Deck 7: How Cells Release Chemical Energy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: How Cells Release Chemical Energy
1
Which of the following breaks down organic molecules and produces ATP,carbon dioxide,and water?
A) Aerobic respiration
B) Fermentation
C) Cellular respiration
D) Anaerobic respiration
E) Glycolysis
A) Aerobic respiration
B) Fermentation
C) Cellular respiration
D) Anaerobic respiration
E) Glycolysis
A
2
When molecules are broken apart in respiration,____.
A) the heat produced is used to drive biological reactions
B) the oxygen in the compounds that are broken apart is used as an energy source
C) the energy released is channeled into molecules of ATP
D) ATP is converted into ADP
E) ADP is released as a waste product
A) the heat produced is used to drive biological reactions
B) the oxygen in the compounds that are broken apart is used as an energy source
C) the energy released is channeled into molecules of ATP
D) ATP is converted into ADP
E) ADP is released as a waste product
C
3
Pyruvate is the end product of ____.
A) glycolysis
B) acetyl-CoA formation
C) fermentation
D) aerobic respiration
E) the citric acid cycle
A) glycolysis
B) acetyl-CoA formation
C) fermentation
D) aerobic respiration
E) the citric acid cycle
A
4
The breakdown of ____ yields acetyl-CoA and carbon dioxide.
A) phosphoglycerate
B) pyruvate
C) oxaloacetate
D) PGAL
E) fructose bisphosphate
A) phosphoglycerate
B) pyruvate
C) oxaloacetate
D) PGAL
E) fructose bisphosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the correct operational sequence of the three processes listed below?
I.Glycolysis
II.Electron transport chain
III.Citric acid cycle
A) I II III
B) II I III.
C) III I II
D) II III I
E) I III II.
I.Glycolysis
II.Electron transport chain
III.Citric acid cycle
A) I II III
B) II I III.
C) III I II
D) II III I
E) I III II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What process requires oxygen to function?
A) Aerobic respiration
B) Anaerobic respiration
C) Alcoholic fermentation
D) Lactate fermentation
E) Substrate-level phosphorylation
A) Aerobic respiration
B) Anaerobic respiration
C) Alcoholic fermentation
D) Lactate fermentation
E) Substrate-level phosphorylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
____ is the first stage of aerobic respiration and fermentation.
A) Anaerobic
B) Substrate-level phosphorylation
C) Glycolysis
D) Cellular respiration
E) Pyruvate
A) Anaerobic
B) Substrate-level phosphorylation
C) Glycolysis
D) Cellular respiration
E) Pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Substrate-level phosphorylation ____.
A) occurs during glycolysis
B) requires the presence of oxygen
C) is a precursor for the phosphorylation of glucose
D) is the source for the majority of the ATP produced in aerobic respiration
E) occurs in the mitochondria
A) occurs during glycolysis
B) requires the presence of oxygen
C) is a precursor for the phosphorylation of glucose
D) is the source for the majority of the ATP produced in aerobic respiration
E) occurs in the mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Glycolysis depends upon a continuous supply of ____.
A) NADP
B) pyruvate
C) NAD+
D) NADH
E) H2O
A) NADP
B) pyruvate
C) NAD+
D) NADH
E) H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is an anaerobic sugar breakdown pathway that produces ATP,CO2,and ethanol?
A) Alcoholic fermentation
B) Lactate fermentation
C) Acetyl-CoA formation
D) Anaerobic respiration
E) Citric acid cycle
A) Alcoholic fermentation
B) Lactate fermentation
C) Acetyl-CoA formation
D) Anaerobic respiration
E) Citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which molecule is a six-carbon compound?
A) PEP
B) PGAL
C) Glucose-6-phosphate
D) Pyruvate
E) Phosphoglycerate (PGA)
A) PEP
B) PGAL
C) Glucose-6-phosphate
D) Pyruvate
E) Phosphoglycerate (PGA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the breakdown of glucose,a phosphorylated six-carbon compound is split into two phosphorylated three-carbon sugars,which are named ____.
