Deck 5: Other Corporate Tax Levies
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/104
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Other Corporate Tax Levies
1
The general business credit can be used to offset the alternative minimum tax.
False
2
The minimum tax credit available for a corporation's alternative minimum tax liability can be carried forward indefinitely and offsets regular tax liabilities in future years.
True
3
The NOL deduction is calculated the same for regular and alternative minimum tax purposes.
False
4
The alternative minimum tax is the excess of the tentative minimum tax amount over the regular tax amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
All corporations, except S corporations and small C corporations, must calculate the ACE adjustment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) The corporate alternative minimum tax rate is 35%.
B) No credits are allowed when computing the tentative minimum tax.
C) Tax preference items always increase alternative minimum taxable income.
D) All of the above are false.
A) The corporate alternative minimum tax rate is 35%.
B) No credits are allowed when computing the tentative minimum tax.
C) Tax preference items always increase alternative minimum taxable income.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To avoid the accumulated earnings tax, a corporation needs to have a definite plan for expending the accumulated earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Wind Corporation is a personal holding company. Its taxable income for this year is $100,000. The corporation's charitable contributions are $5,000 greater than its income tax charitable contribution deduction limitation. Wind's UPHCI is $95,000, assuming no other adjustments must be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the last three years, Wolf Corporation had gross receipts of $3,000,000, $5,000,000, and $10,000,000. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Wolf receives a statutory exemption of $40,000 based on its receipts.
B) Wolf is exempt from the AMT.
C) Wolf is subject to the AMT in the current year.
D) There is insufficient information to determine whether Wolf is subject to the AMT.
A) Wolf receives a statutory exemption of $40,000 based on its receipts.
B) Wolf is exempt from the AMT.
C) Wolf is subject to the AMT in the current year.
D) There is insufficient information to determine whether Wolf is subject to the AMT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify which of the following statements is false.
A) The corporate AMT produces relatively little tax revenue.
B) The small corporation AMT exemption exempts 95% of all corporations from the AMT.
C) The corporate AMT is similar to the AMT for individuals.
D) The starting point for computing a corporation's AMT is book income.
A) The corporate AMT produces relatively little tax revenue.
B) The small corporation AMT exemption exempts 95% of all corporations from the AMT.
C) The corporate AMT is similar to the AMT for individuals.
D) The starting point for computing a corporation's AMT is book income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The ACE adjustment always increases alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Small C corporation exemption from AMT continues as long as average gross receipts for the three preceding tax years are
A) $6.5 million or less.
B) $7.0 million or less.
C) $7.5 million or less.
D) $8.0 million or less.
A) $6.5 million or less.
B) $7.0 million or less.
C) $7.5 million or less.
D) $8.0 million or less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Foggy Corporation has regular taxable income of $1,200,000. It has $250,000 of interest income on private activity bonds and $100,000 of interest on City of New Orleans bonds. How much is Foggy's preadjustment AMTI?
A) $1,200,000
B) $1,350,000
C) $1,450,000
D) $1,550,000
A) $1,200,000
B) $1,350,000
C) $1,450,000
D) $1,550,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Corporations cannot use the installment method in calculating alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI) for noninventory items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Life insurance proceeds are a positive adjustment for adjusted current earnings (ACE), but not alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) Depreciation on real property may be a tax preference item for purposes of computing AMT.
B) Depreciation on real property may be an adjustment item for purposes of computing AMT.
C) Adjustments to taxable income always increase alternative minimum taxable income.
D) Both A and B are true.
A) Depreciation on real property may be a tax preference item for purposes of computing AMT.
B) Depreciation on real property may be an adjustment item for purposes of computing AMT.
C) Adjustments to taxable income always increase alternative minimum taxable income.
D) Both A and B are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When computing a corporation's alternative minimum taxable income, its taxable income is
A) only increased (never decreased) by tax preference items.
B) only increased (never decreased) by adjustments.
C) increased by the statutory exemption of $40,000.
D) increased by 75% of the excess of adjusted current earnings over taxable income.
A) only increased (never decreased) by tax preference items.
B) only increased (never decreased) by adjustments.
C) increased by the statutory exemption of $40,000.
D) increased by 75% of the excess of adjusted current earnings over taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A corporation can be subject to both the accumulated earnings tax and the personal holding company tax in the same year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify which of the following statements is false.
A) The alternative minimum tax is the excess of the tentative minimum tax amount over the regular tax amount.
B) All corporations with gross receipts of less than $10 million are exempt from the AMT.
C) If the firm does not qualify for Small C corporation status, the C corporation statutory exemption amount for alternative minimum tax purposes is phased out when alternative minimum taxable income reaches $310,000.
