Deck 12: Gaseous Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Gaseous Chemical Equilibrium
1
Use the equilibrium constants for the following reactions at 700°C 2SO2(g)+ O2(g) 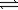 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)
K1 = 4.8
2NO(g)+ O2(g)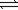 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
K2 = 16
To determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
SO3(g)+ NO(g)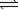 SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
A) 0.30
B) 0.55
C) 0.85
D) 1.8
E) 3.3
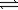 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)K1 = 4.8
2NO(g)+ O2(g)
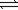 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)K2 = 16
To determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
SO3(g)+ NO(g)
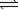 SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)A) 0.30
B) 0.55
C) 0.85
D) 1.8
E) 3.3
1.8
2
What is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? C4H10(g)+ 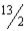 O2(g)
O2(g) 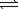 4CO2(g)+ 5H2O(g)
4CO2(g)+ 5H2O(g)
A)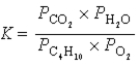
B)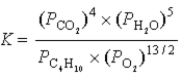
C)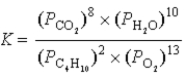
D)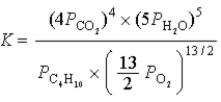
E)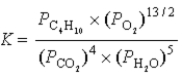
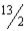 O2(g)
O2(g) 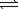 4CO2(g)+ 5H2O(g)
4CO2(g)+ 5H2O(g)A)
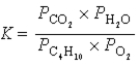
B)
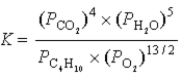
C)
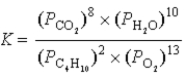
D)
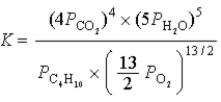
E)
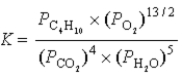
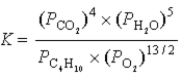
3
What is the relationship between Kp and Kc for the reaction below? N2(g)+ 3 H2(g) 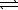 2 NH3(g)
2 NH3(g)
A)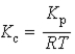
B)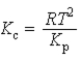
C)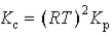
D)
E)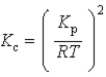
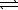 2 NH3(g)
2 NH3(g)A)
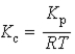
B)
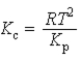
C)
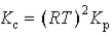
D)

E)
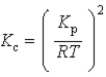
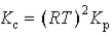
4
For the following reaction, 2SO3(g) 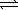 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)
2SO2(g)+ O2(g)
The equilibrium constant,K,is 1.32 at 627°C.What is the equilibrium constant,at 627°C,for the reaction below?
SO2(g)+ 1/2O2(g)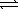 SO3(g)
SO3(g)
A) -1.15
B) -0.66
C) 0.379
D) 0.870
E) 1.52
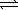 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)
2SO2(g)+ O2(g)The equilibrium constant,K,is 1.32 at 627°C.What is the equilibrium constant,at 627°C,for the reaction below?
SO2(g)+ 1/2O2(g)
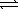 SO3(g)
SO3(g)A) -1.15
B) -0.66
C) 0.379
D) 0.870
E) 1.52

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Write the balanced chemical reaction which corresponds to the following equilibrium constant expression. 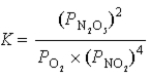
A) 4N2O5(g)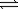 O2(g)+ 2NO2(g)
O2(g)+ 2NO2(g)
B) 2N2O5(g)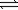 O2(g)+ 4NO2(g)
O2(g)+ 4NO2(g)
C) N2O5(g)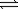 O2(g)+ NO2(g)
O2(g)+ NO2(g)
D) O2(g)+ 2NO2(g) 4N2O5(g)
4N2O5(g)
E) O2(g)+ 4NO2(g) 2N2O5(g)
2N2O5(g)
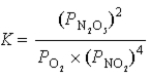
A) 4N2O5(g)
 O2(g)+ 2NO2(g)
O2(g)+ 2NO2(g)B) 2N2O5(g)
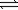 O2(g)+ 4NO2(g)
O2(g)+ 4NO2(g)C) N2O5(g)
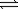 O2(g)+ NO2(g)
O2(g)+ NO2(g)D) O2(g)+ 2NO2(g)
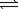 4N2O5(g)
4N2O5(g)E) O2(g)+ 4NO2(g)
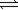 2N2O5(g)
2N2O5(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The reaction below was studied at a high temperature.At equilibrium,the partial pressures of the gases are as follows: PCl5 = 1.4 × 10−4 atm,PCl3 = 2.4 × 10−2 atm,Cl2 = 3.0 × 10−1 atm.What is the value of K for the reaction? PCl5(g)  PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
A) 4.3 × 10−4
B) 0.019
C) 0.32
D) 51
E) 2.3 × 103
 PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)A) 4.3 × 10−4
B) 0.019
C) 0.32
D) 51
E) 2.3 × 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the formation of ammonia gas from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Write a balanced chemical equation which corresponds to the following equilibrium constant expression. 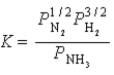
A) 1/2N2(g)+ 3/2H2(g) NH3(g)
NH3(g)
B) N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)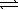 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
C) 2NH3(g)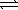 N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
D) NH3(g)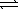 1/2N2(g)+ 3/2H2(g)
1/2N2(g)+ 3/2H2(g)
E) 2N2(g)+ 6H2(g)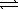 4NH3(g)
4NH3(g)
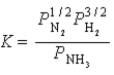
A) 1/2N2(g)+ 3/2H2(g)
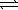 NH3(g)
NH3(g)B) N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)
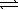 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)C) 2NH3(g)
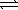 N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
N2(g)+ 3H2(g)D) NH3(g)
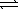 1/2N2(g)+ 3/2H2(g)
1/2N2(g)+ 3/2H2(g)E) 2N2(g)+ 6H2(g)
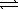 4NH3(g)
4NH3(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For which of the following reactions does Kc equal Kp?
