Deck 7: Ocean Structure and Circulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Ocean Structure and Circulation
1
A water mass at depth in the ocean has temperatures and salinities that are usually determined by the conditions present when the water mass was last at the sea surface.
True
2
The pycnocline of the oceans is usually found at depths exceeding 2000 m.
False
3
The density of Arctic Ocean water is controlled more by salinity than by temperature.
True
4
Wind-driven surface water moves in a complex manner as a function of depth. This is called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Isothermal water is stable and does not overturn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The pycnocline is an area where temperature changes rapidly with depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Many combinations of salinity and temperature of seawater can produce the same density of seawater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Temperature affects density in the Arctic Ocean more than salinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Meanders in the Gulf Stream current can pinch off to form warm and cold core ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The properties of seawater at depth are determined by surface conditions in the area where the water sinks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Usually temperature, salinity, and pressure distributions cause ocean water density to increase with depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The density of Mediterranean Intermediate Water is influenced more by salinity than temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In an area where surface currents converge, the water upwells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Antarctic bottom water has a very narrow range of both salinity and temperature; this water is nearly homogeneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the oceans, the zone where density of water changes rapidly with depth is called a pycnocline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Increasing temperature also increases density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Wind blowing across the sea surface can create paired right- and left-handed circulation cells knows as ________ cells, leading to parallel zones of surface convergence and divergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Water of a lower density usually lies below water of a greater density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Increasing salinity increases density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The large ocean surface-current gyres centered on about 30°N ________.
A) rotate counterclockwise
B) do not rotate
C) have depressed surface elevations
D) rotate clockwise
E) alternate their direction of rotation with the seasons
A) rotate counterclockwise
B) do not rotate
C) have depressed surface elevations
D) rotate clockwise
E) alternate their direction of rotation with the seasons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The South Equatorial current of the Pacific Ocean moves surface water from the Southern Hemisphere to the Northern Hemisphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
North Atlantic deep water ________.
A) flows to the south
B) rises toward the surface in the Southern Ocean
C) is formed off Labrador
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.
A) flows to the south
B) rises toward the surface in the Southern Ocean
C) is formed off Labrador
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The coldest, deepest, densest water in the oceans ________.
A) is formed around Antarctica
B) flows north
C) is Antarctic bottom water
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.
A) is formed around Antarctica
B) flows north
C) is Antarctic bottom water
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If very warm and salty sea water is added on top of average seawater, ________.
A) the warm salty water will float at the surface
B) the warm salty water will sink to the bottom and stagnate
C) the warm salty water will sink and move rapidly out of the area
D) an overturn will begin
E) The answer cannot be determined unless the densities of the warm salty water and average sea water are known.
A) the warm salty water will float at the surface
B) the warm salty water will sink to the bottom and stagnate
C) the warm salty water will sink and move rapidly out of the area
D) an overturn will begin
E) The answer cannot be determined unless the densities of the warm salty water and average sea water are known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The thermocline found in water above 500 m at temperate latitudes disappears and the water column becomes neutral in ________.
A) spring
B) summer
C) fall
D) winter
E) None of these is correct; it does not disappear.
A) spring
B) summer
C) fall
D) winter
E) None of these is correct; it does not disappear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A water type having both high salinity and warm temperature but dense enough to be found at about 1000 m in the central North Atlantic has been formed ________.
A) in equatorial regions
B) in the Red Sea
C) in the Mediterranean Sea
D) near Greenland
E) in the Caribbean Sea
A) in equatorial regions
B) in the Red Sea
C) in the Mediterranean Sea
D) near Greenland
E) in the Caribbean Sea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A surface gyre system in the Southern Hemisphere ________.
A) promotes upwelling and surface depression if it rotates clockwise
B) promotes upwelling and surface elevation if it rotates counterclockwise
C) retards upwelling and decreases surface elevation if rotating counterclockwise
D) retards upwelling and increases surface elevation if rotating counterclockwise
E) Rotation in either direction does not affect upwelling.