D) The purpose of the AMT is to ensure that every taxpayer with substantial economic income pays a minimum tax.
A) The alternative minimum tax is the excess of the tentative minimum tax amount over the regular tax amount.
B) All corporations with gross receipts of less than $10 million are exempt from the AMT.
C) If the firm does not qualify for Small C corporation status, the C corporation statutory exemption amount for alternative minimum tax purposes is phased out when alternative minimum taxable income reaches $310,000.
D) The purpose of the AMT is to ensure that every taxpayer with substantial economic income pays a minimum tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following items are tax preference items for purposes of arriving at alternative minimum taxable income?
A) excess intangible drilling costs on oil and gas properties
B) interest income earned on federal obligations
C) all depreciation claimed on pre-1987 real property acquisitions
D) excess of net long-term capital gains over short-term capital losses
A) excess intangible drilling costs on oil and gas properties
B) interest income earned on federal obligations
C) all depreciation claimed on pre-1987 real property acquisitions
D) excess of net long-term capital gains over short-term capital losses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify which of the following statements is false.
A) Adjusted current earnings (ACE) is the same as E&P.
B) A corporation's positive adjusted current earnings (ACE) adjustment equals 75% of the excess of its ACE over its preadjustment AMTI (AMTI before this adjustment and the alternative tax NOL deduction).
C) A corporation's negative adjusted current earnings (ACE) adjustment equals 75% of the excess of its preadjustment AMTI (AMTI before this adjustment and the alternative tax NOL deduction) over its ACE, but may not exceed the cumulative "net" ACE adjustment amounts from all post-1989 tax years.
D) The ACE adjustment is not required of S corporations.
A) Adjusted current earnings (ACE) is the same as E&P.
B) A corporation's positive adjusted current earnings (ACE) adjustment equals 75% of the excess of its ACE over its preadjustment AMTI (AMTI before this adjustment and the alternative tax NOL deduction).
C) A corporation's negative adjusted current earnings (ACE) adjustment equals 75% of the excess of its preadjustment AMTI (AMTI before this adjustment and the alternative tax NOL deduction) over its ACE, but may not exceed the cumulative "net" ACE adjustment amounts from all post-1989 tax years.
D) The ACE adjustment is not required of S corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) The minimum tax credit carries forward indefinitely and offsets regular tax liabilities in future years.
B) The minimum tax credit available for a corporation's alternative minimum tax liability can be carried over for five years.
C) The general business credit is permitted to offset 100% of the larger of (1) a corporation's regular tax amount, or (2) its tentative minimum tax amount.
D) All of the above are false.
A) The minimum tax credit carries forward indefinitely and offsets regular tax liabilities in future years.
B) The minimum tax credit available for a corporation's alternative minimum tax liability can be carried over for five years.
C) The general business credit is permitted to offset 100% of the larger of (1) a corporation's regular tax amount, or (2) its tentative minimum tax amount.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Certain adjustments must be made to alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI) to arrive at adjusted current earnings (ACE). Which one of the following adjustments increases AMTI to arrive at ACE?
A) federal income taxes paid
B) the 80% dividends-received deduction
C) gain realized on the installment sale of noninventory property
D) excess of capital losses over capital gains
A) federal income taxes paid
B) the 80% dividends-received deduction
C) gain realized on the installment sale of noninventory property
D) excess of capital losses over capital gains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following items are adjustments made to arrive at alternative minimum taxable income?
A) excess percentage depletion
B) excess of deprecation claimed on personalty acquired in the current year for taxable income purposes over that claimed for alternative minimum tax purposes
C) tax-exempt interest income earned on private activity bonds
D) statutory exemption
A) excess percentage depletion
B) excess of deprecation claimed on personalty acquired in the current year for taxable income purposes over that claimed for alternative minimum tax purposes
C) tax-exempt interest income earned on private activity bonds
D) statutory exemption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Beta Corporation incurs an $80,000 regular tax liability and a $20,000 AMT liability. Assuming no restrictions on Beta's ability to use the minimum tax credit, what journal entry would be necessary to record tax expense?
A)
B)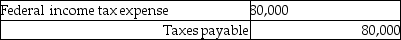
C)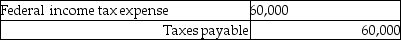
D)
A)

B)
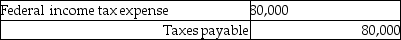
C)
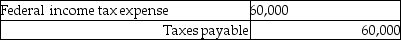
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Becky places five-year property in service during June 2014 using the half-year convention. Depreciation is $1,500 under the 150% declining balance method and $2,000 under 200% declining balance. Becky uses the 150% declining balance method for regular income tax purposes. What is the amount of Becky's AMT adjustment?
