Deck 12: Two-Way Analysis of Variance Anova
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/131
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Two-Way Analysis of Variance Anova
1
According to the figure below, which of the following statements would most likely be true? 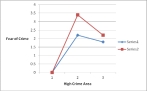
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.

A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.
There is an interaction effect.
2
A single-factor research design can be defined as ______.
A) a research design consisting of all possible combinations of two or more independent variables
B) the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable that changes at the different levels of another independent variable
C) a research design consisting of one independent variable
D) the ability to test interaction effects and the ability to test main effects
A) a research design consisting of all possible combinations of two or more independent variables
B) the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable that changes at the different levels of another independent variable
C) a research design consisting of one independent variable
D) the ability to test interaction effects and the ability to test main effects
a research design consisting of one independent variable
3
According to the figure below, which of the following statements would be true? 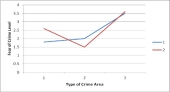
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.

A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.
There is an interaction effect.
4
A ______ is a research design consisting of one independent variable; a ______ is a research design consisting of all possible combination of two or more independent variables.
A) factorial research design; single-factor research design
B) factorial research design; interaction effect
C) single-factor research design; factorial research design
D) single-factor research design; interaction effect
A) factorial research design; single-factor research design
B) factorial research design; interaction effect
C) single-factor research design; factorial research design
D) single-factor research design; interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a researcher examines one independent variable, she would be using a ______ research design; if she was examining the possible combinations of two or more independent variables, she would be using a ______ research design.
A) factorial; single-factor
B) single-factor; factorial
C) factorial; interaction effect
D) single-factor; interaction effect
A) factorial; single-factor
B) single-factor; factorial
C) factorial; interaction effect
D) single-factor; interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
According to the following table, which would be true about the interaction effect? 
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.

A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to the following table, which would be true about the interaction effect? 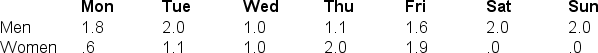
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.
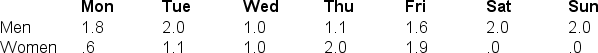
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An advantage of a factorial research design over a single-factor research design is the ability to ______.
A) examine the effects of a single independent variable
B) examine a non-effect between the independent and dependent variables
C) eliminate main effects between the single independent variables
D) examine interaction effects between independent variables
A) examine the effects of a single independent variable
B) examine a non-effect between the independent and dependent variables
C) eliminate main effects between the single independent variables
D) examine interaction effects between independent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
______ are defined as the effect of an independent variable on the dependent variable within a factorial research design.
A) Simple effects
B) Main effects
C) Interaction effects
D) Dependent effects
A) Simple effects
B) Main effects
C) Interaction effects
D) Dependent effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a researcher wanted to examine all of the possible combinations of two or more independent variables, she would want to use a ______ research design.
A) factorial
B) main effect
C) interaction effect
D) single-factor
A) factorial
B) main effect
C) interaction effect
D) single-factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the figure below, which of the following statements would most likely be true? 
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is both a main effect and an interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no main effect.

A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is both a main effect and an interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no main effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A factorial research design can be defined as ______.
A) a research design consisting of all possible combinations of two or more independent variables
B) the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable that changes at the different levels of another independent variable
C) a research design consisting of one independent variable
D) an independent variable consisting of more than two groups
A) a research design consisting of all possible combinations of two or more independent variables
B) the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable that changes at the different levels of another independent variable
C) a research design consisting of one independent variable
D) an independent variable consisting of more than two groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to the following table, which would be true about the interaction effect? 
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is both a main effect and an interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no main effect.

A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is both a main effect and an interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no main effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Factorial research designs allow a researcher to examine what type of effect between variables?
A) non-effect
B) main effect
C) simple effect
D) interaction effect
A) non-effect
B) main effect
C) simple effect
D) interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A ______ research design consists of all possible combinations of two or more independent variables.
A) factorial
B) single-factor
C) interaction
D) main effect
A) factorial
B) single-factor
C) interaction
D) main effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An interaction effect can be defined as the effect ______.
A) of an independent variable within a single-factor research design
B) of one independent variable on the dependent variable changing at the different levels of another independent variable
C) of one independent variable at one of the levels of another independent variable
D) that does not occur between the independent variables and the dependent variables
A) of an independent variable within a single-factor research design
B) of one independent variable on the dependent variable changing at the different levels of another independent variable
C) of one independent variable at one of the levels of another independent variable
D) that does not occur between the independent variables and the dependent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
According to the figure below, which of the following statements would be true? 
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.