A) Sn(s)+ 2H2O(g)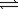 SnO2(s)+ 2H2(g)
SnO2(s)+ 2H2(g)
B) 2C2H6(g)+ 7O2(g)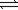 4CO2(g)+ 6H2O(g)
4CO2(g)+ 6H2O(g)
C) NH4Cl(s) NH3(g)+ HCl(g)
NH3(g)+ HCl(g)
D) N2(g)+ 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
E) CaCO3(s) CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
A) Sn(s)+ 2H2O(g)
 SnO2(s)+ 2H2(g)
SnO2(s)+ 2H2(g)B) 2C2H6(g)+ 7O2(g)
 4CO2(g)+ 6H2O(g)
4CO2(g)+ 6H2O(g)C) NH4Cl(s)
 NH3(g)+ HCl(g)
NH3(g)+ HCl(g)D) N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)E) CaCO3(s)
 CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the equilibrium constants for the following reactions 2NO(g) 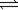 N2(g)+ O2(g)
N2(g)+ O2(g)
K1 = 2.4 × 1030
2NO(g)+ O2(g)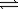 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
K2 = 2.4 × 1012
To determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction below.
N2(g)+ 2O2(g)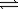 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
A) 1.7 × 10−43
B) 1.0 × 10−18
C) 5.8 × 1018
D) 2.4 × 1030
E) 5.8 × 1042
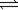 N2(g)+ O2(g)
N2(g)+ O2(g)K1 = 2.4 × 1030
2NO(g)+ O2(g)
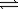 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)K2 = 2.4 × 1012
To determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction below.
N2(g)+ 2O2(g)
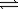 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)A) 1.7 × 10−43
B) 1.0 × 10−18
C) 5.8 × 1018
D) 2.4 × 1030
E) 5.8 × 1042

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? H2(g)+ I2(s) 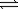 2HI(g)
2HI(g)
A)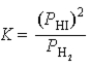
B)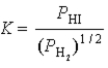
C)
D)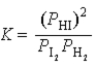
E)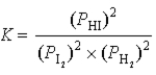
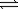 2HI(g)
2HI(g)A)
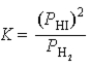
B)
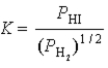
C)

D)
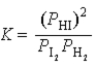
E)
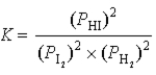

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Given the following equilibrium equations, 2N2O(g) 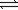 2N2(g)+ O2(g)
2N2(g)+ O2(g)
K1 = 8.3 × 1034
N2O4(g)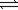 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
K2 = 4.6 × 10−3
2NO2(g)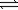 N2(g)+ 2O2(g)
N2(g)+ 2O2(g)
K3 = 5.9 × 1016
Calculate K for the decomposition of dinitrogen tetraoxide to nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
2N2O4(g)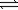 2N2O(g)+ 3O2(g)
2N2O(g)+ 3O2(g)
K4 = ?
A) 1.1 × 10−41
B) 1.3 × 10−20
C) 8.9 × 10−7
D) 3.3 × 1021
E) 2.3 × 1049
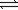 2N2(g)+ O2(g)
2N2(g)+ O2(g)K1 = 8.3 × 1034
N2O4(g)
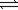 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)K2 = 4.6 × 10−3
2NO2(g)
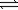 N2(g)+ 2O2(g)
N2(g)+ 2O2(g)K3 = 5.9 × 1016
Calculate K for the decomposition of dinitrogen tetraoxide to nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
2N2O4(g)
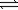 2N2O(g)+ 3O2(g)
2N2O(g)+ 3O2(g)K4 = ?
