the economy.
C)Maintaining a strong level of economic growth.
D)All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The study of microeconomic theory focuses on the
A)Structure and performance of individual markets and the operation of the price system.
B)Operation of the entire economy.
C)Role of the banking system in the economy.
D)Interaction of international trade and domestic production of goods and services.
A)Structure and performance of individual markets and the operation of the price system.
B)Operation of the entire economy.
C)Role of the banking system in the economy.
D)Interaction of international trade and domestic production of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A city's decision to limit smoking in public areas is an example of
A)The invisible hand at work.
B)The market mechanism at work.
C)Market success.
D)Government intervention.
A)The invisible hand at work.
B)The market mechanism at work.
C)Market success.
D)Government intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A mixed economy
A)Is justified by the superiority of laissez faire over government intervention.
B)Utilizes both market and nonmarket signals to allocate goods and services.
C)Relies on the use of central planning by private firms rather than the government.
D)Is one that allows trade with other countries.
A)Is justified by the superiority of laissez faire over government intervention.
B)Utilizes both market and nonmarket signals to allocate goods and services.
C)Relies on the use of central planning by private firms rather than the government.
D)Is one that allows trade with other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Macroeconomics focuses on the performance of
A)Individual consumers.
B)Government agencies.
C)The overall economy.
D)All of the choices are correct.
A)Individual consumers.
B)Government agencies.
C)The overall economy.
D)All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.3 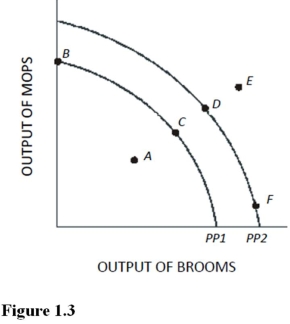
Using Figure 1.3 and PP1,at point A,
A)There is inefficient use of available resources.
B)The available technology keeps production inside PP1.
C)All available resources are being used efficiently.
D)An increase in the production of mops would definitely require a decrease in the production of brooms.

Using Figure 1.3 and PP1,at point A,
A)There is inefficient use of available resources.
B)The available technology keeps production inside PP1.
C)All available resources are being used efficiently.
D)An increase in the production of mops would definitely require a decrease in the production of brooms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Adam Smith's invisible hand is now called
A)Economic growth.
B)The market mechanism.
C)Opportunity cost.
D)Laissez faire.
A)Economic growth.
B)The market mechanism.
C)Opportunity cost.
D)Laissez faire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The invisible hand refers to
A)Intervention in the economy by the government bureaucrats we do not see and over whom we have no control.
B)Undiscovered natural resources.
C)The allocation of resources by market forces.
D)The person who has the responsibility to coordinate all the markets in a market economy.
A)Intervention in the economy by the government bureaucrats we do not see and over whom we have no control.
B)Undiscovered natural resources.
C)The allocation of resources by market forces.
D)The person who has the responsibility to coordinate all the markets in a market economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Economic models are used by economists to
A)Predict economic behavior.
B)Develop economic policies.
C)Explain economic behavior.
D)All of the choices are correct.
A)Predict economic behavior.
B)Develop economic policies.
C)Explain economic behavior.
D)All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The market mechanism may best be defined as
A)The use of market prices and sales to signal desired output.
B)The use of market signals and government directives to select economic outcomes.
C)The process by which the production possibilities curve shifts inward.
D)Price regulation by government.
A)The use of market prices and sales to signal desired output.
B)The use of market signals and government directives to select economic outcomes.
C)The process by which the production possibilities curve shifts inward.
D)Price regulation by government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The doctrine of laissez faire is based on the belief that
A)Markets are likely to do a better job of allocating resources than government directives.
B)Government directives are likely to do a better job of allocating resources than markets.
C)Government failure does not exist.
D)Markets result in an unfair distribution of income.
A)Markets are likely to do a better job of allocating resources than government directives.
B)Government directives are likely to do a better job of allocating resources than markets.
C)Government failure does not exist.
D)Markets result in an unfair distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The market mechanism
A)Is not a very efficient means of communicating consumer demand to the producers of goods and services.
B)Works through central planning by government.
C)Eliminates market failures created by government.
D)Works because prices serve as a means of communication between consumers and producers.
A)Is not a very efficient means of communicating consumer demand to the producers of goods and services.
B)Works through central planning by government.
C)Eliminates market failures created by government.
D)Works because prices serve as a means of communication between consumers and producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following has occurred when government directives do not produce better economic outcomes?
A)Government failure.
B)Market failure.
C)Macroeconomic failure.
D)Scarcity.
A)Government failure.
B)Market failure.
C)Macroeconomic failure.
D)Scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If market signals result in pollution beyond the optimal level,then
A)The economy experiences government failure.
B)A laissez faire approach will reduce the level of pollution.
C)The market mechanism has failed to achieve social efficiency.
D)The government is allocating resources inefficiently.
A)The economy experiences government failure.
B)A laissez faire approach will reduce the level of pollution.
C)The market mechanism has failed to achieve social efficiency.
D)The government is allocating resources inefficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is an example of government failure?
A)Bureaucratic delays.
B)Required use of pollution control technology that is obsolete.
C)Inefficient incentives.
D)All of the choices are correct.
A)Bureaucratic delays.
B)Required use of pollution control technology that is obsolete.
C)Inefficient incentives.
D)All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.3 
A movement from point F to point D in Figure 1.3 results in
A)A reallocation of resources from mop production to broom production.
B)Permanent unemployment of workers producing brooms.
C)A reallocation of resources from broom production to mop production.
D)More efficient production.