A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is a main effect but no interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no interaction effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the figure below, which of the following statements would most likely be true? 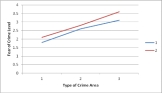
A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is both a main effect and an interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no main effect.

A) There is no interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) There is both a main effect and an interaction effect.
D) There is a simple effect but no main effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
______ is a research design consisting of one independent variable.
A) Factorial research design
B) Single-factor research design
C) Interaction effect
D) Main effect
A) Factorial research design
B) Single-factor research design
C) Interaction effect
D) Main effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
______ occurs when the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable changes at the different levels of another independent variable.
A) An interaction effect
B) A main effect
C) A simple effect
D) A significant effect
A) An interaction effect
B) A main effect
C) A simple effect
D) A significant effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Marginal means are the means ______.
A) of the dependent variable for a particular combination of independent variables
B) in a table that represent a main effect
C) of the independent variables
D) in a table that represent a simple effect
A) of the dependent variable for a particular combination of independent variables
B) in a table that represent a main effect
C) of the independent variables
D) in a table that represent a simple effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the following table for the next five questions

What is the marginal mean for the high crime area?
A) 3.10
B) 3.70
C) 3.40
D) 2.55

What is the marginal mean for the high crime area?
A) 3.10
B) 3.70
C) 3.40
D) 2.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
______ are defined as the means in a table that represent a main effect.
A) Main means
B) Interaction means
C) Cell means
D) Marginal means
A) Main means
B) Interaction means
C) Cell means
D) Marginal means

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
After calculating the marginal means in the table below, which variable has a significant main effect? (assume any difference between the means implies the main effect is significant) 
A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
After calculating the marginal means in the table below, which variable has a significant main effect? (assume any difference between the means implies the main effect is significant) 
A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the following table for the next five questions

What is the marginal mean for the medium crime area?
A) 3.10
B) 3.70
C) 3.40
D) 2.55

What is the marginal mean for the medium crime area?
A) 3.10
B) 3.70
C) 3.40
D) 2.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A(n) ______ is the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable that changes at the different levels of another independent variable, while a ______ is the effect of an independent variable on the dependent variable within a factorial research design.
A) interaction effect; main effect
B) main effect; interaction effect
C) main effect; simple effect
D) interaction effect; simple effect
A) interaction effect; main effect
B) main effect; interaction effect
C) main effect; simple effect
D) interaction effect; simple effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following table for the next five questions

What is the marginal mean for men?
A) 3.07
B) 3.10
C) 3.37
D) 3.70

What is the marginal mean for men?
A) 3.07
B) 3.10
C) 3.37
D) 3.70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Main effects are defined as the effect of ______.
A) the dependent variable on the independent variable within a factorial research design
B) one independent variable at one of the levels of another independent variable
C) an independent variable on the dependent variable within a factorial research design
D) one independent variable on the dependent variable that changes at the different levels of another independent variable
A) the dependent variable on the independent variable within a factorial research design
B) one independent variable at one of the levels of another independent variable
C) an independent variable on the dependent variable within a factorial research design
D) one independent variable on the dependent variable that changes at the different levels of another independent variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Use the following table for the next five questions

What is the marginal mean for women?
A) 3.07
B) 3.10
C) 3.37
D) 3.70

What is the marginal mean for women?
A) 3.07
B) 3.10
C) 3.37
D) 3.70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
______ is the effect of an independent variable on the dependent variable within a factorial research design, while ______ are the means in the table that represent the main effect.
A) Interaction effect; marginal means
B) Interaction effect; cell means
C) Main effect; marginal means
D) Main effect; cell means
A) Interaction effect; marginal means
B) Interaction effect; cell means
C) Main effect; marginal means
D) Main effect; cell means

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the following table for the next nine questions
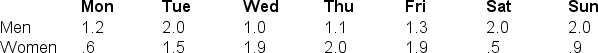
What is the marginal mean for men?
A) 1.25
B) 1.33
C) 1.45
D) 1.51
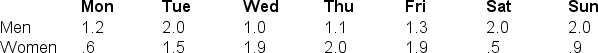
What is the marginal mean for men?
A) 1.25
B) 1.33
C) 1.45
D) 1.51