A) 1.1 × 10−41
B) 1.3 × 10−20
C) 8.9 × 10−7
D) 3.3 × 1021
E) 2.3 × 1049

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For the reaction below,the partial pressures of gases at equilibrium are as follows: H2 = 7.1 × 10−5 atm,Cl2 = 2.5 × 10−6 atm,and HCl = 3.0 atm.What is the value of the equilibrium constant,K? H2(g)+ Cl2(g) 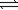 2HCl(g)
2HCl(g)
A) 2.0 × 10−11
B) 5.9 × 10−11
C) 1.6 × 10−9
D) 1.7 × 1010
E) 5.1 × 1010
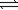 2HCl(g)
2HCl(g)A) 2.0 × 10−11
B) 5.9 × 10−11
C) 1.6 × 10−9
D) 1.7 × 1010
E) 5.1 × 1010

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? MgCO3(s) 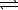 MgO(s)+ CO2(g)
MgO(s)+ CO2(g)
A)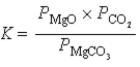
B)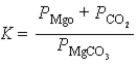
C)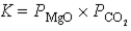
D)
E)
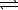 MgO(s)+ CO2(g)
MgO(s)+ CO2(g)A)
B)
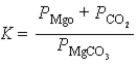
C)
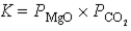
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Given the following chemical equilibria,
Determine the method used to calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction below.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
Determine the method used to calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction below.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following reactions is a homogeneous equilibrium expression?
A) CaCO3(s) CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
B) NH3(g)+ HCl(g) NH4Cl(s)
NH4Cl(s)
C) Mg(s)+ Cl2(g) MgCl2(s)
MgCl2(s)
D) FeO(s)+ CO(g) Fe(s)+ CO2(g)
Fe(s)+ CO2(g)
E) 2NO(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
A) CaCO3(s)
 CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)B) NH3(g)+ HCl(g)
 NH4Cl(s)
NH4Cl(s)C) Mg(s)+ Cl2(g)
 MgCl2(s)
MgCl2(s)D) FeO(s)+ CO(g)
 Fe(s)+ CO2(g)
Fe(s)+ CO2(g)E) 2NO(g)+ O2(g)
 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? CO2(g)+ 2H2O(g) 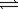 CH4(g)+ 2O2(g)
CH4(g)+ 2O2(g)
A)
B)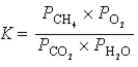
C)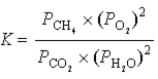
D)
E) none of the above
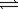 CH4(g)+ 2O2(g)
CH4(g)+ 2O2(g)A)

B)
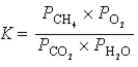
C)
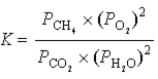
D)

E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following reactions is a heterogeneous equilibrium expression?
A) 2NO(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
B) 2NH3(g) N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
C) 2H2(g)+ O2(g)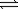 2H2O(g)
2H2O(g)
D) 2S(s)+ 3O2(g)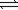 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)
E) C2H4(g)+ H2(g)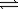 C2H6(g)
C2H6(g)
A) 2NO(g)+ O2(g)
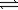 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)B) 2NH3(g)
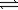 N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
N2(g)+ 3H2(g)C) 2H2(g)+ O2(g)
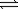 2H2O(g)
2H2O(g)D) 2S(s)+ 3O2(g)
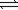 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)E) C2H4(g)+ H2(g)
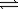 C2H6(g)
C2H6(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
At 25°C,the partial pressure of gases at equilibrium are as follows: N2 = 0.12 atm,O2 = 0.040 atm,and NO = 4.5 × 10−17 atm.What is the value of the equilibrium constant,K? N2(g)+ O2(g) 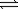 2NO(g)
2NO(g)
A) 4.2 × 10−31
B) 5.2 × 10−21
C) 9.4 × 10−15
D) 1.1 × 1014
E) 2.4 × 1030
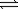 2NO(g)
2NO(g)A) 4.2 × 10−31
B) 5.2 × 10−21
C) 9.4 × 10−15
D) 1.1 × 1014
E) 2.4 × 1030

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 345. A + 2B 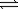 3C + D
3C + D
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction below?
2A + 4B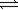 6C + 2D
6C + 2D
A) K = 345
B) K = (345)2 = 1.19 × 105
C) K = (345)1/2 = 18.6
D) K = (2 × 345)2 = 4.76 × 105
E) K = 2 × (345)2 = 2.38 × 105
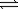 3C + D
3C + DWhat is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction below?
2A + 4B
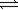 6C + 2D
6C + 2DA) K = 345
B) K = (345)2 = 1.19 × 105
C) K = (345)1/2 = 18.6
D) K = (2 × 345)2 = 4.76 × 105
E) K = 2 × (345)2 = 2.38 × 105

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Nitrosyl bromide decomposes according to the chemical equation below. 2NOBr(g) 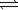 2NO(g)+ Br2(g)
2NO(g)+ Br2(g)
1)00 atm of NOBr is sealed in a flask.At equilibrium,the partial pressure of NOBr is 0.82 atm.What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction?
A) 3.6 × 10−3
B) 8.7 × 10−3
C) 2.8 × 10−2
D) 3.5 × 10−2
E) 4.3 × 10−3
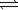 2NO(g)+ Br2(g)
2NO(g)+ Br2(g)1)00 atm of NOBr is sealed in a flask.At equilibrium,the partial pressure of NOBr is 0.82 atm.What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction?
