Deck 9: Testing the Difference Between Two Means
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/132
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Testing the Difference Between Two Means
1
A researcher hypothesizes that women are more in favor of gun control than are men. In conducting an analysis to test this hypothesis, how should the null hypothesis be stated?
A) H0: μD = 0
B) H0: Women > Men
C) H0: Women = Men
D) H0: μ1 = μ2
A) H0: μD = 0
B) H0: Women > Men
C) H0: Women = Men
D) H0: μ1 = μ2
H0: Women = Men
2
The sampling distribution of the difference helps us determine ______.
A) the probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean (µ)
B) the modality of a set of data
C) whether a set of data is skewed (asymmetric)
D) the probability of obtaining a particular difference between sample means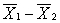
A) the probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean (µ)
B) the modality of a set of data
C) whether a set of data is skewed (asymmetric)
D) the probability of obtaining a particular difference between sample means
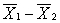
the probability of obtaining a particular difference between sample means 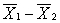
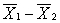
3
The variability of the sampling distribution of the difference is measured by the ______.
A) standard error of the differences
B) sample means
C) modality of a set of data
D) probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean
A) standard error of the differences
B) sample means
C) modality of a set of data
D) probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean
standard error of the differences
4
This distribution illustrates a ______. 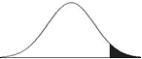
A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional alternative hypothesis
C) non-directional null hypothesis
D) directional alternative hypothesis

A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional alternative hypothesis
C) non-directional null hypothesis
D) directional alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
This distribution illustrates a ______. 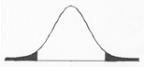
A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional alternative hypothesis
C) non-directional null hypothesis
D) directional alternative hypothesis

A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional alternative hypothesis
C) non-directional null hypothesis
D) directional alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The ______ of the difference help us determine the probability of obtaining a particular difference between sample means.
A) standard error
B) sampling distribution
C) modality of a set of data
D) probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean
A) standard error
B) sampling distribution
C) modality of a set of data
D) probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The ______ of the sampling distribution of the difference is equal to ______.
A) mean; σ
B) standard deviation;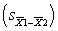
C) mean; 1
D) standard deviation; 0
A) mean; σ
B) standard deviation;
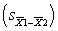
C) mean; 1
D) standard deviation; 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A researcher hypothesizes that Drug A is more effective than Drug B. In conducting an analysis to test this hypothesis, how should the null hypothesis be stated?
A) H0: μ1 = μ2
B) H0: μDrug A > μDrug B
C) H0: μDrug A = μDrug B
D) H0: μDrug A ≠ μDrug B
A) H0: μ1 = μ2
B) H0: μDrug A > μDrug B
C) H0: μDrug A = μDrug B
D) H0: μDrug A ≠ μDrug B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A ______ symbol is part of the ______ hypothesis, and implies this hypothesis is ______.
A) ≠; null; directional
B) ≠; alternative; directional
C) < or >; null; non-directional
D) <; alternative; one-tailed
A) ≠; null; directional
B) ≠; alternative; directional
C) < or >; null; non-directional
D) <; alternative; one-tailed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The ______ of the sampling distribution of the difference is equal to ______.
A) variability; 0
B) mean; 0
C) variability; 1
D) mean; 1
A) variability; 0
B) mean; 0
C) variability; 1
D) mean; 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
This distribution illustrates a ______. 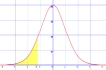
A) directional null hypothesis
B) directional alternative hypothesis
C) non-directional alternative hypothesis
D) non-directional null hypothesis