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Use the following table for the next nine questions
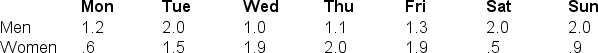
What is the marginal mean for women?
A) 1.25
B) 1.33
C) 1.45
D) 1.51
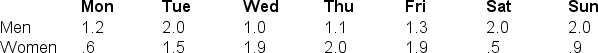
What is the marginal mean for women?
A) 1.25
B) 1.33
C) 1.45
D) 1.51

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
After calculating the marginal means in the table below, which variable has a significant main effect? (assume any difference between the means implies the main effect is significant) 
A) gender
B) day of week
C) both gender and day of week
D) neither gender or day of week

A) gender
B) day of week
C) both gender and day of week
D) neither gender or day of week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
After calculating the marginal means in the table below, which variable has a significant main effect? (assume any difference between the means implies the main effect is significant) 
A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
After calculating the marginal means in the table below, which variable has a significant main effect? (assume any difference between the means implies the main effect is significant) 
A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the following table for the next nine questions
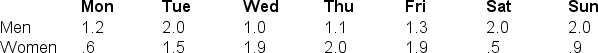
What is the marginal mean for Monday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55
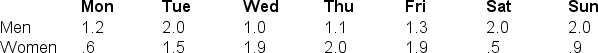
What is the marginal mean for Monday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
After calculating the marginal means in the table below, which variable has a significant main effect? (assume any difference between the means implies the main effect is significant) 
A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

A) gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
After calculating the marginal means in the table below, which variable has a significant main effect? (assume any difference between the means implies the main effect is significant) 
A) Gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

A) Gender
B) crime area
C) both gender and crime area
D) neither gender or crime area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the following table for the next five questions

What is the marginal mean for the low crime area?
A) 3.10
B) 3.70
C) 3.40
D) 2.55

