Deck 11: Accounting Periods and Methods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/114
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Accounting Periods and Methods
1
If the majority of the partners do not have the same tax year, the partnership must use the tax year of its principal partners.
True
Explanation: This conformity is designed to minimize deferral.
Explanation: This conformity is designed to minimize deferral.
2
Partnerships, S corporations, and personal service corporations may elect a taxable year which results in a tax deferral of four months or less.
False
Explanation: A tax deferral of three months or less is allowed.
Explanation: A tax deferral of three months or less is allowed.
3
Emma, a single taxpayer, obtains permission to change from a calendar year to a fiscal year ending June 30, 2015. During the six months ending June 30, 2015, she earns $40,000 and has $8,000 of itemized deductions. What is the amount of her annualized income?
A) $30,000
B) $64,000
C) $60,000
D) $64,300
A) $30,000
B) $64,000
C) $60,000
D) $64,300
C
Explanation: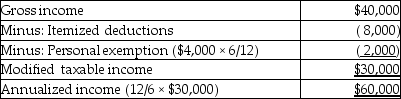
Explanation:

4
An S corporation elects a September 30 taxable year. The S corporation, as a pass-through entity, does not need to make tax payments to the IRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Misha, a single taxpayer, died on July 31, 2015. Her final income tax return (ignoring extensions) is due November 15, 2015.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Generally, an income tax return covers an accounting period of 12 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A subsidiary corporation filing a consolidated return with its parent corporation must change its accounting period to conform with its parent's tax year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A partnership must generally use the same tax year of the partners who own the majority of partnership income and capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All C corporations can elect a tax year other than a calendar year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If Jett Corporation receives a charter in 2013 but does not begin operations and file its first tax return until 2015, Jett may elect a fiscal year on the 2015 return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An improper election to use a fiscal year automatically places the taxpayer on the calendar year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A new business is established. It is not a seasonal business. All of the following are acceptable accounting tax years with the exception of
A) an S corporation year ending October 31.
B) a C corporation (not a personal service corporation) tax year ending on February 15.
C) a C corporation (not a personal service corporation) tax year ending on April 30.
D) a partnership tax year ending on October 31 with three equal partners whose tax years end on September 30, October 31, and November 30.
A) an S corporation year ending October 31.
B) a C corporation (not a personal service corporation) tax year ending on February 15.
C) a C corporation (not a personal service corporation) tax year ending on April 30.
D) a partnership tax year ending on October 31 with three equal partners whose tax years end on September 30, October 31, and November 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which entities may elect a fiscal year? Discuss how certain tax entities may circumvent the requirement of using a calendar year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
All of the following statements are true except:
A) once adopted, an accounting period normally cannot be changed without approval by the IRS.
B) taxpayers who change from one accounting period to another must annualize their income for the resulting short period.
C) taxpayers filing an initial tax return are required to annualize the year's income and prorate exemptions and credits.
D) an existing partnership can change its tax year without prior approval if the partners with a majority interest have the same tax year to which the partnership changes.
A) once adopted, an accounting period normally cannot be changed without approval by the IRS.
B) taxpayers who change from one accounting period to another must annualize their income for the resulting short period.
C) taxpayers filing an initial tax return are required to annualize the year's income and prorate exemptions and credits.
D) an existing partnership can change its tax year without prior approval if the partners with a majority interest have the same tax year to which the partnership changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A fiscal year is a 12-month period that ends on the last day of any month other than December.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Except in a few specific circumstances, once adopted, an accounting period may be changed without IRS approval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A newly married person may change tax years to conform to that of his or her spouse so that a joint return may be filed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Taxpayers who change from one accounting period to another must annualize their income for the resulting short period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When preparing a tax return for a short period, the taxpayer should annualize the income if the short period return
A) is the last return for a decedent who died on June 15.
B) is the first return for a corporation created on June 1.
C) is the last return for a partnership, which was terminated on October 12.
D) is a return for June 1 to December 31, for a corporation changing from a fiscal year to a calendar year.
A) is the last return for a decedent who died on June 15.
B) is the first return for a corporation created on June 1.
C) is the last return for a partnership, which was terminated on October 12.
D) is a return for June 1 to December 31, for a corporation changing from a fiscal year to a calendar year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A taxpayer's tax year must coincide with the year used to keep the taxpayer's books and records.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
C corporations and partnerships with a corporate partner may use the cash method of accounting if average annual gross receipts for the three preceding tax years do not exceed $10 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Under the cash method of accounting, all expenses are deductible when paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following partnerships can elect the cash basis method of accounting?
