Deck 4: Three Major Classes of Chemical Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/111
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Three Major Classes of Chemical Reactions
1
Calcium chloride is used to melt ice and snow on roads and sidewalks and to remove water from organic liquids. Calculate the molarity of a solution prepared by diluting 165 mL of 0.688 M calcium chloride to 925.0 mL.
A) 3.86 M
B) 0.743 M
C) 0.222 M
D) 0.123 M
E) 0.114 M
A) 3.86 M
B) 0.743 M
C) 0.222 M
D) 0.123 M
E) 0.114 M
0.123 M
2
A 0.150 M sodium chloride solution is referred to as a physiological saline solution because it has the same concentration of salts as normal human blood. Calculate the mass of solute needed to prepare 275.0 mL of a physiological saline solution.
A) 41.3 g
B) 31.9 g
C) 16.1 g
D) 8.77 g
E) 2.41 g
A) 41.3 g
B) 31.9 g
C) 16.1 g
D) 8.77 g
E) 2.41 g
2.41 g
3
Sodium hydroxide, also known as caustic soda, is used to neutralize acids and to treat cellulose in making of cellophane. Calculate the number of moles of solute in 1.875 L of 1.356 M NaOH solution.
A) 2.543 mol
B) 1.383 mol
C) 0.7232 mol
D) 0.3932 mol
E) 0.001383 mol
A) 2.543 mol
B) 1.383 mol
C) 0.7232 mol
D) 0.3932 mol
E) 0.001383 mol
2.543 mol
4
What volume, in L, of 10.0 M HCl is needed to make 2.00 L of 2.00 M HCl solution by dilution with water?
A) 0.800 L
B) 0.400 L
C) 0.200 L
D) 0.100 L
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) 0.800 L
B) 0.400 L
C) 0.200 L
D) 0.100 L
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How many moles of H+(aq) ions are present in 750 mL of 0.65 M hydrochloric acid?
A) 1.2 mol
B) 0.98 mol
C) 0.87 mol
D) 0.65 mol
E) 0.49 mol
A) 1.2 mol
B) 0.98 mol
C) 0.87 mol
D) 0.65 mol
E) 0.49 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is most soluble in water?
A) benzene, C6H6
B) potassium nitrate, KNO3
C) carbon tetrachloride, CCl4
D) hexane, C6H14
E) ethane, C2H4
A) benzene, C6H6
B) potassium nitrate, KNO3
C) carbon tetrachloride, CCl4
D) hexane, C6H14
E) ethane, C2H4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following will be least soluble in water?
A) potassium sulfate, K2SO4
B) ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3
C) chloromethane, CH3Cl
D) calcium chloride, CaCl2
E) ethanol, C2H6O
A) potassium sulfate, K2SO4
B) ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3
C) chloromethane, CH3Cl
D) calcium chloride, CaCl2
E) ethanol, C2H6O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Sodium chlorate is used as an oxidizer in the manufacture of dyes, explosives, and matches. Calculate the mass of solute needed to prepare 1.575 L of 0.00250 M NaClO3 ( 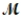 = 106.45 g/mol).
= 106.45 g/mol).
A) 419 g
B) 169 g
C) 0.419 g
D) 0.169 g
E) 0.00394 g
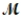 = 106.45 g/mol).
= 106.45 g/mol).A) 419 g
B) 169 g
C) 0.419 g
D) 0.169 g
E) 0.00394 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When 2.61 g of solid Na2CO3 is dissolved in sufficient water to make 250. mL of solution, the concentration of Na2CO3 is:
A) 0.0246 M
B) 10.4 M
C) 0.205 M
D) 0.0985 M
E) 0.141 M
A) 0.0246 M
B) 10.4 M
C) 0.205 M
D) 0.0985 M
E) 0.141 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many moles of H+(aq) ions are present in 1.25 L of 0.75 M nitric acid?
A) 0.60 mol
B) 0.75 mol
C) 0.94 mol
D) 1.7 mol
E) 1.9 mol
A) 0.60 mol
B) 0.75 mol
C) 0.94 mol
D) 1.7 mol
E) 1.9 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How many moles of ions are released when 1.6 mol of ammonium phosphate, (NH4)3PO4, is dissolved in water?