A) directional null hypothesis
B) directional alternative hypothesis
C) non-directional alternative hypothesis
D) non-directional null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The ______ symbol is part of the ______ hypothesis, and implies this hypothesis is ______.
A) ≠; null; directional
B) =; alternative; directional
C) ≠; alternative; two-tailed
D) < or >; null; non-directional
A) ≠; null; directional
B) =; alternative; directional
C) ≠; alternative; two-tailed
D) < or >; null; non-directional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A researcher hypothesizes that nurses have higher average salaries than teachers. In conducting an analysis to test this hypothesis, how might the alternative hypothesis be stated?
A) H1: μD = 0
B) H1: μD ≠ 0
C) H1: μNurses's salaries ≠ μTeacher's salaries
D) H1: μNurses ≠ μTeachers
A) H1: μD = 0
B) H1: μD ≠ 0
C) H1: μNurses's salaries ≠ μTeacher's salaries
D) H1: μNurses ≠ μTeachers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A researcher hypothesizes that there is a difference in level of fear of crime for the elderly and young adults. In conducting an analysis to test this hypothesis, how might the alternative hypothesis be stated?
A) H1: μD = 0
B) H1: μD ≠ 0
C) H1: μElderly ≠ μYoung Adults
D) H1: μElderly > μYoung Adults
A) H1: μD = 0
B) H1: μD ≠ 0
C) H1: μElderly ≠ μYoung Adults
D) H1: μElderly > μYoung Adults

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A ______ symbol is part of the ______ hypothesis, and implies this hypothesis is ______.
A) >; null; one-tailed
B) ≠; null; directional
C) ≠; alternative; directional
D) < or >; alternative; non-directional
A) >; null; one-tailed
B) ≠; null; directional
C) ≠; alternative; directional
D) < or >; alternative; non-directional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In testing the difference between two means, which of these is implied by the null hypothesis (H0)?
A) μ1= μ2
B) μ1 > μ2
C) μ1 < μ2
D)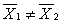
A) μ1= μ2
B) μ1 > μ2
C) μ1 < μ2
D)
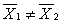

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A ______ symbol is part of the ______ hypothesis, and implies this hypothesis is ______.
A) >; alternative; one-tailed
B) ≠; null; directional
C) ≠; alternative; directional
D) < or >; null; non-directional
A) >; alternative; one-tailed
B) ≠; null; directional
C) ≠; alternative; directional
D) < or >; null; non-directional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
______ represent(s) the variability of differences between two sample means.
A) The probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean (μ)
B) The modality of a set of data
C) Whether a set of data is skewed (asymmetric)
D) Standard error of the differences
A) The probability of obtaining a particular value of the population mean (μ)
B) The modality of a set of data
C) Whether a set of data is skewed (asymmetric)
D) Standard error of the differences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In testing the difference between two means, which of these is implied by the null hypothesis (H0)?
A) μ1= μ2 = 0
B) μ1 - μ2 = 0
C) μ1 - μ2 ≠ 0
D)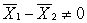
A) μ1= μ2 = 0
B) μ1 - μ2 = 0
C) μ1 - μ2 ≠ 0
D)
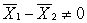

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The mean of the sampling distribution of the difference is equal to ______.
A) the population mean (μ)
B) 0
C) 1
D) the standard error of the difference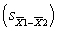
A) the population mean (μ)
B) 0
C) 1
D) the standard error of the difference
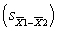

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A study tests the difference between 20 Democrats and 20 Republicans. In this example, the degrees of freedom is equal to ______.
A) 18
B) 19
C) 38
D) 39
A) 18
B) 19
C) 38
D) 39

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A researcher calculates the t-test for independent means and reports the following result: t(48) = 2.97, p < .01. This research study consisted of a TOTAL of ______ participants.
A) 25
B) 48
C) 49
D) 50
A) 25
B) 48
C) 49
D) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A researcher calculates the t-test for independent means and reports the following result: t(24) = 2.16, p < .05. This research study consisted of a TOTAL of ______ participants.
A) 26
B) 25
C) 24
D) 23
A) 26
B) 25
C) 24
D) 23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A researcher hypothesizes that children from middle class families have higher education levels than children from lower class families. In conducting an analysis to test this hypothesis, how might the alternative hypothesis be stated?
A) H1: μD = 0
B) H1: μ Middle Class > μ Lower Class
C) H1: μ Middle Class ≠ μ Lower Class
D) H1: μ Middle Class < μ Lower Class
A) H1: μD = 0
B) H1: μ Middle Class > μ Lower Class
C) H1: μ Middle Class ≠ μ Lower Class
D) H1: μ Middle Class < μ Lower Class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In testing the difference between two means, what is implied by the alternative hypothesis (H1)?
A) μ1 = μ2
B) μ1 - μ2 = 0
C) μ1 - μ2 ≠ 0
D)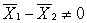
A) μ1 = μ2
B) μ1 - μ2 = 0
C) μ1 - μ2 ≠ 0
D)
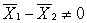