A) $0
B) $1,500 positive adjustment
C) $500 positive adjustment
D) $500 negative adjustment
A) $0
B) $1,500 positive adjustment
C) $500 positive adjustment
D) $500 negative adjustment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The personal holding company tax might be imposed
A) on both partnerships and corporations.
B) on companies whose gross income arises solely from rentals, if the lessors render no services to the lessees.
C) if more than 50% of the company is owned by five or fewer individuals for the entire year.
D) on small business investment companies licensed by the Small Business Administration.
A) on both partnerships and corporations.
B) on companies whose gross income arises solely from rentals, if the lessors render no services to the lessees.
C) if more than 50% of the company is owned by five or fewer individuals for the entire year.
D) on small business investment companies licensed by the Small Business Administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
ASC 740 requires that
A) the AMT is not considered as federal income tax expense.
B) companies must establish a valuation allowance for the minimum tax credit.
C) the minimum tax credit creates a deferred tax asset.
D) the minimum tax credit increases federal income tax expense.
A) the AMT is not considered as federal income tax expense.
B) companies must establish a valuation allowance for the minimum tax credit.
C) the minimum tax credit creates a deferred tax asset.
D) the minimum tax credit increases federal income tax expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) A corporation's adjusted current earnings (ACE) amount is calculated by making adjustments that are similar to those used in computing earnings and profits (E&P).
B) The adjusted current earnings (ACE) adjustment attempts to adjust the AMT tax base towards a corporation's economic income.
C) Adjusted current earnings (ACE) is computed beginning with preadjustment alternative minimum taxable income.
D) All of the above are true.
A) A corporation's adjusted current earnings (ACE) amount is calculated by making adjustments that are similar to those used in computing earnings and profits (E&P).
B) The adjusted current earnings (ACE) adjustment attempts to adjust the AMT tax base towards a corporation's economic income.
C) Adjusted current earnings (ACE) is computed beginning with preadjustment alternative minimum taxable income.
D) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Mountaineer, Inc. has the following results:  What is the amount of the alternative minimum tax?
What is the amount of the alternative minimum tax?
A) $0
B) $60,000
C) $100,000
D) none of the above
 What is the amount of the alternative minimum tax?
What is the amount of the alternative minimum tax?A) $0
B) $60,000
C) $100,000
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How does the deduction for U.S. production activities affect AMTI?
A) The computation of qualified production activities is the same for taxable income and AMTI.
B) The computation of qualified production activities is based on qualified production activities income for AMTI.
C) The computation of qualified production activities is based on AMTI before the deduction for qualified production activities.
D) The computation of qualified production activities is based on the lesser of qualified production activities income or AMTI before the deduction for qualified production activities.
A) The computation of qualified production activities is the same for taxable income and AMTI.
B) The computation of qualified production activities is based on qualified production activities income for AMTI.
C) The computation of qualified production activities is based on AMTI before the deduction for qualified production activities.
D) The computation of qualified production activities is based on the lesser of qualified production activities income or AMTI before the deduction for qualified production activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements regarding the minimum tax credit is correct?
A) It can only be carried forward.
B) It must be carried back before being carried forward.
C) Taxpayers may elect to forgo the carryback period and carry the credit forward.
D) There are not carryforwards or carrybacks of the minimum tax credit.
A) It can only be carried forward.
B) It must be carried back before being carried forward.
C) Taxpayers may elect to forgo the carryback period and carry the credit forward.
D) There are not carryforwards or carrybacks of the minimum tax credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Identify which of the following statements is false.
A) Tax-exempt interest on certain private activity bonds may be taxed under the alternative minimum tax.
B) Tax preference items and adjustments may either increase or decrease taxable income to obtain AMTI.
C) Depending on the date an asset is placed in service, depreciation may be an adjustment to taxable income or a tax preference item for alternative minimum tax purposes.
D) Different depreciation rules are used when computing taxable income and alternative minimum taxable income.
A) Tax-exempt interest on certain private activity bonds may be taxed under the alternative minimum tax.
B) Tax preference items and adjustments may either increase or decrease taxable income to obtain AMTI.
C) Depending on the date an asset is placed in service, depreciation may be an adjustment to taxable income or a tax preference item for alternative minimum tax purposes.
D) Different depreciation rules are used when computing taxable income and alternative minimum taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Tax-exempt interest income on state and local municipal bonds that are not a private activity is
A) a tax preference item.
B) a positive adjustment in calculating alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI).