A movement from point F to point D in Figure 1.3 results in
A)A reallocation of resources from mop production to broom production.
B)Permanent unemployment of workers producing brooms.
C)A reallocation of resources from broom production to mop production.
D)More efficient production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.4 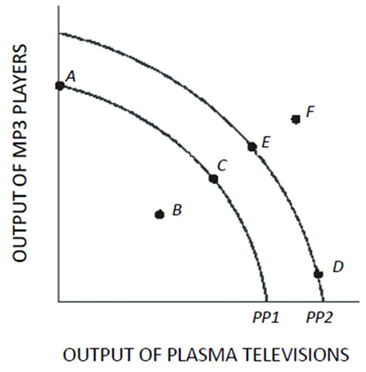
Which of the following is true about the combination of plasma televisions and MP3 players represented by point F in Figure 1.4?
A)Point F is inefficient now.
B)Point F is unattainable even with advances in technology.
C)Point F will be more easily attainable if the government takes control of all privately run factories.
D)Point F can possibly be reached if more economic resources become available or technology improves.

Which of the following is true about the combination of plasma televisions and MP3 players represented by point F in Figure 1.4?
A)Point F is inefficient now.
B)Point F is unattainable even with advances in technology.
C)Point F will be more easily attainable if the government takes control of all privately run factories.
D)Point F can possibly be reached if more economic resources become available or technology improves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.3 
Which of the following is true about the combination of mops and brooms represented by point E in Figure 1.3 and using PP1?
A)Point E is efficient now.
B)Point E is attainable if this economy uses more of its available resources.
C)Point E is unattainable if this economy becomes more efficient.
D)Point E is attainable only if more resources become available or technological advances are made.

Which of the following is true about the combination of mops and brooms represented by point E in Figure 1.3 and using PP1?
A)Point E is efficient now.
B)Point E is attainable if this economy uses more of its available resources.
C)Point E is unattainable if this economy becomes more efficient.
D)Point E is attainable only if more resources become available or technological advances are made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following figure to answer the questions: Figure 1.7:
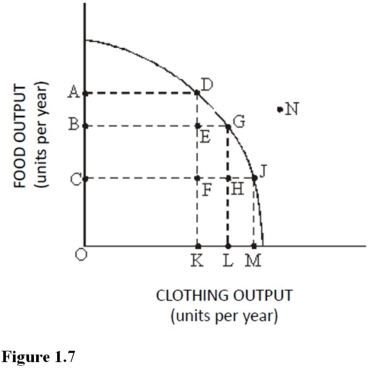
The cost of producing at point D rather than point J is :
A)KM units of clothing.
B)AC units of food.
C)OM units of clothing.
D)OA units of food.