A) 3.6 × 10−3
B) 8.7 × 10−3
C) 2.8 × 10−2
D) 3.5 × 10−2
E) 4.3 × 10−3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
At 25°C,the decomposition of dinitrogen tetraoxide N2O4(g) 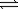 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Has an equilibrium constant (K)of 0.144.If the equilibrium pressure of nitrogen dioxide is 0.298 atm,what is the pressure of dinitrogen tetraoxide?
A) 0.0128 atm
B) 0.617 atm
C) 1.03 atm
D) 1.62 atm
E) 2.07 atm
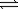 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)Has an equilibrium constant (K)of 0.144.If the equilibrium pressure of nitrogen dioxide is 0.298 atm,what is the pressure of dinitrogen tetraoxide?
A) 0.0128 atm
B) 0.617 atm
C) 1.03 atm
D) 1.62 atm
E) 2.07 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Assume that the following chemical reaction is at equilibrium. 2ICl(g) 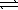 I2(g)+ Cl2(g)
I2(g)+ Cl2(g)
ΔH° = +26.9 kJ
At 25°C,K = 2.0 × 105.If the temperature is increase to 45°C,which statement applies?
A) K will decrease and the reaction will proceed in the backward direction.
B) K will decrease and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction.
C) K will remain unchanged and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction.
D) K will increase and the reaction will proceed in the backward direction.
E) K will increase and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction.
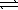 I2(g)+ Cl2(g)
I2(g)+ Cl2(g)ΔH° = +26.9 kJ
At 25°C,K = 2.0 × 105.If the temperature is increase to 45°C,which statement applies?
A) K will decrease and the reaction will proceed in the backward direction.
B) K will decrease and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction.
C) K will remain unchanged and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction.
D) K will increase and the reaction will proceed in the backward direction.
E) K will increase and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For the following reaction,the equilibrium constant (K)equals 21.2. SnO2(s)+ 2H2(g) 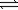 Sn(s)+ 2H2O(g)
Sn(s)+ 2H2O(g)
At equilibrium,the total pressure of the system is 0.390 atm.What is the partial pressure of each gas?
A) 0.0303 atm H2;0.360 atm H2O
B) 0.0522 atm H2;0.339 atm H2O
C) 0.0696 atm H2;0.320 atm H2O
D) 0.320 atm H2;0.0696 atm H2O
E) 0.339 atm H2;0.0522 atm H2O
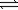 Sn(s)+ 2H2O(g)
Sn(s)+ 2H2O(g)At equilibrium,the total pressure of the system is 0.390 atm.What is the partial pressure of each gas?
A) 0.0303 atm H2;0.360 atm H2O
B) 0.0522 atm H2;0.339 atm H2O
C) 0.0696 atm H2;0.320 atm H2O
D) 0.320 atm H2;0.0696 atm H2O
E) 0.339 atm H2;0.0522 atm H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In which of the following equilibrium systems would an increase in volume (at constant temperature)cause the reaction to shift to the right?
A) N2O4(g)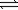 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
B) N2(g)+ 3H2(g)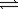 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
C) H2(g)+ Cl2(g)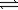 2HCl(g)
2HCl(g)
D) Answers a and b are correct.
E) Answers b and c are correct.
A) N2O4(g)
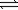 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)B) N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
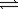 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)C) H2(g)+ Cl2(g)
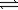 2HCl(g)
2HCl(g)D) Answers a and b are correct.
E) Answers b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For the system CO(g)+ H2O(g) 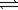 CO2(g)+ H2(g)
CO2(g)+ H2(g)
K is 1.6 at 900 K.If 0.400 atm CO(g)and 0.400 atm H2O(g)are combined in a sealed flask,what is the equilibrium partial pressure of CO2(g)?
A) 0.22 atm
B) 0.31 atm
C) 0.47 atm
D) 0.51 atm
E) 0.65 atm
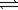 CO2(g)+ H2(g)
CO2(g)+ H2(g)K is 1.6 at 900 K.If 0.400 atm CO(g)and 0.400 atm H2O(g)are combined in a sealed flask,what is the equilibrium partial pressure of CO2(g)?
A) 0.22 atm
B) 0.31 atm
C) 0.47 atm
D) 0.51 atm
E) 0.65 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In which of the following equilibrium systems will an increase in the pressure have no effect on the concentrations of products and reactants?