C) a negative adjustment in calculating alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI).
D) included in calculating ACE (adjusted current earnings).
A) a tax preference item.
B) a positive adjustment in calculating alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI).
C) a negative adjustment in calculating alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI).
D) included in calculating ACE (adjusted current earnings).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) The ACE adjustment is required of S corporations.
B) The 70% dividends-received deduction reduces preadjustment AMTI to arrive at ACE.
C) The 80% dividends-received deduction can be claimed when computing a corporation's adjusted current earnings (ACE).
D) All of the above are false.
A) The ACE adjustment is required of S corporations.
B) The 70% dividends-received deduction reduces preadjustment AMTI to arrive at ACE.
C) The 80% dividends-received deduction can be claimed when computing a corporation's adjusted current earnings (ACE).
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Becky places five-year property in service during June 2014 using the half-year convention. Depreciation is $1,500 under the 150% declining balance method and $2,000 under 200% declining balance. Becky uses the 200% declining balance method for regular income tax purposes. What is the amount of Becky's AMT adjustment?
A) $0
B) $1,500 positive adjustment
C) $500 positive adjustment
D) $500 negative adjustment
A) $0
B) $1,500 positive adjustment
C) $500 positive adjustment
D) $500 negative adjustment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements about the alternative minimum tax depreciation rules is correct?
A) The MACRS depreciation rules are used to calculate the depreciation deduction when calculating alternative minimum taxable income regardless of the date the property was placed in service.
B) The excess of the gain reported on the disposition of tangible personal property for income tax purposes over the gain reported for alternative minimum tax purposes is a positive adjustment to taxable income in arriving at alternative minimum taxable income.
C) A 31.5-year recovery period is used when calculating the commercial real property depreciation deduction for alternative minimum taxable income purposes.
D) No depreciation adjustment is made when computing AMT for real property acquired after 1998.
A) The MACRS depreciation rules are used to calculate the depreciation deduction when calculating alternative minimum taxable income regardless of the date the property was placed in service.
B) The excess of the gain reported on the disposition of tangible personal property for income tax purposes over the gain reported for alternative minimum tax purposes is a positive adjustment to taxable income in arriving at alternative minimum taxable income.
C) A 31.5-year recovery period is used when calculating the commercial real property depreciation deduction for alternative minimum taxable income purposes.
D) No depreciation adjustment is made when computing AMT for real property acquired after 1998.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Foster Corporation has gross income for regular tax purposes of $100,000, which includes a net Sec. 1231 gain of $10,000 and a net capital gain of $10,000. Ordinary gross income for personal holding company purposes is
A) $70,000.
B) $80,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $100,000.
A) $70,000.
B) $80,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Mountaineer, Inc. has the following results:  What is the amount of the tentative minimum tax?
What is the amount of the tentative minimum tax?
A) $500,000
B) $360,000
C) $460,000
D) none of the above
 What is the amount of the tentative minimum tax?
What is the amount of the tentative minimum tax?A) $500,000
B) $360,000
C) $460,000
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not an adjustment in calculating AMTI?
A) gain on installment sales of noninventory property
B) the regular tax NOL deduction
C) production activities deduction
D) the difference between the gains for AMTI and regular tax purposes
A) gain on installment sales of noninventory property
B) the regular tax NOL deduction
C) production activities deduction
D) the difference between the gains for AMTI and regular tax purposes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A personal holding company cannot take a dividends-paid deduction for
A) throwback dividends.
B) consent dividends.
C) deficiency dividends.
D) preferential dividends.
A) throwback dividends.
B) consent dividends.
C) deficiency dividends.
D) preferential dividends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The personal holding company tax
A) may be imposed regardless of the number of equal stockholders in a corporation.
B) may be eliminated by the payment of a deficiency dividend.
C) qualifies as a tax credit, which may be used by the shareholders to reduce their individual income taxes.
D) applies to any corporation whose shareholders satisfy the stock ownership requirement.
A) may be imposed regardless of the number of equal stockholders in a corporation.
B) may be eliminated by the payment of a deficiency dividend.
C) qualifies as a tax credit, which may be used by the shareholders to reduce their individual income taxes.
D) applies to any corporation whose shareholders satisfy the stock ownership requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Dragon Corporation reports a distribution on its return from the third previous year as a stock redemption producing a capital gain. When the return is audited during the current year, the distribution of the third previous year is characterized by the IRS as a dividend. This change causes Dragon Corporation to be classified as a personal holding company for the third previous year. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Dragon Corporation will owe no interest and/or underpayment penalty if the PHC tax is avoided by a deficiency dividend.