A) PGAL
B) pyruvate
C) acetyl-CoA
D) lactate
E) acetaldehyde
A) PGAL
B) pyruvate
C) acetyl-CoA
D) lactate
E) acetaldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For glycolysis to begin,____.
A) glucose must enter the mitochondria
B) there must be an input of energy from ATP
C) oxygen must be available
D) some hydrogen acceptors must be available
E) there must be an input of energy from ADP
A) glucose must enter the mitochondria
B) there must be an input of energy from ATP
C) oxygen must be available
D) some hydrogen acceptors must be available
E) there must be an input of energy from ADP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Aerobic respiration and fermentation ________.
A) evolved in different living organisms to utilize energy stored in glucose with equal efficiency
B) occur only in animal cells because plants carry out photosynthesis
C) utilize fat as primary energy source
D) occur at the same rate throughout all cells of the body
E) start with glycolysis.
A) evolved in different living organisms to utilize energy stored in glucose with equal efficiency
B) occur only in animal cells because plants carry out photosynthesis
C) utilize fat as primary energy source
D) occur at the same rate throughout all cells of the body
E) start with glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is an anaerobic glucose-breakdown pathway that produces ATP without use of an electron transfer chain?
A) Cellular respiration
B) Fermentation
C) Glycolysis
D) Aerobic respiration
E) Anaerobic respiration
A) Cellular respiration
B) Fermentation
C) Glycolysis
D) Aerobic respiration
E) Anaerobic respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
For animals,the final hydrogen acceptor in cellular respiration is ____.
A) NADP+
B) sulfur
C) oxygen
D) magnesium
E) phosphorus
A) NADP+
B) sulfur
C) oxygen
D) magnesium
E) phosphorus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How many net ATP molecules are produced per molecule of glucose broken down during glycolysis?
A) One
B) Two
C) Four
D) 36
E) 38
A) One
B) Two
C) Four
D) 36
E) 38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How many ATP are spent before a glucose molecule can be broken down to release energy?
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
E) Six
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
E) Six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Substrate-level phosphorylation transfers phosphate groups directly from ____ to ADP.
A) a substrate
B) coenzymes
C) the electron transfer chain
D) ATP
E) the citric acid cycle
A) a substrate
B) coenzymes
C) the electron transfer chain
D) ATP
E) the citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Where in a cell does glycolysis occur?
A) Cytoplasm
B) Golgi body
C) Nucleoid
D) Mitochondrion
E) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
A) Cytoplasm
B) Golgi body
C) Nucleoid
D) Mitochondrion
E) Rough endoplasmic reticulum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The electron transfer chain is located ____.
A) on the inner membrane of the mitochondria
B) on the inner membrane of the chloroplasts
C) in the fluid part of the chloroplast
D) throughout the cytoplasm of the cell
E) on the plasma membrane of eukaryotes
A) on the inner membrane of the mitochondria
B) on the inner membrane of the chloroplasts
C) in the fluid part of the chloroplast
D) throughout the cytoplasm of the cell
E) on the plasma membrane of eukaryotes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Fats provide more energy than carbohydrates because they ____.
A) can be stored inside the cell for long periods of time
B) require more oxidation reactions to break down, thus releasing more electrons
C) are hydrophilic, thus entering cells easily
D) are liquid, thus requiring less energy for reactions
E) are partially oxidized initially, thus requiring less ATP for oxidation
A) can be stored inside the cell for long periods of time
B) require more oxidation reactions to break down, thus releasing more electrons
C) are hydrophilic, thus entering cells easily
D) are liquid, thus requiring less energy for reactions
E) are partially oxidized initially, thus requiring less ATP for oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Lactate fermentation transfers the electrons and hydrogen ions carried by NADH directly to ____.