A) promotes upwelling and surface depression if it rotates clockwise
B) promotes upwelling and surface elevation if it rotates counterclockwise
C) retards upwelling and decreases surface elevation if rotating counterclockwise
D) retards upwelling and increases surface elevation if rotating counterclockwise
E) Rotation in either direction does not affect upwelling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A good example of thermohaline circulation is found ________.
A) in equatorial regions
B) in the central South Pacific
C) close to Antarctica
D) along the east coast of the United States
E) in the Gulf of Mexico
A) in equatorial regions
B) in the central South Pacific
C) close to Antarctica
D) along the east coast of the United States
E) in the Gulf of Mexico

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The water type occupying the greatest volume of the Atlantic Ocean is ________.
A) Antarctic bottom water
B) Antarctic intermediate water
C) circumpolar Antarctic water
D) North Atlantic deep water
E) surface water
A) Antarctic bottom water
B) Antarctic intermediate water
C) circumpolar Antarctic water
D) North Atlantic deep water
E) surface water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Thermohaline circulation is driven by changes in ________.
A) viscosity
B) surface tension
C) convection
D) pressure
E) density
A) viscosity
B) surface tension
C) convection
D) pressure
E) density

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following are affected by the density of the surface water?
A) Transparency
B) Density layering
C) Convective overturn
D) Density layering and convective overturn
E) All of these are correct.
A) Transparency
B) Density layering
C) Convective overturn
D) Density layering and convective overturn
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Deep-ocean water in the Atlantic Ocean flows mainly ________.
A) east-west
B) north-south
C) to the right
D) to the left
E) None of these is correct; there is no deep-water flow.
A) east-west
B) north-south
C) to the right
D) to the left
E) None of these is correct; there is no deep-water flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If extremely cold fresh water is added on top of seawater, ________.
A) the cold water will float at the surface
B) the cold water will sink to the bottom and stagnate
C) the cold water will sink and move rapidly out of the area
D) an overturn will begin immediately
E) the wind will control the surface mixing
A) the cold water will float at the surface
B) the cold water will sink to the bottom and stagnate
C) the cold water will sink and move rapidly out of the area
D) an overturn will begin immediately
E) the wind will control the surface mixing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In areas of downwelling, a near-surface ________ is unlikely.
A) halocline.
B) pycnocline.
C) thermocline.
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.
A) halocline.
B) pycnocline.
C) thermocline.
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sigma-t is the oceanographers short-hand for the density of seawater. It is defined as (density − 1.0) × . If the density of seawater is 1.02925 g/cm3, the sigma-t value is 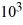
A) 25.29.
B) 2.9925.
C) 0.2925.
D) 29.25.
E) 0.02529.
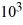
A) 25.29.
B) 2.9925.
C) 0.2925.
D) 29.25.
E) 0.02529.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Order the following water bodies from highest to lowest salinity.
A) Mediterranean intermediate water, North Atlantic deep water, Antarctic bottom water
B) North Atlantic deep water, Mediterranean intermediate water, Antarctic bottom water
C) Antarctic bottom water, Mediterranean intermediate water, North Atlantic deep water
D) Mediterranean intermediate water, Antarctic bottom water, North Atlantic deep water
E) Antarctic bottom water, North Atlantic deep water, Mediterranean intermediate water
A) Mediterranean intermediate water, North Atlantic deep water, Antarctic bottom water
B) North Atlantic deep water, Mediterranean intermediate water, Antarctic bottom water
C) Antarctic bottom water, Mediterranean intermediate water, North Atlantic deep water
D) Mediterranean intermediate water, Antarctic bottom water, North Atlantic deep water
E) Antarctic bottom water, North Atlantic deep water, Mediterranean intermediate water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A rapid change in temperature with depth is called a ________.
A) halocline
B) thermocline
C) photic level
D) midwater current
E) pycnocline
A) halocline
B) thermocline
C) photic level
D) midwater current
E) pycnocline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If two surface water types with the same density but different salinities and temperatures mix, the resulting water will be ________.
A) denser than both parent types
B) less dense than both parent types
C) denser than the more dense parent type
D) less dense than the less dense parent type
E) the same density as the parent types
A) denser than both parent types
B) less dense than both parent types
C) denser than the more dense parent type
D) less dense than the less dense parent type
E) the same density as the parent types

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the density of the water increases with depth, the water column is ________.