B) Dragon Corporation will owe interest and/or underpayment penalty even if the PHC tax is avoided by a deficiency dividend.
C) A deficiency dividend is not permitted to be paid by Dragon.
D) A dividend must be paid within 120 days of establishing the PHC tax liability and a claim for a dividends-paid deduction must be filed within 90 days of the determination date.
A) Dragon Corporation will owe no interest and/or underpayment penalty if the PHC tax is avoided by a deficiency dividend.
B) Dragon Corporation will owe interest and/or underpayment penalty even if the PHC tax is avoided by a deficiency dividend.
C) A deficiency dividend is not permitted to be paid by Dragon.
D) A dividend must be paid within 120 days of establishing the PHC tax liability and a claim for a dividends-paid deduction must be filed within 90 days of the determination date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Identify which of the following statements is false.
A) Askew Corporation has ten unrelated shareholders, each of whom owns 10% of the outstanding stock. This corporation is a personal holding company.
B) Stock owned by an individual, in addition to stock attributed from her spouse, parents, children, and siblings, are all counted towards whether or not the personal holding company stock ownership test has been met.
C) S corporations and tax-exempt organizations are excluded from the personal holding company (PHC) definition.
D) A person who holds an option to acquire stock is considered to own the stock for purposes of the PHC stock requirements.
A) Askew Corporation has ten unrelated shareholders, each of whom owns 10% of the outstanding stock. This corporation is a personal holding company.
B) Stock owned by an individual, in addition to stock attributed from her spouse, parents, children, and siblings, are all counted towards whether or not the personal holding company stock ownership test has been met.
C) S corporations and tax-exempt organizations are excluded from the personal holding company (PHC) definition.
D) A person who holds an option to acquire stock is considered to own the stock for purposes of the PHC stock requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The accumulated earnings tax does not apply to corporations that
A) have more than one class of stock.
B) are personal holding companies.
C) are members of a controlled group.
D) are closely held corporations.
A) have more than one class of stock.
B) are personal holding companies.
C) are members of a controlled group.
D) are closely held corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
All of the following are recognized as reasons for accumulating earnings except
A) working capital needs.
B) product liability loss reserves.
C) redemption of stock of deceased shareholder.
D) All of the above are recognized reasons for accumulating earnings.
A) working capital needs.
B) product liability loss reserves.
C) redemption of stock of deceased shareholder.
D) All of the above are recognized reasons for accumulating earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) The personal holding company tax is levied to prevent closely held corporations from sheltering passive income.
B) Caleb Corporation is owned by a mother and her two daughters. It reports $100,000 of rental income, $30,000 of depreciation, interest, and property taxes on the rental real estate, and $10,000 of dividend income. Caleb Corporation is classified as a personal holding company.
C) Luke Corporation is owned by a father and his son. The corporation employs 10 individuals to provide public accounting services. Father and son make all of the work assignments for the professional employees. The professional fees earned by the corporation are personal holding company income.
D) All of the above are false.
A) The personal holding company tax is levied to prevent closely held corporations from sheltering passive income.
B) Caleb Corporation is owned by a mother and her two daughters. It reports $100,000 of rental income, $30,000 of depreciation, interest, and property taxes on the rental real estate, and $10,000 of dividend income. Caleb Corporation is classified as a personal holding company.
C) Luke Corporation is owned by a father and his son. The corporation employs 10 individuals to provide public accounting services. Father and son make all of the work assignments for the professional employees. The professional fees earned by the corporation are personal holding company income.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) In practice, the accumulated earnings tax applies only to closely held corporations.
B) A corporation bears the burden of proving that its earnings are not being accumulated to avoid income taxes.
C) To avoid the accumulated earnings tax, a corporation needs to have a definite plan for expending the accumulated earnings.
D) All of the above are true.
A) In practice, the accumulated earnings tax applies only to closely held corporations.
B) A corporation bears the burden of proving that its earnings are not being accumulated to avoid income taxes.
C) To avoid the accumulated earnings tax, a corporation needs to have a definite plan for expending the accumulated earnings.
D) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) Consent dividends are cash dividends paid following an authorizing vote of the shareholders.
B) Dividends that are paid in the two preceding tax years can be used as a dividend carryover to reduce the amount of the current year's personal holding company (PHC) tax liability.
C) Dividends paid by a personal holding company in the first 2 1/2 months of a tax year are automatically throwback dividends.
D) All of the above are false.
A) Consent dividends are cash dividends paid following an authorizing vote of the shareholders.
B) Dividends that are paid in the two preceding tax years can be used as a dividend carryover to reduce the amount of the current year's personal holding company (PHC) tax liability.