A) a CPA firm with average revenues of $20 million
B) a chocolate manufacturer with average revenues of $3 million
C) a cleaning service partnership generating average revenues of $5.5 million whose partners are Joe, Larry and Smith Inc.
D) None of the above.
A) a CPA firm with average revenues of $20 million
B) a chocolate manufacturer with average revenues of $3 million
C) a cleaning service partnership generating average revenues of $5.5 million whose partners are Joe, Larry and Smith Inc.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
One criterion which will permit a deduction for an expenditure by the accrual-basis taxpayer prior to economic performance is that either the amount is not material or the earlier accrual of the item results in a better matching of income and expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Under the cash method of accounting, payment by credit card entitles the taxpayer to deduct the expenditure at the time the charge is made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A taxpayer must use the same accounting method on the personal tax return that the taxpayer uses in the taxpayer's trade or business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a cash basis taxpayer gives a note in payment of an expense, the deduction may not be taken until the note is paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Under the cash method of accounting, income is reported for the tax year in which payments are actually or constructively received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For purposes of the accrual method of accounting, the economic performance test is met when
A) the property or services are actually provided.
B) the amount of the item can be reasonably estimated.
C) all events have occurred that establish the fact of a liability.
D) all events have occurred that fix the taxpayer's right to receive income.
A) the property or services are actually provided.
B) the amount of the item can be reasonably estimated.
C) all events have occurred that establish the fact of a liability.
D) all events have occurred that fix the taxpayer's right to receive income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Alvin, a practicing attorney who also owns an office supplies store, may use the cash basis for his legal practice and the accrual basis for his office supplies store.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Under the accrual method of accounting, the two tests to determine when income must be reported and expenses deducted are the all-events test and the economic performance test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Generally, if inventories are an income-producing factor to the business, the accrual method must be used for sales and cost of goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A taxpayer may use a combination of accounting methods as long as income is clearly reflected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The all-events test requires that the accrual-basis taxpayer report income when all events have occurred that fix the taxpayer's right to the income and when the amount can be determined with reasonable accuracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A retailing business may use the cash basis method of accounting for purposes of determining sales and cost of goods sold if average gross receipts do not exceed $1 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Points paid on a mortgage to buy a personal residence are deductible in the year paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A taxpayer who uses the cash method in computing gross income from his or her business must use the cash method in computing expenses of such business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Under the cash method of accounting, all of the following are true with the exception of:
A) Fixed assets are always expensed as the taxpayer pays for the assets.
B) Gross income includes the value of property received.
C) To some extent, a taxpayer may control the year in which an expense is deductible by choosing when to make the payment.
D) Income is reported in the tax year in which payments are actually or constructively received.
A) Fixed assets are always expensed as the taxpayer pays for the assets.
B) Gross income includes the value of property received.
C) To some extent, a taxpayer may control the year in which an expense is deductible by choosing when to make the payment.
D) Income is reported in the tax year in which payments are actually or constructively received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An accrual of a reserve for bad debt expense by an accrual-basis taxpayer meets the standards of all-events and economic performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A business which provides a warranty on goods sold will deduct a reserve for warranty expense consistent with the reporting on its financial statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For tax purposes, the lower of cost or market method must ordinarily be applied to each separate inventory item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In 2015, Richard's Department Store changes its inventory method from FIFO to LIFO. Richard's uses the simplified LIFO method. Richard's year-end inventory under FIFO is as follows: 2014 - $300,000; 2015 - $350,000. The 2014 price index is 110% and the 2015 index is 120%. The 2015 layer is
A) $19,097.
B) $20,833.
C) $22,727.
D) $50,000.
A) $19,097.
B) $20,833.
C) $22,727.
D) $50,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Contracts for services including accounting, legal and architectural services do not qualify for long-term contract treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A taxpayer must use the same accounting method, either percentage of completion or completed contract method, for all long-term contracts in the same trade or business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Many taxpayers use the LIFO method of inventory valuation because during inflationary periods, LIFO normally results in the lowest inventory value and hence the lowest taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A taxpayer who uses the LIFO method of inventory valuation may use the lower of cost or market method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The installment sale method may be used on the sale of property at a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The uniform capitalization rules (UNICAP) require the capitalization of some overhead costs that are expensed for financial accounting purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Under UNICAP, all of the following overhead costs are included in inventory except
A) factory utilities, rent, insurance and depreciation.