A) stagnant
B) unstable
C) stable
D) neutral
E) well mixed
A) stagnant
B) unstable
C) stable
D) neutral
E) well mixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Layering in the ocean occurs because ________.
A) surface processes form water layers of differing combinations of salinity and temperature
B) processes at depth add and subtract salt and heat
C) atmospheric processes control conditions at the surface
D) surface processes form water layers of differing combinations of salinity and temperature and atmospheric processes control conditions at the surface
E) All of these choices are correct.
A) surface processes form water layers of differing combinations of salinity and temperature
B) processes at depth add and subtract salt and heat
C) atmospheric processes control conditions at the surface
D) surface processes form water layers of differing combinations of salinity and temperature and atmospheric processes control conditions at the surface
E) All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Upwelling along the coast of Peru is very seasonal, due to the continually shifting wind patterns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Upwelling occurs along the coast of California when winds blow from the north.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Ekman Spiral causes current speed to increase with depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Eddies are found at all depths of the oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Downwellings occur at surface convergences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Currents in the northern Indian Ocean change direction seasonally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The Indian Ocean gyre rotates counterclockwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Geostrophic flow occurs when the Coriolis deflection is balanced by an opposite gravitational flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Prevailing westerly winds cause easterly currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The clockwise gyre of the Arctic Ocean is driven by the polar easterlies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Southern Hemisphere winds move surface water 90 degrees to the left of the direction of the wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A convergence of water occurs at the eastern side of each of the main ocean basins as a result of Ekman transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The highly productive seas along the equator are the result of the tropical convergence located there.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Surface eddies can be tracked by satellites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A south wind produces a ________ surface current in the Northern Hemisphere.
A) northern
B) southwest
C) northwest
D) southeast
E) northeast
A) northern
B) southwest
C) northwest
D) southeast
E) northeast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the Northern Hemisphere, the water surface of the open ocean moves ________.
A) at right angles to the wind
B) against the wind
C) parallel to the wind
D) 45 degrees to the right of the wind
E) 45 degrees to the left of the wind
A) at right angles to the wind
B) against the wind
C) parallel to the wind
D) 45 degrees to the right of the wind
E) 45 degrees to the left of the wind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Downwelling is produced by diverging surface currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The sea surface at the center of the Sargasso Sea is depressed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The North Atlantic gyre rotates counterclockwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Ocean currents are deflected to a greater degree by the Coriolis effect than by wind systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The speed of the Florida current is high because ________.
A) the winds are strong at this latitude
B) the water has a high salinity
C) the channel through which it flows is narrow
D) the Coriolis effect is large
E) None of these is correct; it is a slow current.
A) the winds are strong at this latitude
B) the water has a high salinity
C) the channel through which it flows is narrow
D) the Coriolis effect is large
E) None of these is correct; it is a slow current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The North Atlantic current is produced by the ________.
A) northeast trade winds
B) southeast trade winds
C) prevailing westerlies
D) polar easterlies
E) seasonal monsoon
A) northeast trade winds
B) southeast trade winds
C) prevailing westerlies
D) polar easterlies
E) seasonal monsoon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which current moves cold water to warm latitudes?
A) Gulf Stream
B) Kuroshio
C) Peru
D) Agulhas
E) Brazil
A) Gulf Stream
B) Kuroshio
C) Peru
D) Agulhas
E) Brazil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A current meter measures water's ________.
A) speed
B) viscosity
C) direction
D) speed and viscosity
E) speed and direction
A) speed
B) viscosity
C) direction
D) speed and viscosity
E) speed and direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Currents are more intense on the ________ side of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans.
A) northern
B) southern
C) eastern
D) western
E) None of these is correct; they are not more intense on one side.
A) northern
B) southern
C) eastern
D) western
E) None of these is correct; they are not more intense on one side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Currents are less intense on the ________ side of the North Pacific and North Atlantic oceans.
A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west
E) None of these is correct; they are not more intense on one side.