A) 0.40 mol
B) 1.6 mol
C) 3.2 mol
D) 4.8 mol
E) 6.4 mol
A) 0.40 mol
B) 1.6 mol
C) 3.2 mol
D) 4.8 mol
E) 6.4 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Calculate the molarity of a 23.55-mL solution which contains 28.24 mg of sodium sulfate (used in dyeing and printing textiles, 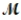 = 139.04 g/mol).
= 139.04 g/mol).
A) 8.625 M
B) 1.199 M
C) 0.8339 M
D) 0.2031 M
E) 0.008625 M
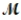 = 139.04 g/mol).
= 139.04 g/mol).A) 8.625 M
B) 1.199 M
C) 0.8339 M
D) 0.2031 M
E) 0.008625 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What will be the final volume of a solution prepared by diluting 25 mL of 8.25 M sodium hydroxide to a concentration of 2.40 M?
A) 330 mL
B) 210 mL
C) 86 mL
D) 60 mL
E) 7.3 mL
A) 330 mL
B) 210 mL
C) 86 mL
D) 60 mL
E) 7.3 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How many mL of concentrated nitric acid (HNO3, 16.0 M) should be diluted with water in order to make 2.00 L of 2.00 M solution?
A) 32.0 mL
B) 62.5 mL
C) 125 mL
D) 250. mL
E) 500. mL
A) 32.0 mL
B) 62.5 mL
C) 125 mL
D) 250. mL
E) 500. mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How many sodium ions are present in 325 mL of 0.850 M Na2SO4?
A) 1.66 × 1023 sodium ions
B) 3.33 × 1023 sodium ions
C) 4.99 × 1023 sodium ions
D) 6.20 × 1023 sodium ions
E) 1.57 × 1024 sodium ions
A) 1.66 × 1023 sodium ions
B) 3.33 × 1023 sodium ions
C) 4.99 × 1023 sodium ions
D) 6.20 × 1023 sodium ions
E) 1.57 × 1024 sodium ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Hydrochloric acid is widely used as a laboratory reagent in refining ore for the production of tin and tantalum, and as a catalyst in organic reactions. Calculate the number of moles of HCl in 62.85 mL of 0.453 M hydrochloric acid.
A) 28.5 mol
B) 1.04 mol
C) 0.139 mol
D) 0.0285 mol
E) 0.00721 mol
A) 28.5 mol
B) 1.04 mol
C) 0.139 mol
D) 0.0285 mol
E) 0.00721 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How many moles of ions are released when 0.27 mol of cobalt(II) chloride, CoCl2, is dissolved in water?
A) 0.81 mol
B) 0.54 mol
C) 0.27 mol
D) 0.18 mol
E) 0.090 mol
A) 0.81 mol
B) 0.54 mol
C) 0.27 mol
D) 0.18 mol
E) 0.090 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Potassium carbonate, K2CO3, sodium iodide, NaI, potassium bromide, KBr, methanol, CH3OH, and ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, are soluble in water. Which produces the largest number of dissolved particles per mole of dissolved solute?
A) K2CO3
B) NaI
C) KBr
D) CH3OH
E) NH4Cl
A) K2CO3
B) NaI
C) KBr
D) CH3OH
E) NH4Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Lithium hydroxide is used in alkaline batteries. Calculate the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 1.495 moles of LiOH in enough water to give a final volume of 750. mL.
A) 1.99 M
B) 1.50 M
C) 1.12 M
D) 0.502 M
E) 0.00199 M
A) 1.99 M
B) 1.50 M
C) 1.12 M
D) 0.502 M
E) 0.00199 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Potassium chloride, KCl, sodium sulfate, Na2SO4, glucose, C6H12O6, carbon dioxide, CO2 and ammonium phosphate, (NH4)3PO4, are soluble in water. Which one produces the largest number of dissolved particles per mole of dissolved solute?