B) officers' salaries and factory administration.
C) research and experimentation.
D) factory payroll, purchasing and warehouse costs.
A) factory utilities, rent, insurance and depreciation.
B) officers' salaries and factory administration.
C) research and experimentation.
D) factory payroll, purchasing and warehouse costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Generally, economic performance must occur before an expense may be deducted. In some cases, this requirement of economic performance may be waived. Discuss the conditions under which economic performance may be waived and an earlier deduction may be allowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Lloyd Corporation, a calendar year accrual basis taxpayer, pays its insurance premium each year on June 1, the anniversary of the policy. The premium paid this year is $9,600 while last year's was $9,000. How much of is Lloyd's deduction for insurance this year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A business uses the same inventory method for both financial reporting and tax reporting. Because of the UNICAP requirement, ending inventory is likely to be
A) higher for tax reporting purposes than for financial reporting purposes.
B) higher for financial reporting purposes than for tax reporting purposes.
C) the same for both financial and tax reporting as UNICAP requires uniform inventory accounting methods.
D) none of the above.
A) higher for tax reporting purposes than for financial reporting purposes.
B) higher for financial reporting purposes than for tax reporting purposes.
C) the same for both financial and tax reporting as UNICAP requires uniform inventory accounting methods.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the significance of the Thor Power Tool Co. case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For tax purposes, "market" for purposes of applying the lower of cost or market method means the price at which the taxpayer can sell the inventory item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The installment method is not applicable to sales of inventory and marketable securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A taxpayer may use the FIFO or average cost methods for financial statement purposes, while using the LIFO method for tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Xerxes Manufacturing, in its first year of operations, produces solar panels which are sold through large building supply and home improvement stores. Xerxes' year-end results include the following:  You are preparing Xerxes' first year tax return. Xerxes has elected a calendar year as its tax accounting period and the accrual method. What additional information would you need to prepare the tax return?
You are preparing Xerxes' first year tax return. Xerxes has elected a calendar year as its tax accounting period and the accrual method. What additional information would you need to prepare the tax return?
 You are preparing Xerxes' first year tax return. Xerxes has elected a calendar year as its tax accounting period and the accrual method. What additional information would you need to prepare the tax return?
You are preparing Xerxes' first year tax return. Xerxes has elected a calendar year as its tax accounting period and the accrual method. What additional information would you need to prepare the tax return?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Inventory may be valued on the tax return at the lower of cost or market unless
A) replacement cost is higher than historical cost.
B) the taxpayer determines inventory cost using the LIFO method.
C) the taxpayer determines inventory cost using the FIFO method.
D) the cash method of accounting is used by the taxpayer.
A) replacement cost is higher than historical cost.
B) the taxpayer determines inventory cost using the LIFO method.
C) the taxpayer determines inventory cost using the FIFO method.
D) the cash method of accounting is used by the taxpayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In 2014 Anika Co. adopted the simplified dollar-value LIFO method. Inventory under FIFO in 2014 and 2015 is $400,000 and $600,000, respectively. The Consumer Price Index for 2014 is 115 and the Consumer Price Index in 2015 is 125 percent. How much is Anika's inventory at the end of year 2015 under simplified LIFO?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements regarding UNICAP is incorrect?
A) The UNICAP rules result in more costs being included in inventory for tax purposes than for financial accounting.
B) Taxpayers with gross receipts averaging more than $10,000,000 or more for the prior three years must apply the UNICAP provisions.
C) Interest must be included in inventory if the property produced is real property or long-lived property.
D) UNICAP requires that advertising and selling costs be allocated between inventory and cost of sales.
A) The UNICAP rules result in more costs being included in inventory for tax purposes than for financial accounting.
B) Taxpayers with gross receipts averaging more than $10,000,000 or more for the prior three years must apply the UNICAP provisions.
C) Interest must be included in inventory if the property produced is real property or long-lived property.
D) UNICAP requires that advertising and selling costs be allocated between inventory and cost of sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following conditions are required for the use of the installment method?
A) The taxpayer must realize a gain on the sale of the property.
B) The taxpayer cannot be on the cash method.
C) The value of the obligations received is determinable at the date of sale.
D) All of the above are required.
A) The taxpayer must realize a gain on the sale of the property.
