Deck 23: Population Genetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Population Genetics
1
The frequency of sickle cell anemia,caused by a homozygous condition (Hb?Hb?)is approximately 0.0016.The normal condition is also a homozygous condition (Hb?Hb?).Assuming the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium applies,what is the frequency of the Hb? allele?
A) 0.0004
B) 0.04
C) 0.4
D) 0.9216
E) 0.96
A) 0.0004
B) 0.04
C) 0.4
D) 0.9216
E) 0.96
E
2
The frequency of sickle cell anemia,caused by a homozygous condition (Hb?Hb?)is approximately 0.0016.The normal condition is also a homozygous condition (Hb?Hb?).Assuming the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium applies,what is the frequency of the carrier state (Hb?Hb?)?
A) 0.0228
B) 0.0432
C) 0.0768
D) 0.0987
E) 0.0384
A) 0.0228
B) 0.0432
C) 0.0768
D) 0.0987
E) 0.0384
C
3
Which of the following is a force that could upset the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) Mutation
B) Migration
C) Natural selection
D) Genetic drift
E) All of these
A) Mutation
B) Migration
C) Natural selection
D) Genetic drift
E) All of these
E
4
In a sample of 400 men,48 have X-linked color blindness and all the others have normal color vision.If men are hemizygous for the allele,what is the frequency for the X-linked color blindness allele?
A) 0.1
B) 0.12
C) 0.24
D) 0.48
E) 0.88
A) 0.1
B) 0.12
C) 0.24
D) 0.48
E) 0.88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a sample of 600 individuals (400 men and 200 women)48 men have X-linked color blindness (X?)and all the others have normal color vision (X?).What is the frequency of women who are carriers?
A) 0.12
B) 0.88
C) 0.346
D) 0.02
E) 0.21
A) 0.12
B) 0.88
C) 0.346
D) 0.02
E) 0.21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a key assumption underlying the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
1)The members of the population mate at random with respect to the gene under study.
2)The members of the population are artificially selected with respect to the gene under study.
3)The members of the population must live on an island.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3
1)The members of the population mate at random with respect to the gene under study.
2)The members of the population are artificially selected with respect to the gene under study.
3)The members of the population must live on an island.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The A-B-O blood types are determined by three alleles I?,I?,and i.In one population the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type A blood is 0.063,the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type B blood is 0.015,and the frequency of individuals who are blood type O is 0.44.What is the frequency of individuals are blood type AB?
A) 0.251
B) 0.122
C) 0.031
D) 0.061
E) 0.5
A) 0.251
B) 0.122
C) 0.031
D) 0.061
E) 0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following can be calculated using a major population genetics theory?
1)The frequency of homozygous dominant and recessive individuals
2)The frequency of heterozygous individual
3)The frequency of a dominant allele
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) All of these
1)The frequency of homozygous dominant and recessive individuals
2)The frequency of heterozygous individual
3)The frequency of a dominant allele
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The frequency of sickle cell anemia,caused by a homozygous condition (Hb?Hb?)is approximately 0.0016.Assuming the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium applies,what is the frequency of the Hb? allele?
A) 0.01
B) 0.00008
C) 0.08
D) 0.04
E) 0.4
A) 0.01
B) 0.00008
C) 0.08
D) 0.04
E) 0.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
There are 300 individuals in sample group #1 taken from population X.Seventy-five individuals of sample group are homozygous for the trait in question (I?I?).Seventy five individuals are homozygous for the trait (I?I?).Everyone else is heterozygous (I?I?)for the trait.What is the frequency of allele A in the sample group,assuming the trait is controlled by a single gene?
A) 0
B) 0.375
C) 0.5
D) 0.75
E) 1
A) 0
B) 0.375
C) 0.5
D) 0.75
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
There are 300 individuals in sample group #1 taken from population X.How many total alleles for the trait in question are present in the sample group,assuming the trait is controlled by a single codominant gene?
A) 150
B) 300
C) 600
D) 900
E) 1200
A) 150
B) 300
C) 600
D) 900
E) 1200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a population,whenever the second most frequent allele of a gene has a frequency greater than 0.01,we refer to the situation as a
A) genetic polymorphism.
B) genetic anomaly.
C) genetic mutation.
D) genetic abnormality.