What is the marginal mean for the low crime area?
A) 3.10
B) 3.70
C) 3.40
D) 2.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is an advantage of using factorial designs versus single-factor designs?
A) The interpretation of factorial research designs is simplified by the presence or absence of interaction effects.
B) Testing and interpreting effects in a factorial research design is less complicated than single-factor designs.
C) Factorial designs allow for test the significance of each dependent variable separately from the others.
D) Factorial designs have the ability to study multiple effects in one study.
A) The interpretation of factorial research designs is simplified by the presence or absence of interaction effects.
B) Testing and interpreting effects in a factorial research design is less complicated than single-factor designs.
C) Factorial designs allow for test the significance of each dependent variable separately from the others.
D) Factorial designs have the ability to study multiple effects in one study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In a two-factor research design, if one independent variable has 3 levels and the other has 2 levels, what is the total number of combinations?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 5
D) 6
A) 2
B) 3
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is a disadvantage of using factorial designs versus single-factor designs?
A) Factorial designs allow for the opportunity to determine whether independent variables combine or interact to influence the dependent variable.
B) Testing and interpreting effects in a factorial research design is more complicated than single-factor designs.
C) Factorial designs allow researchers to determine whether interaction effects are present among independent variables.
D) Factorial designs have the ability to study multiple effects in one study.
A) Factorial designs allow for the opportunity to determine whether independent variables combine or interact to influence the dependent variable.
B) Testing and interpreting effects in a factorial research design is more complicated than single-factor designs.
C) Factorial designs allow researchers to determine whether interaction effects are present among independent variables.
D) Factorial designs have the ability to study multiple effects in one study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is a conceptual benefit of using factorial designs versus single-factor designs?
A) Factorial designs provide the opportunity to determine whether independent variables combine or interact to influence the dependent variable.
B) Testing and interpreting factorial designs is less complicated than single-factor designs.
C) Factorial designs allow for test the significance of each dependent variable separately from the others.
D) The interpretation of factorial designs is simplified by the presence or absence of interaction effects.
A) Factorial designs provide the opportunity to determine whether independent variables combine or interact to influence the dependent variable.
B) Testing and interpreting factorial designs is less complicated than single-factor designs.
C) Factorial designs allow for test the significance of each dependent variable separately from the others.
D) The interpretation of factorial designs is simplified by the presence or absence of interaction effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to the following table, which type of effects are present? 
A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is one aspect of the relationship between main effects and interaction effects?
A) The presence or absence of main effects provides no indication of whether an interaction effect is present or absent.
B) The presence or absence of main effects provides an indication as to whether an interaction effect is present or absent.
C) The presence or absence of main effects provides an indication as to whether a simple effect is present or absent.
D) The presence or absence of an interaction effects provides an indication as to whether a simple effect is present or absent.
A) The presence or absence of main effects provides no indication of whether an interaction effect is present or absent.
B) The presence or absence of main effects provides an indication as to whether an interaction effect is present or absent.
C) The presence or absence of main effects provides an indication as to whether a simple effect is present or absent.
D) The presence or absence of an interaction effects provides an indication as to whether a simple effect is present or absent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
According to the following table, which type of effects are present? 
A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
According to the following table, which type of effects are present? 
A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The total number of combinations in a factorial research design may be calculated by ______.
A) adding the total number of cases for each variable
B) multiplying the number of levels of the independent variables
C) adding the number of levels of the independent variables
D) multiplying the number of levels by the number of cases
A) adding the total number of cases for each variable
B) multiplying the number of levels of the independent variables
C) adding the number of levels of the independent variables
D) multiplying the number of levels by the number of cases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Graphs that have two parallel lines for the variables indicates______.
A) an interaction effect is present for only one variable
B) an interaction effect is present
C) an interaction effect is not present
D) main effects are absent
A) an interaction effect is present for only one variable
B) an interaction effect is present
C) an interaction effect is not present
D) main effects are absent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following table for the next nine questions
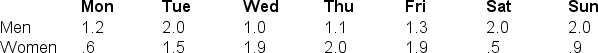
What is the marginal mean for Friday?
A) 1.60
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55
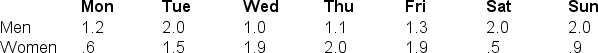
What is the marginal mean for Friday?
A) 1.60
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the following table for the next nine questions
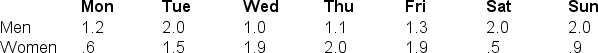
What is the marginal mean for Saturday?
A) 1.75
B) 1.60
C) 1.45
D) 1.25
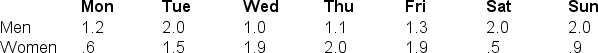
What is the marginal mean for Saturday?
A) 1.75
B) 1.60
C) 1.45
D) 1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the following table for the next nine questions
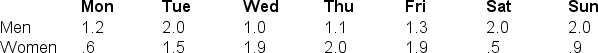
What is the marginal mean for Tuesday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55
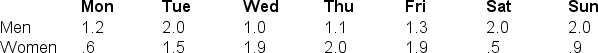
What is the marginal mean for Tuesday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
According to the following table, which type of effects are present? 
A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for crime area
C) main effects for both gender and crime area and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and crime area but no interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following table for the next nine questions
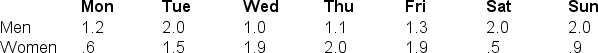
What is the marginal mean for Sunday?
A) 1.75
B) 1.60
C) 1.45
D) 1.25
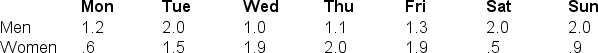
What is the marginal mean for Sunday?
A) 1.75
B) 1.60
C) 1.45
D) 1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Factorial research design can contain both ______.
A) main effects and interaction effects
B) main effects and major effects
C) simple effects and complex effects
D) main effects and dependent effects
A) main effects and interaction effects
B) main effects and major effects
C) simple effects and complex effects
D) main effects and dependent effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Use the following table for the next nine questions
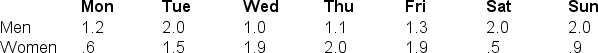
What is the marginal mean for Wednesday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55
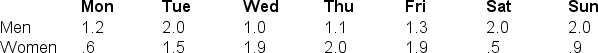
What is the marginal mean for Wednesday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
According to the following table, which type of effects are present? 
A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for day of week
C) main effects for both gender and day of week and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and day of week but no interaction effect