B) The taxpayer cannot be on the cash method.
C) The value of the obligations received is determinable at the date of sale.
D) All of the above are required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
This year, John purchased property from William by assuming an existing mortgage of $40,000 and agreed to pay an additional $60,000, plus interest, in the 3 years following the year of sale (i.e. $20,000 annual payments for three years, plus interest). William had an adjusted basis of $44,000 in the building. What are the sales price and the contract price in this transaction?
A)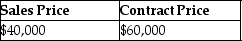
B)
C)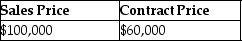
D)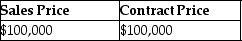
A)
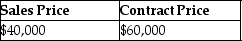
B)

C)
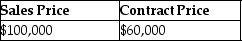
D)
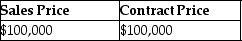

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Kevin sold property with an adjusted basis of $58,000. The buyer assumed Kevin's existing mortgage of $40,000 and agreed to pay an additional $60,000 consisting of a cash down payment of $40,000, and payments of $4,000, plus interest, per year for the next 5 years. Kevin paid selling expenses totaling $2,000. What is Kevin's gross profit percentage?
A) 33 1/3%
B) 40%
C) 60%
D) 66 2/3%
A) 33 1/3%
B) 40%
C) 60%
D) 66 2/3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The installment sale method can be used for all of the following transactions except
A) the sale of an painting by an art collector.
B) the sale of a sole proprietor's office building.
C) the sale of an individual's personal car.
D) the sale of a yacht by a shipbuilder.
A) the sale of an painting by an art collector.
B) the sale of a sole proprietor's office building.
C) the sale of an individual's personal car.
D) the sale of a yacht by a shipbuilder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
This year, a contractor agrees to build a building for $2,000,000, which will be completed by the end of next year. The builder's cost is estimated to be $1,700,000. The actual costs this year are $800,000 and next year's actual costs are $800,000. If the tax rate is 20% and the interest rate is 10%, the look back interest for the percentage of completion method is
A) $ 0.
B) $1,176.
C) $2,000.
D) $6,000.
A) $ 0.
B) $1,176.
C) $2,000.
D) $6,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In year 1 a contractor agrees to build a building for $2,500,000 by the end of year 2. The builder's cost is estimated to be $1,800,000. The actual costs year 1 are $900,000 and year 2's actual costs are $1,300,000. Under the completed contract method the gross profit for year 2 is
A) $0.
B) $300,000.
C) $350,000.
D) $700,000.
A) $0.
B) $300,000.
C) $350,000.
D) $700,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The installment sale method can be used for all of the following transactions except
A) the sale of an antique by a collector.
B) the sale of shares of publicly-traded corporate stock.
C) the sale of farmland used in a farming business.
D) the sale of a boat held for personal use.
A) the sale of an antique by a collector.
B) the sale of shares of publicly-traded corporate stock.
C) the sale of farmland used in a farming business.
D) the sale of a boat held for personal use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The look-back interest adjustment involves the
A) calculation of interest on an installment sale.
B) calculation of gross profit on an installment sale collection.
C) calculation of additional tax due if actual cost rather than estimated cost had been used on the percentage of completion method.
D) calculation of interest on additional tax that would have been due if actual cost rather than estimated cost had been used on the percentage of completion method.
A) calculation of interest on an installment sale.
B) calculation of gross profit on an installment sale collection.
C) calculation of additional tax due if actual cost rather than estimated cost had been used on the percentage of completion method.
D) calculation of interest on additional tax that would have been due if actual cost rather than estimated cost had been used on the percentage of completion method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In year 1 a contractor agrees to build a building for $2,500,000 by the end of year 2. The builder's cost is estimated to be $1,800,000. The actual costs year 1 are $900,000 and year 2's actual costs are $1,100,000. Under the percentage of completion method year 1's gross profit is
A) $0.
B) $300,000.
C) $350,000.
D) $700,000.
A) $0.
B) $300,000.
C) $350,000.
D) $700,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Freida is an accrual-basis taxpayer who owns a furniture store. The furniture store had the following sales of inventory: 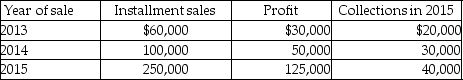 For tax purposes, Freida should report gross profit for 2015 of
For tax purposes, Freida should report gross profit for 2015 of
A) $40,000.
B) $65,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $125,000.