The cost of producing at point D rather than point J is :
A)KM units of clothing.
B)AC units of food.
C)OM units of clothing.
D)OA units of food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Table 1.2 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S.capacity,ceteris paribus.Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both the B-1 and Stealth bombers. 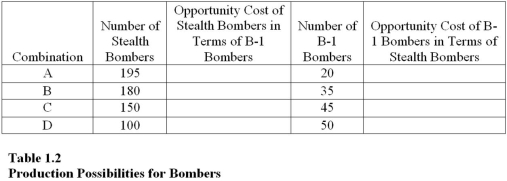 On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2
On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2
The law of increasing opportunity costs applies to
A)Both B-1 and Stealth bombers.
B)B-1 bombers but not to Stealth bombers.
C)Stealth bombers but not to B-1 bombers.
D)Neither bomber.
 On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2
On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2The law of increasing opportunity costs applies to
A)Both B-1 and Stealth bombers.
B)B-1 bombers but not to Stealth bombers.
C)Stealth bombers but not to B-1 bombers.
D)Neither bomber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 1.1 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S.capacity,ceteris paribus.Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both the B-1 and Stealth bombers. 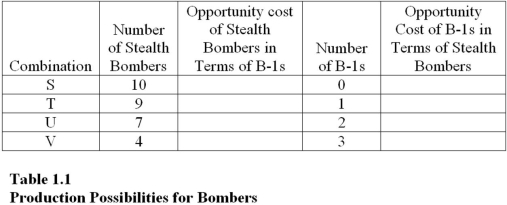 On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.1
On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.1
what is the opportunity cost of producing at point S rather than point T?
A)1 Stealth bomber.
B)1 B-1 bomber.
C)10 Stealth bombers.
D)0.9 Stealth bombers.
 On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.1
On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.1what is the opportunity cost of producing at point S rather than point T?
A)1 Stealth bomber.
B)1 B-1 bomber.
C)10 Stealth bombers.
D)0.9 Stealth bombers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.4 1
In Figure 1.4,a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
A)An increase in the unemployment rate.
B)Implementation of training programs that improve the skills of workers.
C)A flu epidemic that makes many workers sick.
D)Tougher pollution controls for the producers of plasma televisions and MP3 players.

In Figure 1.4,a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
A)An increase in the unemployment rate.
B)Implementation of training programs that improve the skills of workers.
C)A flu epidemic that makes many workers sick.
D)Tougher pollution controls for the producers of plasma televisions and MP3 players.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.4 
A movement from point C to point A in Figure 1.4 results in
A)More efficient production.
B)Permanent unemployment of workers producing plasma televisions.
C)A reallocation of resources from MP3 player production to plasma television production.
D)A reallocation of resources from plasma television production to MP3 player production.

A movement from point C to point A in Figure 1.4 results in
A)More efficient production.
B)Permanent unemployment of workers producing plasma televisions.
C)A reallocation of resources from MP3 player production to plasma television production.
D)A reallocation of resources from plasma television production to MP3 player production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.3 
In Figure 1.3,a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
A)A decrease in the quantity of raw materials available.
B)A decline in the production skills of workers.
C)The use of improved production technology.
D)All of the choices are correct.