A) a main effect for gender
B) a main effect for day of week
C) main effects for both gender and day of week and an interaction effect
D) main effects for both gender and day of week but no interaction effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the following table for the next nine questions
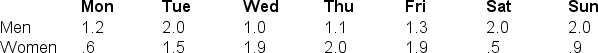
What is the marginal mean for Thursday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55
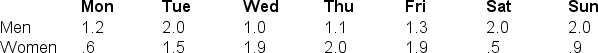
What is the marginal mean for Thursday?
A) .90
B) 1.75
C) 1.45
D) 1.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is an advantage of using factorial designs versus single-factor designs?
A) Factorial designs allow researchers to determine whether interaction effects are present among independent variables.
B) The interpretation of factorial designs is simplified by the presence or absence of interaction effects.
C) Testing and interpreting effects in a factorial research design is less complicated than single-factor designs.
D) Factorial designs allow for test the significance of each dependent variable separately from the others.
A) Factorial designs allow researchers to determine whether interaction effects are present among independent variables.
B) The interpretation of factorial designs is simplified by the presence or absence of interaction effects.
C) Testing and interpreting effects in a factorial research design is less complicated than single-factor designs.
D) Factorial designs allow for test the significance of each dependent variable separately from the others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The degrees of freedom for a factor A that has 3 levels would equal ______.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In a two-factor research design, if one independent variable has 4 levels and the other has 3 levels, what is the total number of combinations?
A) 12
B) 7
C) 4
D) 3
A) 12
B) 7
C) 4
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The degrees of freedom for factor A is the number of ______.
A) levels minus one
B) levels for factor A
C) cases for factor A
D) cases for factor A minus one
A) levels minus one
B) levels for factor A
C) cases for factor A
D) cases for factor A minus one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In a two way ANOVA, how many effects (main effects and interaction) are tested?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the total mean for the data in the table below? 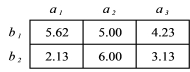
A) 3.75
B) 4.35
C) 4.95
D) 5.50

A) 3.75
B) 4.35
C) 4.95
D) 5.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which is the proper way to state the alternative hypothesis for a main effect?
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which is the proper way to state the null hypothesis for the interaction effect?
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which is the proper way to state the alternative hypothesis for the interaction effect?
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Within the A*B design, how many different degrees of freedom are calculated to test the main and interaction effects?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the total mean for the data in the table below? 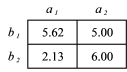
A) 2.13
B) 3.88
C) 4.07
D) 4.69

A) 2.13
B) 3.88
C) 4.07
D) 4.69

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the total mean for the data in the table below? 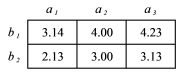
A) 3.27
B) 3.79
C) 4.13
D) 6.54

A) 3.27
B) 3.79
C) 4.13
D) 6.54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which symbol represents the number of scores in each combination of the two independent variables?
A) a1
B) b1
C) ab
D) NAB
A) a1
B) b1
C) ab
D) NAB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The hypotheses for the A * B interaction effect take into consideration ______.
A) the main effects
B) the separate effects
C) the interaction effects
D) the main and interaction effects
A) the main effects
B) the separate effects
C) the interaction effects
D) the main and interaction effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the total mean for the data in the table below? 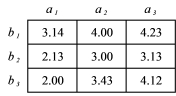
A) 3.24
B) 3.79
C) 4.86
D) 9.73

A) 3.24
B) 3.79
C) 4.86
D) 9.73

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A researcher is studying the effect of race and crime level. The first factor, race has four groups while the second factor, crime level has three groups. Which of the following would be the correct notation for these factors?
A) a = 3 and b = 4
B) a = 4 and b =3
C) ab = 7
D) NAB = 7
A) a = 3 and b = 4
B) a = 4 and b =3
C) ab = 7
D) NAB = 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When stating the null and alternative hypotheses, the two main effects are treated as ______.
A) a factorial design
B) single-factor designs
C) independent factor designs
D) dependent factor designs
A) a factorial design
B) single-factor designs
C) independent factor designs
D) dependent factor designs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which is the proper way to state the null hypothesis for a main effect?
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal
A) H0: an interaction effect does not exist
B) H1: not all µs are equal
C) H1: an interaction effect exists
D) H0: all µs are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the total mean for the data in the table below? 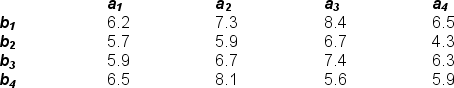
A) 25.85
B) 12.93
C) 6.46
D) 6.25

A) 25.85
B) 12.93
C) 6.46
D) 6.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the total mean for the data in the table below? 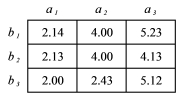
A) 3.24
B) 3.46
C) 5.19
D) 10.38

A) 3.24
B) 3.46
C) 5.19
D) 10.38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the total mean for the data in the table below? 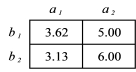
A) 4.44
B) 4.57
C) 5.50
D) 6.00

A) 4.44
B) 4.57
C) 5.50
D) 6.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