A) KCI
B) Na2SO4
C) C6H12O6
D) CO2
E) (NH4)3PO4
A) KCI
B) Na2SO4
C) C6H12O6
D) CO2
E) (NH4)3PO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following solutions will be the best conductor of electrical current?
A) methyl alcohol, CH3OH(aq)
B) glucose, C6H12O6(aq)
C) potassium chloride, KCl(aq)
D) bromine, Br2(aq)
E) ethylene glycol, C2H6O2(aq)
A) methyl alcohol, CH3OH(aq)
B) glucose, C6H12O6(aq)
C) potassium chloride, KCl(aq)
D) bromine, Br2(aq)
E) ethylene glycol, C2H6O2(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider the reaction: 3Co2+(aq) + 6NO3(aq) + 6Na+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Co3(PO4)2(s) + 6Na+(aq) + 6NO3(aq)
Identify the net ionic equation for this reaction.
A) Na+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → NaNO3(aq)
B) 3Co2+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + Na+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Co3(PO4)2(s) + NaNO3(aq)
C) 3Co2+(aq) + 6NO3-(aq) + 6Na+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Co3(PO4)2(s) + 6NaNO3(aq)
D) 3Co2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Co3(PO4)2(s)
E) None of these choices are correct.
Identify the net ionic equation for this reaction.
A) Na+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → NaNO3(aq)
B) 3Co2+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + Na+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Co3(PO4)2(s) + NaNO3(aq)
C) 3Co2+(aq) + 6NO3-(aq) + 6Na+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Co3(PO4)2(s) + 6NaNO3(aq)
D) 3Co2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Co3(PO4)2(s)
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which one of the following substances is the best electrolyte?
A) CO
B) CH3Cl
C) CH4
D) C2H5OH
E) HCl
A) CO
B) CH3Cl
C) CH4
D) C2H5OH
E) HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Select the precipitate that forms when aqueous lead(II) nitrate reacts with aqueous sodium sulfate.
A) NaNO3
B) Na2NO3
C) PbSO4
D) Pb2SO4
E) PbS
A) NaNO3
B) Na2NO3
C) PbSO4
D) Pb2SO4
E) PbS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Select the net ionic equation for the reaction between sodium chloride and mercury(I) nitrate. 2NaCl(aq) + Hg2(NO3)2(aq) → 2NaNO3(aq) + Hg2Cl2(s)
A) Na+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → NaNO3(aq)
B) Hg22+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → Hg2Cl2(s)
C) NaCl(aq) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
D) Hg2(NO3)2(aq) → Hg22+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq)
E) Hg22+(aq) → Hg2(s)
A) Na+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → NaNO3(aq)
B) Hg22+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → Hg2Cl2(s)
C) NaCl(aq) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
D) Hg2(NO3)2(aq) → Hg22+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq)
E) Hg22+(aq) → Hg2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Select the precipitate that forms when the following reactants are mixed. Na2CO3(aq) + BaCl2(aq) →
A) Ba2CO3
B) BaCO3
C) NaCl
D) NaCl2
E) BaO
A) Ba2CO3
B) BaCO3
C) NaCl
D) NaCl2
E) BaO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Copper(II) sulfide, CuS, is used in the development of aniline black dye in textile printing. What is the maximum mass of CuS which can be formed when 38.0 mL of 0.500 M CuCl2 are mixed with 42.0 mL of 0.600 M (NH4)2S? Aqueous ammonium chloride is the other product.
A) 2.41 g
B) 1.82 g
C) 1.21 g
D) 0.909 g
E) 0.044 g
A) 2.41 g
B) 1.82 g
C) 1.21 g
D) 0.909 g
E) 0.044 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What, if any, are the spectator ions when aqueous solutions of HBr and RbOH neutralize each other?
A) H+ and OH-
B) H+ and Rb+
C) Rb+ and Br-
D) Br- and OH-
E) There are no spectator ions in this reaction.
A) H+ and OH-
B) H+ and Rb+
C) Rb+ and Br-
D) Br- and OH-
E) There are no spectator ions in this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Select the precipitate that forms when aqueous ammonium sulfide reacts with aqueous copper(II) nitrate.