A) H2(g)+ F2(g)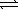 2 HF(g)
2 HF(g)
B) N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)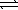 2 NH3(g)
2 NH3(g)
C) CaCO3(s) CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
D) 2 NOBr(g) 2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)
2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)
E) 2 H2O(g)+ O2(g) 2 H2O2(g)
2 H2O2(g)
A) H2(g)+ F2(g)
 2 HF(g)
2 HF(g)B) N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)
 2 NH3(g)
2 NH3(g)C) CaCO3(s)
 CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)D) 2 NOBr(g)
 2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)
2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)E) 2 H2O(g)+ O2(g)
 2 H2O2(g)
2 H2O2(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The equilibrium constant,Kp,for the reaction below is 0.24 at 1500°C. SO3(g)+ NO(g) 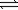 SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
If 0.30 atm of sulfur trioxide,0.15 atm of nitrogen monoxide,0.55 atm of sulfur dioxide,and 0.030 atm of nitrogen dioxide are mixed,what changes in pressure will occur?
A) The pressures of SO3 and NO decrease;the pressures of SO2 and NO2 increase.
B) The pressures of SO3 and NO increase;the pressures of SO2 and NO2 decrease.
C) The pressures of SO3 and SO2 decrease;the pressures of NO and NO2 increase.
D) The pressures of SO3 and SO2 increase;the pressures of NO and NO2 decrease.
E) Equal numbers of particles exist on both sides of the equation;no reaction will occur.
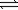 SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)If 0.30 atm of sulfur trioxide,0.15 atm of nitrogen monoxide,0.55 atm of sulfur dioxide,and 0.030 atm of nitrogen dioxide are mixed,what changes in pressure will occur?
A) The pressures of SO3 and NO decrease;the pressures of SO2 and NO2 increase.
B) The pressures of SO3 and NO increase;the pressures of SO2 and NO2 decrease.
C) The pressures of SO3 and SO2 decrease;the pressures of NO and NO2 increase.
D) The pressures of SO3 and SO2 increase;the pressures of NO and NO2 decrease.
E) Equal numbers of particles exist on both sides of the equation;no reaction will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
At 25°C,the decomposition of dinitrogen tetraoxide N2O4(g) 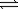 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Has an equilibrium constant (K)of 0.144.At equilibrium,the total pressure of the system is 0.500 atm.What is the partial pressure of each gas?
A) N2O4 = 0.206 atm;NO2 = 0.294 atm
B) N2O4 = 0.212 atm;NO2 = 0.288 atm
C) N2O4 = 0.288 atm;NO2 = 0.212 atm
D) N2O4 = 0.294 atm;NO2 = 0.206 atm
E) N2O4 = 0.437 atm;NO2 = 0.063 atm
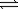 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)Has an equilibrium constant (K)of 0.144.At equilibrium,the total pressure of the system is 0.500 atm.What is the partial pressure of each gas?
A) N2O4 = 0.206 atm;NO2 = 0.294 atm
B) N2O4 = 0.212 atm;NO2 = 0.288 atm
C) N2O4 = 0.288 atm;NO2 = 0.212 atm
D) N2O4 = 0.294 atm;NO2 = 0.206 atm
E) N2O4 = 0.437 atm;NO2 = 0.063 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The equilibrium constant for a gas phase reaction is measured at two temperatures.At 100°C,the equilibrium constant is 36.At 200°C,the equilibrium constant is 147.Which of the following statements is correct for this equilibrium?
A) The reaction must be first-order.
B) The reaction is endothermic.
C) A catalyst must be present.
D) Each reactant molecule decomposes into two or more product molecules.
E) One of the products must be a solid.
A) The reaction must be first-order.
B) The reaction is endothermic.
C) A catalyst must be present.
D) Each reactant molecule decomposes into two or more product molecules.
E) One of the products must be a solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Hydrogen iodide can decompose into hydrogen and iodine gases. 2HI(g) 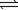 H2(g)+ I2(g)
H2(g)+ I2(g)
K for the reaction is 0.016.If 0.148 atm of HI(g)is sealed in a flask,what is the pressure of each gas when equilibrium is established?
A) HI = 0.118 atm;H2 = 0.015 atm;I2 = 0.015 atm
B) HI = 0.133 atm;H2 = 0.015 atm;I2 = 0.015 atm
C) HI = 0.110 atm;H2 = 0.019 atm;I2 = 0.019 atm
D) HI = 0.126 atm;H2 = 0.022 atm;I2 = 0.022 atm
E) HI = 0.174 atm;H2 = 0.022 atm;I2 = 0.022 atm
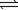 H2(g)+ I2(g)
H2(g)+ I2(g)K for the reaction is 0.016.If 0.148 atm of HI(g)is sealed in a flask,what is the pressure of each gas when equilibrium is established?
A) HI = 0.118 atm;H2 = 0.015 atm;I2 = 0.015 atm
B) HI = 0.133 atm;H2 = 0.015 atm;I2 = 0.015 atm
C) HI = 0.110 atm;H2 = 0.019 atm;I2 = 0.019 atm
D) HI = 0.126 atm;H2 = 0.022 atm;I2 = 0.022 atm
E) HI = 0.174 atm;H2 = 0.022 atm;I2 = 0.022 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The formation of ammonia from elemental nitrogen and hydrogen is an exothermic process.