A) acetaldehyde
B) pyruvate
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen
E) myoglobin
A) acetaldehyde
B) pyruvate
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen
E) myoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the substrate of the first step in the citric acid cycle?
A) Pyruvate
B) Coenzyme A
C) Fructose bisphosphate
D) Oxaloacetate
E) Citrate
A) Pyruvate
B) Coenzyme A
C) Fructose bisphosphate
D) Oxaloacetate
E) Citrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the mitochondria,hydrogen is actively pumped to the ____.
A) inner membrane
B) outer membrane
C) intermembrane space
D) matrix
E) cytoplasm
A) inner membrane
B) outer membrane
C) intermembrane space
D) matrix
E) cytoplasm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Complex carbohydrates such as starch need to be first broken down to ____________ before they are quickly taken up by cells.
A) oligosaccharides
B) amino acids
C) monosaccharides
D) pyruvate
E) acetyl-CoA
A) oligosaccharides
B) amino acids
C) monosaccharides
D) pyruvate
E) acetyl-CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The energy used to generate most of the ATP formed in aerobic respiration is released when electrons are passed from NADH along a chain to ____.
A) oxygen
B) acetyl CoA
C) FADH
D) CO2.
E) NADPH
A) oxygen
B) acetyl CoA
C) FADH
D) CO2.
E) NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the conversion of pyruvate to ethanol,what is produced?
A) Acetaldehyde only
B) Carbon dioxide only
C) NADH only
D) Acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide
E) Acetaldehyde, carbon dioxide, and NADH
A) Acetaldehyde only
B) Carbon dioxide only
C) NADH only
D) Acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide
E) Acetaldehyde, carbon dioxide, and NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The breakdown of ____ into cellular energy can involve glycolysis.
A) carbohydrates
B) fats
C) proteins
D) carbohydrates and fats
E) fats and proteins
A) carbohydrates
B) fats
C) proteins
D) carbohydrates and fats
E) fats and proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
During which phase of aerobic respiration is FADH2 produced?
A) Glycolysis
B) Ethanol production
C) Acetyl-CoA formation
D) The citric acid cycle
E) Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
A) Glycolysis
B) Ethanol production
C) Acetyl-CoA formation
D) The citric acid cycle
E) Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When glucose is used as the energy source,the largest amount of ATP is produced in ____.
A) glycolysis
B) acetyl-CoA formation
C) the citric acid cycle
D) substrate-level phosphorylation
E) electron transfer phosphorylation
A) glycolysis
B) acetyl-CoA formation
C) the citric acid cycle
D) substrate-level phosphorylation
E) electron transfer phosphorylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not a product of the breakdown of dietary proteins for energy?
A) Amino acids
B) Ammonia
C) Pyruvate
D) Acetyl-CoA
E) Mitrate
A) Amino acids
B) Ammonia
C) Pyruvate
D) Acetyl-CoA
E) Mitrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Bakers use alcoholic fermentation to produce ____,which causes dough to rise.
A) alcohol
B) ATP
C) butyric acid
D) carbon dioxide
E) none of these
A) alcohol
B) ATP
C) butyric acid
D) carbon dioxide
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The breakdown of ____ for energy production results in the formation of ammonia as a waste product.
A) carbohydrates
B) fats
C) proteins
D) carbohydrates and fats
E) fats and proteins
A) carbohydrates
B) fats
C) proteins
D) carbohydrates and fats
E) fats and proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Electron transfer phosphorylation yields ____ ATPs.
A) four
B) Two
C) Three
D) 32
E) Zero
A) four
B) Two
C) Three
D) 32
E) Zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
During the citric acid cycle,____.
A) four CO2 molecules are produced
B) oxaloacetate is consumed
C) electrons and H+ are removed from the coenzymes NADH and FADH
D) molecules of carbon dioxide are consumed
E) oxidative phosphorylation occurs
A) four CO2 molecules are produced
B) oxaloacetate is consumed
C) electrons and H+ are removed from the coenzymes NADH and FADH
D) molecules of carbon dioxide are consumed
E) oxidative phosphorylation occurs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Select the one most appropriate choice for each.