E) None of these
A) genetic polymorphism.
B) genetic anomaly.
C) genetic mutation.
D) genetic abnormality.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a sample of 600 individuals (400 men and 200 women)48 men have X-linked color blindness (X?)and all the others have normal color vision (X?).What is the frequency of women who are colorblind? A)0.12
B)0)88
C)0)346
D)0)02
E)0)21
B)0)88
C)0)346
D)0)02
E)0)21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a sample of 500 men,240 have X-linked hemophilia and all the others have normal blood clotting.If men are hemizygous for the allele,what is the frequency for the X-linked hemophilia allele?
A) 0.1
B) 0.12
C) 0.24
D) 0.48
E) 0.88
A) 0.1
B) 0.12
C) 0.24
D) 0.48
E) 0.88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
There are 300 individuals in sample group #1 taken from population X.Seventy-five individuals of sample group are homozygous for the trait in question (I?I?).Seventy five individuals are homozygous for the trait (I?I?).Everyone else is heterozygous (I?I?)for the trait.What is the frequency of allele B in the sample group,assuming the trait is controlled by a single gene?
A) 0
B) 0.375
C) 0.5
D) 0.75
E) 1
A) 0
B) 0.375
C) 0.5
D) 0.75
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is true regarding determining the number of alleles in a population sample? 1.It may be impossible to count the number of alleles if one allele is dominant.
2)When counting X-linked alleles it is only important to count the different alleles in males.
3)Codominant alleles can always be counted because they produce unique phenotypes.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) All of these
2)When counting X-linked alleles it is only important to count the different alleles in males.
3)Codominant alleles can always be counted because they produce unique phenotypes.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is explained by a major population genetics theory?
1)The number of individuals in a population
2)The allelic frequencies within a population
3)The number of individuals outside a population
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) All of these
1)The number of individuals in a population
2)The allelic frequencies within a population
3)The number of individuals outside a population
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following individuals described a mathematical relationship between allele frequencies and genotype frequencies?
A) G.H. Hardy
B) Wilhelm Weinberg
C) Edward East
D) G.H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg
E) Wilhelm Weinberg and Edward East
A) G.H. Hardy
B) Wilhelm Weinberg
C) Edward East
D) G.H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg
E) Wilhelm Weinberg and Edward East

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following allows one to predict a population's genotype frequencies from its allele frequencies?
A) Hardy-Weinberg principle
B) East-Hayflick principle
C) Hooke-Van Leuwenhoek principle
D) Morgan-Hunt principle
E) None of these
A) Hardy-Weinberg principle
B) East-Hayflick principle
C) Hooke-Van Leuwenhoek principle
D) Morgan-Hunt principle
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following accurately describes the Hardy-Weinberg genotype frequency expression?
A) P² + 2p +q²
B) P² + 2pq + q³
C) P²+2pq+q²
D) P³ + 3pq+q³
E) (p+q)³
A) P² + 2p +q²
B) P² + 2pq + q³
C) P²+2pq+q²
D) P³ + 3pq+q³
E) (p+q)³

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What general effect does random genetic drift have on populations?
1)It reduces the dominant homozygosity.
2)It reduces the heterozgosity.
3)It reduces the recessive homozygosity.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) All of these
1)It reduces the dominant homozygosity.
2)It reduces the heterozgosity.
3)It reduces the recessive homozygosity.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What causes allele frequencies to change unpredictably in populations because of reproductive uncertainties?
A) Random genetic abnormalities
B) Random genetic drift
C) Random mating
D) Natural selection
E) Artificial selection
A) Random genetic abnormalities
B) Random genetic drift
C) Random mating
D) Natural selection
E) Artificial selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a type of non-random mating?
A) Consanguinous mating
B) Assortative mating
C) Discoursive mating
D) Consanguinous mating and assortative mating
E) Assortative mating and discoursive mating
A) Consanguinous mating
B) Assortative mating
C) Discoursive mating
D) Consanguinous mating and assortative mating
E) Assortative mating and discoursive mating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which assumption of the Hardy-Weinberg principle is violated by the concept of population subdivision?
A) Random-mating
B) Allele frequencies are uniform throughout the population
C) Individuals are diploid
D) Individuals are haploid
E) None of these
A) Random-mating
B) Allele frequencies are uniform throughout the population
C) Individuals are diploid
D) Individuals are haploid
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Selection that favors intermediate values of a trait at the expense of extreme values is known as
A) directional selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) stabilizing selection.