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A study compares the means of two groups, each having N = 11. If the standard deviations of the two groups are 5.00 and 3.00, what is the value for the standard error of the difference 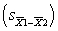 ?
?
A) .60
B) .85
C) 1.76
D) 3.09
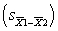 ?
?A) .60
B) .85
C) 1.76
D) 3.09

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A researcher states the following hypotheses: H0: μDogs = μCats and H1: μDogs ≠ μ Cats. Assuming she collects data from 9 dogs and 9 cats, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) 1.734
B) 2.120
C) 2.110
D) 2.101
A) 1.734
B) 2.120
C) 2.110
D) 2.101

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A study compares the means of two groups, each having N = 15. If the standard deviations of the two groups are 1.67 and 2.98, what is the value for the standard error of the difference 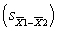 ?
?
A) .19
B) .778
C) .880
D) .882
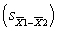 ?
?A) .19
B) .778
C) .880
D) .882

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A researcher states the following hypotheses: H0: μMales = μ Females and H1: μMales ≠ μFemales. Assuming she collects data from 15 males and 15 females, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) 1.697
B) 1.701
C) 2.042
D) 2.048
A) 1.697
B) 1.701
C) 2.042
D) 2.048

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A study compares the means of two groups, each having N = 20. If the standard deviations of the two groups are 10.00 and 6.00, what is the value for the standard error of the difference 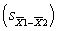 ?
?
A) .89
B) 2.61
C) 5.43
D) 6.80
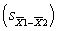 ?
?A) .89
B) 2.61
C) 5.43
D) 6.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A researcher comparing the means of two groups calculates the t-test for independent means and reports the following result: t(32) = -3.54, p <.01. This research study consisted of a TOTAL of ______ participants.
A) 16
B) 30
C) 32
D) 34
A) 16
B) 30
C) 32
D) 34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A researcher comparing the means of two groups calculates the t-test for independent means and reports the following result: t(22) = -3.54, p <.01. This research study consisted of a TOTAL of ______ participants.
A) 20
B) 22
C) 24
D) 26
A) 20
B) 22
C) 24
D) 26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A study compares the means of two groups, each having N = 10. If the standard deviations in the two groups are 4.00 and 6.00, what is the value for the standard error of the difference 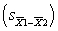 ?
?
A) 2.28
B) 1.00
C) 10.00
D) 5.20
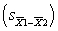 ?
?A) 2.28
B) 1.00
C) 10.00
D) 5.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A study tests the difference between 15 ants and 15 ladybugs. In this example, the degrees of freedom is ______.
A) 14
B) 15
C) 28
D) 30
A) 14
B) 15
C) 28
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In testing the difference between two means, which of the following is implied by the alternative hypothesis (H1)?
A) The two population means are equal to each other.
B) The difference between the two population means is equal to 0.
C) The difference between the two population means is not equal to 0.
D) The difference between the two sample means is equal to 0.
A) The two population means are equal to each other.
B) The difference between the two population means is equal to 0.
C) The difference between the two population means is not equal to 0.
D) The difference between the two sample means is equal to 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A researcher comparing the means of two groups calculates the t-test for independent means and reports the following result: t(28) = 2.11, p <.05. This research study consisted of a TOTAL of ______ participants.
A) 14
B) 15
C) 28
D) 30
A) 14
B) 15
C) 28
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A researcher states the following hypotheses: H0: μ Freshmen = μ Sophomores and H1: μ Freshmen ≠ μ Sophomores. Assuming she collects data from 13 freshmen and 13 sophomores, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) 1.706
B) 1.711
C) 2.056
D) 2.064
A) 1.706
B) 1.711
C) 2.056
D) 2.064

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A researcher states the following hypotheses: H0: μCity1 = μCity2 and H1: μCity1 > μCity2. Assuming she collects data from 30 people who live in city 1 and 30 people who live in city 2, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) 1.672
B) 1.700
C) 1.960
D) 2.002
A) 1.672
B) 1.700
C) 1.960
D) 2.002