-Acetyl-CoA formation
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP
-Acetyl-CoA formation
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The final step of the citric acid cycle regenerates ____.
A) pyruvate
B) acetyl-CoA
C) fructose bisphosphate
D) oxaloacetate
E) citrate
A) pyruvate
B) acetyl-CoA
C) fructose bisphosphate
D) oxaloacetate
E) citrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Select the one most appropriate choice for each.
-Fermentation
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP
-Fermentation
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Select the one most appropriate choice for each.
-Glycolysis
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP
-Glycolysis
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8
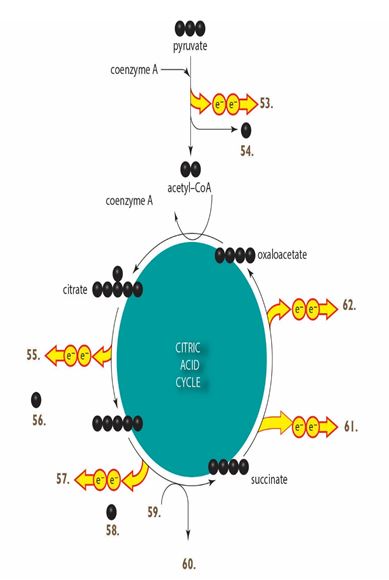
-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "59" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "59" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Classification. Use the five compounds listed below for the following questions.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is produced by fast-twitch muscle fibers.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is produced by fast-twitch muscle fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Classification. Use the five compounds listed below for the following questions.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is a product of both alcoholic and lactate fermentation.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is a product of both alcoholic and lactate fermentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Classification. Use the five compounds listed below for the following questions.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is produced from acetaldehyde when it accepts electrons and a hydrogen ion from NADH.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is produced from acetaldehyde when it accepts electrons and a hydrogen ion from NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Select the one most appropriate choice for each.
-Electron transfer phosphorylation
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP
-Electron transfer phosphorylation
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Classification. Use the five processes listed below for the following questions.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
This process is responsible for the largest ATP production.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
This process is responsible for the largest ATP production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "54" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "54" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Classification. Use the five processes listed below for the following questions.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
In this process,the net energy yield is equal to two molecules of ATP,and the final product is ethanol.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
In this process,the net energy yield is equal to two molecules of ATP,and the final product is ethanol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "57" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "57" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "53" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "53" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "56" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "56" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "58" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "58" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Classification. Use the five compounds listed below for the following questions.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is an intermediate product of alcoholic fermentation but not lactate fermentation.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is an intermediate product of alcoholic fermentation but not lactate fermentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "55" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "55" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Select the one most appropriate choice for each.
-The citric acid cycle
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP
-The citric acid cycle
A)Produces NADH and CO2; pyruvate oxidized
B)Produces ATP, NADH, and CO2
C)Splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules
D)Regenerates NAD+ as pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactate
E)Uses a membrane-bound system that sets up production of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "60" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "60" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Classification. Use the five processes listed below for the following questions.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
This process yields the most energy overall.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
This process yields the most energy overall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Classification. Use the five processes listed below for the following questions.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
This process precedes the citric acid cycle.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
This process precedes the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Classification. Use the five processes listed below for the following questions.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
In this one-step process,the final product is the ionized form of lactic acid.
a.Glycolysis
b.Aerobic respiration
c.Electron transfer phosphorylation
d.Alcoholic fermentation
e.Lactate fermentation
In this one-step process,the final product is the ionized form of lactic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Classification. Use the five compounds listed below for the following questions.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is utilized in alcoholic fermentation and lactate fermentation.
a.Ethanol
b.Pyruvate
c.Lactate
d.Carbon dioxide
e.Acetaldehyde
This compound is utilized in alcoholic fermentation and lactate fermentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is true regarding lactate fermentation in muscle cells?