C) Dividends paid by a personal holding company in the first 2 1/2 months of a tax year are automatically throwback dividends.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Identify which of the following statements is false.
A) The 80% dividends-received deduction can be claimed when computing a corporation's undistributed personal holding company income (UPHCI).
B) Rental expenses in excess of rental income are added back to taxable income to arrive at personal holding company income (PHCI).
C) Wind Corporation is a personal holding company. Its taxable income for this year is $100,000. The corporation's charitable contributions are $5,000 greater than its income tax charitable contribution deduction limitation. Wind's UPHCI is $95,000, assuming no other adjustments must be made.
D) The PHC tax is assessed at 15%.
A) The 80% dividends-received deduction can be claimed when computing a corporation's undistributed personal holding company income (UPHCI).
B) Rental expenses in excess of rental income are added back to taxable income to arrive at personal holding company income (PHCI).
C) Wind Corporation is a personal holding company. Its taxable income for this year is $100,000. The corporation's charitable contributions are $5,000 greater than its income tax charitable contribution deduction limitation. Wind's UPHCI is $95,000, assuming no other adjustments must be made.
D) The PHC tax is assessed at 15%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) The personal holding company taxes that are paid by a corporation can be used as a credit against its regular tax amount.
B) Whether a corporation is subject to the personal holding company tax is determined by using two objective tests, while the determination of whether a corporation is subject to the accumulated earnings tax is determined subjectively.
C) Income from personal service contracts are not included in personal holding company income.
D) All of the above are false.
A) The personal holding company taxes that are paid by a corporation can be used as a credit against its regular tax amount.
B) Whether a corporation is subject to the personal holding company tax is determined by using two objective tests, while the determination of whether a corporation is subject to the accumulated earnings tax is determined subjectively.
C) Income from personal service contracts are not included in personal holding company income.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of following generally does not indicate an unreasonable earnings accumulation?
A) loans to shareholders
B) expenditure of corporate funds for the personal benefit of the shareholders
C) planned expansion of business facilities
D) investments in properties or securities unrelated to the activities of the corporation
A) loans to shareholders
B) expenditure of corporate funds for the personal benefit of the shareholders
C) planned expansion of business facilities
D) investments in properties or securities unrelated to the activities of the corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following entities is subject to the accumulated earnings tax?
A) Sec. 501 tax-exempt corporation
B) personal holding company
C) C corporation
D) S corporation
A) Sec. 501 tax-exempt corporation
B) personal holding company
C) C corporation
D) S corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following actions cannot be used to eliminate a possible personal holding company tax liability involving a corporation owned by a mother and a father?
A) Sell additional stock to other family members.
B) Make a cash distribution within 2 1/2 months of the end of the tax year.
C) Make a deficiency distribution within 90 days of the date on which the IRS determines that a personal holding company liability is owed.
D) Liquidate the corporation.
A) Sell additional stock to other family members.
B) Make a cash distribution within 2 1/2 months of the end of the tax year.
C) Make a deficiency distribution within 90 days of the date on which the IRS determines that a personal holding company liability is owed.
D) Liquidate the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) A corporation can be subject to both the accumulated earnings tax and the personal holding company tax in the same year.
B) The accumulated earnings tax is applied to a corporation's earnings. If the earnings are not subsequently distributed, the earnings will be taxed again under the accumulated earnings tax the next year.
C) The accumulated earnings tax is not levied on the corporation's total accumulated earnings balance, but only on its current-year addition to the balance.
D) All of the above are false.
A) A corporation can be subject to both the accumulated earnings tax and the personal holding company tax in the same year.
B) The accumulated earnings tax is applied to a corporation's earnings. If the earnings are not subsequently distributed, the earnings will be taxed again under the accumulated earnings tax the next year.
C) The accumulated earnings tax is not levied on the corporation's total accumulated earnings balance, but only on its current-year addition to the balance.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) A deficiency dividend is included in the shareholder's gross income for his/her tax year that includes the last day of the tax year in which the personal holding company claims a dividends-paid deduction.
B) A shareholder who receives a deficiency dividend must report the dividend as gross income for the tax year that includes the last day of the distributing corporation's tax year on which it was a PHC.
C) A personal holding company's payment of a deficiency dividend eliminates its need to pay the personal holding company tax as well as any interest and underpayment penalties on the tax deficiency.
D) All of the above are false.
A) A deficiency dividend is included in the shareholder's gross income for his/her tax year that includes the last day of the tax year in which the personal holding company claims a dividends-paid deduction.
B) A shareholder who receives a deficiency dividend must report the dividend as gross income for the tax year that includes the last day of the distributing corporation's tax year on which it was a PHC.