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In testing the difference between two sample means 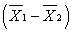 , the greater the difference between the two means, the more the value of the t-statistic (t) differs from ______.
, the greater the difference between the two means, the more the value of the t-statistic (t) differs from ______.
A) 0
B) μ
C) the alternative hypothesis
D) the region of rejection
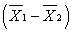 , the greater the difference between the two means, the more the value of the t-statistic (t) differs from ______.
, the greater the difference between the two means, the more the value of the t-statistic (t) differs from ______.A) 0
B) μ
C) the alternative hypothesis
D) the region of rejection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A study compares the means of two groups, each having N = 10. If the standard deviations in the two groups are 3.00 and 5.00, what is the value for the standard error of the difference 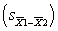 ?
?
A) .89
B) 1.84
C) 3.40
D) 8.00
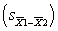 ?
?A) .89
B) 1.84
C) 3.40
D) 8.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In reporting a statistical analysis, a researcher writes "p < .01". By definition this implies that ______.
A) the null hypothesis was not rejected
B) p < .05
C) the statistic was in the region of non-rejection
D) the research hypothesis was proven to be true
A) the null hypothesis was not rejected
B) p < .05
C) the statistic was in the region of non-rejection
D) the research hypothesis was proven to be true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You ______ the null hypothesis when the value of the statistic falls in the region of ______ because this means ______.
A) do not reject; rejection; p > .05
B) reject; rejection; p < .05
C) do not reject; non-rejection; p < .05
D) reject; non-rejection; p > .05
A) do not reject; rejection; p > .05
B) reject; rejection; p < .05
C) do not reject; non-rejection; p < .05
D) reject; non-rejection; p > .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In testing the difference between two sample means 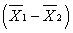 , a negative (-) value of the t-statistic (t) indicates ______.
, a negative (-) value of the t-statistic (t) indicates ______.
A) the sample mean is greater than the hypothesized population mean
B) the score is less than the mean
C) the second group's mean is larger than the first group's mean
D) you've made an error in your calculations
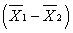 , a negative (-) value of the t-statistic (t) indicates ______.
, a negative (-) value of the t-statistic (t) indicates ______.A) the sample mean is greater than the hypothesized population mean
B) the score is less than the mean
C) the second group's mean is larger than the first group's mean
D) you've made an error in your calculations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In conducting the t-test for independent means, if you ______, the two means ______.
A) do not reject the null hypothesis; do not significantly differ from each other
B) do not accept the null hypothesis; are significantly equal to each other
C) reject the null hypothesis; do not significantly differ from each other
D) reject the alternative hypothesis; are significantly different from each other
A) do not reject the null hypothesis; do not significantly differ from each other
B) do not accept the null hypothesis; are significantly equal to each other
C) reject the null hypothesis; do not significantly differ from each other
D) reject the alternative hypothesis; are significantly different from each other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In conducting the t-test for independent means, if you ______, the two means ______ significantly different from each other.
A) do not reject the null hypothesis; are not
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; are
C) reject the null hypothesis; are not
D) reject the alternative hypothesis; are
A) do not reject the null hypothesis; are not
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; are
C) reject the null hypothesis; are not
D) reject the alternative hypothesis; are

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A value of -2.01 for the t-statistic necessarily implies that ______.
A) the mean for the first group is less than the mean of the second group
B) the mean for the first group is greater than the mean of the second group
C) the difference between the two means is statistically significant
D) the distribution of scores for the dependent variable is negatively skewed
A) the mean for the first group is less than the mean of the second group
B) the mean for the first group is greater than the mean of the second group
C) the difference between the two means is statistically significant
D) the distribution of scores for the dependent variable is negatively skewed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When you ______, this implies the probability of the statistic is ______.
A) do not reject the null hypothesis; in the region of rejection
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; < 5%
C) do not reject the null hypothesis; high
D) reject the null hypothesis; in the region of acceptance
A) do not reject the null hypothesis; in the region of rejection
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; < 5%
C) do not reject the null hypothesis; high
D) reject the null hypothesis; in the region of acceptance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If your value of a statistic like the t-test falls in the ______ area of this distribution, you will ______ the null hypothesis because the probability of the statistic is ______. 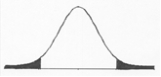
A) shaded; reject; high
B) shaded; not reject; high
C) unshaded; reject; low
D) unshaded; not reject; high