In Figure 1.3,a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
A)A decrease in the quantity of raw materials available.
B)A decline in the production skills of workers.
C)The use of improved production technology.
D)All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Table 1.1 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S.capacity,ceteris paribus.Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both the B-1 and Stealth bombers. 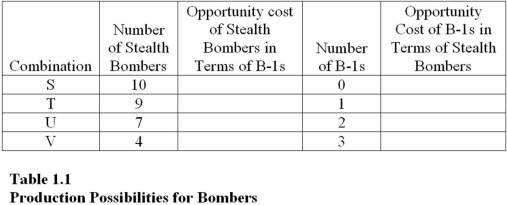
The highest opportunity cost anywhere in Table 1.1 for Stealth bombers in terms of B-1 bombers is
A)1 B-1 bomber per Stealth bomber.
B)3 B-1 bombers per Stealth bomber.
C)2 B-1 bombers per Stealth bomber.
D)0.5 B-1 bomber per Stealth bomber.

The highest opportunity cost anywhere in Table 1.1 for Stealth bombers in terms of B-1 bombers is
A)1 B-1 bomber per Stealth bomber.
B)3 B-1 bombers per Stealth bomber.
C)2 B-1 bombers per Stealth bomber.
D)0.5 B-1 bomber per Stealth bomber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following figure to answer questions: Figure 1.5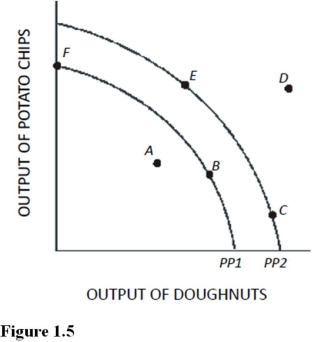
Using Figure 1.5,if an economy has the capacity to produce represented by PP2,then point E represents
A)A constant trade-off between potato chips and doughnuts.
B)A combination of potato chips and doughnuts that is not attainable.
C)An efficient use of resources.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Using Figure 1.5,if an economy has the capacity to produce represented by PP2,then point E represents
A)A constant trade-off between potato chips and doughnuts.
B)A combination of potato chips and doughnuts that is not attainable.
C)An efficient use of resources.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following figure to answer the questions: Figure 1.5
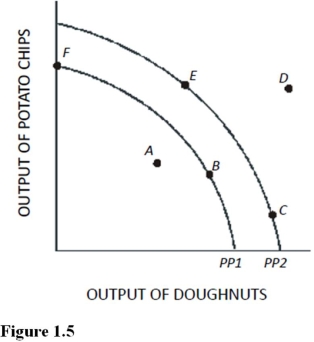
if an economy is currently producing on PP2,which of the following would shift the production possibilities curve toward PP1?
A)An increase in the quantity of labor available.
B)A decrease in the amount of capital available.
C)An increase in the level of unemployment above the normal level.
D)An advancement in technology.

if an economy is currently producing on PP2,which of the following would shift the production possibilities curve toward PP1?
A)An increase in the quantity of labor available.
B)A decrease in the amount of capital available.
C)An increase in the level of unemployment above the normal level.
D)An advancement in technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Table 1.2 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S.capacity,ceteris paribus.Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both the B-1 and Stealth bombers. 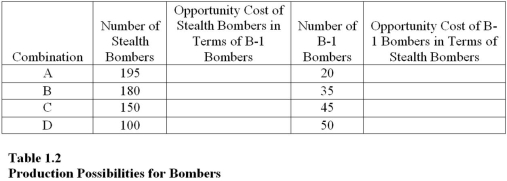 On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2,
On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2,
what is the opportunity cost of producing at point B rather than point C?
A)45 B-1 bombers.
B)35 Stealth bombers.
C)180 Stealth bombers.
D)10 B-1 bombers.
 On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2,
On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.2,what is the opportunity cost of producing at point B rather than point C?
A)45 B-1 bombers.
B)35 Stealth bombers.
C)180 Stealth bombers.
D)10 B-1 bombers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following figure to answer the questions: Figure 1.7:

The cost of producing at point G rather than point D is
A)OA units of food.
B)KL units of clothing.
C)AB units of food.
D)OL units of clothing.