Assuming the reaction is at equilibrium,which one of the following changes will drive the reaction to the right?
A) adding ammonia
B) increasing the temperature
C) increasing the pressure
D) removing hydrogen
E) adding a catalyst
Assuming the reaction is at equilibrium,which one of the following changes will drive the reaction to the right?
A) adding ammonia
B) increasing the temperature
C) increasing the pressure
D) removing hydrogen
E) adding a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Nitrosyl chloride decomposes according to the chemical equation below. 2NOCl(g) 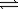 2NO(g)+ Cl2(g)
2NO(g)+ Cl2(g)
A pressure of 0.320 atm of nitrosyl chloride is sealed in a flask and allowed to reach equilibrium.If 22.6% of the NOCl decomposes,what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction?
A) 0.00153
B) 0.00308
C) 0.00611
D) 0.00730
E) 0.02471
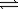 2NO(g)+ Cl2(g)
2NO(g)+ Cl2(g)A pressure of 0.320 atm of nitrosyl chloride is sealed in a flask and allowed to reach equilibrium.If 22.6% of the NOCl decomposes,what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction?
A) 0.00153
B) 0.00308
C) 0.00611
D) 0.00730
E) 0.02471

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Hydrogen iodide can decompose into hydrogen and iodine gases. 2HI(g) 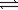 H2(g)+ I2(g)
H2(g)+ I2(g)
Kp for the reaction is 0.016.If 0.350 atm of HI(g)is sealed in a flask,what is the total pressure of the system when equilibrium is established?
A) 0.258 atm
B) 0.279 atm
C) 0.350 atm
D) 0.385 atm
E) 0.412 atm
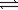 H2(g)+ I2(g)
H2(g)+ I2(g)Kp for the reaction is 0.016.If 0.350 atm of HI(g)is sealed in a flask,what is the total pressure of the system when equilibrium is established?
A) 0.258 atm
B) 0.279 atm
C) 0.350 atm
D) 0.385 atm
E) 0.412 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Nitrogen can react with oxygen to form nitrogen monoxide. N2(g)+ O2(g) 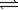 2NO(g)
2NO(g)
K = 1.0 × 10−30 at 25°C
When equilibrium is established,the partial pressures of nitrogen and oxygen are 1.2 atm and 3.1 atm,respectively.What is the equilibrium pressure of nitrogen monoxide?
A) 3.7 × 10−30 atm
B) 1.9 × 10−15 atm
C) 2.7 × 10−13 atm
D) 1.9 × 10−10 atm
E) 3.7 × 10−7 atm
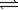 2NO(g)
2NO(g)K = 1.0 × 10−30 at 25°C
When equilibrium is established,the partial pressures of nitrogen and oxygen are 1.2 atm and 3.1 atm,respectively.What is the equilibrium pressure of nitrogen monoxide?
A) 3.7 × 10−30 atm
B) 1.9 × 10−15 atm
C) 2.7 × 10−13 atm
D) 1.9 × 10−10 atm
E) 3.7 × 10−7 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
At sufficiently high temperatures,ammonium iodide decomposes to ammonia and hydrogen iodide. NH4I(s) 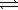 NH3(g)+ HI(g)
NH3(g)+ HI(g)
A mass of 5.00 g of NH4I is sealed in a 2.00-L flask and heated to 673 K.If 2.56 g NH4I(s)remain unreacted when the system has reached equilibrium,what is the equilibrium constant (Kp)for the reaction? (R = 0.0821 L⋅atm/mol⋅K)
A) 0.15
B) 0.22
C) 0.47
D) 0.59
E) 0.89
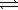 NH3(g)+ HI(g)
NH3(g)+ HI(g)A mass of 5.00 g of NH4I is sealed in a 2.00-L flask and heated to 673 K.If 2.56 g NH4I(s)remain unreacted when the system has reached equilibrium,what is the equilibrium constant (Kp)for the reaction? (R = 0.0821 L⋅atm/mol⋅K)
A) 0.15
B) 0.22
C) 0.47
D) 0.59
E) 0.89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
At a given temperature,the equilibrium constant (Kp)for the decomposition of dinitrogen tetraoxide to nitrogen dioxide is 0.172.If 0.224 atm N2O4 is sealed in a flask,what partial pressure of NO2 will exist at equilibrium? N2O4(g) 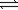 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
A) 0.0385 atm
B) 0.158 atm
C) 0.196 atm
D) 0.257 atm
E) 0.379 atm
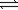 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)A) 0.0385 atm
B) 0.158 atm
C) 0.196 atm
D) 0.257 atm
E) 0.379 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
For the reaction 2A 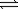 3B
3B
Kc = 1.37.If the concentrations of A and B are equal,what is the value of that concentration?
A) 0.685 M
B) 0.822 M
C) 1.17 M
D) 1.37 M
E) 1.88 M
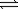 3B
3BKc = 1.37.If the concentrations of A and B are equal,what is the value of that concentration?