A) CuS
B) Cu2S
C) NH4NO3
D) NH4(NO3)2
E) CuSO4
A) CuS
B) Cu2S
C) NH4NO3
D) NH4(NO3)2
E) CuSO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which one of the following ionic compounds is soluble in water?
A) Na2S
B) PbI2
C) AgCl
D) CuS
E) Ca3(PO4)2
A) Na2S
B) PbI2
C) AgCl
D) CuS
E) Ca3(PO4)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Magnesium carbonate, MgCO3, is insoluble. Identify the spectator ions when aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate and magnesium chloride are combined.
A) Mg2+ and CO32-
B) Na+ and Cl-
C) Mg2+ and Cl-
D) Na+ and CO32-
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Mg2+ and CO32-
B) Na+ and Cl-
C) Mg2+ and Cl-
D) Na+ and CO32-
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following solutions will be the poorest conductor of electrical current?
A) sucrose, C12H22O11(aq)
B) sodium chloride, NaCl(aq)
C) potassium nitrate, KNO3(aq)
D) lithium hydroxide, LiOH(aq)
E) sulfuric acid, H2SO4(aq)
A) sucrose, C12H22O11(aq)
B) sodium chloride, NaCl(aq)
C) potassium nitrate, KNO3(aq)
D) lithium hydroxide, LiOH(aq)
E) sulfuric acid, H2SO4(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which one of the following ionic compounds is insoluble in water?
A) Na3PO4
B) AgNO3
C) NaCl
D) CaCO3
E) MgCl2
A) Na3PO4
B) AgNO3
C) NaCl
D) CaCO3
E) MgCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Select the correct name and chemical formula for the precipitate that forms when the following reactants are mixed. CuCl2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) →
A) copper(I) carbonate, Cu2CO3
B) copper(II) carbonate, Cu2CO3
C) copper(I) carbonate, CuCO3
D) copper(II) carbonate, CuCO3
E) sodium chloride, NaCl
A) copper(I) carbonate, Cu2CO3
B) copper(II) carbonate, Cu2CO3
C) copper(I) carbonate, CuCO3
D) copper(II) carbonate, CuCO3
E) sodium chloride, NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which one of the following substances, when dissolved in water at equal molar concentrations, will give the solution with the lowest electrical conductivity?
A) CaCl2
B) HNO3
C) NH3
D) C6H12O6 (glucose)
E) CO2
A) CaCl2
B) HNO3
C) NH3
D) C6H12O6 (glucose)
E) CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
1.0 M aqueous solutions of the following substances are prepared. Which one would you expect to have the lowest electrical conductivity?
A) NaOH
B) CH3CH2OH (ethanol)
C) KBr
D) CH3COOH (acetic acid)
E) HClO4
A) NaOH
B) CH3CH2OH (ethanol)
C) KBr
D) CH3COOH (acetic acid)
E) HClO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Select the correct name and chemical formula for the precipitate that forms when the following reactants are mixed. CoSO4(aq) + (NH4)3PO4(aq) →
A) cobalt(II) phosphate, Co3(PO4)2
B) cobalt(III) phosphate, Co3(PO4)2
C) cobalt(II) phosphate, CoPO4
D) cobalt(III) phosphate, CoPO4
E) ammonium sulfate, (NH4)2SO4
A) cobalt(II) phosphate, Co3(PO4)2
B) cobalt(III) phosphate, Co3(PO4)2
C) cobalt(II) phosphate, CoPO4
D) cobalt(III) phosphate, CoPO4
E) ammonium sulfate, (NH4)2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Select the precipitate that forms when the following reactants are mixed. Mg(CH3COO)2(aq) + LiOH(aq) →
A) LiCH3COO
B) Li(CH3COO)2
C) MgOH
D) Mg(OH)2
E) CH3OH
A) LiCH3COO
B) Li(CH3COO)2
C) MgOH
D) Mg(OH)2
E) CH3OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the following reaction, what ions, if any, are spectator ions? Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaCl(aq) → PbCl2(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
A) Pb2+(aq), Cl-(aq)
B) Na+(aq), NO3-(aq)
C) Pb2+(aq), NO3-(aq)
D) Na+(aq), Cl-(aq)
E) There are no spectator ions.