A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west
E) None of these is correct; they are not more intense on one side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A zone of surface divergence is an area of ________ and ________ biological productivity.
A) upwelling; high
B) upwelling; low
C) downwelling; high
D) downwelling; low
E) no vertical motion; average
A) upwelling; high
B) upwelling; low
C) downwelling; high
D) downwelling; low
E) no vertical motion; average

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Gulf Stream forms eddies, or rings, with cold water cores at the ________ edge of the Gulf Stream current.
A) northern
B) southern
C) eastern
D) western
E) either eastern or western
A) northern
B) southern
C) eastern
D) western
E) either eastern or western

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When geostrophic flow is achieved, the ________ force is balanced by the ________ force.
A) centrifugal; centripetal
B) Coriolis; centrifugal
C) Coriolis, gravitational
D) gravitational; centrifugal
E) centripetal; centrifugal
A) centrifugal; centripetal
B) Coriolis; centrifugal
C) Coriolis, gravitational
D) gravitational; centrifugal
E) centripetal; centrifugal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the Southern Hemisphere, the speed of the wind-driven water ________ with depth and the water moves to the ________ of the wind.
A) increases; right
B) increases; left
C) decreases; right
D) decreases; left
E) does not change; left
A) increases; right
B) increases; left
C) decreases; right
D) decreases; left
E) does not change; left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The current at the eastern boundary of the Sargasso Sea is the ________ Current.
A) Gulf Stream
B) North Equatorial
C) Canary
D) Greenland
E) Labrador
A) Gulf Stream
B) North Equatorial
C) Canary
D) Greenland
E) Labrador

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which current flows south along the west coast of the United States?
A) North Pacific
B) California
C) Japanese
D) Gulf Stream
E) Kuroshio
A) North Pacific
B) California
C) Japanese
D) Gulf Stream
E) Kuroshio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The southeast trade winds directly produce the ________ current.
A) Gulf Stream
B) Equatorial Counter
C) South Equatorial
D) West Wind Drift
E) East Australia
A) Gulf Stream
B) Equatorial Counter
C) South Equatorial
D) West Wind Drift
E) East Australia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A seasonal north wind blowing along the west coast of a landmass in the Northern Hemisphere produces ________.
A) downwelling in winter
B) downwelling in summer
C) upwelling in winter
D) upwelling in summer
E) overturn in all seasons
A) downwelling in winter
B) downwelling in summer
C) upwelling in winter
D) upwelling in summer
E) overturn in all seasons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The Atlantic prevailing westerlies drive the ________.
A) Gulf Stream and Canary currents
B) North Atlantic and West Wind Drift
C) Brazil and Benguela currents
D) North and South Equatorial currents
E) None of these is correct.
A) Gulf Stream and Canary currents
B) North Atlantic and West Wind Drift
C) Brazil and Benguela currents
D) North and South Equatorial currents
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which current flows north to south along the northeast coast of the United States?
A) Gulf Stream
B) Labrador
C) Canary
D) North Equatorial
E) North Atlantic
A) Gulf Stream
B) Labrador
C) Canary
D) North Equatorial
E) North Atlantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The average movement of all water affected by the wind is ________ degrees to the ________ of the wind motion in the Southern Hemisphere.
A) 45; right
B) 45; left
C) 90; right
D) 90; left
E) 180; no direction
A) 45; right
B) 45; left
C) 90; right
D) 90; left
E) 180; no direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A south wind produces a ________ flowing surface current in the Southern Hemisphere.
A) northwest
B) northeast
C) south
D) southwest
E) southeast
A) northwest
B) northeast
C) south
D) southwest
E) southeast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A doppler current meter shows an increase in sound frequency if the water flow is ________.
A) moving away from the meter
B) moving toward the meter
C) moving around the meter
D) increasing
E) decreasing
A) moving away from the meter
B) moving toward the meter
C) moving around the meter
D) increasing
E) decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Prevailing ________ winds are needed to provide the net movement of surface water seaward along the west coast of North America.
A) northerly
B) easterly
C) westerly
D) southerly
E) seasonal coastal
A) northerly
B) easterly
C) westerly
D) southerly
E) seasonal coastal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