A) shaded; reject; high
B) shaded; not reject; high
C) unshaded; reject; low
D) unshaded; not reject; high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In reporting a statistical analysis, a researcher writes "p > .05". By definition this implies that ______.
A) the null hypothesis was proven to be true
B) p < .01
C) the statistic was in the region of non-rejection
D) the differences between the means of the groups was insignificant
A) the null hypothesis was proven to be true
B) p < .01
C) the statistic was in the region of non-rejection
D) the differences between the means of the groups was insignificant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
You ______ when your statistic falls in the region of ______ because this means ______.
A) reject the null hypothesis; rejection; p < .05
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; non-rejection; p < .01
C) reject the alternative hypothesis; non-rejection; p < .05
D) reject the null hypothesis; rejection; p > .01
A) reject the null hypothesis; rejection; p < .05
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; non-rejection; p < .01
C) reject the alternative hypothesis; non-rejection; p < .05
D) reject the null hypothesis; rejection; p > .01

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Imagine the value of a statistic is greater than the critical value for α = .05 but less than the critical value for α = .01. In this situation you would ______ and state the level of significance as ______.
A) reject the null hypothesis; p > .05
B) not reject the null hypothesis; p > .05
C) reject the null hypothesis; p > .01
D) reject the null hypothesis; p < .05
A) reject the null hypothesis; p > .05
B) not reject the null hypothesis; p > .05
C) reject the null hypothesis; p > .01
D) reject the null hypothesis; p < .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In conducting the t-test for independent means, if you ______, the two means ______.
A) reject the null hypothesis; are significantly different from each other
B) accept the null hypothesis; are significantly different from each other
C) do not reject the null hypothesis; are significantly equal to each other
D) reject the null hypothesis; are significantly equal to each other
A) reject the null hypothesis; are significantly different from each other
B) accept the null hypothesis; are significantly different from each other
C) do not reject the null hypothesis; are significantly equal to each other
D) reject the null hypothesis; are significantly equal to each other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If your value of a statistic like the t-test falls in the ______ area of this distribution, you will ______ the null hypothesis ______ because the probability of the statistic is ______. 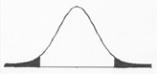
A) shaded; reject; low
B) shaded; not reject; high
C) unshaded; reject; low
D) unshaded; not reject; low

A) shaded; reject; low
B) shaded; not reject; high
C) unshaded; reject; low
D) unshaded; not reject; low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
You determine whether the probability of a statistic is less than .01 (p < .01) ______.
A) when you do not reject the null hypothesis
B) when you reject the null hypothesis
C) whenever you analyze a set of data
D) when you accept the null hypothesis
A) when you do not reject the null hypothesis
B) when you reject the null hypothesis
C) whenever you analyze a set of data
D) when you accept the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Imagine the value of a statistic is greater than the critical value for α = .05 but less than the critical value for α = .01. Which is the MOST appropriate way to report the level of significance?
A) p < .01
B) p > .01
C) p < .05
D) p > .05
A) p < .01
B) p > .01
C) p < .05
D) p > .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When do you determine whether the probability of a statistic such as the t-test is less than .01?
A) when you have rejected the null hypothesis
B) when you have not rejected the null hypothesis
C) when you have already concluded that p > .01
D) when you have already concluded that p > .05
A) when you have rejected the null hypothesis
B) when you have not rejected the null hypothesis
C) when you have already concluded that p > .01
D) when you have already concluded that p > .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
You ______ the null hypothesis when your statistic falls in the region of ______ because this means ______.
A) do not reject; rejection; p < .05
B) accept; rejection; p > .05
C) do not reject; non-rejection; p > .05
D) reject; non-rejection; p < .05
A) do not reject; rejection; p < .05
B) accept; rejection; p > .05
C) do not reject; non-rejection; p > .05
D) reject; non-rejection; p < .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Imagine the value of a t-test is greater than the α = .05 critical value but less than the α = .01 critical value. Which of the following statements is true?
A) p > .05
B) p < .01
C) You have rejected the null hypothesis.
D) The means of the two groups are significantly equal to each other.
A) p > .05
B) p < .01
C) You have rejected the null hypothesis.
D) The means of the two groups are significantly equal to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When you ______, this implies the probability of the statistic is ______.
A) reject the null hypothesis; > .05
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; non-directional
C) reject the null hypothesis; low
D) do not reject the null hypothesis; < .05
A) reject the null hypothesis; > .05
B) do not reject the null hypothesis; non-directional
C) reject the null hypothesis; low
D) do not reject the null hypothesis; < .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Your value of a statistic such as the t-test is greater than the critical value for α = .05 but less than the critical value for α = .01; consequently, you ______ the null hypothesis and state the level of significance as ______.
A) reject; p > .05
B) do not reject; p > .01
C) reject; p < .01
D) reject; p < .05
A) reject; p > .05
B) do not reject; p > .01
C) reject; p < .01
D) reject; p < .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In writing the results of the t-test in standard APA format, the letters "n.s." imply ______.
A) p < .05
B) p < .01
C) p > .05
D) the null hypothesis was rejected
A) p < .05
B) p < .01
C) p > .05
D) the null hypothesis was rejected