A) Pb2+(aq), Cl-(aq)
B) Na+(aq), NO3-(aq)
C) Pb2+(aq), NO3-(aq)
D) Na+(aq), Cl-(aq)
E) There are no spectator ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An acid
A) produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.
B) changes the color of phenolphthalein indicator from colorless to pink.
C) donates electrons in an electron transfer reaction.
D) donates protons in a proton transfer reaction.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.
B) changes the color of phenolphthalein indicator from colorless to pink.
C) donates electrons in an electron transfer reaction.
D) donates protons in a proton transfer reaction.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Ammonia, NH3, produces hydroxide ions in aqueous solution by
A) donating a proton to an acid molecule.
B) donating a proton to a water molecule.
C) donating a hydrogen ion to a water molecule.
D) accepting an electron from an acid molecule.
E) accepting a proton from a water molecule.
A) donating a proton to an acid molecule.
B) donating a proton to a water molecule.
C) donating a hydrogen ion to a water molecule.
D) accepting an electron from an acid molecule.
E) accepting a proton from a water molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Select the correct set of products for the following reaction. Ba(OH)2(aq) + HNO3(aq) →
A) BaN2(s) + H2O(l)
B) Ba(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l)
C) Ba(s) + H2(g) + NO2(g)
D) Ba2O(s) + NO2(g) + H2O(l)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) BaN2(s) + H2O(l)
B) Ba(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l)
C) Ba(s) + H2(g) + NO2(g)
D) Ba2O(s) + NO2(g) + H2O(l)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 0.00100 mol sample of Ca(OH)2 requires 25.00 mL of aqueous HCl for neutralization according to the reaction below. What is the concentration of the HCl? Equation: Ca(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
A) 0.0200 M
B) 0.0400 M
C) 0.0800 M
D) 4.00 × 10-5 M
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) 0.0200 M
B) 0.0400 M
C) 0.0800 M
D) 4.00 × 10-5 M
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is a weak base?
A) NH3
B) Ca(OH)2
C) Ba(OH)2
D) NaOH
E) CH3COOH
A) NH3
B) Ca(OH)2
C) Ba(OH)2
D) NaOH
E) CH3COOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid, CH3COOH, dissolved in water. A 5.54-g sample of vinegar was neutralized by 30.10 mL of 0.100 M NaOH. What is the percent by weight of acetic acid in the vinegar?
A) 0.184%
B) 1.63%
C) 3.26%
D) 5.43%
E) 9.23%
A) 0.184%
B) 1.63%
C) 3.26%
D) 5.43%
E) 9.23%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which, if any, of the following properties applies to weak acids?
A) They are strong electrolytes.
B) They are excellent conductors of electricity.
C) When dissolved in water, they do not ionize completely.
D) All of these choices are correct.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) They are strong electrolytes.
B) They are excellent conductors of electricity.
C) When dissolved in water, they do not ionize completely.
D) All of these choices are correct.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A base
A) causes phenolphthalein indicator to change from colorless to pink.
B) donates a proton in a proton transfer reaction.
C) accepts electrons in an electron transfer reaction.
D) produces hydrogen ions in solution.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) causes phenolphthalein indicator to change from colorless to pink.
B) donates a proton in a proton transfer reaction.
C) accepts electrons in an electron transfer reaction.
D) produces hydrogen ions in solution.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A standard solution of 0.243 M NaOH was used to determine the concentration of a hydrochloric acid solution. If 46.33 mL of NaOH is needed to neutralize 10.00 mL of the acid, what is the molar concentration of the acid?