A) 0.685 M
B) 0.822 M
C) 1.17 M
D) 1.37 M
E) 1.88 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the following equilibrium: N2(g)+ O2(g) 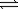 2NO(g)
2NO(g)
At a certain temperature the equilibrium constant for the reaction is 0.0255.What is the partial pressure of NO gas at equilibrium if the initial pressure of all the gases (both reactants and products)is 0.300 atm?
A) 6.65 × 10−2
B) 0.183
C) 0.234
D) 0.252
E) 0.417
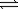 2NO(g)
2NO(g)At a certain temperature the equilibrium constant for the reaction is 0.0255.What is the partial pressure of NO gas at equilibrium if the initial pressure of all the gases (both reactants and products)is 0.300 atm?
A) 6.65 × 10−2
B) 0.183
C) 0.234
D) 0.252
E) 0.417

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The reaction of nitrogen gas and oxygen gas to form nitrogen monoxide, N2(g)+ O2(g) 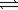 2NO(g)
2NO(g)
Has an equilibrium constant of 1.0 × 10−30 at 298 K.What equilibrium partial pressure of NO(g)will form if 0.50 atm of N2 and 0.50 atm of O2 are sealed in a flask at 298 K?
A) 1.0 × 10−60 atm
B) 5.0 × 10−31 atm
C) 1.0 × 10−30 atm
D) 1.0 × 10−15 atm
E) 5.0 × 10−16 atm
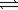 2NO(g)
2NO(g)Has an equilibrium constant of 1.0 × 10−30 at 298 K.What equilibrium partial pressure of NO(g)will form if 0.50 atm of N2 and 0.50 atm of O2 are sealed in a flask at 298 K?
A) 1.0 × 10−60 atm
B) 5.0 × 10−31 atm
C) 1.0 × 10−30 atm
D) 1.0 × 10−15 atm
E) 5.0 × 10−16 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
"If a chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed by adding a gaseous species (reactant or product),the reaction will proceed in such a direction as to consume part of the added species" is a statement of
A) the ideal gas law.
B) Le Châtelier's principle.
C) the de Broglie equation.
D) the van't Hoff equation.
E) the first law of thermodynamics.
A) the ideal gas law.
B) Le Châtelier's principle.
C) the de Broglie equation.
D) the van't Hoff equation.
E) the first law of thermodynamics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Calcium carbonate decomposes to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. CaCO3(s) 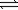 CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
ΔH° = +179 kJ
The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 9.7 × 10−24 at 298 K.What is the equilibrium constant at 575 K? (R = 8.31 J/mol⋅K)
A) 7.5 × 10−16
B) 1.3 × 10−8
C) 1.4 × 1038
D) 1.3 × 1015
E) 1.0 × 1023
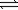 CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)ΔH° = +179 kJ
The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 9.7 × 10−24 at 298 K.What is the equilibrium constant at 575 K? (R = 8.31 J/mol⋅K)
A) 7.5 × 10−16
B) 1.3 × 10−8
C) 1.4 × 1038
D) 1.3 × 1015
E) 1.0 × 1023

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the reaction A(g) 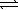 2B(g)where Kp = 4.1 at 25°C.If 0.75 atm A(g)and 1.5 atm B(g)are initially present in a 1.0 L flask at 25°C,what change in partial pressures (if any)will occur in time?
2B(g)where Kp = 4.1 at 25°C.If 0.75 atm A(g)and 1.5 atm B(g)are initially present in a 1.0 L flask at 25°C,what change in partial pressures (if any)will occur in time?
A) The partial pressure of A will decrease and the partial pressure of B will decrease.
B) The partial pressure of A will decrease and the partial pressure of B will increase.
C) The partial pressure of A will increase and the partial pressure of B will decrease.
D) The partial pressure of A will increase and the partial pressure of B will increase.
E) The partial pressures of both A and B will remain unchanged.
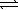 2B(g)where Kp = 4.1 at 25°C.If 0.75 atm A(g)and 1.5 atm B(g)are initially present in a 1.0 L flask at 25°C,what change in partial pressures (if any)will occur in time?
2B(g)where Kp = 4.1 at 25°C.If 0.75 atm A(g)and 1.5 atm B(g)are initially present in a 1.0 L flask at 25°C,what change in partial pressures (if any)will occur in time?A) The partial pressure of A will decrease and the partial pressure of B will decrease.
B) The partial pressure of A will decrease and the partial pressure of B will increase.
C) The partial pressure of A will increase and the partial pressure of B will decrease.
D) The partial pressure of A will increase and the partial pressure of B will increase.