D) directional selection and disruptive selection.
E) All of these
A) directional selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) stabilizing selection.
D) directional selection and disruptive selection.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The A-B-O blood types are determined by three alleles I?,I?,and i.In one population the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type A blood is 0.063,the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type B blood is 0.015,and the frequency of individuals who are blood type O is 0.44.What is the frequency of the i allele?
A) 0.251
B) 0.663
C) 0.166
D) 0.333
E) 0.061
A) 0.251
B) 0.663
C) 0.166
D) 0.333
E) 0.061

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a population is a single interbreeding unit,it is said to be
A) panmitic.
B) non-panmitic.
C) heterozygous.
D) homozygous.
E) None of these
A) panmitic.
B) non-panmitic.
C) heterozygous.
D) homozygous.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following prevent the Hardy-Weinberg principle from applying to a population?
A) The population experiences random mating for the gene in question.
B) The zygotes produced by random mating have different survival rates.
C) The population is panmitic.
D) The population is not subject to migration.
E) All of these
A) The population experiences random mating for the gene in question.
B) The zygotes produced by random mating have different survival rates.
C) The population is panmitic.
D) The population is not subject to migration.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
At the level of the phenotype,natural selection influences the
A) distribution of alleles.
B) distribution of quantitative traits.
C) distribution of genotypes.
D) distribution of alleles and distribution of genotypes.
E) None of these
A) distribution of alleles.
B) distribution of quantitative traits.
C) distribution of genotypes.
D) distribution of alleles and distribution of genotypes.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following occurs when genotypes differ in the ability to survive and reproduce?
A) Unequal population division
B) Population subdivision
C) Natural selection
D) Inbreeding
E) None of these
A) Unequal population division
B) Population subdivision
C) Natural selection
D) Inbreeding
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is most effective at fixing the recessive allele in a population?
A) Selection for a recessive allele
B) Selection against a recessive allele
C) Selection against homozygous recessive individuals
D) Selection against heterozygotes
E) All of these
A) Selection for a recessive allele
B) Selection against a recessive allele
C) Selection against homozygous recessive individuals
D) Selection against heterozygotes
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
At the level of the gene,natural selection changes the frequencies of
A) genotypes in biomes.
B) genotypes in populations.
C) alleles in biomes.
D) alleles in populations.
E) All of these
A) genotypes in biomes.
B) genotypes in populations.
C) alleles in biomes.
D) alleles in populations.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What effect does consanguineous mating and assortative mating have on genotypic frequencies in populations?
1)Reduce the frequency of homozyotes
2)Increase the frequency of homozygotes
3)Reduce the frequency of heterozygotes
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3
1)Reduce the frequency of homozyotes
2)Increase the frequency of homozygotes
3)Reduce the frequency of heterozygotes
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The A-B-O blood types are determined by three alleles I?,I?,and i.In one population the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type A blood is 0.063,the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type B blood is 0.015,and the frequency of individuals are blood type O is 0.44.What is the frequency of individuals who are heterozygous for type A blood?
A) 0.251
B) 0.663
C) 0.166
D) 0.333
E) 0.061
A) 0.251
B) 0.663
C) 0.166
D) 0.333
E) 0.061

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The intensity of natural selection is quantified by the
A) correlation coefficient.
B) selection coefficient.
C) cosanguinous coefficient.
D) fitness number.
E) All of these
A) correlation coefficient.
B) selection coefficient.
C) cosanguinous coefficient.
D) fitness number.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Selection that favors extreme values of a trait at the expense of intermediate values is known as
A) directional selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) stabilizing selection.
D) directional selection and disruptive selection.
E) All of these
A) directional selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) stabilizing selection.
D) directional selection and disruptive selection.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a population that experiences migration (i.e.the merging of two separate populations),why are observed allelic and genotypic frequencies different than what is predicted by the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) The observed genotype frequencies were not created by random mating within the entire merged population.
B) The observed genotype frequencies were created by random mating within the entire merged population.
C) The observed genotype frequencies were subject to inbreeding.
D) The populations experienced unequal survival rates.