A) 0.0524 M
B) 0.888 M
C) 1.13 M
D) 2.26 M
E) 2.43 M
A) 0.0524 M
B) 0.888 M
C) 1.13 M
D) 2.26 M
E) 2.43 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How many milliliters of 1.58 M HCl are needed to react completely with 23.2 g of NaHCO3 (  = 84.02 g/mol)? HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) → NaCl(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
= 84.02 g/mol)? HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) → NaCl(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
A) 638 mL
B) 572 mL
C) 536 mL
D) 276 mL
E) 175 mL
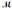 = 84.02 g/mol)? HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) → NaCl(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
= 84.02 g/mol)? HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) → NaCl(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)A) 638 mL
B) 572 mL
C) 536 mL
D) 276 mL
E) 175 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Sodium tripolyphosphate is used in detergents to make them effective in hard water. Calculate the oxidation number of phosphorus in Na5P3O10.
A) +3
B) +5
C) +10
D) +15
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) +3
B) +5
C) +10
D) +15
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is a strong acid?
A) H3PO4
B) HNO3
C) HF
D) CH3COOH
E) H2O
A) H3PO4
B) HNO3
C) HF
D) CH3COOH
E) H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Select the best statement relating to the following reaction: 2MnO2(s) + KClO3(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → 2KMnO4(aq) + KCl(aq) + H2O(l)
A) Mn in MnO2 is oxidized.
B) O in KClO3 is the oxidizing agent.
C) K in KClO3 is the reducing agent.
D) H in KOH is oxidized.
E) Cl in KClO3 is the reducing agent.
A) Mn in MnO2 is oxidized.
B) O in KClO3 is the oxidizing agent.
C) K in KClO3 is the reducing agent.
D) H in KOH is oxidized.
E) Cl in KClO3 is the reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is a strong base?
A) NH3
B) Ca(OH)2
C) Al(OH)3
D) B(OH)3
E) CH3OH
A) NH3
B) Ca(OH)2
C) Al(OH)3
D) B(OH)3
E) CH3OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Calculate the oxidation number of sulfur in sodium metabisulfite, Na2S2O5.
A) -2
B) +2
C) +4
D) +5
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) -2
B) +2
C) +4
D) +5
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Calculate the oxidation number of the chlorine in perchloric acid, HClO4, a strong oxidizing agent.
A) -1
B) +4
C) +5
D) +7
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) -1
B) +4
C) +5
D) +7
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is a weak acid?
A) H2SO4
B) HNO3
C) HF
D) HBr
E) HCl
A) H2SO4
B) HNO3
C) HF
D) HBr
E) HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Automobile batteries use 3.0 M H2SO4 as an electrolyte. How much 1.20 M NaOH will be needed to neutralize 225 mL of battery acid? H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Na2SO4(aq)
A) 0.045 L
B) 0.28 L
C) 0.56 L
D) 0.90 L
E) 1.1 L
A) 0.045 L
B) 0.28 L
C) 0.56 L
D) 0.90 L
E) 1.1 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a redox reaction, electrons are transferred
A) from the substance being oxidized to the reducing agent.
B) from the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent.
C) from the substance being reduced to the oxidizing agent.
D) from the substance being oxidized to the substance being reduced.
E) from the substance being reduced to the substance being oxidized.
A) from the substance being oxidized to the reducing agent.
B) from the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent.
C) from the substance being reduced to the oxidizing agent.
D) from the substance being oxidized to the substance being reduced.
E) from the substance being reduced to the substance being oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which one of the following substances is a strong acid?