E) The partial pressures of both A and B will remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen to form ammonia is thermodynamically favorable. N2(g)+ 3H2(g) 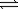 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
ΔH° = −92.2 kJ
The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 6.0 × 105 at 298 K.At what temperature is the equilibrium constant equal to 1.0 × 103? (R = 8.31 J/mol⋅K)
A) 85 K
B) 110 K
C) 310 K
D) 360 K
E) 2800 K
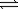 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)ΔH° = −92.2 kJ
The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 6.0 × 105 at 298 K.At what temperature is the equilibrium constant equal to 1.0 × 103? (R = 8.31 J/mol⋅K)
A) 85 K
B) 110 K
C) 310 K
D) 360 K
E) 2800 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the value of Q is less than Kp,then
A) the system is in equilibrium.
B) a catalyst is necessary to achieve equilibrium.
C) the reaction will go left or right depending upon the reaction stoichiometry.
D) the reaction will proceed to the right until equilibrium is established.
E) the reaction will proceed to the left until equilibrium is established.
A) the system is in equilibrium.
B) a catalyst is necessary to achieve equilibrium.
C) the reaction will go left or right depending upon the reaction stoichiometry.
D) the reaction will proceed to the right until equilibrium is established.
E) the reaction will proceed to the left until equilibrium is established.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A 2.5 L flask is filled with 0.25 atm SO3,0.20 atm SO2,and 0.40 atm O2,and allowed to reach equilibrium.Assume the temperature of the mixture is chosen so that Kp = 0.12.Predict the effect on the partial pressure of SO3 as equilibrium is achieved by using Q,the reaction quotient. 2 SO3(g) 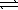 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)
A) The partial pressure of SO3 will decrease because Q > K.
B) The partial pressure of SO3 will decrease because Q < K.
C) The partial pressure of SO3 will increase because Q < K.
D) The partial pressure of SO3 will increase because Q > K.
E) The partial pressure of SO3 will remain the same because Q = K.
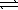 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)A) The partial pressure of SO3 will decrease because Q > K.
B) The partial pressure of SO3 will decrease because Q < K.
C) The partial pressure of SO3 will increase because Q < K.
D) The partial pressure of SO3 will increase because Q > K.
E) The partial pressure of SO3 will remain the same because Q = K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The Haber process for the production of ammonia relies on high temperatures and pressures.Which of these,high temperatures or pressures,actually reduce the yield of the reaction at equilibrium? N2(g)+ 3H2(g) 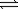 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
ΔH° = −92.2 kJ
A) High pressure
B) High temperature
C) Both
D) Neither
E) Can't be determined
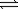 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)ΔH° = −92.2 kJ
A) High pressure
B) High temperature
C) Both
D) Neither
E) Can't be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For the reaction C(s)+ CO2(g) ![<strong>For the reaction C(s)+ CO<sub>2</sub>(g) 2CO(g) K<sub>c</sub> = 168.A mixture contains some C(s),[CO] = 0.50 M and [CO<sub>2</sub>] = 0.75 M.Therefore the system ____ at equilibrium,because ____.</strong> A) is not;the value of Q is 0.67 B) is not;the value of Q is 1.5 C) is;the value of Q is 0.67 D) is not;the value of Q is 0.33 E) is;the value of Q is 0.33](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7574/11eac50a_b318_7284_b234_ddf2b9577846_TB7574_11.jpg) 2CO(g)
2CO(g)
Kc = 168.A mixture contains some C(s),[CO] = 0.50 M and [CO2] = 0.75 M.Therefore the system ____ at equilibrium,because ____.
A) is not;the value of Q is 0.67
B) is not;the value of Q is 1.5
C) is;the value of Q is 0.67
D) is not;the value of Q is 0.33
E) is;the value of Q is 0.33
![<strong>For the reaction C(s)+ CO<sub>2</sub>(g) 2CO(g) K<sub>c</sub> = 168.A mixture contains some C(s),[CO] = 0.50 M and [CO<sub>2</sub>] = 0.75 M.Therefore the system ____ at equilibrium,because ____.</strong> A) is not;the value of Q is 0.67 B) is not;the value of Q is 1.5 C) is;the value of Q is 0.67 D) is not;the value of Q is 0.33 E) is;the value of Q is 0.33](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7574/11eac50a_b318_7284_b234_ddf2b9577846_TB7574_11.jpg) 2CO(g)
2CO(g)Kc = 168.A mixture contains some C(s),[CO] = 0.50 M and [CO2] = 0.75 M.Therefore the system ____ at equilibrium,because ____.
A) is not;the value of Q is 0.67
B) is not;the value of Q is 1.5
C) is;the value of Q is 0.67
D) is not;the value of Q is 0.33
E) is;the value of Q is 0.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Haber process for the production of ammonia relies on a heterogeneous catalyst.How does the use of this catalyst effect the yield of the reaction at equilibrium?
A) Yield is increased
B) Yield is decreased
C) Depends on the catalyst used
D) Doesn't effect yield
E) Can't be determined
A) Yield is increased
B) Yield is decreased
C) Depends on the catalyst used
D) Doesn't effect yield
E) Can't be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