E) None of these
A) The observed genotype frequencies were not created by random mating within the entire merged population.
B) The observed genotype frequencies were created by random mating within the entire merged population.
C) The observed genotype frequencies were subject to inbreeding.
D) The populations experienced unequal survival rates.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the ultimate source of all genetic variability?
A) Natural selection
B) Artificial selection
C) Mutation
D) Natural selection and artificial selection
E) None of these
A) Natural selection
B) Artificial selection
C) Mutation
D) Natural selection and artificial selection
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How does random genetic drift affect large populations?
A) It may be the primary evolutionary force.
B) It has a moderate effect.
C) It has very little effect.
D) It is not currently known what kind of effect it has on large populations.
E) It does not affect large populations at all.
A) It may be the primary evolutionary force.
B) It has a moderate effect.
C) It has very little effect.
D) It is not currently known what kind of effect it has on large populations.
E) It does not affect large populations at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which type of selection can affect the distribution of a quantitative trait?
A) Directional selection
B) Disruptive selection
C) Stabilizing selection
D) Directional selection and Disruptive selection
E) All of these
A) Directional selection
B) Disruptive selection
C) Stabilizing selection
D) Directional selection and Disruptive selection
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
There are 800 individuals in sample group #1 taken from population X that were examined to the codominant trait R.When sampled 30 individuals were homozygous for allele Z (R?R?),100 individuals were homozygous for allele K (R?R?)and the rest were heterozygous (R?R?)).Determine how many total alleles for the trait in question are present in the sample group,the frequency of allele Z,and the frequency of allele Q,assuming the trait is controlled by a single codominant gene?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In diploid organisms,the rate at which genetic variability is lost by random genetic drift is
A) 1/2N, where N is the population size.
B) 1/3N, where N is the population size.
C) 1/4N, where N is the population size.
D) 1/5N, where N is the population size.
E) None of these
A) 1/2N, where N is the population size.
B) 1/3N, where N is the population size.
C) 1/4N, where N is the population size.
D) 1/5N, where N is the population size.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In a sample of 3000 individuals,1000 men and 2000 women,200 men have hemophilia and all the others have normal clotting function.All the women have normal clotting function.What are the frequencies for the hemophilia allele (X?)and normal allele (X?)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Selection against a deleterious recessive allele is replenished in the population by mutation,and leads to a dynamic equilibrium in which the frequency of the recessive allele is a simple function of the mutation rate and the selection coefficient.Which formula represents this situation?
A) p²+2pq+q²
B)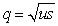
C)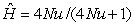
D) 1/2N
E) None of these
A) p²+2pq+q²
B)
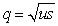
C)
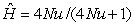
D) 1/2N
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The A-B-O blood types are determined by three alleles I?,I?,and i.In a population the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type A blood is 0.063,the frequency of individuals who are homozygous for type B blood is 0.015,and the frequency of individuals are blood type O is 0.44.What is the frequency of all genotypes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which type of selection creates a dynamic equilibrium in which different alleles are retained in a population despite their being harmful in homozygotes?
A) Balancing selection
B) Disruptive selection
C) Stabilizing selection
D) Directional selection
E) None of these
A) Balancing selection
B) Disruptive selection
C) Stabilizing selection
D) Directional selection
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A population's acquisition of selectively neutral alleles through mutation is balanced by the loss of these alleles through genetic drift.At equilibrium,the frequency of heterozygotes involving these alleles is a function of the population's size and the mutation rate is
A) p²+2pq+q²
B)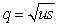
C)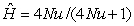
D) 1/2N
E) None of these
A) p²+2pq+q²
B)
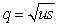
C)
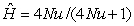
D) 1/2N
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following human diseases is associated with balancing selection?
A) Tay Sachs
B) Down Syndrome
C) Sickle Cell Anemia
D) Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
E) Alzheimers Disease
A) Tay Sachs
B) Down Syndrome
C) Sickle Cell Anemia
D) Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
E) Alzheimers Disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The frequency of cystic fibrosis found in those of European descent,caused by a homozygous recessive gene is approximately 0.04.Assuming the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium applies,what are the frequencies of the recessive/affected allele,the dominant/normal allele,the homozygous normal condition,and the carrier/heterozygous genotype?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What type of selection is demonstrated by the following chart?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