A) HNO3
B) H2CO3
C) NH3
D) CH3COOH
E) H3PO4
A) HNO3
B) H2CO3
C) NH3
D) CH3COOH
E) H3PO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Select the net ionic equation for the reaction between lithium hydroxide and hydrobromic acid. LiOH(aq) + HBr(aq) → H2O(l) + LiBr(aq)
A) LiOH(aq) → Li+(aq) + OH-(aq)
B) HBr(aq) → H+(aq) + Br-(aq)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
D) Li+(aq) + Br-(aq) → LiBr(aq)
E) Li+(aq) + OH-(aq) + H+(aq) + Br-(aq) → H2O(l) + LiBr(aq)
A) LiOH(aq) → Li+(aq) + OH-(aq)
B) HBr(aq) → H+(aq) + Br-(aq)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
D) Li+(aq) + Br-(aq) → LiBr(aq)
E) Li+(aq) + OH-(aq) + H+(aq) + Br-(aq) → H2O(l) + LiBr(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Identify the oxidizing agent in the following redox reaction. Hg2+(aq) + Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + Hg(l)
A) Hg2+(aq)
B) Cu(s)
C) Cu2+(aq)
D) Hg(l)
E) Hg2+(aq) and Cu2+(aq)
A) Hg2+(aq)
B) Cu(s)
C) Cu2+(aq)
D) Hg(l)
E) Hg2+(aq) and Cu2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following is not a redox reaction?
A) 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
B) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
C) BaCl2(aq) + K2CrO4(aq) → BaCrO4(aq) + 2KCl(aq)
D) 2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) → Al2O3(s) + 2Fe(s)
E) 2H2O(g) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
A) 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
B) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
C) BaCl2(aq) + K2CrO4(aq) → BaCrO4(aq) + 2KCl(aq)
D) 2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) → Al2O3(s) + 2Fe(s)
E) 2H2O(g) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Sodium thiosulfate, Na2S2O3, is used as a "fixer" in black and white photography. Identify the reducing agent in the reaction of thiosulfate with iodine. 2S2O32-(aq) + I2(aq) → S4O62-(aq) + 2I-(aq)
A) I2(aq)
B) I-(aq)
C) S2O32-(aq)
D) S4O62-(aq)
E) S2O32-(aq) and I-(aq)
A) I2(aq)
B) I-(aq)
C) S2O32-(aq)
D) S4O62-(aq)
E) S2O32-(aq) and I-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the statements below correctly describes the combustion of glucose, shown below? C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
A) Hydrogen in C6H12O6 is being reduced.
B) Oxygen in O2 is being oxidized.
C) Hydrogen in C6H12O6 is the reducing agent.
D) Oxygen in C6H12O6 is the oxidizing agent.
E) Carbon in C6H12O6 is being oxidized.
A) Hydrogen in C6H12O6 is being reduced.
B) Oxygen in O2 is being oxidized.
C) Hydrogen in C6H12O6 is the reducing agent.
D) Oxygen in C6H12O6 is the oxidizing agent.
E) Carbon in C6H12O6 is being oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The amount of calcium present in milk can be determined by adding oxalate to a sample and measuring the mass of calcium oxalate precipitated. What is the mass percent of calcium if 0.429 g of calcium oxalate forms in a 125-g sample of milk when excess aqueous sodium oxalate is added? Na2C2O4(aq) + Ca2+(aq) → CaC2O4(s) + 2Na+(aq)
A) 0.107%
B) 0.202%
C) 0.343%
D) 1.10%
E) 1.37%
A) 0.107%
B) 0.202%
C) 0.343%
D) 1.10%
E) 1.37%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Select the classification for the following reaction. KOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l)
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Combination
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Combination
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Select the classification for the following reaction. H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
A) Combination
B) Decomposition
C) Displacement
D) Acid-base
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Combination
B) Decomposition
C) Displacement
D) Acid-base
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Select the classification for the following reaction. NH3(aq) + HNO3(aq) → NH4NO3(aq)
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Aqueous potassium iodate (KIO3) and potassium iodide (KI) react in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid, as shown below. KIO3(aq) + 5KI(aq) + 6HCl(aq) → 3I2(aq) + 6KCl(aq) + 3H2O(l)
What mass of iodine (I2) is formed when 50.0 mL of 0.020 M KIO3 solution reacts with an excess of KI and HCl?
A) 0.13 g I2
B) 0.25 g I2
C) 0.38 g I2
D) 0.76 g I2
E) None of these choices are correct.
What mass of iodine (I2) is formed when 50.0 mL of 0.020 M KIO3 solution reacts with an excess of KI and HCl?