C) A personal holding company's payment of a deficiency dividend eliminates its need to pay the personal holding company tax as well as any interest and underpayment penalties on the tax deficiency.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The personal holding company penalty tax rate is
A) 15%.
B) 10%.
C) 20%.
D) 35%.
A) 15%.
B) 10%.
C) 20%.
D) 35%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is not an adjustment to taxable income when computing the personal holding company tax?
A) dividends-received deduction
B) dividends-paid deduction
C) NOL carryover from immediately preceding tax year
D) All of the above are adjustments.
A) dividends-received deduction
B) dividends-paid deduction
C) NOL carryover from immediately preceding tax year
D) All of the above are adjustments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) The Bardahl formula is based on the firm's inventory period, receivables period, credit period, and total cash expenditures for cost of sales and operating expenses.
B) The Bardahl formula uses the concept of working capital, cash over current liabilities.
C) The Bardahl formula provides mathematical exactness when calculating reasonable working capital needs for accumulated earnings tax purposes.
D) All of the above are false.
A) The Bardahl formula is based on the firm's inventory period, receivables period, credit period, and total cash expenditures for cost of sales and operating expenses.
B) The Bardahl formula uses the concept of working capital, cash over current liabilities.
C) The Bardahl formula provides mathematical exactness when calculating reasonable working capital needs for accumulated earnings tax purposes.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When using the Bardahl formula, an increase in annual credit sales (while holding the average accounts receivable balance constant) has which of the following effects on the working capital requirements?
A) increase
B) decrease
C) no effect
D) increase, decrease, or no effect, depending on other factors
A) increase
B) decrease
C) no effect
D) increase, decrease, or no effect, depending on other factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Identify which of the following statements is false.
A) A corporation files a Schedule AE to report the amount of its accumulated earnings tax liability for the tax year.
B) A corporation that is subject to the accumulated earnings tax may also be subject to interest and underpayment penalties on the amount of the unpaid liability.
C) A corporation files a Schedule PH to report its PHC tax for the tax year.
D) The corporate AMT liability is reported on Form 4626.
A) A corporation files a Schedule AE to report the amount of its accumulated earnings tax liability for the tax year.
B) A corporation that is subject to the accumulated earnings tax may also be subject to interest and underpayment penalties on the amount of the unpaid liability.
C) A corporation files a Schedule PH to report its PHC tax for the tax year.
D) The corporate AMT liability is reported on Form 4626.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When computing the accumulated earnings tax, the dividends-paid deduction is not available for
A) dividends paid during the tax year.
B) throwback dividends.
C) stock dividends.
D) All of the above are deductible.
A) dividends paid during the tax year.
B) throwback dividends.
C) stock dividends.
D) All of the above are deductible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The accumulated earnings tax is imposed at what rate?
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 20%
D) 35%
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 20%
D) 35%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Flower Corporation, a C corporation but not a personal service corporation, has taxable income of $200,000 plus $125,000 of positive adjustments plus $150,000 of tax preferences. Its regular tax liability is $68,000. Calculate Flower Corporation's minimum tax credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) Payment of deficiency dividends will prevent the imposition of the accumulated earnings tax.
B) All corporations are exempt from the accumulated earnings tax on their first $250,000 of accumulated earnings.
C) A health service corporation can claim an accumulated earnings credit of $250,000.
D) All of the above are false.
A) Payment of deficiency dividends will prevent the imposition of the accumulated earnings tax.
B) All corporations are exempt from the accumulated earnings tax on their first $250,000 of accumulated earnings.
C) A health service corporation can claim an accumulated earnings credit of $250,000.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Drury Corporation, which was organized three years ago, reports the following adjusted current earnings (ACE) and preadjustment alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI) amounts.
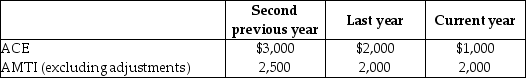 What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the current year?
What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the current year?
 What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the current year?
What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the current year?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the current year, Sun Corporation's federal income taxes before credits are $220,000. Its TMT is $100,000. Their only available credit is a research credit (part of the general business credit) of $160,000. The general business credit is limited to what amount?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In determining accumulated taxable income for the purpose of the accumulated earnings tax, which one of the following is allowed as a deduction?
A) excess charitable contributions
B) dividends-received deduction
C) net operating loss deduction
D) net capital loss for the current year
A) excess charitable contributions
B) dividends-received deduction
C) net operating loss deduction
D) net capital loss for the current year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is not permitted an accumulated earnings credit based on reasonable needs of the business?