The cost of producing at point G rather than point D is
A)OA units of food.
B)KL units of clothing.
C)AB units of food.
D)OL units of clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following figure to answer the questions: Figure 1.6
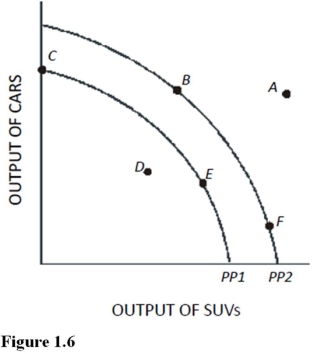
If an economy has the capacity to produce represented by PP1,then point E represents
A)A combination of cars and SUVs that is not attainable.
B)A constant trade-off between cars and SUVs.
C)A change in technology.
D)An efficient use of resources.

If an economy has the capacity to produce represented by PP1,then point E represents
A)A combination of cars and SUVs that is not attainable.
B)A constant trade-off between cars and SUVs.
C)A change in technology.
D)An efficient use of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Table 1.1 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S.capacity,ceteris paribus.Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both the B-1 and Stealth bombers. 
On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.1,you may infer that the law of increasing opportunity costs applies to
A)Stealth bombers but not to B-1 bombers.
B)B-1 bombers but not to Stealth bombers.
C)Both B-1 bombers and Stealth bombers.
D)Neither B-1 bombers nor Stealth bombers.

On the basis of your calculations in Table 1.1,you may infer that the law of increasing opportunity costs applies to
A)Stealth bombers but not to B-1 bombers.
B)B-1 bombers but not to Stealth bombers.
C)Both B-1 bombers and Stealth bombers.
D)Neither B-1 bombers nor Stealth bombers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following figure to answer the questions: Figure 1.6

If the opportunity cost of producing cars was zero at all levels of production,the production possibilities curve would be best be represented by a
A)Vertical line.
B)45-degree line starting at the origin.
C)Horizontal line.
D) Circle.

If the opportunity cost of producing cars was zero at all levels of production,the production possibilities curve would be best be represented by a
A)Vertical line.
B)45-degree line starting at the origin.
C)Horizontal line.
D) Circle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following figure to answer the questions: Figure 1.7:

The benefit of producing at point G rather than point D is :
A)OA units of food.
B)KL units of clothing.
C)AB units of food.
D)OL units of clothing.

The benefit of producing at point G rather than point D is :
A)OA units of food.
B)KL units of clothing.
C)AB units of food.
D)OL units of clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Table 1.1 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S.capacity,ceteris paribus.Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both the B-1 and Stealth bombers. 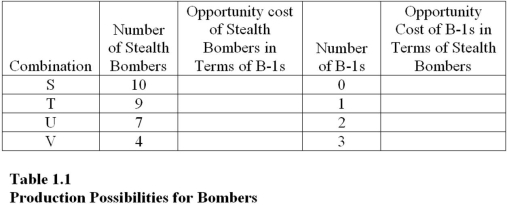
The lowest opportunity cost anywhere in Table 1.1 for B-1 bombers in terms of Stealth bombers is
A)0 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
B)2 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
C)1 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.
D)0.5 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.

The lowest opportunity cost anywhere in Table 1.1 for B-1 bombers in terms of Stealth bombers is
A)0 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
B)2 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
C)1 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.
D)0.5 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Table 1.1 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S.capacity,ceteris paribus.Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both the B-1 and Stealth bombers. 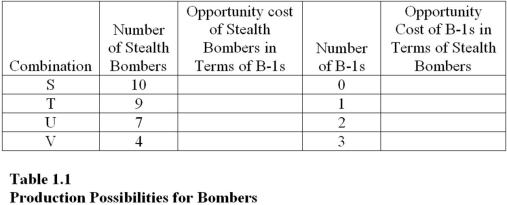
The highest opportunity cost anywhere in Table 1.1 for B-1 bombers in terms of Stealth bombers is
A)1 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.
B)3 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
C)2 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
D)0.5 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.

The highest opportunity cost anywhere in Table 1.1 for B-1 bombers in terms of Stealth bombers is
A)1 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.
B)3 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
C)2 Stealth bombers per B-1 bomber.
D)0.5 Stealth bomber per B-1 bomber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