A) 0.13 g I2
B) 0.25 g I2
C) 0.38 g I2
D) 0.76 g I2
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The oxidation numbers of P, S, and Cl in H2PO2-, H2S, and KClO4 are, respectively
A) -1, -1, +3.
B) -1, -2, +7.
C) +1, -2, +7.
D) -1, -2, +3.
E) +1, +2, +7.
A) -1, -1, +3.
B) -1, -2, +7.
C) +1, -2, +7.
D) -1, -2, +3.
E) +1, +2, +7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Select the classification for the following reaction. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Combination
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Combination
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which one of the following is a redox reaction?
A) 2Na(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
B) Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s)
C) K2Cr2O7(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → 2K2CrO4(aq) + H2O(l)
D) Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
E) H2O(l) → H+(aq) + OH-(aq)
A) 2Na(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
B) Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s)
C) K2Cr2O7(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → 2K2CrO4(aq) + H2O(l)
D) Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
E) H2O(l) → H+(aq) + OH-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Identify all the spectator ions in the following reaction. 2KMnO4(aq) + 10FeSO4(aq) + 8H2SO4(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2MnSO4(aq) + 5Fe2(SO4)3(aq) +8H2O(l)
A) only K+
B) only SO42-
C) only K+ and SO42-
D) only K+, SO42-, and Fe2+
E) only K+, SO42-, Fe2+, and Mn2+
A) only K+
B) only SO42-
C) only K+ and SO42-
D) only K+, SO42-, and Fe2+
E) only K+, SO42-, Fe2+, and Mn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Select the classification for the following reaction. Fe2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) → Fe(OH)2(s)
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Aqueous potassium iodate (KIO3) and potassium iodide (KI) react in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl), as shown below. KIO3(aq) + 5KI(aq) + 6HCl(aq) → 3I2(aq) + 6KCl(aq) + 3H2O(l)
What mass of iodine (I2) is formed when 15.0 mL of 0.0050 M KIO3 solution reacts with 30.0 mL of 0.010 M KI solution in the presence of excess HCl?
A) 0.023 g I2
B) 0.029 g I2
C) 0.057 g I2
D) 0.046 g I2
E) 0.076 g I2
What mass of iodine (I2) is formed when 15.0 mL of 0.0050 M KIO3 solution reacts with 30.0 mL of 0.010 M KI solution in the presence of excess HCl?
A) 0.023 g I2
B) 0.029 g I2
C) 0.057 g I2
D) 0.046 g I2
E) 0.076 g I2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Select the classification for the following reaction. BaCl2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2KCl(aq)
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which one of the following is not a redox reaction?
A) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
B) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
C) 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
D) Fe2O3(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) → Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2O(l)
E) 2KMnO4(aq) + 10FeSO4(aq) + 8H2SO4(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2MnSO4(aq) + 5Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + 8H2O(l)
A) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
B) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
C) 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
D) Fe2O3(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) → Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2O(l)
E) 2KMnO4(aq) + 10FeSO4(aq) + 8H2SO4(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2MnSO4(aq) + 5Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + 8H2O(l)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the oxidation number of iodine in I2.
A) -1
B) 0
C) +1
D) +7
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) -1
B) 0
C) +1
D) +7
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Select the classification for the following reaction. Fe(s) + 2Fe3+(aq) → 3Fe2+(aq)
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Precipitation
B) Acid-base
C) Redox
D) Decomposition
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which one of the following is not a redox reaction?
A) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
B) Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
C) H2O(l) + NH3(g) → NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
D) 6FeSO4(aq) + K2Cr2O7(aq) + 7H2SO4(aq) → Cr2(SO4)3(aq) + 3Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + K2SO4(aq) + 7H2O(l)
E) Cl2(g) + 2KBr(aq) → Br2(l) + 2KCl(aq)
A) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
B) Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
C) H2O(l) + NH3(g) → NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
D) 6FeSO4(aq) + K2Cr2O7(aq) + 7H2SO4(aq) → Cr2(SO4)3(aq) + 3Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + K2SO4(aq) + 7H2O(l)
E) Cl2(g) + 2KBr(aq) → Br2(l) + 2KCl(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