A) It provides a quick burst of ATP.
B) It sustains muscle contractions during prolonged exercise.
C) It causes muscle soreness.
D) It is the predominant form of respiration in muscles.
E) Its products accumulate in muscle for extended periods of time.
A) It provides a quick burst of ATP.
B) It sustains muscle contractions during prolonged exercise.
C) It causes muscle soreness.
D) It is the predominant form of respiration in muscles.
E) Its products accumulate in muscle for extended periods of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Acetyl-CoA is produced when ____________________ is broken down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The electron transport chain begins when ____________________ or ____________________ are oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the ultimate fate of the carbon atoms in a glucose molecule that goes through aerobic respiration?
A) It is turned into starch.
B) It is converted to pyruvate.
C) It is converted to glycogen.
D) It is released as carbon dioxide.
E) It is recycled in the citric acid cycle.
A) It is turned into starch.
B) It is converted to pyruvate.
C) It is converted to glycogen.
D) It is released as carbon dioxide.
E) It is recycled in the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which process might be affected by the mutation of a transmembrane protein in the mitochondrial membrane?
A) establishment of hydrogen ion gradient
B) reduction of coenzyme NADH
C) reduction of coenzyme FADH2
D) glucose transport into the mitochondrion
E) transfer of acetyl CoA into the mitochondrion
A) establishment of hydrogen ion gradient
B) reduction of coenzyme NADH
C) reduction of coenzyme FADH2
D) glucose transport into the mitochondrion
E) transfer of acetyl CoA into the mitochondrion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "62" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "62" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
During alcoholic fermentation,____________________ is converted into ethanol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
About how many net molecules of ATP are produced at the end of the three stages of aerobic respiration?
A) 38
B) 36
C) 32
D) 16
E) 4
A) 38
B) 36
C) 32
D) 16
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What substance causes yeast bread to rise?
A) alcohol
B) lactic acid
C) sugar
D) carbon dioxide
E) oxygen
A) alcohol
B) lactic acid
C) sugar
D) carbon dioxide
E) oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Labeling. Use these molecules to label the major inputs and/or outputs of the citric acid cycle on the figure below.Figure 7.8

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "61" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

-What molecule corresponds to the item labeled as "61" in the accompanying figure?
A)CO2
B)NADH
C)ADP + Pi
D)FADH2
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Cells dismantle triglycerides by first breaking the bonds that connect fatty acid tails to _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Fatty acids must first be converted to which substance before they can enter the citric acid cycle?
A) PGAL
B) pyruvate
C) acetyl-CoA
D) amino acids
E) glucose
A) PGAL
B) pyruvate
C) acetyl-CoA
D) amino acids
E) glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following equations summarizes glycolysis?
A) C6H12O6 + O2 ® CO2 + H2O
B) CO2 + H2O ® C6H12O6 + O2
C) C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 ® C12H22O11 + H2O
D) C6H12O6 ® 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2
E) 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2 ® C6H12O6
A) C6H12O6 + O2 ® CO2 + H2O
B) CO2 + H2O ® C6H12O6 + O2
C) C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 ® C12H22O11 + H2O
D) C6H12O6 ® 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2
E) 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2 ® C6H12O6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which stage of aerobic respiration requires an input of two ATP?
A) glycolysis
B) acetyl CoA formation
C) citric acid cycle
D) electron transfer phosphorylation
E) fermentation
A) glycolysis
B) acetyl CoA formation
C) citric acid cycle
D) electron transfer phosphorylation
E) fermentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Aerobic respiration produces two substances that are used in photosynthesis.Which ones are these?
A) Glucose and oxygen
B) Water and carbon dioxide
C) Citric acid and carbon dioxide
D) Starch and alcohol
E) Glucose and carbon dioxide
A) Glucose and oxygen
B) Water and carbon dioxide
C) Citric acid and carbon dioxide
D) Starch and alcohol
E) Glucose and carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