A) an operating company
B) an investment company
C) an incorporated engineer
D) All of the above are permitted a credit based on reasonable business needs.
A) an operating company
B) an investment company
C) an incorporated engineer
D) All of the above are permitted a credit based on reasonable business needs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Arnold Corporation reports taxable income of $250,000, tax preference items of $20,000, and positive AMT adjustments of $20,000. What is its statutory exemption, when computing alternative minimum taxable income?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When using the Bardahl formula, an increase in accounts payable (while holding purchases and operating expenses constant) has which of the following effects on the working capital requirements?
A) increase
B) decrease
C) no effect
D) increase, decrease, or no effect, depending on other factors
A) increase
B) decrease
C) no effect
D) increase, decrease, or no effect, depending on other factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following actions cannot be used to eliminate a potential accumulated earnings tax liability situation involving a corporation owned by a mother and a father?
A) Create plans to invest retained earnings in a plant expansion.
B) Make a cash distribution within 2 1/2 months after the end of the tax year.
C) Make a deficiency distribution within 90 days of the date on which the IRS determines that an accumulated earnings tax liability is owed.
D) Liquidate the corporation.
A) Create plans to invest retained earnings in a plant expansion.
B) Make a cash distribution within 2 1/2 months after the end of the tax year.
C) Make a deficiency distribution within 90 days of the date on which the IRS determines that an accumulated earnings tax liability is owed.
D) Liquidate the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Hydrangia Corporation reports the following results for the current year:
 Depreciation claimed for:
Depreciation claimed for:
 What is Hydrangia Corporation's alternative minimum tax liability?
What is Hydrangia Corporation's alternative minimum tax liability?
 Depreciation claimed for:
Depreciation claimed for: What is Hydrangia Corporation's alternative minimum tax liability?
What is Hydrangia Corporation's alternative minimum tax liability?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A corporation cannot reasonably accumulate earnings to
A) protect against pending litigation.
B) fund an employee retirement plan.
C) self-insure.
D) redeem stock of an elderly shareholder where such accumulation occurs prior to the shareholder's death.
A) protect against pending litigation.
B) fund an employee retirement plan.
C) self-insure.
D) redeem stock of an elderly shareholder where such accumulation occurs prior to the shareholder's death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Identify which of the following statements is true.
A) A corporation accumulates earnings to fund the redemption of a shareholder's stock following her death so as to provide her estate with liquidity to pay death taxes. Such an accumulation of earnings is a reasonable business need.
B) A corporation accumulates earnings to fund a buy-sell agreement. Such an accumulation of earnings is a reasonable business need.
C) A corporation's net capital gain (minus any federal income taxes paid with respect to such gain) increases the tax base for the accumulated earnings tax.
D) All of the above are false.
A) A corporation accumulates earnings to fund the redemption of a shareholder's stock following her death so as to provide her estate with liquidity to pay death taxes. Such an accumulation of earnings is a reasonable business need.
B) A corporation accumulates earnings to fund a buy-sell agreement. Such an accumulation of earnings is a reasonable business need.
C) A corporation's net capital gain (minus any federal income taxes paid with respect to such gain) increases the tax base for the accumulated earnings tax.
D) All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Barker Corporation, a personal service company, has $200,000 of taxable income. Barker has tax preferences and positive adjustments of $200,000 and negative adjustments of $140,000 for alternative minimum tax purposes. No credits are available. Barker's regular tax liability is $70,000. How much is its alternative minimum tax liability?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When computing the accumulated earnings tax, which of the following is not a reduction to arrive at accumulated taxable income?
A) accumulated earnings credit
B) NOL deduction claimed
C) accrued federal income taxes
D) dividends-paid deduction
A) accumulated earnings credit
B) NOL deduction claimed
C) accrued federal income taxes
D) dividends-paid deduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Door Corporation's alternative minimum taxable income before the statutory exemption is $200,000. What is Door's tentative minimum tax before credits?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Barker Corporation, a personal service company, has $200,000 of taxable income. Barker has tax preferences and positive adjustments of $200,000 and negative adjustments of $140,000 for alternative minimum tax purposes. No credits are available. Barker's regular tax liability is $70,000. What is the tentative minimum tax amount?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Drury Corporation, which was organized three years ago, reports the following adjusted current earnings (ACE) and preadjustment alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI) amounts.
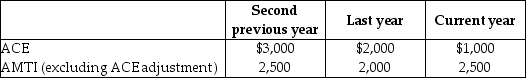 What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the second previous year?
What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the second previous year?
 What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the second previous year?
What is the ACE adjustment to increase (or decrease) taxable income to arrive at AMTI for the second previous year?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