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
According to the textbook, what is the difference between the terms "nonsignificant" and "insignificant"?
A) "Insignificant" is not a statistical concept.
B) You use the term "insignificant" when you make the decision to reject the null hypothesis.
C) "Insignificant" implies p < .05; "nonsignificant" implies p < .01.
D) There is no difference between the two concepts-they mean the same thing.
A) "Insignificant" is not a statistical concept.
B) You use the term "insignificant" when you make the decision to reject the null hypothesis.
C) "Insignificant" implies p < .05; "nonsignificant" implies p < .01.
D) There is no difference between the two concepts-they mean the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
According to the textbook, what is the difference between the terms "nonsignificant" and "insignificant"?
A) "Nonsignificant" is less precise than "insignificant."
B) "Nonsignificant" is a statistical concept; "insignificant" is a value judgment.
C) "Nonsignificant" refers to α = .05; "insignificant" refers to α = .01.
D) "Insignificant" is a statistical concept; "nonsignificant" is a value judgment.
A) "Nonsignificant" is less precise than "insignificant."
B) "Nonsignificant" is a statistical concept; "insignificant" is a value judgment.
C) "Nonsignificant" refers to α = .05; "insignificant" refers to α = .01.
D) "Insignificant" is a statistical concept; "nonsignificant" is a value judgment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which type of statistic would be appropriate for analyzing a within-subjects research design?
A) z-test for one mean
B) t-test for independent means
C) t-test for dependent means
D) t-test for one mean
A) z-test for one mean
B) t-test for independent means
C) t-test for dependent means
D) t-test for one mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For a study analyzing the difference between test scores before and after a treatment was applied, which statistic would be most appropriate for this study?
A) z-test for one mean
B) t-test for one mean
C) t-test for independent means
D) t-test for dependent means
A) z-test for one mean
B) t-test for one mean
C) t-test for independent means
D) t-test for dependent means