 For tax purposes, Freida should report gross profit for 2015 of
For tax purposes, Freida should report gross profit for 2015 ofA) $40,000.
B) $65,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $125,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In year 1 a contractor agrees to build a building for $2,500,000 by the end of year 2. The builder's cost is estimated to be $1,800,000. The actual costs year 1 are $900,000 and year 2's actual costs are $1,300,000. Under the completed contract method the gross profit for year 1 is
A) $0.
B) $300,000.
C) $350,000.
D) $700,000.
A) $0.
B) $300,000.
C) $350,000.
D) $700,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
This year, Hamilton, a local manufacturer of off-shore drilling platforms, entered into a contract to construct a drilling platform that will be placed in the North Atlantic Ocean. The total contract price is $5,000,000, and Hamilton estimates the total construction cost at $3,000,000. Actual costs incurred this year are $600,000. If Hamilton uses the percentage of completion method, the gross profit for this year is
A) $0.
B) $400,000.
C) $600,000.
D) $2,000,000.
A) $0.
B) $400,000.
C) $600,000.
D) $2,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Kyle sold land on the installment basis for $100,000. His basis in the land was $70,000. Kyle received a $40,000 down payment and a real estate installment sale contract calling for $60,000 in additional payments in future years. In addition, Kyle paid $6,000 in commissions on the sale. What is the gross profit to be recognized in the current year?
A) $0
B) $9,600
C) $12,000
D) $24,000
A) $0
B) $9,600
C) $12,000
D) $24,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In year 1 a contractor agrees to build a building for $2,500,000 by the end of year 2. The builder's cost is estimated to be $1,800,000. The actual costs year 1 are $900,000 and year 2's actual costs are $1,100,000. Under the percentage of completion method year 2's gross profit is
A) $150,000.
B) $500,000.
C) $700,000.
D) $350,000.
A) $150,000.
B) $500,000.
C) $700,000.
D) $350,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Under the percentage of completion method, gross income is reported
A) when the contract is completed.
B) using a percentage that is determined by dividing current year costs by the expected total revenue.
C) based on the portion of work that is incomplete.
D) based on the portion of work that has been completed.
A) when the contract is completed.
B) using a percentage that is determined by dividing current year costs by the expected total revenue.
C) based on the portion of work that is incomplete.
D) based on the portion of work that has been completed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The installment method may be used for sales of all kinds of property with the exception of
A) real property.
B) personal property.
C) capital assets.
D) marketable securities.
A) real property.
B) personal property.
C) capital assets.
D) marketable securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Bergeron is a local manufacturer of off-shore drilling platforms. This year, Bergeron entered into a contract to construct a drilling platform, which will be placed in the North Atlantic Ocean. The total contract price is $5,000,000, and Bergeron estimates the total construction cost at $2,000,000. Actual costs incurred this year are $600,000. If Bergeron uses the completed contract method, the gross profit for this year is
A) $0.
B) $400,000.
C) $600,000.
D) $2,000,000.
A) $0.
B) $400,000.
C) $600,000.
D) $2,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An installment sale is best defined as
A) any disposition of property in which at least three payments are received.
B) any disposition of property in which the installment method is elected by the taxpayer.
C) any disposition of property where at least one payment is received after the close of the taxable year in which disposition occurs.
D) any disposition of publicly traded property or inventory where at least one payment is received after the close of the taxable year in which disposition occurs.
A) any disposition of property in which at least three payments are received.
B) any disposition of property in which the installment method is elected by the taxpayer.
C) any disposition of property where at least one payment is received after the close of the taxable year in which disposition occurs.
D) any disposition of publicly traded property or inventory where at least one payment is received after the close of the taxable year in which disposition occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When accounting for long-term contracts (other than those for services), all of the following accounting methods may be acceptable with the exception of
A) the allocated completion method of accounting.
B) the completed contract method.
C) the percentage of completion method.
D) the modified percentage of completion method.
A) the allocated completion method of accounting.
B) the completed contract method.
C) the percentage of completion method.
D) the modified percentage of completion method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
On July 25 of this year, Raj sold land with a cost of $15,000 for $40,000. Raj collected $20,000 this year and is scheduled to receive $5,000 each year for four years starting next year plus an acceptable rate of interest. Raj's gain recognized this year is
A) $7,500.
B) $12,500.
C) $20,000.
D) $25,000.
A) $7,500.
B) $12,500.
C) $20,000.
D) $25,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