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A researcher asks 10 people to take sips out of two cups of soda (one with Coke and the other Pepsi) and rate the flavor of both sodas. In analyzing this data, how should the null hypothesis be stated?
A) H0: µD = 0
B) H0: Coke > Pepsi
C) H0: Coke = Pepsi
D) H0: µ1 = µ2
A) H0: µD = 0
B) H0: Coke > Pepsi
C) H0: Coke = Pepsi
D) H0: µ1 = µ2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A study compares 5 Democrats and 5 Republicans and obtains a value of 2.27 for the t-statistic. For α = .05 (two-tailed), which of the following is the correct way to present this analysis?
A) t(10) = 2.27, p > .05
B) t(8) = 2.27, p < .05
C) t(9) = 2.27, p < .05
D) t(8) = 2.27, p > .05
A) t(10) = 2.27, p > .05
B) t(8) = 2.27, p < .05
C) t(9) = 2.27, p < .05
D) t(8) = 2.27, p > .05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A researcher asks 10 people to take a bite of two different cheese pizzas (Dominos and Round Table) and rate the flavor of both pizzas. In analyzing this data, how should the null hypothesis be stated?
A) µD = 0
B) µD ≠ 0
C) Dominos = Round Table
D) µ1 = µ2
A) µD = 0
B) µD ≠ 0
C) Dominos = Round Table
D) µ1 = µ2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a researcher has developed a research design in which each participant appears in all levels or categories, this would be considered which type of research design?
A) within-subjects design
B) t-test for independent means
C) between-subjects design
D) t-test for one mean
A) within-subjects design
B) t-test for independent means
C) between-subjects design
D) t-test for one mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A ______ is a research design in which each participant appears in all levels or categories of the independent variable.
A) t-test for independent means
B) t-test for one mean
C) between subjects research design
D) within-subjects research design
A) t-test for independent means
B) t-test for one mean
C) between subjects research design
D) within-subjects research design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In testing the difference between two sample means, you would examine the ______ of the two groups to test the assumption of homogeneity of variance.
A) standard deviations
B) t-tests
C) means
D) sample sizes
A) standard deviations
B) t-tests
C) means
D) sample sizes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the null hypothesis is ______, this typically means the research hypothesis is ______.
A) not rejected; supported
B) rejected; supported
C) rejected; not supported
D) rejected; proven
A) not rejected; supported
B) rejected; supported
C) rejected; not supported
D) rejected; proven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The assumption of normality is primarily concerned with ______.
A) the difference between two sample means
B) the shape of the distribution of the dependent variable
C) how samples are drawn from populations
D) the difference between a sample mean and a population mean
A) the difference between two sample means
B) the shape of the distribution of the dependent variable
C) how samples are drawn from populations
D) the difference between a sample mean and a population mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In reporting the results of a statistical analysis in standard APA format, the letters "n.s." mean ______.
A) "nonsignificant"
B) "not sure"
C) "non-statistical"
D) "not standard"
A) "nonsignificant"
B) "not sure"
C) "non-statistical"
D) "not standard"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The within-subjects research design tests differences ______.
A) between different groups of participants
B) within the same participant
C) between different groups of participants and within the same participants
D) between a sample mean and a hypothesized population mean
A) between different groups of participants
B) within the same participant
C) between different groups of participants and within the same participants
D) between a sample mean and a hypothesized population mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When the null hypothesis is ______, this typically means the research hypothesis is ______.
A) not rejected; not supported
B) rejected; supported
C) rejected; not supported
D) rejected; proven
A) not rejected; not supported
B) rejected; supported
C) rejected; not supported
D) rejected; proven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A researcher asks 20 people to take a sip of two different colas (first Coke and then Pepsi) and rate the flavor of both. In analyzing this data, how should the null hypothesis be stated?
A) H0: µD ≠ 0
B) H0: µD = 20
C) H0: Coke = Pepsi
D) H0: µD = 0
A) H0: µD ≠ 0
B) H0: µD = 20
C) H0: Coke = Pepsi
D) H0: µD = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following would be the most informative way to report the results of a t-test?
A) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group (M = 2.45) is significantly higher than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group (M = .95), t(40) = 3.41, p < .01.
B) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group (M = 2.45) is significantly higher than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group (M = .95).
C) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group (M = 2.45) is significantly different than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group (M = .95), t(40) = 3.41, p < .01.
D) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group is significantly higher than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group, t(40) = 3.41, p < .01.
A) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group (M = 2.45) is significantly higher than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group (M = .95), t(40) = 3.41, p < .01.
B) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group (M = 2.45) is significantly higher than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group (M = .95).
C) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group (M = 2.45) is significantly different than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group (M = .95), t(40) = 3.41, p < .01.
D) The mean number of crimes for juveniles in the poverty group is significantly higher than the mean number of crimes for juveniles in the non-poverty group, t(40) = 3.41, p < .01.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A study compares 6 full-time students and 6 part-time students and obtains a value of 2.31 for the t-statistic. For α = .05 (two-tailed), which of the following is the correct way to present this analysis?
A) t(5) = 2.31, p > .05
B) t(6) = 2.31, p < .05
C) t(10) = 2.31, p < .05
D) t(12) = 2.31, p < .01
A) t(5) = 2.31, p > .05
B) t(6) = 2.31, p < .05
C) t(10) = 2.31, p < .05
D) t(12) = 2.31, p < .01

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In reporting a statistical analysis, a researcher writes "p > .05". By definition this implies that ______.
A) the null hypothesis was rejected
B) p < .01
C) the statistic was in the region of rejection
D) the means of the groups are not different from each other
A) the null hypothesis was rejected
B) p < .01
C) the statistic was in the region of rejection
D) the means of the groups are not different from each other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



